Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Different Parts of Steel Bridges
Caricato da
rims26Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Different Parts of Steel Bridges
Caricato da
rims26Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Training Programme on Steel/Composite Bridge
TIME 14.00 15.30
Venue : Dehradun, UTTARAKHAND
PRESENTER Reepak; Kallot; Abhijit Ghosh
TOPICS Different parts/components/steel & Composite Bridges
DIFFERENT PARTS/COMPONENTS/STEEL & COMPOSITE BRIDGES
Earlier, for the second set of this campaign at Uttaranchal, a 110m long Truss and its
alternatives of a Flat Arch 110m from springing point to Springing point and a
continuous plate Girder/RC deck composite structure of spans 30m 50m 30m(=
110m) were chosen for hands on exercise.
As, three A3 size drawing have been made, a descriptive itemization of the
components may be useful.
(1) THE TRUSS (Proportions in Second set) the truss is meant to be a modified
warren Truss, which is good looking as well as efficient.
The Truss will have these following components:
1(1) Bottom Chord (Tension) with maximum section size in the middle, as there
tension will be most severe.
1(2) Top Chord (Compression) with maximum Section size at the middle, where
there would be maximum compression.
This member, cannot buckle, upwards or downwards, because of Diagonals and
Verticals, which are called Shear Members or Web Members but it can buckle sid
ways.
Therefore it should be restrained by Plan Bearings provided at the centre of the Top
chords, connected by a Triangulated framework to both the chods.
1(3) The Web Members e.g. the Diagonals and the Verticals
The first Diagonal is over the Bearing and is subjected to very severe compression. It
is called Raker.
The Second Member is a Vertical which by virtue of its 90 angle between itself and
the bottom chord, should have Zero Force but it is used to support Two Cross
girders and thus reduces the local bending stress in the bottom chord.
The third member is a Diagonal which is in Tension being connected with the
Raker at the Top.
As these are Shear Members the forces will be progressively less, as the members
approach the centre of the span.
= DAY-1 = (ITEM-30 (14.00 15.30) DIFFERENT PARTS/COMPONENTS/STEEL & COMPOSITE
BRIDGES Page 1 of 4
Training Programme on Steel/Composite Bridge
Venue : Dehradun, UTTARAKHAND
So, these are three types of Web members namely, The Compression Diagonals,
including the Raker, the Tension Diagonals and the Verticals, which are perpendicular
to the bottom chord.
1(4) PLAN BEARINGS AT OF TOP CHORD.
These members are supposed to give lateral stability to the Top chords, which can
buckle sideways. The forces for which these members are to be designed, are 2%
of the local compressive force, in the Top chord.
1(5) Cross Girders Composite Sections which are connected to the deck slab by
Shear Connectors and are called Ladder type Floor Duck Supports
With an overhang at both sides, they constitute the carriage way for vehicles and
footways at sides.
These in a nutshell, are the 5 types of main members, which can be analysed as a
SPACE FRAME if desired and the member size assumptions justified by any
modern code, such as BS 5400 Parts 3, 4 (for design) and 5, Bearings, Splices, Web
Member to chord girder connections, RCC abutments etc. are extra.
2.0 THE FLAT ARCH
An open Web truss configuration albeit lighter than a system of plate
girder or one single box girder, will be still fairly heavy.
The alternative is flat Arch which would be much lighter.
Here the components are
The Arch Rib
The Spandrel Columns
The side girders continuous
The cross girders which would be composite.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
1. THE ARCH RIBS :The arch ribs are usually made up of built up I section to ease connections to
spandrel columns. Modern concepts use CHS or SHS but here both the connections
and the resulting joint designs are complex and lends to good quality site welding
only. Blind bolts etc. for connecting tube to tube are not available in India yet.
Therefore the Arch Ribs interconnected with In Plane Triangulated Bracings will be
of built up HTS section.
= DAY-1 = (ITEM-30 (14.00 15.30) DIFFERENT PARTS/COMPONENTS/STEEL & COMPOSITE
BRIDGES Page 2 of 4
Training Programme on Steel/Composite Bridge
Venue : Dehradun, UTTARAKHAND
A Two Pin or rather a fixed base such Rib, happens to be of variable section depth
and subjected to combined Bending and Compression the compressive forces being
dominant.
The Thurst goes in the foundation Rock and chances of slip circle failures will be
absent.
Splices can be welded Rectangular End plate type which is efficient for a
compressive member but may be considered ugly. All connections should be made
of HSFG bolts.
1. THE SPANDREL COLUMNS:The Spandrel columns behave like the verticals of a vierendeel Frame and should be
having moment connections with both the Edge Girder and the Arch Rib.
The Spandrel columns too should be of built up or Rolled parallel flange I sections
with bolted base plate on the arch Rib and bolted Cap Plate under the Edge girder.
Spandrel columns should be braced together in the transverse direction, so as to
distribute Earthquake. The column tops should be braced in plan.
2. THE EDGE GIRDER:The Edge Girder or Side Girders too should be of built up I section and continuous
over the Spandrel column.
The Edge Girder will be expected to go beyond the Springing points of the Arch
ending up on, say, Dwarf Abutments
The length of the overhand depends on the slope of the Gorge side.
3. THE CROSS GIRDERS :The Cross Girders are expected to be composite and thus made up of flanges of unequal widths. Top Flange will narrower and Bottom Flange will be wider.
Like the concept in the Truss, the Ladder Type cross Girder would have overhangs,
which would double up as footpaths, as well as for carriage of services.
The Cross Girders are to be laterally supported at the wet concrete stage
to prevent lateral torsional buckling of the top flange which would be in
compression.
(3)CONTINUOUS COMPOSITE HTS (Gr 450)
FCU 35; PARAPET, UPSTAND GR FCU 40.
PLATE GIRDERS RC DECK. GR.
COMPONENTS OF 30, 50, 30 = 110, TOTAL LENGTHS 4 GIRDER BRIDGE.
= DAY-1 = (ITEM-30 (14.00 15.30) DIFFERENT PARTS/COMPONENTS/STEEL & COMPOSITE
BRIDGES Page 3 of 4
Training Programme on Steel/Composite Bridge
Venue : Dehradun, UTTARAKHAND
For a typical plate Girder/RC deck continuous composite, the principal components
would be as follows :1.1
1.2
1) Main plate girders much be of Even Number e.g. 2, 4, 6 or 8.
Span Sections
Pier Sections
1) Intermediate Cross Bracings between pairs of girder for ensuing lateral
to compression flanges.
stability
2) Cross Bracings over Piers continuous to laterally support compression flange at
bottom and also to share, Transvene horizontal loads (Earthquake, wind, impact etc.)
3) Web stiffeners vertical at Span.
4) Web stiffener Horizontal at Piers.
5) Web stiffener Horizontal at Piers.
6) Bearing stiffeners
7) Jacking stiffeners
8) Splices
9) Shear studs
10)
Hooks for restraing Earthquake
These are general topics which need to be checked with the codal demand for Safety.
Each component described above has its BS 5400 Parts 3,4 & 5 clauses and the
Designer is supposed to see, codal safety provisions are honoured.
The RC part of them e.g. Deck, will be supported by Part 4 and shear stud etc. will be
supported by Part 5. Most of the steel component are to be checked by clauses from
Part 3.
Once the real life hands on job are started, the day to day Design Office involvement
will be clear.
= DAY-1 = (ITEM-30 (14.00 15.30) DIFFERENT PARTS/COMPONENTS/STEEL & COMPOSITE
BRIDGES Page 4 of 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- S 73 532 WC 57 2004Documento9 pagineS 73 532 WC 57 2004rims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Inst Design PhilosophyDocumento21 pagineInst Design Philosophyrims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
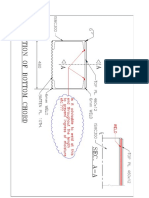
- Details of Bottom Chord-202-ModelDocumento1 paginaDetails of Bottom Chord-202-Modelrims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Chinyalisaur Bridge Presentation 12.03.12Documento17 pagineChinyalisaur Bridge Presentation 12.03.12rims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Expertise of Powergen in Design & Engineering of Steel BridgesDocumento23 pagineExpertise of Powergen in Design & Engineering of Steel Bridgesrims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Expertise of Powergen in Design & Engineering of Steel BridgesDocumento23 pagineExpertise of Powergen in Design & Engineering of Steel Bridgesrims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Were Or: ONE D. BDocumento12 pagineWere Or: ONE D. BAhmad Al MataanyNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Were Or: ONE D. BDocumento12 pagineWere Or: ONE D. BAhmad Al MataanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- B-01Operation Instruction and Manual For PumpDocumento50 pagineB-01Operation Instruction and Manual For Pumprims26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Industrial Flow MeasurementDocumento244 pagineIndustrial Flow MeasurementRoxana Gligor100% (3)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Conveyor ControlDocumento6 pagineConveyor ControlrobinrastogigcetNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Architecture of Neural NWDocumento79 pagineArchitecture of Neural NWapi-3798769Nessuna valutazione finora
- DPP On Mole Concept (Ncert)Documento47 pagineDPP On Mole Concept (Ncert)Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Light Dimmer CircuitsDocumento14 pagineLight Dimmer CircuitskapilasriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Grange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDocumento44 pagineGrange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDan Joleys100% (1)
- Accounting For A Service CompanyDocumento9 pagineAccounting For A Service CompanyAnnie RapanutNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- One God One People February 2013Documento297 pagineOne God One People February 2013Stig DragholmNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFDocumento24 pagineWa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFOktiano BudiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- 10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupDocumento4 pagine10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupArvin ArmojallasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Castle CrashesDocumento21 pagineCastle Crasheswicked wolfNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Bill - AKIJDocumento3 pagineBill - AKIJm.tanjil2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- 28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsDocumento14 pagine28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsniallNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocumento6 pagineAppendicitis Case StudyKimxi Chiu LimNessuna valutazione finora
- ROXAS FARM SCHOOL Trifold BrochureDocumento2 pagineROXAS FARM SCHOOL Trifold BrochureJude IledanNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Paper 1Documento7 pagineGeography Paper 1Sudhir TewatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Committee and Corporate Governance: CA Pragnesh Kanabar Sir's The Audit Academy-CA Final AuditDocumento17 pagineAudit Committee and Corporate Governance: CA Pragnesh Kanabar Sir's The Audit Academy-CA Final AuditPULKIT MURARKANessuna valutazione finora
- Family History Timeline Rubric HonorsDocumento1 paginaFamily History Timeline Rubric Honorsapi-291510568Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Manual Bms8n2 e LowDocumento58 pagineManual Bms8n2 e Lowzoranbt80_324037655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIDocumento18 pagineReviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIAngelica Faye95% (20)
- Bill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingsDocumento3 pagineBill of Quantity: Supply of Pipes and FittingssubxaanalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Poly (Lactic Acid) - Based - 1Documento20 pagineComplex Poly (Lactic Acid) - Based - 1Irina PaslaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Kitchen Equipment Handling and Maintaining Standard Procedure and PoliciesDocumento2 pagineKitchen Equipment Handling and Maintaining Standard Procedure and PoliciesChef Chef75% (4)
- Keira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocumento12 pagineKeira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchCrina LupuNessuna valutazione finora
- Articles About Social Issues - Whiter SkinDocumento9 pagineArticles About Social Issues - Whiter Skinf aNessuna valutazione finora
- G2A Glitch DONT LEAK 2Documento7 pagineG2A Glitch DONT LEAK 2qDeficiencyNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed 4way D54 Proposed 2way D56: Issue Date DescriptionDocumento3 pagineProposed 4way D54 Proposed 2way D56: Issue Date DescriptionADIL BASHIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Misc Ar2019Documento207 pagineMisc Ar2019Sharon12 ArulsamyNessuna valutazione finora
- 7094 Bangladesh Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocumento11 pagine7094 Bangladesh Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersmstudy123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Content Analysis of Tea BrandsDocumento49 pagineContent Analysis of Tea BrandsHumaRiaz100% (1)
- NUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsDocumento2 pagineNUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsJorge ParraNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- A Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsDocumento7 pagineA Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsAhmed ShoeebNessuna valutazione finora