Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Long Quiz 2: Mipmalgapo (Chem 17 X2)
Caricato da
Paolo QuinteroTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Long Quiz 2: Mipmalgapo (Chem 17 X2)
Caricato da
Paolo QuinteroCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MIPMalgapo (Chem 17 X2)
Long Quiz 2
Due: May 4, 2012 1 PM, Room 1318
I.
Multiple Choice (34 pts)
1. Which of the following does not describe Keqs?
A.) Keq = e^(-G/RT)
B.) Keq = kf/kr
C.) Keq = [products]yeq/[reactants]xeq
D.) Keq does not vary with temperature.
2. Which of the following will happen to the Q of the
reaction Fe3+ + 4Cl = FeCl4 if AgNO3 is added?
A.) It will increase
B.) It will decrease
C.) It will remain the same
D.) The effect on Q cannot be determined
3. Which of the following will remain the same when
the concentration of the blood-red colored
[Fe(SCN)]2+ is increased? There can be more than one
answer.
A.) Molar Absorptivity
B.) max
C.) Path Length
D.) Absorbance
4. Which of the following limitations of the Beers Law
is accounted for by the value of the y-intercept during
calibration?
A.) Real deviation
B.) Chemical deviation
C.) Instrumental deviation
D.) Human error
5. Which of the following will happen to the measured
absorbance if the experimenter held the cuvette at its
lower transparent side and neglected to wipe it with
tissue paper.
A.) It will increase
B.) It will decrease
C.) It will remain the same
D.) The effect cannot be determined
6. Which of the following is true for a sample of pure
water at 80C. (Kw at 80C is 5.47x10-14)
A.) Its pH is equal to 7.00
B.) Its pOH is equal to 6.63
C.) It is acidic
May 2, 2012
D.) It is basic
7. Which of the following will happen to the percent
ionization of HNO3 if it is diluted with water?
A.) It will increase
B.) It will decrease
C.) It will remain the same
D.) The effect cannot be determined
8. Which of the following compounds has the highest
degree of ionization?
A.) acetic acid
B.) bromoacetic acid
C.) dibromoacetic acid
D.) tribromoacetic acid
9. Which of the following is the strongest acid that can
exist in liquid water?
A.) HNO3
B.) HCl
C.) H3O+
D.) H2SO4 (1st ionization)
10. Which of the following will have the lowest pKa?
A.) Al(H2O)62+
B.) Mn(H2O)62+
C.) Mn(H2O)63+
11. Which of the following buffer components should
be chosen to prepare a buffer of pH 7.00.
A.) H2CO3/ NaHCO3 (Ka1 = 4.2x10-7)
B.) NaH2PO4/Na2HPO4 (Kb2 = 1.61x10-7)
C.) HCOOH/Na(HCOO) (Ka = 1.8x10-4)
D.) NH3/NH4Cl (Kb = 1.8x10-5)
12. A 50.00 mL of 0.0500 M H3PO4 is titrated with
0.050 M NaOH. What is the volume of the base added
when the pH of the solution is equal to pKa2?
A.) 25.0 mL
B.) 50.0 mL
C.) 75.0 mL
D.) 100.0 mL
Page 1
MIPMalgapo (Chem 17 X2)
13. Which of the following will happen to the molar
solubility of Ca(OH)2 if it was suspended in 0.50 M
MgSO4 instead of 0.50 M KCl?
A.) It will increase
B.) It will decrease
C.) It will remain the same
D.) The effect cannot be determined
14. When a saturated solution of NaCl is mixed with
ethanol, the amount of solid NaCl _______.
A.) Increases due to the decrease in the dielectric
constant of the solution
B.) Decreases since ethanol enhances the solubility of
NaCl in water
C.) Remains the same since ethanol is also polar like
water and thus wouldnt affect the polarity of the
solution
D.) Remains the same since ethanol wouldnt mix with
water
15. Which of the following should be added to
Cu(OH)2(s) so that its amount will increase?
A.) H2C2O4
B.) Zn
C.) Na3PO4
D.) NH3
16. Which of the following will happen to the
calculated ionic strength of a solution of Ca(OH)2 in
0.01 M KCl if the Ca(OH)2 precipitate was not washed
with water before it was suspended?
A.) It will increase
B.) It will decrease
C.) It will remain the same
D.) The effect cannot be determined
17. What is the Ksp of AgBr given that the reaction
AgBr(s) + 2CN(aq) = Ag(CN)2(aq) + Br(aq) has a
Keq=5.0x108 and that the Kf of Ag(CN)2 is 1.0x1021.
A.) 5.0 x 10-5
B.) 2.0 x 10-12
C.) 5.0 x 10-13
D.) 2.5 x 10-13
II. Problem Solving
1. In the reaction 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2 SO3(g), 0.500 mol SO2, 0.200 mol O2, and 0.600 mol SO3 are introduced
simultaneously into a 2.00 L vessel at 1000 K.
a. To which direction does the reaction proceed (to the left or to the right)? Support your answer with
calculations. No calculations, no point.
b. If Kc = 280, calculate the equilibrium concentrations in terms of molarity of all the species present.
c. What is Kp at 1000K?
d. What is the effect of the following parameters on the directionality of the equilibrium (to the right, to
the left, or no shift)
i. Adding more O2.
ii. Transferring the system into a 4.00 L vessel.
iii. Adding an appropriate catalyst.
2. Consider the titration of 10.0 mL 0.20 M Na2CO3 against 0.1 M HCl.
a. Which is the analyte? Titrant?
b. Write the stepwise titration reaction and label all the CO3 containing species based on how you
should calculate their pH (i.e. weak acid, neutral salt, etc.)
c. Calculate the volume of titrant needed to completely neutralize the analyte.
d. Calculate the pH of the solution after addition of the following volumes of titrant.
i. 0.00 mL
ii. 10.00 mL
iii. 20.00 mL
iv. 40.00 mL
May 2, 2012
Page 2
MIPMalgapo (Chem 17 X2)
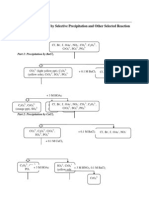
3. Consider a 1.00 L solution containing 0.05 moles of each of the ions Ag+, Mg2+, Mn2+ and Fe3+. To this
solution, sodium hydroxide was slowly added. Assume there is negligible volume change after each addition.
Solid
AgOH
Mg(OH)2
Mn(OH)2
Fe(OH)3
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Ksp
2.00x10-8
2.00x10-11
1.90 x 10-13
4.00x10-38
Calculate the amount (in molarity) of NaOH needed to precipitate each metal cation.
Calculate the solubility of each metal hydroxide.
Predict the order of precipitation. Explain in one sentence using at most ten words including articles.
At what pH value will the first cation start to precipitate?
When the second cation starts to precipitate, what concentration (in molarity) of the second first
remains in solution?
4. The calibration data in the spectrophotometric determination of Keq of the reaction Fe3+ + SCN = Fe(SCN)2+
is given below.
[Fe(SCN) 2+] eq
0.00004
0.00008
0.00012
0.00016
A
0.108
0.182
0.260
0.333
a. Write the equation of the line for the calibration.
b. Calculate the molar extinction coefficient with the correct unit.
c. An unknown solution was prepared by mixing 5.00 mL of 0.002 M FeCl3, 2.00 mL 0.002 M KSCN, and
3.00 mL 0.1 M HCl. The absorbance was found to be 0.188. Calculate the experimental Keq for the
reaction.
5. A student was assigned to prepare a 250 mL of 0.7 M buffer with a pH of 6.00 using only the available
reagents in the lab.
Citric Acid (H3A) Structure
Reagents available in the lab:
Solid NaOH (MW: 40 g/mol), 2 M HCl
2 M Citric Acid H3A (Ka1 = 7.4 x 10-3, Ka2 = 1.7 x 10-5 and Ka3 = 7.4 x 10-7)
a. What should be the buffer components such that the pH is 6.00?
b. Describe the preparation of the buffer by indicating the amounts of reagents (in g or in mL) that
you should mix to generate the desired pH.
May 2, 2012
Page 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Documento2 pagineChemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Nyka C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 LE 2 2nd SemDocumento3 pagineChem 17 LE 2 2nd SemMark ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 - 3rd Lab Long ExamDocumento4 pagineChem 17 - 3rd Lab Long ExamMarko Grant Albos OrozcoNessuna valutazione finora
- KEM Tutorials Chem 17 Module (3rd Exam)Documento10 pagineKEM Tutorials Chem 17 Module (3rd Exam)Nyka C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 LE 1 Answers1Documento11 pagineChem 17 LE 1 Answers1alyssa100% (1)
- KEM MAD Sample Exam (Chem 17, 3rd LE)Documento3 pagineKEM MAD Sample Exam (Chem 17, 3rd LE)Nyka C.100% (1)
- Chem 17 Lab 3rd LE ReviewerDocumento3 pagineChem 17 Lab 3rd LE ReviewerJamie Joice Noche100% (1)
- Chem 17 Expt 8 Fr2 FinalDocumento12 pagineChem 17 Expt 8 Fr2 FinalMarrod CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Calorimetry Chem17Documento6 pagineCalorimetry Chem17Frances Abegail QuezonNessuna valutazione finora
- UP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Documento10 pagineUP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Jerremiah YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1: CalorimetryDocumento4 pagineExperiment 1: CalorimetryNeil Mark EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 Lab Manual 2Documento28 pagineChem 17 Lab Manual 2Chrizamae BarlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 16 Finals ReviewDocumento4 pagineChem 16 Finals ReviewRalph John UgalinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator TitrationDocumento2 pagineQuantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator TitrationAlexander Gordon InesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem16 LE3 SamplexDocumento3 pagineChem16 LE3 SamplexmariemfranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- UP ACME - Chem 28 - 2nd LE SamplexDocumento4 pagineUP ACME - Chem 28 - 2nd LE SamplexDoom RefugeNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Redox ReactionDocumento3 pagineSelected Redox ReactionJesha LibreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 28.1 Midterm PSDocumento2 pagineChem 28.1 Midterm PSAnonymous ee5dOjNessuna valutazione finora
- UP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Documento6 pagineUP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)kennethleo69100% (1)
- Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator TitrationDocumento4 pagineQuantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator TitrationYamiyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 28 Problem Set 3Documento1 paginaChem 28 Problem Set 3Anonymous ee5dOj0% (1)
- Chem 28.1 Problem Set Coplex TitrationsDocumento1 paginaChem 28.1 Problem Set Coplex TitrationsIda Anne Cacharel FuentespinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash or Alkali Mixture by Double-Indicator TitrationDocumento2 pagineQuantitative Analysis of Soda Ash or Alkali Mixture by Double-Indicator TitrationZyrle Nikko UchidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 Formal ReportDocumento5 pagineChem 17 Formal ReportPatricia Frances P. FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- E6 AtqDocumento2 pagineE6 AtqSOUPINESSNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDocumento14 pagineQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA Titrationabcd efgNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 28 Problem Set 2Documento1 paginaChem 28 Problem Set 2Anonymous ee5dOjNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 31.1 Postlab 9Documento1 paginaChem 31.1 Postlab 9Sellina SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Samples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsDocumento2 pagineSamples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsAlyssa CubillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 154 LE4 SamplexDocumento3 pagineChem 154 LE4 SamplexLin Xian XingNessuna valutazione finora
- SOURCE: General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications 10Documento3 pagineSOURCE: General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications 10Jerremiah YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium Hydroxide Chem 17Documento7 pagineDetermination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium Hydroxide Chem 17Frances Abegail QuezonNessuna valutazione finora
- (Final) Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionDocumento8 pagine(Final) Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report Experiment 2 and 3Documento5 pagineFormal Report Experiment 2 and 3Zyra Camille Giron HacheroNessuna valutazione finora
- ATQ4Documento2 pagineATQ4Julius Alfredo ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator Titration Chem 28Documento2 pagineQuantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double Indicator Titration Chem 28Frances Abegail QuezonNessuna valutazione finora
- S D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentDocumento14 pagineS D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentKenneth Dionysus SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- FR3 CalculationsDocumento5 pagineFR3 CalculationsJoeco Abay-abayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 17 Finals ReviewerDocumento9 pagineChem 17 Finals ReviewerJamie Joice Noche100% (1)
- PS1Documento1 paginaPS1Elah PalaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium HydroxideDocumento2 pagineDetermination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium HydroxideJunko TsukudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 31 Probset First ExamDocumento2 pagineChem 31 Probset First ExamNat DabuétNessuna valutazione finora
- FR1 Chem 28.1 Expt 1Documento11 pagineFR1 Chem 28.1 Expt 1Marrod CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 - Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator TitrationDocumento2 pagineExperiment 4 - Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator TitrationMelchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3 Transference NumberDocumento3 pagineExperiment 3 Transference NumberRicky JayNessuna valutazione finora
- S E C H: Olubility Quilibrium of Alcium YdroxideDocumento6 pagineS E C H: Olubility Quilibrium of Alcium YdroxideGiselle ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 31 Prob Set Org Mech NucleophilicDocumento3 pagineChem 31 Prob Set Org Mech NucleophilicJolaine ValloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex (ANSWER KEY For Non-PSolv)Documento5 pagineChemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex (ANSWER KEY For Non-PSolv)Laia Valencia100% (1)
- (Chem 17.1) FR ValerioDocumento5 pagine(Chem 17.1) FR ValerioRupert ValerioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 31.1 FR1 SantosDocumento5 pagineChem 31.1 FR1 SantosClaire SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Multiple Choice. Write The Best Answer From The Following ChoicesDocumento5 pagineI. Multiple Choice. Write The Best Answer From The Following ChoicesDoom Refuge100% (1)
- Chem 28.1 E10 ATQDocumento5 pagineChem 28.1 E10 ATQSheenly Anne SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- FR PDFDocumento4 pagineFR PDFGoku SanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationDocumento12 pagineQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationmariemfranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in SamplesDocumento2 pagineApplication of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in SamplesCharlette InaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesDocumento3 pagineApplication of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesMicah PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 40.1 LabDocumento21 pagineChem 40.1 LabEve YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Hardness and Calcium in The SampleDocumento8 pagineDetermination of Hardness and Calcium in The SampleGobe JamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Solubility SgizzDocumento4 pagineChem Solubility Sgizzkagabejan_emo29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry G12 - 2Documento9 pagineChemistry G12 - 2fikerdereje697Nessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Heat RatioDocumento5 pagineSpecific Heat RatioPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- GradesDocumento6 pagineGradesPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis JournalDocumento8 pagineThesis JournalPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric GraphsDocumento6 pagineTrigonometric GraphsPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkalinity Determination For LBS171LDocumento2 pagineAlkalinity Determination For LBS171LDwiyana YogasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws, Contracts and EthicsDocumento7 pagineLaws, Contracts and EthicsPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- IE3 Cheat Sheet LE2Documento1 paginaIE3 Cheat Sheet LE2Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 73 PS3Documento5 paginePhysics 73 PS3Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- 73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersDocumento12 pagine73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersNikkei Pfeiffer TadiliNessuna valutazione finora
- 122 - Thermo AnalysisDocumento6 pagine122 - Thermo AnalysisPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- 122 LE 2 SamplexDocumento1 pagina122 LE 2 SamplexPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Dipole MomentDocumento17 pagineDipole MomentPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhiannename 1Documento1 paginaRhiannename 1Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 72 PS2Documento13 paginePhysics 72 PS2Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Ion Concentration On Equipotential Lines and Electric FieldDocumento4 pagineEffects of Ion Concentration On Equipotential Lines and Electric FieldPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Newton's Law of Cooling For Different Liquids at Varying Ambient TemperaturesDocumento5 pagineA Study On Newton's Law of Cooling For Different Liquids at Varying Ambient TemperaturesPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 53 LE4Documento1 paginaMath 53 LE4Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelab E6Documento2 paginePrelab E6Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- ChE 123 HW 2Documento2 pagineChE 123 HW 2Paolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QuestionsDocumento1 paginaInterview QuestionsPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Molecular Reaction DynamicsDocumento13 pagine10 Molecular Reaction DynamicsPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- MuL 9 Reaction PaperDocumento2 pagineMuL 9 Reaction PaperPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- CWTS LectureDocumento20 pagineCWTS LecturePaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- DenisovansDocumento6 pagineDenisovansPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Peer Review: Florensiensis Were Presented, Such As Insular Dwarfism, Microcephaly, ME Hypothyroidism andDocumento2 paginePeer Review: Florensiensis Were Presented, Such As Insular Dwarfism, Microcephaly, ME Hypothyroidism andPaolo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No.1 (DSP Lab)Documento9 pagineExperiment No.1 (DSP Lab)Omer SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- OptiFDTD Tutorials PDFDocumento36 pagineOptiFDTD Tutorials PDFKhải NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- DBT 203 Metal Extractive Technology: Topic 1: Extracting Metal From OresDocumento24 pagineDBT 203 Metal Extractive Technology: Topic 1: Extracting Metal From OresSollehah SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Metering - Manual - Eastern - RegionDocumento65 pagineMetering - Manual - Eastern - RegionAmit PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- The Key To Super Consciousness Chapter 1Documento6 pagineThe Key To Super Consciousness Chapter 1Will FortuneNessuna valutazione finora
- On Oxygen-Induced Corrosion of An Oil Refinery Condensate Fraction at Ion UnitDocumento17 pagineOn Oxygen-Induced Corrosion of An Oil Refinery Condensate Fraction at Ion UnitAzmi Mohammed NorNessuna valutazione finora
- The Aircraft Engineer 1928Documento130 pagineThe Aircraft Engineer 1928Mark Evan SalutinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Folio Soap and DetergentDocumento13 pagineChemistry Folio Soap and DetergentMarinda YieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sajb 411952 969Documento18 pagineSajb 411952 969samirNessuna valutazione finora
- T13mra001 Mra STR 103 SLD 010 Rev B Lifting AnalysisDocumento12 pagineT13mra001 Mra STR 103 SLD 010 Rev B Lifting AnalysisTannaz HadizadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Documento8 pagineConduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Nihad MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Documento68 pagineSdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Zeicel Allijah De Los SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Method For Assessing The Audibility of Tones in Noise Joint Nordic MethodDocumento18 pagineObjective Method For Assessing The Audibility of Tones in Noise Joint Nordic MethodSheetaltwuNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackDocumento8 pagineApplication of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackClaudio PazNessuna valutazione finora
- PCF8833 1Documento112 paginePCF8833 1Raphael AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- MEMS Design Chap 5 (P1-New) - MEMS DESIGN ProcessDocumento27 pagineMEMS Design Chap 5 (P1-New) - MEMS DESIGN ProcessvuonglupNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Shear Walls For Multi-Storey Timber BuildingsDocumento54 pagineAnalysis of Shear Walls For Multi-Storey Timber BuildingsrahimmullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ExerciseDocumento6 paginePhysics ExerciseLaw Jing SeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas BookDocumento202 pagineGas Bookomiitg67% (3)
- 05 PDFDocumento1 pagina05 PDFdruwid6Nessuna valutazione finora
- TIME TABLE - M.E/M.Tech. - APRIL/MAY-2010 Regulations: 2005Documento12 pagineTIME TABLE - M.E/M.Tech. - APRIL/MAY-2010 Regulations: 2005Sathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Quantum-Particle (Students Copy)Documento12 pagine6-Quantum-Particle (Students Copy)Kunal kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiometric CorrectionDocumento32 pagineRadiometric CorrectionOluwafemi Opaleye100% (1)
- Service Manual Kaeser SK 19Documento75 pagineService Manual Kaeser SK 19Joe100% (8)
- Datasheet For Steel Grades Carbon Steel 1.1141: 1.1141 Standard NumberDocumento2 pagineDatasheet For Steel Grades Carbon Steel 1.1141: 1.1141 Standard NumberCricri CriNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Site Earthwork CalculationDocumento4 pagineConstruction Site Earthwork CalculationmasteriragaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Handbook For Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields by R. F. HarringtonDocumento23 pagineSolution Handbook For Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields by R. F. HarringtonwesNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Signal AnalysisDocumento4 pagineSmall Signal Analysissamaiyasamp3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bearings Exam Question HomeworkDocumento3 pagineBearings Exam Question Homeworkabbey4623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arfken Solutions Manual 7th Ed PDFDocumento524 pagineArfken Solutions Manual 7th Ed PDFBolaybalam84% (77)