Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Handout No. 5 Ethics
Caricato da
taz_taz3Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Handout No. 5 Ethics
Caricato da
taz_taz3Copyright:
Formati disponibili
ETHICS
Ethics is not a precept (means commandment) nor it is something mutually
exclusive from quality.
Quality and Ethics have a common care premise, which is do right things right.
"Ethics is a body of principles or standards of human conduct that
govern the behavior of individuals and organizations"
1. The Deming philosophy:
Create and publish the aims and purposes of the organization.
Management must demonstrate strong and constant commitment to this
statement.
The aims and purposes of organization must include the interest of investors,
customers, suppliers, employees, and the community and quality philosophy
Long term goals must be set by the organization and resources must be
allocated accordingly (for Research, training and continuing education etc)
Innovation must be promoted to ensure that the product or service does not
become obsolete.
2. Learn the new philosophy:
Organization must seek never-ending improvement and refuse to accept nonconformance.
Organization must concentrate on defect prevention rather than defect
detection.
By improving the process, the quality and productivity will improve.
3. Understand the purpose of inspection:
The purpose of inspection is to improve the process and reduce its cost.
Mass inspection is costly and unreliable, where appropriate; it should be
replaced by never-ending improvement using statistical techniques.
ETHICS
Page 1
4. Stop awarding business based on price alone:
The organization must stop awarding business based on the low bid, because
price has no meaning without quality.
The goal is to have single suppliers for each item to develop a long term r/s of
loyalty and trust, thereby providing improved products and services.
Purchasing agents must be trained in SPC and require it from suppliers.
Material quality must be followed throughout the entire life cycle and
customer expectation be evaluated through feedback.
5. Improve constantly and forever the system:
Management must take more responsibility for problems by actively finding
and correcting problems so that productivity and quality are continuously and
permanently improved and costs are reduced.
Focus must be on preventing problems before they occur.
Variation is expected, but there must be continual striving for its reduction
using control charts.
Responsibilities are assigned to teams to remove the cause of problems and
continually improve the process.
6. Institute training:
Each employee must be oriented to the organization's philosophy of
commitment to never-ending improvements.
Management must allocate resources to train their employees to perform their
jobs in the best possible manner.
Everyone should be trained in statistical methods and these methods should be
used to monitor the need for further training.
7. Teach and institute leadership:
Improving supervision is management's responsibility.
Instead of focusing on negatives, fault-finding atmosphere, supervisors should
create a positive, supportive one where pride in workmanship can flourish. All
communication must be clear from top management to bottom management.
ETHICS
Page 2
8. Drive out fear, create trust and create a climate for
innovation:
Management must encourage open, effective communication and teamwork.
Fear is caused by a general feeling of being powerless.
Fear is also caused by:
Lack of job security.
Possible physical harm.
Performance appraisals.
Ignorance of organization's goals.
Poor supervision.
Not knowing the job.
When people are treated with dignity, fear can be eliminated and people will
work for the general welfare of the organization and this climate will provide
ideas for improvement.
9. Optimize the efforts of teams, groups and staff areas:
Barriers exist internally among levels of management, among departments,
within departments, and among shifts.
Externally they exist between the organization and its customers and
suppliers.
These barriers exist because of:
Poor communication.
Ignorance of the organization mission.
Competition.
Personal grudges or jealousies.
To break down the barriers, management needs to resort for a
long-term perspective.
All the different areas must work together.
Altogether need to be changed.
Communication channels opened.
Project teams organized.
Training in teamwork implemented.
Multifunctional teams.etc
ETHICS
Page 3
11. Eliminate exhortations for the workforce:
Exhortations that ask for increased productivity without providing specific
improvement methods can handicap an organization.
Workers cannot produce anything if the system limits them from doing it.
11(a). Eliminate numerical quotes for the workforce:
Quotes and work standards focus on quantity rather than quality.
They encourage poor workmanship in order to meet their quotes.
11(b). Eliminate management by objective:
Instead of MBO, management must learn the capabilities of the processes and
how to improve them.
12. Remove barriers that rob people of pride of
workmanship:
ETHICS
Loss of pride in workmanship exists because of:
1. Workers do not know how to relate to the organization's mission.
2. They are being blamed for systems problems.
3. Poor designs lead to the production of junk.
4. Inadequate training is provided.
5. Punitive (meaning: inflicting punishment) supervision exists.
6. Inadequate or ineffective equipment is provided for performing the
required work.
Restoring pride will require a long-term commitment by management.
Management must give employees:
Operational job descriptions.
Provide the proper tools and materials.
Stress the workers understanding of their role in the total process.
Page 4
13.Encourage education and self-improvement for everyone:
What an organization needs are people who are continuously improving
with education.
A long-term commitment to continuously train and educate people must be
made by management.
On-going education and training must be according to organization
requirements and changing environment.
14.Take action to accomplish transformation:
Management has to accept the primary responsibility for the never- ending
improvement of the process.
It has to create a corporate culture and a corporate structure to implement
the philosophy
Management must be committed, involved and accessible if the
organization is to succeed in implementing the new philosophy.
QUALITY COUNCIL:
In order to build quality into the culture, a quality council is
establishing to provide overall direction. It is the driver for TQM engine.
It comprises of CEO, senior managers of functional areas (such as
design, marketing, finance, production quality) and a co-coordinator
/consultant. If there is a union consideration should be given to having a
representative on the council.
ETHICS
Page 5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Deming PhilosophyDocumento4 pagineDeming PhilosophyAhmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership: (Chapter 2 Part-II)Documento23 pagineLeadership: (Chapter 2 Part-II)maimoonasaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Deming Quality Management ApproachDocumento28 pagineDeming Quality Management ApproachEngr Minna Minerva Aclan100% (1)
- Total Quality Management: 14 Points, Benefits, Models & PrinciplesDocumento19 pagineTotal Quality Management: 14 Points, Benefits, Models & Principlesshubham chikuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakambini R. Maputi, RN August 28, 2010Documento53 pagineLakambini R. Maputi, RN August 28, 2010praxis_anaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of TQMDocumento12 pagineConcepts of TQMSavantNessuna valutazione finora
- QMS Assignment 2Documento4 pagineQMS Assignment 2John Michael PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of TQM Philosophies: Ms. Irum Shahzadi 6Documento12 pagineEvolution of TQM Philosophies: Ms. Irum Shahzadi 6Fiaz juttNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Lesson 2 (QMS)Documento26 pagineChapter 3 - Lesson 2 (QMS)giesielyngoNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer-focused quality principles for business excellenceDocumento14 pagineCustomer-focused quality principles for business excellenceRoseann Hidalgo ZimaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Standards For ISODocumento5 pagineQuality Standards For ISORaj kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management Q&ADocumento11 pagineQuality Management Q&AMuhaimin ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Management and LeadershipDocumento26 pagineManagement and LeadershipLeadership Course100% (4)
- Quality Management Principles Standardized by ISODocumento18 pagineQuality Management Principles Standardized by ISOmuneerppNessuna valutazione finora
- William Edwards Deming: - Statistical Process Control (SPC) Is A Method of QualityDocumento11 pagineWilliam Edwards Deming: - Statistical Process Control (SPC) Is A Method of QualitymaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Total Quality Management Approach to Organizational ExcellenceDocumento16 pagineChapter 1: Total Quality Management Approach to Organizational ExcellenceKhabirIslamNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.introduction To Quality ManagementDocumento6 pagine1.introduction To Quality ManagementKurikuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Dina BelalDocumento6 pagineDina Belalkhalid osmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Retail TrainingDocumento41 pagineRetail Trainingvikastiwari84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operations MGT TQM NotesDocumento13 pagineOperations MGT TQM NotesRaynon AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Focus and Continuous Improvement PrinciplesDocumento3 pagineCustomer Focus and Continuous Improvement PrinciplesChee HowNessuna valutazione finora
- Compare The Ideas of Deming and JuranDocumento4 pagineCompare The Ideas of Deming and JuranSjlmasiMohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- William Edward S Deming PhilosophyDocumento11 pagineWilliam Edward S Deming PhilosophyIQa SalehNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization Development Techniques and InterventionsDocumento5 pagineOrganization Development Techniques and InterventionsRK VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Participative Management: SynergyDocumento17 pagineParticipative Management: SynergyHameedullah AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Deming's 10 Principles:: The 10 Principles Are As FollowsDocumento4 pagineDr. Deming's 10 Principles:: The 10 Principles Are As FollowsSanket SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro to Quality Management PrinciplesDocumento28 pagineIntro to Quality Management PrinciplesLakshmi KumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Managment معدلةDocumento21 pagineTotal Quality Managment معدلةShimaa KashefNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Human Resources: Case Study - HRD InterventionDocumento6 pagineManaging Human Resources: Case Study - HRD InterventionAditi RathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Employee Development & Talent ManagementDocumento10 pagineEmployee Development & Talent ManagementsnehabasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management - Deming's 14 PointsDocumento3 pagineTotal Quality Management - Deming's 14 PointsSoojoo HongNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSIGNMENT No. 1 Course: Total Quality Management (890) Semester: SpringDocumento10 pagineASSIGNMENT No. 1 Course: Total Quality Management (890) Semester: SpringNadir Shah76% (17)
- The Three Quality Philosophies ComparedDocumento12 pagineThe Three Quality Philosophies ComparedRamesh AlhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Bsbhrm613 Task 1Documento7 pagineBsbhrm613 Task 1Fasih ur Rehman AbidNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management - Lecture 4 4Documento23 pagineQuality Management - Lecture 4 4nithishNessuna valutazione finora
- TQMDocumento342 pagineTQMDinesh KcNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 4Documento40 pagineDocument 4vineeth pNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why Performance Management Fails and How To Remedy ThemDocumento5 pagine10 Reasons Why Performance Management Fails and How To Remedy ThemCharlotte Hall100% (1)
- Human Resources Management - Andrey Mark P. CabuntocanDocumento2 pagineHuman Resources Management - Andrey Mark P. CabuntocanAndrey CabuntocanNessuna valutazione finora
- Retail ManagementDocumento15 pagineRetail ManagementMohini MalakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Class: Semester: Roll No.: Enrollment No.: SubjectDocumento9 pagineName: Class: Semester: Roll No.: Enrollment No.: SubjectCeegi Singh SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of QualityDocumento24 pagineCost of QualityMuhammad HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Deming'S 14 Points: (The Guide For Transforming Japan Into A World Power)Documento3 pagineDeming'S 14 Points: (The Guide For Transforming Japan Into A World Power)Rami Ibrahim AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 basic TQM concepts compared to previous quality elementsDocumento3 pagine6 basic TQM concepts compared to previous quality elementsArdalan_mar2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Training and MeghmaDocumento5 pagineTraining and MeghmaMeghma BasuNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM PrinciplesDocumento20 pagineTQM PrinciplesShakeel AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento5 pagineTotal Quality ManagementJESSICA TABUTOLNessuna valutazione finora
- Deming 14 Point ISO 9001 ImplementationDocumento2 pagineDeming 14 Point ISO 9001 Implementationiqbal khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Abhishek PathakDocumento18 pagineFinal Project: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Abhishek PathakmpimcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jablonski's 5 Phases of TQM ImplementationDocumento10 pagineJablonski's 5 Phases of TQM ImplementationKENNETH IAN MADERANessuna valutazione finora
- Mu 0017 Talent ManagementDocumento8 pagineMu 0017 Talent ManagementSandeep KanyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Facilitating & Hindering Continuous ImprovementDocumento5 pagineFactors Facilitating & Hindering Continuous ImprovementKatrina PaquizNessuna valutazione finora
- IM-130 Slide-1Documento35 pagineIM-130 Slide-1santillan91100% (1)
- Workplace Project Report 1Documento4 pagineWorkplace Project Report 1Israr AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management Principles for HealthcareDocumento21 pagineQuality Management Principles for HealthcareDoroy ManlosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of TQM - February 2016Documento3 paginePrinciples of TQM - February 2016dmugalloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsDa EverandHuman Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustaining Creativity and Innovation in Organizations: a Tool Kit: Employee Suggestion SystemDa EverandSustaining Creativity and Innovation in Organizations: a Tool Kit: Employee Suggestion SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP2000 v15 Steel P-M Interaction RatiosDocumento1 paginaSAP2000 v15 Steel P-M Interaction Ratiostaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- PB SectionDocumento1 paginaPB Sectiontaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- S4 PDFDocumento1 paginaS4 PDFtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
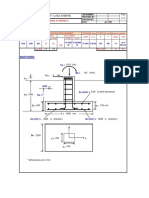
- Design Summary:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)Documento1 paginaDesign Summary:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)taz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Design Calc Slide 5Documento1 paginaStructural Design Calc Slide 5taz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
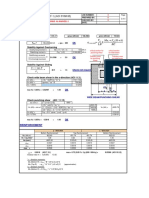
- Input Data:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)Documento1 paginaInput Data:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)taz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Isolated Foundation Shear and Reinforcement CheckDocumento1 paginaIsolated Foundation Shear and Reinforcement Checktaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
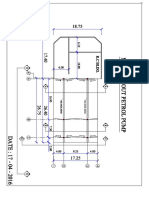
- JZERROOF Plan View DiagramDocumento1 paginaJZERROOF Plan View Diagramtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
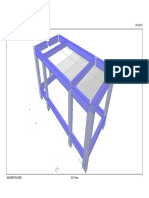
- 3d ViewDocumento1 pagina3d Viewtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- F3Documento1 paginaF3taz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Bracing SketchDocumento1 paginaSteel Bracing Sketchtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Residential Apartment Structural Design BriefDocumento5 pagineResidential Apartment Structural Design Brieftaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- F2 PDFDocumento1 paginaF2 PDFtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- JobDocumento1 paginaJobtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- DL LL W M: Structural Al-Nakheel 6 Two Way SlabDocumento1 paginaDL LL W M: Structural Al-Nakheel 6 Two Way Slabtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Truss Detail - 2 Inch 1-7300Documento1 paginaTruss Detail - 2 Inch 1-7300taz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Culvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement DetailsDocumento1 paginaCulvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Detailstaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Truss Detail - 2 InchDocumento1 paginaTruss Detail - 2 Inchtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Culvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Details PDFDocumento1 paginaCulvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Details PDFtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H DDocumento7 pagineDraw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H Dtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- View Project Schedules with Timescaled Logic DiagramsDocumento4 pagineView Project Schedules with Timescaled Logic Diagramstaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- School Name Remarks Generic/Non GenericDocumento1 paginaSchool Name Remarks Generic/Non Generictaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project Planning & Control-IDocumento3 pagineProject Planning & Control-Itaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Course StudiesDocumento16 pagine3 Course Studiestaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- DWG 03 ModelDocumento1 paginaDWG 03 Modeltaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento17 pagineAssignmenttaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H DDocumento7 pagineDraw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H Dtaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionDocumento4 pagineQuestiontaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- DWG 01 ModelDocumento1 paginaDWG 01 Modeltaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- DWG 02 ModelDocumento1 paginaDWG 02 Modeltaz_taz3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento55 pagineProject Reportshrestha mobile repringNessuna valutazione finora
- Peta in Business MathDocumento2 paginePeta in Business MathAshLeo FloridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Find Offshore JobsDocumento2 pagineFind Offshore JobsWidianto Eka PramanaNessuna valutazione finora
- SSS Presentation PDFDocumento50 pagineSSS Presentation PDFEMMANUEL SSEWANKAMBO100% (2)
- Benno Przybylski Righteousness in Matthew and His World of Thought Society For New Testament Studies Monograph Series 1981Documento198 pagineBenno Przybylski Righteousness in Matthew and His World of Thought Society For New Testament Studies Monograph Series 1981alenin1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Office 365 - Information Security Management System (ISMS) ManualDocumento18 pagineOffice 365 - Information Security Management System (ISMS) ManualahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pinagsanhan Elementary School Kindergarten AwardsDocumento5 paginePinagsanhan Elementary School Kindergarten AwardsFran GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Procter &gamble: Our PurposeDocumento39 pagineProcter &gamble: Our Purposemubasharabdali5373Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice 4Documento5 paginePractice 4Nguyễn Tuấn ĐịnhNessuna valutazione finora
- National University's Guide to Negligence PrinciplesDocumento35 pagineNational University's Guide to Negligence PrinciplesSebin JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bud APAC - Prospectus PDFDocumento506 pagineBud APAC - Prospectus PDFtaixsNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Have A BEAUTIFUL MIND Edward de BDocumento159 pagineHow To Have A BEAUTIFUL MIND Edward de BTsaqofy Segaf100% (1)
- 03 A - Court-Annexed MediationDocumento3 pagine03 A - Court-Annexed MediationXaye CerdenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 The Seven Years' War, 1756-1763Documento3 pagineLecture 4 The Seven Years' War, 1756-1763Aek FeghoulNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Shopee - Final Project SummaryDocumento3 pagineComputer Shopee - Final Project Summarykvds_2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Concepts: Source: Managing Business Process Flows by Anupindi, Et AlDocumento7 pagineFlow Concepts: Source: Managing Business Process Flows by Anupindi, Et AlKausik KskNessuna valutazione finora
- The Paradox ChurchDocumento15 pagineThe Paradox ChurchThe Paradox Church - Ft. WorthNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Edward The Confessor Catholic Church: San Felipe de Jesús ChapelDocumento16 pagineSt. Edward The Confessor Catholic Church: San Felipe de Jesús ChapelSt. Edward the Confessor Catholic ChurchNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Questions of FinanceDocumento126 pagineInterview Questions of FinanceAnand KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Eschatology in The Old Testament PDFDocumento175 pagineEschatology in The Old Testament PDFsoulevansNessuna valutazione finora
- Immigration and Exploration of The USADocumento6 pagineImmigration and Exploration of The USAТетяна МешкоNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital GoodsDocumento18 pagineChapter-10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital GoodsHASNAT ABULNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual GPF Statement for NGO TORA N SINGHDocumento1 paginaAnnual GPF Statement for NGO TORA N SINGHNishan Singh Cheema56% (9)
- Century 21 Broker Properti Jual Beli Sewa Rumah IndonesiaDocumento2 pagineCentury 21 Broker Properti Jual Beli Sewa Rumah IndonesiaAyunk SyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Organized Crime in Central America The Northern Triangle, Report On The Americas #29 DRAFTDocumento125 pagineOrganized Crime in Central America The Northern Triangle, Report On The Americas #29 DRAFTLa GringaNessuna valutazione finora
- Afi11 214Documento3 pagineAfi11 214amenendezamNessuna valutazione finora
- Allodial InterestDocumento17 pagineAllodial InterestSarah75% (4)
- Jack Mierzejewski 04-09 A4Documento7 pagineJack Mierzejewski 04-09 A4nine7tNessuna valutazione finora
- Forecasting - Penilaian BisnisDocumento63 pagineForecasting - Penilaian BisnisyuliyastutiannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taxation Reviewer.Documento176 pagineTaxation Reviewer.francesNessuna valutazione finora