Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
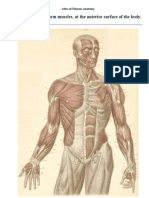
Anatomy
Caricato da
DrGandhi Bhaskar Patrudu LankaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Anatomy
Caricato da
DrGandhi Bhaskar Patrudu LankaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ANATOMY
medpgnotes
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
CONTENTS
UPPER LIMB .................................................................................................................................................................. 6
MUSCLES OF UPPER LIMB ......................................................................................................................................... 6
NERVES OF UPPER LIMB............................................................................................................................................ 7
ARTERIES OF UPPER LIMB ......................................................................................................................................... 8
VEINS OF UPPER LIMB ............................................................................................................................................... 9
LIGAMENTS OF UPPER LIMB ..................................................................................................................................... 9
FASCIA OF UPPER LIMB ............................................................................................................................................. 9
JOINTS OF UPPER LIMB ............................................................................................................................................. 9
MOVEMENTS OF UPPER LIMB .................................................................................................................................. 9
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF UPPER LIMB .......................................................................................................... 11
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SHOULDER ................................................................................................. 12
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR SCAPULAR REGION ................................................................. 12
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA ANTERIOR ................................................................................... 12
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA MEDIAL ........................................................................................ 13
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA-LATERAL & POSTERIOR .................................................................. 13
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF ARM ......................................................... 13
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF FOREARM ................................................ 13
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF FOREARM .............................................. 13
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF HAND ................................................................................... 14
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THENAR MUSCLES ..................................................................................... 14
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - HYPOTHENAR MUSCLES ............................................................................ 14
LOWER LIMB ............................................................................................................................................................... 14
MUSCLES OF LOWER LIMB ...................................................................................................................................... 14
NERVES OF LOWER LIMB ........................................................................................................................................ 15
ARTERIES OF LOWER LIMB ...................................................................................................................................... 17
LYMPHATICS OF LOWER LIMB ................................................................................................................................ 17
LIGAMENTS OF LOWER LIMB .................................................................................................................................. 17
FASCIA OF LOWER LIMB .......................................................................................................................................... 18
JOINTS OF LOWER LIMB .......................................................................................................................................... 18
MOVEMENTS OF LOWER LIMB ............................................................................................................................... 18
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF LOWER LIMB ......................................................................................................... 19
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - GLUTEAL REGION ...................................................................................... 20
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR THIGH ....................................................................................... 21
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MEDIAL THIGH ........................................................................................... 21
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR THIGH ..................................................................................... 21
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR LEG ......................................................................................... 21
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - LATERAL LEG .............................................................................................. 21
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR LEG ........................................................................................... 22
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - DORSAL FOOT ............................................................................................ 22
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - FIRST LAYER OF SOLE ................................................................................. 22
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SECOND LAYER OF SOLE ............................................................................ 22
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THIRD LAYER OF SOLE ............................................................................... 22
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - FOURTH LAYER OF SOLE ............................................................................ 22
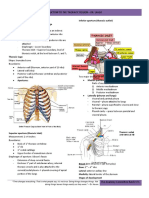
THORAX ....................................................................................................................................................................... 23
DIAPHRAGM ............................................................................................................................................................ 23
MUSCLES OF THORAX ............................................................................................................................................. 23
NERVES OF THORAX ................................................................................................................................................ 23
SYMPATHETIC CHAIN .............................................................................................................................................. 24
ARTERIES OF THORAX ............................................................................................................................................. 24
VEINS OF THORAX ................................................................................................................................................... 24
LYMPHATICS OF THORAX ........................................................................................................................................ 24
FASCIA OF THORAX ................................................................................................................................................. 25
JOINTS OF THORAX ................................................................................................................................................. 25
MOVEMENTS OF THORAX ....................................................................................................................................... 25
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF THORAX ................................................................................................................. 25
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THORACIC WALL ........................................................................................ 26
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ............................................................................................................................................... 27
MUSCLES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS...................................................................................................................... 27
NERVES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ........................................................................................................................ 27
ARTERIES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS...................................................................................................................... 28
VEINS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ........................................................................................................................... 30
LYMPHATICS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ................................................................................................................ 30
LIGAMENTS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS .................................................................................................................. 30
FASCIA OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ......................................................................................................................... 31
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS ......................................................................................... 31
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL ................................................................... 32
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL ................................................................. 32
HEAD AND NECK ......................................................................................................................................................... 33
MUSCLES OF HEAD AND NECK ................................................................................................................................ 33
NERVES OF HEAD AND NECK .................................................................................................................................. 33
ARTERIES OF HEAD AND NECK ................................................................................................................................ 35
VEINS OF HEAD AND NECK...................................................................................................................................... 36
LYMPHATICS OF HEAD AND NECK .......................................................................................................................... 36
LIGAMENTS OF HEAD AND NECK ............................................................................................................................ 36
FASCIA OF HEAD AND NECK .................................................................................................................................... 37
JOINTS OF HEAD AND NECK .................................................................................................................................... 37
MOVEMENTS OF HEAD AND NECK ......................................................................................................................... 37
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF HEAD AND NECK ................................................................................................... 38
GANGLIA ................................................................................................................................................................. 39
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SUBOCCIPITAL GROUP OF MUSCLES ......................................................... 40
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY FACE .......................................................................................................... 40
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES ........................................................................... 40
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MIDDLE EAR MUSCLES .............................................................................. 41
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF MASTICATION ...................................................................... 41
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF ANTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK............................................. 41
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK ........................................... 42
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - PREVERTEBRAL AND LATERAL MUSCLES ................................................... 42
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - CONSTRICTORS OF PHARYNX .................................................................... 42
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - LONGITUDINAL MUSCLES OF PHARYNX .................................................... 42
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF LARYNX ................................................................................ 42
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF SOFT PALATE ........................................................................ 43
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - INTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE .............................................................. 43
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE ............................................................. 43
OSTEOLOGY................................................................................................................................................................. 43
BASICS IN OSTEOLOGY ............................................................................................................................................ 43
EPIPHYSIS ................................................................................................................................................................ 44
METAPHYSIS ............................................................................................................................................................ 44
CARTILAGE .............................................................................................................................................................. 45
OSSIFICATION .......................................................................................................................................................... 45
TYPES OF JOINTS ..................................................................................................................................................... 45
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
FORAMINA .............................................................................................................................................................. 46
RIB NOTCHING ........................................................................................................................................................ 48
HISTOLOGY .................................................................................................................................................................. 48
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
KEY TO THIS DOCUMENT
Text in normal font Must read point.
Asked in any previous medical entrance
examinations
Text in bold font Point from Harrisons
th
text book of internal medicine 18
edition
Text in italic font Can be read if
you are thorough with above two.
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
UPPER LIMB
MUSCLES OF UPPER LIMB
Muscles attached to greater tubercle of humerus
Muscles attached to coracoid process
Rotator cuff
Downward dislocation of glenohumeral joint while
carrying heavy suitcase prevented by
Downward dislocation of glenohumeral joint while
carrying heavy suitcase NOT prevented by
Lattisimus dorsi
Levator scapulae is attached to
Pectoralis major
Finger by which all muscles in hand can be tested
Tendon frequently absent in hand
First extensor compartment of wrist has
Subcutaneous muscle
Dual blood supply
Composite muscle
Composite muscle
NOT a composite muscle
Digastrics muscles
NOT a digastrics muscles
Muscle commonly affected by congenital absence
Isolated function of flexor digitorum
superficialis is best assessed by
Flexion of DIP with fixing of PIP tests action of
MC absent congenital muscle
Serratus anterior muscle
Subclavian vein and subclavian artery separated by
Scalenus anticus muscle
Short head of Biceps is attached to
Biceps brachii is attached to
Responsible for pronator syndrome
NOT responsible for pronator syndrome
Pronator quadrates has same innervations of
Trapezius is NOT attached to
Third head of Coracobrachialis is denoted as
Forgotten muscle
Muscle of back functionally related to thorax
Winging of scapula due to paralysis of
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor
Coracobrachialis, Short head of biceps, Pectoralis minor
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor,
Subscapularis
Deltoid, Coracobrachialis, Short head of biceps
Latissiums dorsi
Inserted into bicipital groove of humerus, Used to fill up
back defects
Transverse process of C1, C2, C3 and C4
Blood supply by perforating branch of internal thoracic
artery, Nerve supply by pectoral nerve
Thumb
Palmaris longus
Extensor pollicis brevis, Abductor pollicis longus
Palmaris brevis
Brachialis, Pectineus, Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor digitorum profundus, Pectineus, Biceps femoris,
Adductor magnus
Pectineus, Adductor magnus, Biceps femoris
Flexor carpi ulnaris, Rectus femoris
Muscle fibres in ligament of Treitz, Omohyoid,
Occipitofrontalis
Sternocleidomastoid
Pectoralis major
Flexion of PIP with adjacent digits held in
extension
Flexor digitorum profundus
Pectoralis major
Helps in forceful inspiration
Scalenus anterior
Separates subclavian vein from subclavian artery
Coracoid process
Posterior surface of radial head
Struthers ligament, Bicipital aponeurosis, Flexor
digitorum superficialis
Pronator quadratus
Flexor pollicis longus (anterior interosseous nerve)
First rib
Struthers ligament
Subscapularis
Latissimus dorsi
Serratus anterior
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
Trapezius palsy also cause
Abductor pollicis longus
Winging of scapula
Splits in to two parts, one part is attached
to base of first metacarpal, second part is
attached to trapezium
Musculocutaneous nerve and radial nerve
C5, C6 and C7 (radial nerve)
Dorsal interossei, 3rd and 4th lumbricals
Flexor pollicis longus tendon
Accessory head of flexor pollicis longus
Brachialis is supplied by
Brachioradialis is supplied by
Bipennate muscles
Hammer thumb is due to
Gantzers muscle
NERVES OF UPPER LIMB
Nerves piercing scaleneus medius
MC nerve affected in neuralgic
amyotrophy
Lateral pectoral nerve
Medial pectoral nerve pierces
Coracobrachialis syndrome is associated
with
Long thoracic nerve tested by
Nerve supply to Pronator muscle of Distal Radioulnar
joint
Winged scapula associated with injury to
Nerves directly related to humerus
Pronator quadratus has same innervations as that of
Flexor pollicis is supplied by
Wrist drop caused by
Saturday night palsy
Wartenberg syndrome
Supinator channel syndrome
Arcade of Frohn
Supracondylar syndrome
Pronator teres syndrome is associated
with
Martin gruber connections are
Tip of shoulder is supplied by
Supraclavicular branches of brachial plexus
Palmaris brevis
Dorsal scapular nerve, long thoracic
nerve
Thoracodorsal nerve (nerve to lattissimus
dorsi)
C5, C6, C7. Pierces clavipectoral fascia,
makes a loop with medial pectoral nerve
in front of first part of axillary artery
Pectoralis minor and major
Loss of musculocutaneous nerve
Raising the arm above the head on affected side
Anterior Interosseous Nerve
Long thoracic nerve
Axillary nerve, radial nerve, ulnar nerve
Flexor pollicis longus
Anterior interosseous nerve
Lead poisoning, Radial nerve palsy
Radial nerve
Superficial sensory branch of radial nerve
Compression of deep branch of radial
nerve
Seen in some persons, one head of pronator
is a sharp tendon, leads to radial nerve
damage
Entrapment of medial nerve beneath
ligament of struthers
Median nerve
Connection between median and ulnar nerve in hand
(30 % of population)
Supraclavicular nerve
Suprascapular nerve, long thoracic nerve, subclavian
nerve, dorsal scapular nerve
Superficial branch of ulnar nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
T1 Dermatome
Root value of long thoracic nerve
Dermatome of index finger and thumb
Root value of Thoracodorsal Nerve
Over lateral deltoid
Thumb and index finger
Middle finger
Little finger of hand corresponds to
Axilla and medial arm
Ulnar collateral Nerve is a branch of
Dorsal scapular nerve supplies
Nerve to Serratus anterior
Pseudoganglion of axillary nerve is
situated in
Baxter nerve
Maximum crossing and sensory
innervations in hand
Medial side of forearm to base of little finger
C5, C6, C7
C6,C6
C6,C7,C8
C5
C6
C7
C8
T1
Radial Nerve To Medial Head Of Triceps
Levator Scapulae
C5,C6,C7
Posterior branch supplying teres minor
Motor branch to abductor digiti minimi
Dorsal aspect of middle phalanx of ring
finger
ARTERIES OF UPPER LIMB
Branches of first part of subclavian artery
Branches of second part of subclavian
artery
Branch of third part of subclavian artery
Branches of first part of axillary artery
Branches of second part of axillary artery
Branches of third part of axillary artery
Largest branch of axillary artery
Subscapular artery
Course of subscapular artery
Direct branch of subclavian artery
involved in anastomosis around shoulder
Artery NOT involved in scapular
anastomosis
Pectoralis major is supplied by
Vertebral artery, internal thoracic artery
(superior epigastric and musculophrenic
artery), thyrocervical trunk
(suprascapular artery, inferior thyroid
artery), transverse cervical artery
Costocervical branch, deep cervical
artery, superior intercostals artery
Dorsal scapular artery
Superior thoracic artery
Thoracoacromial artery, lateral thoracic
artery
Subscapular artery (circumflex scapular
and thoracodorsal artery), anterior
circumflex humeral artery, posterior
circumflex humeral artery
Subscapular artery
Largest part, from 3rd part of axillary
artery, accompanied at distal part by
nerve to latissimus dorsi
Runs downwards on posterior axillary
wall to inferior angle of scapula
Dorsal scapular artery
Superior thoracic artery
Pectoral branch of thoracoacromial artery, Intercostal
artery, Lateral thoracic artery, Internal mammary artery
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
Troebe arcade is between
Deep palmar arch
Superior and inferior ulnar collateral
arteries are branches of
Anastomosis around elbow joint
Blood supply to thumb
Two layers of supinator
Direct continuation of radial artery
Brachial artery
Between branches of brachial artery and
proximal parts of radial and ulnar artery
Deep palmar arch
VEINS OF UPPER LIMB
Cephalic vein is a content in
Deltopectoral triangle
LIGAMENTS OF UPPER LIMB
Weight of upper limb transmitted to axial skeleton by
NOT involved in transmission of weight to axial ligament
Medial collateral ligament of elbow is
closely related to
Ligament of testus
Only carpal bone with tendinous
attachment
Coracoclavicular ligament
Coracoacromial ligament
Ulnar nerve
Radioscapholunate ligament
Pisiform (flexor carpi ulnaris)
FASCIA OF UPPER LIMB
Axillary sheath is derived from
Fascia around nerve bundle of brachial plexus is derived
from
Fascia bridging two heads of flexor carpii
ulnaris
Prevertebral fascia
Prevertebral fascia
Osbome fascia
JOINTS OF UPPER LIMB
Supination and pronation occur at
Adduction of thumb occurs at
Part of interphalangeal joint in which articular capsule is
deficient
Dynamic stabilizer of shoulder joint
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
stabilizes
Radioulnar joint
Carpometacarpal joint
Dorsal
Rotator cuff
Distal radioulnar joint
MOVEMENTS OF UPPER LIMB
Ratio of scapulohumeral rhythm
2:1
www.medpgnotes.com
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
Compressed during flexion and abduction of shoulder
joint
NOT compressed during flexion and abduction of
shoulder joint
Teres major helps in
Clavicular portion of deltoid helps in
Action of deltoid and supraspinatus
0 15* abduction by
15 90* abduction by
More than 90* abduction by
NOT involved in shoulder abduction
Rupture of supraspinatus manifests as
NOT involved in retraction of shoulder
Movements during abduction of shoulder
Abduction of shoulder joint above 90* is due to the
action of
Extensor of shoulder joint
Initiation of abduction in shoulder joint
Movement NOT taking place during abduction of
shoulder joint
Does NOT occur during abduction of shoulder
Structures that may be compressed during flexion and
abduction of shoulder joint
Bursa over shoulder joint that does NOT
communicate with joint cavity
Muscle NOT used to abduct shoulder
Muscles retracting scapula
Muscle does NOT retract scapula
Action of anconeus
Flexion of elbow with forearm in
midprone position is done by
Pronation in mid flexed forearm by
Flexors of forearm
NOT a flexor of forearm
When a heavy object is lowered, extension of elbow is
brought about by
Powerful supinator of semiflexed elbow
Art of blessing is associated with
Adduction of wrist is done by
Function of lumbricals
Action of Lumbricals
Paralysis of opponens pollicis muscle leads to
Pronation and supination occurs in
Long head of biceps tendon, Supraspinatus tendon,
Subacromial bursa
Suprascapular nerve
Adduction and medial rotation
Medial rotation
Shoulder abduction
Supraspinatus
Deltoid
Trapezius and serratus anterior
Pectoralis major
Difficulty in initiation of abduction
Levator scapulae
Lateral rotation of scapula, Axial rotation at
acromioclavicular joint, elevation of humerus,
Movements at clavicular end of sternoclavicular joint
Serratus anterior
Deltoid
Supraspinatus
Medial rotation of scapula
Medial rotation of scapula
Long head of biceps tendon, supraspinatus tendon,
subacromial bursa
Subacromial bursa, subdeltoid bursa
Deltoid
Trapezius , Rhomboid major, Rhomboid minor
Levator scapulae
Screwing movements
Brachioradialis
Brachioradialis
Brachialis, Brachioradialis, Biceps brachii
Anconeus, Flexor pollicis longus, Pronator teres
Active lengthening of flexors
Biceps brachii
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexion at MCP joint, Extension of IP joint
Flexion at MCP joint and Extension at IP joint
Loss of flexion of thumb
Radioulnar joint
www.medpgnotes.com
10
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF UPPER LIMB
Medial wall of axilla is formed by
Lower angle of scapula
Contents of bicipital groove
Contents of upper triangular space
Contents of lower triangular space
Structures passing through quadrangular
space
Axillary hiatus syndrome
Axillary arch
Boundary of auscultation formed by
NOT a boundary of triangle of auscultation
Retromammary space is between
Structures piercing clavipectoral fascia
Ligament formed by Clavipectoral Fascia
NOT true about axilla
Lateral boundary of cubital fossa
Floor of cubital fossa
Contents of cubital fossa
Lateral border of cubital fossa formed by
Infection of index finger spreads to
Parona space in
Radial bursa encloses tendon of
Ulnar bursa
Artery in anatomical snuff box
Anatomical snuff box
Anatomical snuff box
NOT a component forming anatomical snuff box
Attached to hook of hamate
NOT pass under flexor retinaculum
Pass under flexor retinaculum
Supination pronation axis pass through
Superficial cut of flexor retinaculum spares
Carpal tunnel contains
Serratus
T7
Ascending branch of anterior circumflex artery, Synovial
membrane of shoulder joint
Circumflex scapular artery, subscapular
vessels
Radial nerve, profunda brachii vessels
Axillary nerve, posterior circumflex
humeral vessels
Compression of axillary nerve in
quadrangular space
Muscular arch extending from lattissimus
dorsi to pectoralis major
Scapula , Trapezius, Lattisimus dorsi
Serratus anterior
Deep pectoral fascia and breast
Lateral pectoral nerve, Cephalic vein, Thoracoacromial
artery
Costocoracoid Ligament
Hexagonal
Brachioradialis
Brachialis and supinator
Brachial artery, Ulnar artery, Median nerve, Tendon of
biceps brachii
Brachioradialis
Thenar space
Forearm
Flexor pollicis longus
Around tendon of flexor digitorum
superficialis and flexor digitorum
profundus
Radial artery
Radial artery, Superficial Cutaneous branch of radial
nerve, Abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis
brevis form anterior wall
Abductor pollicis longus and external pollicis brevis
form anterior wall
Extensor carpii radialis brevis
Flexor retinaculum
Ulnar nerve
Median nerve, Flexor digitorum superficialis, Flexor
digitorum profundus
Centre of radial head to distal ulnar
articular disc
Median nerve
Median nerve, Flexor pollicis longus, Flexor digitorum
www.medpgnotes.com
11
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
NOT a content of carpal tunnel
Carpal tunnel does NOT contain
Guyon canal
NOT a cause of carpal tunnel syndrome
Axillary abscess safely drained by
Structure NOT attached to coracoid process
Structures attached to greater tuberosity of humerus
Pisiform bone give attachment to
Infraspinatus syndrome due to
Midpalmar space
Dorsal digital expansion
Creland, Grayson, Landsnee ligaments
Vincula
superficialis
Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi radialis
Convey ulnar nerve, Lies at wrist
Addisons disease
Floor approach
Long head of biceps
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor
Pisohamate ligament
Suprascapular nerve
Space lying medial to a fibrous septum
attaching palmar aponeurosis to 3rd
metacarpal bone
Base of expansion over head of
metacarpal, apex is attached to distal
phalanx
Digital facial complex
Each finger has 2 vincula brevia and 3
vincula longa (filiform)
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SHOULDER
Trapezius
Deltoid
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid Major
Rhomboid Minor
Spinal Part of Accessory Nerve
Axillary Nerve
Anterior rami of C3,C4
Dorsal Scapular Nerve
Dorsal Scapular Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR SCAPULAR REGION
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Major
Teres Minor
Long Head of Triceps Brachii
Suprascapular Nerve
Lower Subscapular Nerve
Axillary Nerve
Radial Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA ANTERIOR
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Subclavius
Medial & Lateral Pectoral Nerve
Medial Pectoral Nerve
Nerve to Subclavius
www.medpgnotes.com
12
UPPER LIMB
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA MEDIAL
Serratus Anterior
Long Thoracic Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - AXILLA-LATERAL & POSTERIOR
Subscapularis
Lattisimus Dorsi
Upper & Lower Subscapular Nerve
Thoracodorsal Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF ARM
Coracobrachialis
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Musculocutaneous Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF
FOREARM
Flexor carpii Ulnaris
Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi radialis
Pronator teres
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Pronator Quadratus
Ulnar Nerve
Median Nerve
Median Nerve
Medial half Ulnar Nerve
Lateral Half Anterior Interosseous
Nerve
Anterior Interosseous Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF
FOREARM
Brachiradialis
Extensor carpi Radialis longus
Extensor carpi Radialis brevis
Anconeus
Extensor Digitorum
Radial Nerve
Posterior Interosseous Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
13
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Extensor digiti minimi
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor Indicis
Extensor Pollicis Longus
Extensor Pollicis brevis
Abductor pollics Longus
Supinator
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF HAND
Palmaris brevis
Dorsal Interossei
Palmar interossei
Adductor pollicis
Lumbricals
Ulnar Nerve
Medial two Ulnar nerve
Lateral two Median Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THENAR MUSCLES
Opponens Pollicis
Abductor Pollicis brevis
Flexor Pollicis brevis
Median Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - HYPOTHENAR MUSCLES
Opponens digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi
Ulnar Nerve
LOWER LIMB
MUSCLES OF LOWER LIMB
Key muscle of gluteal region
Lurching gait is due to paralysis of
Trendelenberg sign is positive in paralysis of
Hamstrings
Attached to ischial tuberosity
Adductor component of thigh in upper
Piriformis
Gluteus medius
Tensor fascia lata, Gluteus medius, Gluteus minimus
Long head of biceps femoris, Semitendinosus,
Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris
Coracobrachialis
www.medpgnotes.com
14
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
limb is represented by
Triceps coxa
Spare part
Piriformis syndrome is associated with
Anterior division of pectineus is supplied
by
Posterior division of pectineus is supplied
by
Violent inversion of foot will lead to avulsion of tendon
th
of which of the muscle attached to tuberosity of 5
metatarsal
Stance phase muscles
Muscles acting both at knee and ankle joint
Muscle flexing knee and also plantar
flexion
Blood supply of gastrocnemius
Nerve supply of gastrocnemius
NOT a muscle of anterior compartment of leg
Muscles of anterior compartment of leg
Stimulation of skin overlying Sartorius muscle at lower
part of Hunters canal would lead to stimulation of
Intraarticular tendon
Biceps femoris is inserted into
Muscle pathology associated with too
many toes sign
Masters knot of Henry
Claw to deformity
Muscle passing on the groove on lower
surface of talus (Sustentaculum tali)
Hallux saltans
Powerful push off muscle
Beef to calf
Muscle passing through groove on cuboid
Medial longitudinal arch provides
Lateral longitudinal arch provides
Keystone to lateral longitudinal arch
Jack great toe test for
Obturator internus, superior and inferior
gemelli
Gracilis
Sciatic nerve
Femoral nerve
Anterior division of obturator nerve
Peroneus brevis
Quadriceps, Gastrocnemius
Gastrocnemius, Soleus
Gastrocnemius
Sural artery
Tibial nerve
Peroneus brevis
Peroneus tertius, Extensor hallucis longus, Tibialis
anterior
Iliopsoas muscle
Popliteus
Head of Fibula
Tibialis posterior
Crossing of flexor digitorum longus and
flexor hallucis longus tendon on medial
side of foot
Due to scarring of quadrates plantar
Flexor hallucis longus
Thickening of flexor hallucis longus
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor hallucis longus
Peroneus longus
Resiliency
Rigidity
Cuboid
Arch of foot
NERVES OF LOWER LIMB
Iliacus and psoas are supplied by
Sleeping foot is associated with
L2, L3
Compression of sciatic nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
15
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Gluteus medius is supplied by
Superior gluteal nerve does NOT supply
NOT supplied by Superior Gluteal Nerve
Superior gluteal nerve supplies
Tensor fascia Lata is supplied by
Skin over femoral triangle is supplied by
S1 root irritation will result in pain along
Pain felt between great toe and second toe is due to
involvement of
Two branches of obturator nerve are
supplied by
Muscles supplied by obturator nerve
Nerve associated with adduction of thigh at hip
Lateral rotators of thigh are supplied by
Defective adduction of hip joint and pain in hip and
knee joint. Nerve involved
Posterior division of obturator nerve
innervates
Posterior division of obturator nerve
innervates
Nerve to obturator internus supplies
Supplied by Obturator Nerve
Thickest nerve of the body
Anterior relations of Sciatic nerve in Gluteal region
Does NOT supply gluteal region
Branch of sacral plexus
Root value for Lumbar Plexus
Largest branch of lumbar plexus
Nerve in the groove between iliacus and
psoas major
Pectineus is supplied by
Largest branch of Lumbar plexus
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh supplies skin over
Lateral cutaneous nerve
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (lateral
cutaneous nerve of thigh)
Referred pain from following sites felt on inner side of
thigh
Great saphenous vein associated with
Sensory supply of medial border of foot
Longest cutaneous branch of Femoral nerve
Skin overlying region where a venous cut down is made
to access greater saphenous vein is supplied by
Altered sensation over area of greater saphenous vein
in leg is seen due to an injury to
Tibial nerve
Nervus hesitans
Medial plantar nerve supplies
Superior gluteal nerve
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus Maximus
Gluteal medius, gluteal minimus
Superior Gluteal Nerve
Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve
Lateral side of foot
L5
Adductor brevis
Adductor component
Obturator nerve
Obturator nerve
Obturator nerve
Knee joint
Obturator externus, adductor brevis,
adductor magnus
Obturator internus, superior gemelli
Gracilis
Sciatic nerve
Obturator internus, Quadratus femoris, Gemelli
Sciatic nerve
Nerve to gemelli
L4,L5
Femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
Medial aspect of thigh, posteroinferior aspect of
buttock, scrotum, back of thigh, popliteal fossa
L2,L3
L2, L3. NOT a branch of femoral nerve,
NOT a part of subsartorial plexus
Inflamed pelvic appendix, inflamed ovaries, stone in
pelvic ureter
Saphenous nerve
Saphenous nerve
Saphenous nerve
Femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
Ventral division of L4, L5, S1, S2
Deep fibular nerve
Abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis,
www.medpgnotes.com
16
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
flexor hallucis brevis, 1st lumbricals
ARTERIES OF LOWER LIMB
Companion artery of sciatic artery is a
branch of
Gluteus medius is supplied by
Arterial supply to ACL
Popliteal artery difficult to palpable because
Femoral artery is the division of external iliac artery at
the level of
Branch of femoral artery that does NOT
pierce cribriform fascia
Arteria comitans nervi ischidici
In children, head of femur is NOT supplied
by
Extracapsular arterial ring of femoral
neck is formed by
Artery in adductor canal
Blood supply to posterior compartment of
thigh
Lateral circumflex femoral artery is a
branch of
Superficial femoral artery becomes
popliteal artery
Accessory obturator artery is a branch of
Popliteal artery pulse is difficult to feel because
Artery of tarsal canal is a branch of
Nutrient artery to tibia
Peroneal artery is a branch of
Posterior tibial artery pulse
Blood supply of great toe
Dorsalis pedis pulse
Blood supply to calf and sole of foot
Inferior gluteal artery
Superior gluteal artery
Middle genicular artery
NOT superficial, Does NOT pass over prominent bony
structure
Beyond Inguinal Ligament
Superficial circumflex iliac artery
Branch of internal iliac artery
Nutrient artery
Trochanteric anastomosis
Femoral artery
Deep femoral artery
Profunda femoral artery
At a hiatus in adductor magnus
Inferior epigastric artery
It is not superficial and does not cross prominent bone
Posterior tibial artery
Posterior tibial artery
Posterior tibial artery
Felt behind medial malleolus
Dorsalis pedis artery, Medial plantar artery
Between extensor hallucis longus and
extensor digitorum longus
Posterior tibial artery
LYMPHATICS OF LOWER LIMB
Lymphatic supply of heel and lateral part of foot
Popliteal lymph nodes
LIGAMENTS OF LOWER LIMB
Iliofemoral ligament arise from
Anterior inferior iliac spine
www.medpgnotes.com
17
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Prevents hyperextension of hip and thigh
Bigelow ligament at
Cruciate ligaments are supplied by
Anterior cruciate ligament prevents
Posterior cruciate ligament prevents
Ligament of Humphry
Ligament of Wrisbery
Expansion of Semimembranosus tendon
NOT contributing to stability of ankle joint
Posterior dislocation of tibia prevented by
Coronary ligament is present between
Anterior cruciate Ligament attaches to
Abduction of leg at knee prevented by
Lisfranc ligament
Medial deltoid ligament arise from
Iliofemoral ligament
Hip joint
Middle geniculate branch of popliteal
artery
Anterior dislocation of tibia
Posterior dislocation of tibia
Anterior meniscofemoral ligament
Posterior meniscofemoral ligament
Oblique Popliteal ligament
Calcaneonavicular or spring ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Meniscus and tibial cartilage
Medial part of anterior intercondylar area
Medial or tibial collateral ligament
Interosseous cuneometatarsal ligament
Medial malleolus
FASCIA OF LOWER LIMB
Iliotibial tract
Modification of deep fascia, attached to
Gerdy tubercle
Iliac crest to lateral condyle of tibia
Obturator fascia
Iliotibial tract extends from
Hiatus of schwalbe is defect in
JOINTS OF LOWER LIMB
Synovial membrane of knee joint
Stability of ankle NOT maintained by
Deltoid ligament is NOT attached to
Deltoid ligament is attached to
NOT a component of deltoid ligament
Ankle joint
Inversion and eversion occurs at
Inversion of foot at
Talocrural
Cuboid bone
Synonymous with plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
Ligament preventing hyperextension of hip
Invaginated posteriorly by cruciate ligament
Cruciate ligaments, Spring ligament
Medial cuneiform
Medial malleolus, Spring ligament, Sustentaculum tali
Tibiofibular ligament
Hinge joint, Joint is strengthened by deltoid ligament,
more stable at dorsiflexed position
Subtalar and mid tarsal joint
Talocalcaneal joint (subtalar joint)
Ankle joint
Articulates with calcaneum
Spring Ligament
Iliofemoral ligament
MOVEMENTS OF LOWER LIMB
Hip joint
Abductor of Hip joint
Medial rotation and abduction of hip is caused by
Medial rotation and abduction is caused by gluteus
medius and minimus
Gluteus medius
Gluteus medius and gluteus minimus
www.medpgnotes.com
18
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Abductors of thigh
NOT an abductor of thigh
Nerve associated with extension of hip
Lateral rotator of thigh
Piriformis
NOT a lateral rotator of thigh
Contraction of tensor fascia lata
Main action of gemelli
Chief extensor of knee joint in hip flexion
Extension of knee joint by
Flexion of knee by
Nerve associated with inability to stand
at tip toe
Knee movements
NOT true about knee movements
Young athlete sitting at the edge of table with knee at
90* flexion. He fully extends it
Patient gets up from sitting position, events taking place
in knee joint
When foot is off the ground medial rotation of tibia is
brought about by
Pair of muscles attached symmetrical to medial
cuneiform bone
Stability of ankle joint is greatest at
Strongest dorsiflexor of foot
Muscles causing dorsiflexion of foot
Plantar flexion is brought about by
Eversion and dorsiflexion of foot
Inversion and Eversion occurs at
Eversion is associated with
In forceful inversion of foot, fracture of tuberosity of
5th metatarsal is due to pull exerted by
Kinetic energy of the body is LEAST in which phase of
walking cycle
Kinetic energy of body is least in
Muscle used in normal walk during stance and swing
Gluteus maximus, Gluteus minimus, Gluteus medius,
Sartorius
Piriformis
Tibial branch of sciatic nerve
Quadratus femoris, Piriformis, Obturator internus
Lateral rotator of hip
Gluteus medius
Flexion of hip, Flexion of knee, abduction of hip
Lateral rotator of thigh
Rectus femoris
Quadriceps femoris
Tibial nerve
Tibial nerve (plantar flexion)
Flexion is coupled with lateral rotation, differential
motion in medial and lateral compartments, in full
extension collateral ligaments are taut, Cruciate
ligaments are taut in full extension and full flexion
Posterior horn of menisci move more than anterior
Movement of tibial tuberosity towards lateral border of
patella
Medial rotation of femur on fixed tibia
Popliteus
Tibialis posterior and Peroneus Longus
Dorsiflexion
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum longus, Extensor hallucis longus,
Tibialis anterior
Plantaris, Flexor hallucis longus, Soleus
Peroneus Tertius
Subtalar joint
Lateral compartment, superficial fibular
nerve
Peroneus brevis tendon
Mid stance phase
Mid stance
Tibialis anterior
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF LOWER LIMB
Langenbeck triangle
Structures between ASIS and pubic symphysis
Lateral compartment of femoral triangle
Apex is formed by anterior superior iliac
spine, base is formed by neck of femur
Femoral artery
Femoral artery, femoral branch of
www.medpgnotes.com
19
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Intermediate compartment of femoral
triangle
Medial most structure of femoral triangle
Content of femoral canal
Floor of femoral triangle
Femoral ring bounded by
Femoral ring NOT bounded by
Anterior wall of femoral sheath is formed
by
Posterior wall of femoral sheath is formed
by
Femoral sheath does NOT contain
Boundaries of popliteal fossa
Floor of popliteal fossa
Structures passing deep to extensor
retinaculum
Structure passing deep to flexor retinaculum
Tendon having attachment on sustentaculum tali
Tibialis posterior NOT involved in
Tendon passing below sustentaculum tali
Undersurface of sustentacular tali
Sustentacular tali gives attachment to
NOT a content of adductor canal
NOT a content of Adductor canal
Flexor digitorum brevis
Upper end of tibia
Upper end of tibia
genitofemoral triangle
Femoral vein
Lymphatics
Lymph node
Iliopsoas, pectineus, adductor longus
Femoral vein, Inguinal ligament, Lacunar ligament
Femoral artery, Femoral Nerve
Fascia transversalis
Fascia iliaca
Femoral Nerve
Both heads of gastrocnemius, Adductor magnus, Biceps
femoris, Semitendinosus
Oblique popliteal ligament
Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus,
anterior tibial artery, deep peroneal
nerve, extensor digitorum longus,
peroneus tertius
Posterior tibial artery, Tibialis posterior
Tibilais posterior
Talus
Flexor hallucis longus
Tendons medial to lateral, anterior to posterior, tibialis
posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus
Tibialis posterior
Popliteal artery
Nerve to vastus lateralis
First layer of sole
Ossification centre at the upper end fuses by 20 years,
gives attachment to menisceal cartilage on
intercondylar ridge, gives attachment to
semimembranous
Patella do NOT articulate with tibia or fibula
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - GLUTEAL REGION
Piriformis
Obturator Intenus
Superior Gemelli
Quadratus Femoris
Inferior Gemelli
Tensor Fascia Lata
Gluteus Medius
Gluteus minimi
Gluteus MAXIMUS
L5,S1,S2
Nerve to Obturator internus
Nerve to Quadratus femoris
Superior Gluteal Nerve
Inferior Gluteal Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
20
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR THIGH
Psoas Major
Iliacus
Vastus Medialis
Vastus Lateralis
Vastus Intermedius
Rectus Femoris
Sartorius
Anterior rami of L1,L2,L3
Femoral Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MEDIAL THIGH
Pectineus
Adductor Magnus
Gracilis
Adductor Longus
Adductor Brevis
Obturator Externus
Femoral Nerve
Adductor Part Obturator Nerve
Hamstring Part Sciatic Nerve
Obturator Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR THIGH
Biceps Femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Sciatic Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR LEG
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
Soleus
Tibialis Posterior
Popliteus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Tibial Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - LATERAL LEG
Peroneus Longus
Superficial Fibular Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
21
LOWER LIMB
ANATOMY
Peroneus brevis
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR LEG
Tibialis anterior
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Peroneus tertius
Deep Fibular Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - DORSAL FOOT
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Deep Fibular Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - FIRST LAYER OF SOLE
Flexor digitorum brevis
Abductor Hallucis
Abductor digiti minimi
Medial Plantar Nerve (Branch of Tibial
Nerve)
Lateral Plantar Nerve (Branch of Tibial
Nerve)
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SECOND LAYER OF SOLE
Quadratus Plantae
Lumbricals
Lateral Plantar Nerve
First Medial Plantar Nerve
Second,third ,Fourth Lateral Plantar
Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THIRD LAYER OF SOLE
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Adductor Hallucis
Flexor Digiti minimi Brevis
Medial Plantar Nerve
Lateral Plantar Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - FOURTH LAYER OF SOLE
Dorsal Interossei
Lateral Plantar Nerve
(First & Second also by Deep Fibular
Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
22
THORAX
ANATOMY
Palmar Interossei
Lateral Plantar Nerve
THORAX
DIAPHRAGM
Diaphragm develops from
Septum transversum, Pleuroperitoneal membrane,
Cervical myotome
Ligamentum teres
Dorsal mesocardium
Pleuropericardial membrane, dorsal mesocardium
Left side lower than right, Left side pushed down by
heart, Hernia occur in left because of weak origin
Phrenic nerve
Sitting position
NOT a derivative of septum transversum
Diaphragm does NOT develop from
Diaphragm is NOT developed from
Diaphragm
Motor supply of diaphragm
Diaphragm is lowest in
MUSCLES OF THORAX
Serratus anterior
Laterally rotates scapula, Attached to medial side of
scapula, Protects scapula, Used in forced inspiration
NERVES OF THORAX
nd
Intercostobrachial nerve is a branch of
Intercostobrachial nerve
Phrenic nerve lies on
Right phrenic nerve
Right phrenic nerve passes through
Left phrenic nerve
Left phrenic nerve
Root value of phrenic nerve
Right crus of diaphragm is supplied by
Incision to avoid iatrogenic phrenic nerve
injury
Typical Intercostal nerves
In case of chest pain with pericarditis and pericardial
effusion referred by
Structure between Suprapleural Membrane and First rib
Typical intercostals space
2 intercostal nerve (lateral cutaneous branch of T2)
Communicates with medial cutaneous
nerve of arm, supplies medial side of arm
Scalenus medius muscle
Motor branch, Sensory branch, Arise from C4, Shorter
course than left phrenic nerve
Vena caval opening
Anterior to scalenus anterior
Supplies mediastinal diaphragmatic pleura on left side
and diaphragmatic peritoneum
C3,C4,C5
Both right and left phrenic nerve
Thoracoabdominal incision in
circumferential manner in periphery
th
3,4,5,6 Intercostal nerves
Phrenic nerve
Thyrocervical Trunk
3, 4, 5, 6
www.medpgnotes.com
23
THORAX
ANATOMY
SYMPATHETIC CHAIN
Thoracic sympathetic chain
Sympathetic trunk lies
Sympathetic trunk enters abdominal cavity through
Ansa subclavia
Greater splanchnic nerve
Lesser splanchnic nerve
Least splanchnic nerve
nd
th
Near heads of 2 to 10 rib
Anterior to IVC
Medial lumbosacral arch behind medial arcurate
ligament
Cord connecting middle and inferior
cervical ganglion
T5 T9
T10 T11
T12
ARTERIES OF THORAX
Arterial supply of lattisimus dorsi
Posterior marking on barium column in barium swallow
study is caused by
Structure related to lower part of manubrium sterni
Musculophrenic artery give rise to
Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
pass between
Branches of thoracoacromial trunk
Artery maintaining blood flow in ligation
of thoracoacromial trunk
Subscapular artery
Aberrant right subclavian artery
Arch of Aorta
Anterior intercostal arteries for
intercostal spaces 7 to 9
Internal and innermost intercostalis
muscle
Pectoral, deltoid, acromial, clavicular
Superior thoracic artery
VEINS OF THORAX
Internal thoracic veins are tributaries of
Azygous vein
Azygous vein
Hemiazygous vein
Brachiocephalic vein
NOT true about brachiocephalic vein
Brachiocephalic veins
In posterior mediastinum, paravertebral,
does not accompany corresponding
arteries
Posterior to esophagus
Often connected with left renal vein
Formed behind sternoclavicular joint, Left vein is longer,
Right vein is vertical, Superior intercostals is tributary of
left vein
st
Right vein unite at left 1 costal cartilage
LYMPHATICS OF THORAX
Delphic nodes
Thoracic duct is also called
Thoracic duct starts at
Pretracheal nodes
Pecquet duct
Continuation of cisterna chyli, Passes through aortic
www.medpgnotes.com
24
THORAX
ANATOMY
Thoracic duct
Thoracic duct does NOT receive tributary from
Thoracic duct receive tributary from
Thoracic duct terminates into
Thoracic duct drains
Thoracic duct injury cause
Thoracic duct crosses right to left at the level of
opening
Arches 3-4 cm above left clavicle at C7
Right bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunk
Bilateral ascending lumbar trunk, Left upper intercostals
duct, Bilateral descending thoracic trunk
Left brachiocephalic vein at the junction of internal
jugular vein and subclavian vein
Whole body except right head and neck,
right hemi thorax, right lung, right heart,
right upper limb, right hemidiaphragm,
right lobe of liver. These structures drain
in to right lymphatic duct
Chylothorax, Lymphopenia, Dehydration, Electrolyte
imbalance
T5
FASCIA OF THORAX
Prevertebral fascia is NOT anterior to
Thoracolumbar fascia
Sympathetic chain
Attached to spinous process and transverse process of
lumbar vertebra, gives attachment to transverse
abdominal and internal oblique
JOINTS OF THORAX
Articular part of rib articulates with
Transverse process of vertebra
MOVEMENTS OF THORAX
Flexor of trunk
Rectus abdominis
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF THORAX
Stiles space
Formen of morgagni
Pass through superior aperture of thorax
Does NOT Pass through superior aperture of thorax
Vena caval opening
Esophageal hiatus
Esophagus enters through
Esophageal hiatus
Esophagus crosses diaphragm at the level of
NOT passing through esophageal hiatus
Aortic opening is at the level of
Between trachea and pretracheal fascia
Superficial epigastric vessels pass through
Left common carotid artery, Left sympathetic trunk,
Thoracic duct
Right recurrent laryngeal nerve
Quadrilateral, right phrenic nerve
Vagus pass through it, Lie in right crura of diaphragm
Muscular part of diaphragm, Right crus
Right vagus, Left vagus, Left gastric artery
T10
Left phrenic nerve
T12
www.medpgnotes.com
25
THORAX
ANATOMY
Aortic opening
Aortic hiatus contain
Structure passing through Aortic opening
Structures passing along with aorta in diaphragmatic
opening
Greater and lesser splanchnic nerve pass
through
Foramen of morgagni
Foramen of morgagni is in
Structure found in cross section of thorax at T4
NOT seen at T4
Pass through posterior to diaphragm
NOT passing posterior to diaphragm
NOT a structure that pass from thorax to abdomen
behind the diaphragm
Exposure of left subclavian artery by supraclavicular
approach does NOT require cutting
Attachment of first rib
NOT an attachment to first rib
Junction of left and right brachiocephalic
veins to form superior vena cava
Trachea bifurcates at
Level of sternal angle
Level of nipple
Level of xiphisternum
Level of inferior angle of scapula
Level of umbilicus
Osseoaponeurotic opening
Azygous vein and thoracic duct
Thoracic duct, Azygous vein
Thoracic duct, Azygous vein
Medial arcurate ligament of diaphragm
Diaphragmatic opening, Superior epigastric vessels pass
through it
Diaphragm
Arch of aorta, Thymus, Thoracic duct
Azygous vein
Aorta, Azygous vein, Thoracic duct
Greater splanchnic nerve
Greater splanchnic nerve
Scalenus medius
Scalenus anterior, Scalenus medius, suprapleural
membrane
Scalenus posterior
T4
T4,T5
T4,T5
T4
T6
T7
T10
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - THORACIC WALL
External Intercostal
Internal Intercostal
Innermost Intercostal
Subcostales
Transversus Thoracis
Intercostal Nerves T1-T11
Related Intercostal Nerves
www.medpgnotes.com
26
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
MUSCLES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Rectus abdominis is inserted into
Fothergills sign
Superficial perineal muscles include
Herring bone pattern muscle
Muscles attached to perineal body
Muscles NOT attached to perineal body
Urogenital diaphragm is also known as
Urogenital diaphragm
NOT a part of urogenital diaphragm
Urogenital diaphragm is NOT made of
NOT a component of urogenital diaphragm
NOT a muscle of Pelvic floor
Xiphod process
Rectus muscle hematoma
Bulbospongiosus, Ischiocavernous
Bulbospongiosus
Bulbospongiosus, Superfical transverse perinei, Deep
transverse perinei
Ischiocavernous
Triangular ligament
Deep transverse perinei, perineal membrane, sphincter
urethra, left and right transverse perinei profundus
Colles fascia, Transverse perinea superficialis
Colles fascia
Transverse perineii muscle
Obturator internus
NERVES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Nervus furcalis
Cremasteric muscle supplied by
Mediate erection
Nervi erigentes
Parasympathetic outflow from sacral plexus is through
One of the branches of Sacral plexus
Mediate ejacualation
Superior hypogastric plexus is located at
Pudendal nerve
Pudendal nerve block involve
Pudendal nerve
Course of pudendal nerve
Preganglionic parasympathetic nerves supplying pelvic
viscera
Abdominal autonomic plexus
NOT supplied by pelvic splachnic nerve
Pelvic splanchnic nerve is formed by
L4
Genital branch of genitofermoral nerve
Pudendal nerve, Sacral plexus, Nervi erigentes
(S2,S3,S4)
Parasympathetic
Nerve of Erigentes
Nerve to Quadratus and Gemelli Inferior
Hypogastric plexus
Anterior aspect of aortic bifurcation and fifth lumbar
vertebra
Main nerve of perineum, Chief sensory nerve of
external genitalia, Sensory and motor, S2,S3,S4, Comes
out through greater sciatic foramen
S2,S3,S4
Sensory and motor, S2,S3,S4, comes out through lesser
sciatic foramen
Sacral plexus greater sciatic foramen lesser sciatic
foramen pudendal canal
Ventral rami of S2,S3,S4, Pelvic splanchnic nerve
Aorticorenal ganglia is a part of celiac plexus, Greater
and lesser splanchnic nerve is sympathetic, Posterior
vagal is parasympathetic, Abdominal aortic plexus is
intermesentric in location
Appendix
Anterior rami of S2,S3,S4
www.medpgnotes.com
27
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
ARTERIES OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Inferior epigastric vessels are covered by
Anterior branch of abdominal aorta
Posterior branch of abdominal aorta
Lateral branches of abdominal aorta
Terminal branch of abdominal aorta
Both gonadal artery arise from
NOT a lateral branch of abdominal aorta
Inferior mesenteric artery is a branch of
Lateral branch of abdominal aorta
Ovarian artery is a branch of
Branches of external iliac artery
In rectus sheath, branch of aorta make anastomosis
with superior epigastric artery
Branches of anterior division of internal
iliac artery
Branches of posterior division of internal
iliac artery
Uterine artery is a branch of
Branch of anterior division of internal iliac artery
NOT a branch of internal iliac artery
Branches of internal pudendal artery
Branches of celiac artery
Branch of celiac trunk
NOT a branch of celiac artery
NOT a branch of celiac artery
NOT a branch of celiac axia
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of
Gastroduodenal artery derived from
Cystic artery arise from
Branches of hepatic artery
Branch of hepatic artery
Lateral umbilical fold
Celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery,
inferior mesenteric artery
Lumbar artery, median sacral artery
Inferior phrenic artery, middle suprarenal
artery, renal artery, testicular or ovarian
artery
Common iliac artery
Aorta
Inferior mesenteric artery
Abdominal aorta
Right testicular artery, Left renal artery, Middle
suprarenal artery
Abdominal aorta
Deep circumflex iliac artery, inferior
epigastric artery, femoral artery
External iliac artery
Superior vesical artery, inferior vesical
artery, middle rectal artery, obturator
artery, internal pudendal artery, inferior
gluteal artery
Ileolumbar artery, lateral sacral artery,
superior gluteal artery
Internal iliac artery
Uterine, Obturator, Internal pudendal, Inferior gluteal,
Superior vesical
Ovarian artery
Inferior rectal artery, perineal artery,
artery of penis/clitoris, urethral artery
Left gastric artery, splenic artery, hepatic
artery
Left gastric artery, Splenic artery, Hepatic artery
Right gastric artery
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
Inferior phrenic artery
Superior mesenteric artery
Hepatic artery
Right hepatic artery
Right hepatic artery, left hepatic artery,
gastroduodenal artery
Right gastric artery, Cystic artery, Left gastroepiploic
artery
www.medpgnotes.com
28
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
Right gastroepiploic artery is a branch of
Left gastroepiploic artery is a branch of
Branches of gastroduodenal artery
Groove for gastroduodenal artery
Arch of Buhler
Branches of splenic artery
Splenic artery
Splenic artery
Posterior gastric artery is a branch of
Arteria cauda pancreatica
NOT true about splenic artery
NOT a branch of splenic artery
Normal obturator artery is a branch of
Abnormal obturator artery is a branch of
Branches of superior mesenteric artery
NOT a branch of Superior Mesenteric artery
Ileocolic artery is a branch of
Branches of ileocoloic artery
Branches of inferior mesenteric artery
Least harm caused by damage to
Artery of Hind Gut
Inferior mesenteric artery does NOT
supply
Structures passing between head and
uncinate process of pancreas
Watershed area between SMA and IMA commonly
result in ischemia is
Marginal artery covering splenic flexure
Arch of Riolan connects
Marginal artery of Rimond
Artery giving blood supply to vas deferens
Artery that can be safely ligated in emergency
Deep Circumflex artery is a branch of
Superficial external pudendal artery is a branch of
Internal pudendal artery is a branch of
Lumbar arteries are
Deoxygenated blood to fetus is carried by
Gastroduodenal artery
Splenic artery
Right gastroepiploic artery, superior
pancreaticoduodenal artery
Junction of head and neck of pancreas
Connecting gastroduodenal artery with
superior mesenteric artery
Left gastroepiploic artery, short gastric
artery, pancreatic artery, splenic hilar
branches
Short gastric artery, hilar branches, arteria pancreatica
magna
Tortuous course, Branch of celiac trunk, Supplies
greater curvature of stomach
Splenic artery
Branch of splenic artery
Has branches freely anastomose within spleen
Right gastroepiploic artery
Internal iliac artery
Inferior epigastric artery
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery,
middle colic artery, right colic artery,
ileocolic artery
Left colic artery
Superior Mesentric artery
Superior and inferior branch, anterior
cecal artery, posterior cecal artery, jejuna
and ileal artery
Left colic artery, sigmoid artery, superior
rectal artery
Inferior mesenteric artery
Inferior Mesenteric artery
Right colic flexure
Superior mesenteric artery and superior
mesenteric vein
Splenic flexure
Arch of Riolan
Superior and inferior mesenteric artery
Throughout intestine
Superior vesical artery
Internal iliac
External Iliac artery
Femoral artery
Anterior division of internal iliac artery
5 in number
Umbilical artery
www.medpgnotes.com
29
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
VEINS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Portal vein
Portal vein is formed at
Portal vein related to
Portal vein not related to
Left gastric vein drains into
Present in peritoneal reflection forms one of the
borders of paraduodenal fossa
Blood vessel related to paraduodenal fossa
Inferior mesenteric vein drains into
Intricately and prodigiously looped system of veins and
arteries that lie on the surface of epididymis
Prostatic venous plexus is NOT related with
Prostatic venous plexus related with
Inferior vena cava
Vein draining to IVC
Does NOT cross midline
NOT a tributary of IVC
Right Inferior phrenic vein drains into
Left gonadal vein drains into
Umbilical vein carry
Formed behind neck of pancreas by superior
mesenteric vein and splenic vein, Pressure 5-10 mm Hg,
Valveless
L2
Pancreas, Inferior vena cava, CBD
Gall bladder
Portal vein
Inferior mesenteric vein
Inferior mesenteric vein
Splenic vein
Pampiniform plexus
Superior rectal vein
Vertebral plexus of Bateson, Internal iliac vein, Deep
dorsal vein of penis
It forms posterior wall of epiploic foramen, related to
psoas muscle
Right suprarenal vein
Left gonadal vein, Left suprarenal vein, Right renal vein
Left gonadal vein
Inferior Vena cava
Left renal vein
Oxygenated blood
LYMPHATICS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Lymphatic drainage of umbilicus
Superficial inguinal nodes drain
Enlarged superficial inguinal lymph node caused by
inflammation of
NOT drained by superficial inguinal node
Lymphatic drainage of ovaries and rectum is to
Celiac Lymph node receive lymphatics from
Both axillary and inguinal lymph node
Perineum, Gluteal region, Anterior abdominal wall
below umbilicus
Isthmus, Inferior part of anal canal, Great toe
Toes and finger, Clitoris
Aortic, Common Iliac, Internal Iliac, Inguinal Nodes
Liver, Spleen, Pancreas
LIGAMENTS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Downward displacement of enlarged spleen is
prevented by
True ligament of bladder which extends from bladder
neck to inferior aspect of Pubic bone
Phrenicocolic ligament
Pubovesical Ligament
www.medpgnotes.com
30
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
FASCIA OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Thoracolumbar fascia
Hypogastric sheath is a condensation of
Components of hypogastric sheath
Psoas sheath
Bucks Fascia is related to
Alcox canal
Pudendal canal is a continuation of
Pudendal canal runs along
Facia of Waldeyer belongs to
Waldeyer's fascia
Scarpas fascia is attached to
Denovillers fascia
Posterior wall of rectus sheath below the
level of anterior superior iliac spine is
formed by
Rectus sheath hematoma
Structure does NOT penetrate Perineal membrane
NOT a content of mesorectal fascia
Attached to spinous process of lumbar vertebra,
Attached to transverse process of lumbar vertebra,
Fascia lies both anterior and posterior abdominal wall
muscles, Gives attachment to transverse abdominal and
internal oblique
Pelvic fascia
Uterosacral ligament, transverse cervical ligament,
lateral ligament of bladder
Tranversalis fascia
Penis
Pudendal canal
Lunate fascia
Medial surface of ischial tuberosity,
lateral wall of ischiorectal fossa
Fascia of Pelvic wall to anorectal junction
Between sacrum and posterior rectal wall
Fascia lata of thigh
Rectoprostatic fascia
Fascia transversalis
Common in females
Internal Pudendal artery
Inferior rectal vein
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
Lower one fourth of anterior abdominal wall
Triangle of doom is bounded by
NOT a boundary of triangle of doom
Content of triangle of doom
Boundaries of triangle of pain
Content of triangle of pain
A missile hits the body just above pubic ramus through
the anterior abdominal wall, it will pierce
Level of Hilum of kidney
Transpyloric plane
Highest point on iliac crest
Structures present in Transpyloric Plane
Linea alba is poorly formed, External oblique poorly
formed
Vas deferens, Gonadal vessels (laterally), Peritoneal fold
Cooper ligament
External iliac vessels
Medially gonadal vessels, laterally
iliopubic tract, inferiorly inferior edge of
skin incision
Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve,
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, aanterior
femoral cutaneous nerve
Urinary bladder
L1
L1,L2
L3-L4
st
Tip of 9th Costal cartilage,1 Lumbar vertebra, Fundus
of Gall bladder
www.medpgnotes.com
31
ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
ANATOMY
th
Renal angle lies between
Does NOT drain into Inguinal Lymph nodes
Structures crossing dorsal surface of ischial spine
Structures NOT crossing dorsal surface of ischial spine
Structures passing through lesser sciatic foramen
Does NOT pass through lesser sciatic foramen
Contents of deep perineal pouch
NOT a content of deep perineal pouch
Deep Perineal pouch in males
Superficial perineal pouch
NOT found in superficial perineal pouch
Pudendal canal lies in
Pudendal Canal does NOT contain
Space of retzius
Space of Retzius is between
Level of inguinal ligament
Highest point of iliac crest
Supracristal plane
Transtubercular plane
Inferior vena cava is formed at the level
of
Level of anterior superior iliac spine
Level of posterior superior iliac spine
Level of rectosigmoid junction
12 rib and lateral border of sacrospinalis (erector
spinae)
Ischiorectal fossa
Internal pudendal vessel, pudendal nerve, nerve to
obturator internus
Obturator nerve
Internal pudendal vessel, Pudendal nerve, Nerve to
obturator internus
Inferior gluteal vessels
Dorsal nerve of penis, Bulbourethral gland, Sphincter
urethrae, Membranous urethra, Internal urethral
sphincter
Root of penis, Bulb of penis
Membranous urethra, Bulbourethral glands, Internal
Pudendal artery
Bulbospongiosus, Posterior scrotal nerve, Duct of
bulbourethral gland
Sphincter urethra
Lateral wall of Ischiorectal fossa
Nerve to Obturator Internus
Retropubic space
Bladder and pubic symphysis
L1
L4 L5
L4
L5
L5
S1
S2
S3
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
External Oblique
Internal Oblique
Transversus Abdominis
Rectus Abdominis
Pyramidalis
Anterior rami of T7-T12
Anterior Ramus of T12
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
Psoas Major
Psoas Minor
Quadratus Lumborum
Iliacus
Anterior Rami of L1,L2,L3
Anterior Rami of L1
Anterior Rami of T12,L1,L2,L3,L4
Femoral Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
32
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
HEAD AND NECK
MUSCLES OF HEAD AND NECK
Muscle attached to coronoid process of
mandible
Only pair of muscle attached to posterior
tubercle of atlas
To give alveolar nerve block, nerve is approached lateral
to pterygomandibular raphae between buccinators and
Ridge of passavant is present in
In dislocation of jaw, displacement of articular disc
beyond articular tubercle of temporomandibular joint
results from spasm or excessive contraction of
Lateral pterygoid muscle
Lateral pterygoid muscle
NOT true about lateral pterygoid muscle
NOT a muscle of mastication
Structure piercing buccinators
Structures piercing buccinators muscle
NOT supplied by mandibular nerve
Muscle NOT inserted in to angle of mouth
Muscle attached to mental spine
Diaphragma oris is formed by
Suprahyoid muscles
Omohyoid
Digastric muscles
Structures lying deep to posterior belly of digastrics
NOT lying deep to posterior belly of digastrics
Sternocleidomastoid
Subcutaneous muscle from clavicle to mandible
Temporalis
Rectus capitis posterior minor
Superior constrictor
Superior constrictor
Lateral pterygoid
Protrude mandible, Arise from infratemporal fossa,
Bipolar head, Inserted into fovea of mandible
Attached to pterygoid fossa
Unipolar head
Buccinators
Parotid duct
Parotid duct, buccal branch of facial nerve, molar glands
of cheek
Buccinator
Depressor septi
Geniohyoid
Mylohyoid
Digastric, Stylohyoid, Mylohyoid, Geniohyoid
Infrahyoid muscle
Muscle fibres in ligament of Trietz, Omohyoid,
occipitofrontalis
Hypoglossal nerve, Hyoglossus nerve, Occipital artery
Retromandibular vein
Arises from sternum and clavicle, Turns head to
opposite side, Shortened in congenital torticollis,
Supplied by spinal accessory nerve, Supplied by occipital
artery
Platysma
NERVES OF HEAD AND NECK
Nerve supplying scalp
Lesser occipital nerve
Zygomaticotemporal nerve, Greater occipital nerve,
Auriculotemporal nerve
Hooks around spinal accessory nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
33
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
Ventral rami of C1 supplies
Dorsal rami NOT giving cutaneous
branches
Sensory supply of skin over lower eye lid
Nerve compromised by a mass in Infratemporal fossa
Buccal nerve
Nerve obeying Hiltons rule
Massteric nerve
Masseteric nerve
Sensation at angle of mandible
Middle superior alveolar nerve is mediated by
Middle superior alveolar nerve is a branch of
Mandibular nerve
Main trunk of mandibular nerve supply
Muscles supplied by mandibular nerve
Muscles of mastication supplied by
Anterior division of mandibular nerve supply
Tensor veli palatine is supplied by
Muscle supplied by mandibular nerve
NOT supplied by anterior division of mandibular nerve
Mandibular nerve does NOT supply
Nerve in close relationship with root of lower third
molar
Upper premolars supplied by
Ansa cervicalis
Ansa cervicalis supply
NOT supplied by Ansa cervicalis
Relation of Ansa Cervicalis to Carotid Sheath
Supplied by first cervical nerve through hypoglossal
nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve supplies
Cranial accessory nerve supplies
Cranial accessory nerve supplies
Turn neck to same side, Face to Opposite side
Inability to raise arm above head following surgical
procedure of posterior triangle suggests injury to
Cranial part of accessory nerve supplies
Spared by complete transaction of cranial part of
accessory nerve
Could not extend her right hand above her head to
brush her hair
Cranial part of accessory nerve supplies all palatal
Rectus capitis lateralis, rectus capitis
anterior, thyrohyoid, geniohyoid, superior
belly of omohyoid
C1, C6, C7, C8, L4, L5
Maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve
Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Only sensory branch of anterior division of mandibular
nerve, supplies skin of cheeks, buccal nerve does NOT
supply buccinators muscle
Nerve to Masseter
Branch of anterior division of mandibular
nerve
Supplies massetor muscle, temporalis muscle
Greater auricular nerve
Anterior nasal division of maxillary nerve
Palatine branch of maxillary nerve
NOT pure motor, Lingual nerve runs with chorda
tympani, Auriculotemporal nerve embrace middle
meningeal artery, Otic ganglion is medial to nerve,
Formed in foramen ovale
Medial pterygoid
Tensor veli palate, Masseter, Tensor tympani
Mandibular nerve
Lateral pterygoid, Temporalis, Masseter
Mandibular nerve
Tensor veli palatini
Medial pterygoid
Buccinators
Lingual nerve
Middle superior alveolar nerve
Sternothyroid, Sternohyoid, Inferior belly of omohyoid
Sternohyoid
Thyrohyoid
Anterior
Thyrohyoid, geniohyoid
Stylopharyngeus
Soft palate, Phayngeal constrictors
Levator palatini
Spinal Accessory nerve
Spinal part of accessory nerve
Superior constrictor
Styopharyngeus
Injury to spinal part of accessory nerve
Tensor veli palatini
www.medpgnotes.com
34
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
muscles EXCEPT
ARTERIES OF HEAD AND NECK
Common carotid artery divides at level of
Bifurcation of common carotid artery
Common carotid artery palpated at
Internal carotid artery at bifurcation from common
carotid is
Branches of cervical part of internal
carotid artery
Branches of petrous part of internal
carotid artery
Branches of intracavernous part of
internal carotid artery
NOT a branch of intracavernous part of internal carotid
artery
Branches of cerebral part of internal
carotid artery
Posterior communicating artery is a branch of
Branches of external carotid artery
Only medial branch of external carotid artery
Number of branches of external carotid artery in neck
NOT a branch of external carotid artery
Ophthalmic artery is a branch of
NOT a branch of Ophthalmic artery
NOT a direct branch of aorta
Maxillary artery is divided into three parts by
Branches of first part of maxillary artery
Branches of second part of maxillary
artery
Branches of third part of maxillary artery
Branch of maxillary artery
Middle meningeal artery is a branch of
Posterior superior alveolar artery
Superior border of thyroid cartilage
C4
Upper border of cricoid cartilage
Lateral to external carotid
None
Caroticotympanic branch, pterygoid
branch
Hypophyseal branch, branch to trigeminal
ganglion, meningeal artery
Ophthalmic artery
Ophthalmic artery, choroidal artery,
anterior cerebral artery, middle cerebral
artery, posterior communicating artery
Internal carotid
Superior thyroid artery, lingual artery,
facial artery, occipital artery, posterior
auricular artery, ascending pharyngeal
artery, superficial temporal artery,
maxillary artery
Ascending pharyngeal
None
Anterior ethmoidal artery
Intracerebral part of internal carotid artery
Superficial temporal artery
Right common carotid artery
Lateral pterygoid
Anterior tympanic artery, middle
meningeal artery, accessory middle
meningeal artery, inferior alveolar
artery, deep auricular artery
Branch to pterygoid, masseter, buccinator
Posterior superior alveolar artery,
pharyngeal artery, artery to pterygoid
canal, greater palatine artery,
sphenopalatine artery, infraorbital artery
Anterior tympanic artery, Middle meningeal artery,
Infraorbital artery
Internal maxillary artery
Palatal branch of maxillary artery
www.medpgnotes.com
35
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
NOT a branch of maxillary artery
Left subclavian artery is a branch of
Branches of subclavian artery
Posterior ethmoidal artery
Arch of aorta
Vertebral artery, Thyrocervical trunk, Internal thoracic
artery
Subscapular artery
Axillary artery
Thyrocervical branch of subclavian artery
Occipital artery, Posterior auricular artery, Superior
thyroid artery
Common carotid artery
NOT a branch of subclavian artery
Subscapular artery is a branch of
Suprascapular artery is a branch of
Sternocleidomastoid is supplied by
Felt at lower part of medial border of
sternocleidomastoid
Facial artery
Artery palpable at anterior border of masseter is
Muscles of mastication is supplied by
Branch of third part of maxillary artery
Main source of oxygenated blood to palatine tonsil,
Branch of external carotid artery, Supplies branches to
both upper and lower lips, Conveys postganglionic
sympathetic nerve fibres
Facial artery
Second part of maxillary artery
Sphenopalatine artery
VEINS OF HEAD AND NECK
Diploic vein
Vascular layer of scalp
Common facial vein is formed by
Vein NOT draining into Facial Vein
Scalp bleeds profusely because
Tributaries of internal jugular vein
Does NOT drain directly into Internal Jugular Vein
Does NOT drain into internal jugular vein
Lined by single layer of endothelium supported by
elastic tissue, Present in cranial bones, Valveless or thin
walled, Develop by 2 years of age
Subcutaneous layer
Facial vein and anterior division of
retromandibular vein
Transverse Facial Vein
Vessels are bound within subcutaneous space
Superior thyroid vein, Middle thyroid vein, common
facial vein, Lingual vein, Inferior Petrosal sinus
Retromandibular vein
Superior petrosal sinus
LYMPHATICS OF HEAD AND NECK
Lymphatic supply of scalp
Occipital nodes, mastoid nodes,
submandibular nodes
Tonsils drain into upper deep cervical nodes, Inevitably
all lymphatics ultimately supply to lower deep cervical
nodes, Anterior half of nasal septum drain into
submandibular node
Lymphatic drainage of neck
LIGAMENTS OF HEAD AND NECK
Ligamentum denticulatum
Extension of piamater, 22 pairs of
triangular structure
www.medpgnotes.com
36
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
Ligaments connecting axis with occiput
bypassing atlas
Transverse ligament of atlas is a part of
Ossified posterior longitudinal ligament
NOT true about ossified posterior longitudinal ligament
Membrana tectoria, located at Craniovertebral junction
is a continuation of
McGregor patch
Apical ligament, alar ligament, cruciform
ligament, membrana tectoria
Cruciate ligament
Common in cervical spine, Gradient echo MR sequence
may overestimate the canal stenosis, MRI is best for
diagnosis, Low signal intensity on all MR sequence
Most commonly involves thoracic spine
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Zygomatic ligament
FASCIA OF HEAD AND NECK
Parotid fascia
Face is devoid of
Buccopharyngeal fascia
Investing layer of deep cervical fascia
Deep fascia
Pretracheal fascia
JOINTS OF HEAD AND NECK
In temporomandibular joint least vascularity is seen in
Least vascularity in temperomandibular joint
Ligament of TM joint
Sphenomandibular ligament
NOT a ligament of TM joint
Pterion
NOT true about pterion
Central part of articular disc
Articular cartilage
Lateral temporomandibular ligament,
Sphenomandibular ligament, Stylomandibular ligament
Derived from Meckel cartilage, pierced by
mylohyoid nerve
Alar joint, Tympanomandibular joint
Four bones meet here, Burr hole is made here,
Important structure behind is middle meningeal artery
Strongest point in skull
MOVEMENTS OF HEAD AND NECK
Protrusion of mandible by
Retraction of protruded mandible is done by
Depressor of mandible
Depressor of mandible
Opening of jaw
NOT a depressor of mandible
Muscles closing jaw (elevation)
In dislocation of jaw, displacement of articular disc
beyond the articular tubercle of TM joint results from
spasm or excessive contraction of
Movement at which of the joint permits a person to
look towards right or left
Lateral pterygoid, medial pterygoid
Temporalis
Geniohyoid, Digastric, Mylohyoid
Lateral pterygoid
Lateral pterygoid
Hyoglossus
Medial pterygoid, Masseter, Temporalis
Lateral pterygoid
Atlantoaxial joint
www.medpgnotes.com
37
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS OF HEAD AND NECK
Level of hyoid bone
Bifurcation of common carotid
Level of cricoid
Carotid tubercle
Lesser supraclavicular fossa is between
Nerve embedded in anterior wall of
carotid sheath
Carotid sheath is around
NOT a content of carotid sheath
Structure NOT enclosed in carotid sheath
NOT a communication route of
infratemporal fossa
Structures between hyoglossus and
mylohyoid
Masticator space
Kraissal line
Vestibule is present in
Boundaries of submental triangle
Content of submental triangle
Boundaries of digastric triangle
Content of anterior digastric triangle
Contents of posterior digastric triangle
Boundaries of muscular triangle
Contents of muscular triangle
Boundaries of carotid triangle
Content of carotid triangle
C3
C4
C6
Transverse process of C6
Two heads of sternocleidomastoid
Ansa cervicalis
Common carotid artery, internal carotid
artery, internal jugular vein, vagus
Ansa cervicalis
Cervical Sympathetic chain
Foramen rotundum
Styloglossus, lingual nerve, submandibular
ganglion, deep part of submandibular
gland, hypoglossal nerve, suprahyoid
branch of lingual artery
Muscles of mastication, mandibular nerve,
buccal pad of fat
Tension free lines in face for incision
Larynx, Nose, Pharynx
Base body of hyoid, apex chin, each
side anterior belly of digastrics, floor
mylohyoid
Submental lymph nodes and vein
Base base of mandible, anteroinferiorly
anterior belly of digastric,
posteroinferiorly posterior belly of
digastric, floor mylohyoid, hyoglossus
Submandibular gland, hypoglossal nerve
Parotid, external carotid artery, internal
carotid artery, internal jugular vein,
vagus, styloglossus, stylopharyngeus
Anteriorly midline of neck,
posterosuperiorly superior belly of
omohyoid, posteroinferiorly
sternocleidomastoid
Infrahyoid muscle
Anterosuperiorly posterior belly of
digastrics, stylohyoid. Anteroinferiorly
superior belly of omohyoid, posterior
sternocleidomastoid
Common carotid artery, external carotid
artery, internal jugular vein, hypoglossal
www.medpgnotes.com
38
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
nerve, external and internal laryngeal
nerve, spinal accessory nerve, vagus
nerve, sympathetic chain, deep cervical
lymph nodes
Divided by inferior belly of omohyoid into
occipital triangle and supraclavicular
triangle
Posterior triangle
GANGLIA
Sympathetic ganglion
Sympathetic ganglion arise from
Otic ganglion
Otic ganglion is topographically related to
Otic ganglion is functionally related to
Secretomotor fibres of parotid gland passes through
Secretomotor fibres of parotid pass
through
Paraganglionic fibres to parotid gland relay at
Functionally Otic ganglion is a part of
Ciliary ganglion
Ciliary ganglion is located between
Largest ganglion in neck
Lacrimal gland is supplied by
Sphenopalatine ganglion is formed by
Sphenopalatine ganglion is
topographically related to
Sphenopalatine ganglion is functionally
related to
Sphenopalatine gland supply
Tear secretion in lacrimal gland is due to
Sphenoplatine gland does NOT supply
Lacrimal secretion decreased when the site of injury of
facial nerve at
Lacrimal secretion is diminished when which part of
nerve is damaged
Nerve supply to pterygopalatine ganglia
Taste fibres relay in
Submandibular ganglion is
topographically related to
Submandibular ganglion is functionally
related to
Scarpa ganglion
Extends from base of skull to coccyx
Thoracolumbar
Lesser petrosal nerve forms parasympathetic root,
Secretomotor to parotid, Nerve to medial pterygoid
connected to ganglion
Mandibular nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Otic ganglion
Otic ganglion, tympanic plexus,
auriculotemporal nerve
Otic ganglion
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Contains sensory nerve, Motor root arise from inferior
oblique, Parasympathetic fibres edinger westphal
nucleus
Lateral rectus and optic nerve
Superior ganglion
Sphenopalatine ganglion
Superficial greater Petrosal nerve
Maxillary nerve
Greater petrosal branch of facial nerve
Nasal mucosa, Palate
Sphenopalatine ganglion
Sublingual gland
Pterygopalatine ganglion, Geniculate ganglion
Pterygopalatine ganglion
Maxillary nerve
Geniculate and petrous ganglion
Lingual nerve
Chorda tympani branch of facial nerve
Vestibular ganglion
www.medpgnotes.com
39
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
Pseudounipolar neuron
Pseudobipolar neuron
Pseudounipolar ganglion
Neurons of dorsal root ganglia
Semilunar ganglion is
Semilunar ganglion
Preganglionic fibres of submandibular ganglion is
formed by
Spinal dorsal root ganglion
Sensory root ganglion cell
Dorsal root ganglion
Centrally located nuclei, Derived from neural crest cells,
Unipolar or pseudounipolar, Contain lipofuscin granules
Sensory Ganglion
Gasserian ganglion
Chorda tympani and lingual nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - SUBOCCIPITAL GROUP OF MUSCLES
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major
Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor
Obliquus Capitis Superior
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
Posterior Ramus of C1
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY FACE
Orbicularis Oculi
Corrugator Supercili
Nasalis
Procerus
Depressor Septi
Depressor Anguli Oris
Depressor Labii Inferioris
Mentalis
Risorius
Zygomaticus Major
Zygomaticus Minor
Levator Labii Superioris
Levator Labii Superioris alaeque nasi
Levator anguli Oris
Buccinator
Anterior auricular
Superior auricular
Posterior auricular
Occipitofrontalis
FACIAL NERVE
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES
Superior Oblique
Lateral Rectus
Levator Palpebrae Superioris
Trochlear Nerve
Abduscent Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
40
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
Superior Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Medial Rectus
Inferior Oblique
Occulomotor Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MIDDLE EAR MUSCLES
Tensor Tympani
Stapedius
Nerve to Medial Pterygoid from
Mandibular Nerve
Facial Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF MASTICATION
Masseter
Temporalis
Medial Pterygoid
Lateral Pterygoid
Masseteric Nerve from Anterior Trunk of
Mandibular Nerve
Deep Temporal Nerve from Anterior
Trunk of Mandibular Nerve
Nerve to Medial Pterygoid from
Mandibular Nerve
Nerve to Lateral Pterygoid from Anterior
Trunk of Mandibular Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF ANTERIOR TRIANGLE
OF NECK
Stylohyoid
Mylohyoid
Sternohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Genihyoid
Thyrohyoid
Anterior Belly of Digastric
Posterior Belly of Digastric
Facial Nerve
Nerve to Mylohoid from Inferior Alveolar
branch of Mandibular Nerve
Anterior rami of C1,C2,C3 through Ansa
Cervicalis
Anterior rami of C1 carried along
Hypoglossal Nerve
Nerve to Mylohoid from Inferior Alveolar
branch of Mandibular Nerve
Facial Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
41
HEAD AND NECK
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF POSTERIOR TRIANGLE
OF NECK
Sternocleidomastoid
Splenius Capitus
Anterior Scalene
Middle Scalene
Posterior Scalene
Accessory Nerve
Posterior Rami of Middle Cervical Nerve
Anterior Rami of C4 to C7
Anterior Rami of C3 to C7
Anterior Rami of C5 to C7
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - PREVERTEBRAL AND LATERAL
MUSCLES
Rectus Capitis Anterior
Rectus Capitis Lateralis
Longus Colli
Longus Capitis
Anterior Rami of C1,C2
Anterior Rami of C2 to C6
Anterior Rami of C1 to C3
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - CONSTRICTORS OF PHARYNX
Superior Constrictor
Middle Constrictor
Inferior Constrictor
Vagus Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - LONGITUDINAL MUSCLES OF
PHARYNX
Stylopharyngeus
Salpingopharyngeus
Palatopharyngeus
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Vagus Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF LARYNX
Cricothyroid
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
Lateral Cricoarytenoid
Transverse Arytenoid
Oblique Arytenoid
Thyroarytenoid
Vocalis
External Branch of Superior Laryngeal
Nerve
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
42
OSTEOLOGY
ANATOMY
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - MUSCLES OF SOFT PALATE
Tensor Veli Palatini
Nerve to Medial Pterygoid from
Mandibular Nerve
Levator Veli Palatini
Palatopharyngeus
Palatoglossus
Musculus Uvulae
Vagus Nerve via Pharyngeal branch to
Pharyngeal Plexus
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - INTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE
Superior Longitudinal
Inferior Longitudinal
Transverse
Vertical
Hypoglossal Nerve
MUSCLES AND THEIR NERVE SUPPLY - EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE
Palatoglossus
Vagus Nerve via Pharyngeal branch to
Pharyngeal Plexus
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Hypoglossal Nerve
OSTEOLOGY
BASICS IN OSTEOLOGY
Zone of polarizing activity is related to
Osteon
Haversian system is found in
True
Chief mineral of bone
Periosteum is attached to deep bone by
Pneumatic bone
NOT a pneumatic bone
Craniofacial angle
Growth of bone
Present in compact bone, Concentric lamellae is
present, Haversian canal is present
Diaphysis of long bone
Osetoblast give rise to osteocyte
Hydroxyappatite
Sharpeys fibres
Maxillary, ethmoidal
Mandible
130*
www.medpgnotes.com
43
OSTEOLOGY
ANATOMY
Skull consists of
Large interparietal bone
Goeths ossicle
Pterion overlies
22 bones
Inca bone
Large intraparietal ossicle
Anterior branch of middle meningeal
artery and lateral fissure of cerebral
hemisphere
Posterior end of sphenoparietal suture
3-4 months of age
Sylvian
Axis
Inion
Point pterion corresponds to
Pterion usually closes by
Pterion is also known as
Dens (odontoid process)
Most prominent external orbital
protuberance
Growth in length of skull
True ribs
False ribs
Floating ribs
Intercostal space
Devoid of muscle attachment
Normal metacarpal index
Newtonian force
Blood is not Newtonian fluid because
Basiocciput with basisphenoid
1-7
8-10
11,12
VAN (superior to inferior)
Talus
5.4 to 7.9
No relation between viscosity and velocity
Viscosity changes with velocity
EPIPHYSIS
Pressure epiphysis
Traction epiphysis
Atavistic epiphysis
Type of epiphysis in os trigonum
Aberrant epiphysis
Physiological process during growth of epiphyseal plate
NOT occur during growth of epiphyseal plate
Epiphysis of knee, wrist and medial end of
ankle fuse at
Head of femur, Condyles of tibia
Tubercles of humerus, Mastoid process, Trochanter of
femur
Coracoid process of scapula
Atavistic
Head of first metacarpal
Proliferation and hypertrophy, calcification and
ossification, vasculogenesis and erosion
Replacement of red bone marrow with yellow bone
marrow
20 25 years of age
METAPHYSIS
Metaphysis
Zone of active growth
NOT true about metaphysis
Most vascular part of bone, Growth activity is
maximized here, Region favoring hematogenous spread
of infection
Metaphysis
Strongest part of bone
www.medpgnotes.com
44
OSTEOLOGY
ANATOMY
CARTILAGE
Aricular cartilage
Devoid of perichondrium, avascular, lacks capacity to
regenerate
Total proteoglycan content reduced, synthesis of
proteoglycan reduced, total water content of cartilage
decreased
Hyaline cartilage covers articular surface of synovial
joints
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Changed in articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Cell Nests
Articular surface of synovial joints covered by
OSSIFICATION
Number of ossification centres at birth
Kerckring centre of ossification associated with
Bone ossified at birth
Number of ossification centres for hyoid bone
Ossification of ear ossicles
Ossification of lower end of femur
First primary ossification centre to appear in carpal
bone
Distal tibial epiphysis appear at the age of
Ossification centre appears just before birth
Lower end of femur can help to determine
Enchondral ossification
First centers of ossification appears during
First ossification centre
Ossification at second month
Earliest ossification centre for
Ossification centre last to appear
450
Bones of skull
Lower end of femur, Calcaneum, Upper tibia
6
th
4 fetal month
th
40 week
Capitate
34 weeks
Lower end of femur
Age
Long bones
At the end of second month of pregnancy
Clavicle
Capitate
Os calcis talus
Inner end of clavicle
TYPES OF JOINTS
Type of joint in growth plate
Type of joint between epiphysis and diaphysis
Joint between epiphysis and diaphysis of long bone
Primary cartilaginous joint
(synchondroses)
First costochondral joint
Secondary cartilaginous joint (symphyses)
Secondary cartilaginous joint
Manubriosternal joint
Primary cartilaginous
Primary cartilaginous
Synchondrosis
Joint between epiphysis and metaphysis,
spheno occipital joint, first chondrosternal
joint, costochondral joint
Synchondroses/syncendrosis
Symphysis pubis, manubrosternal joint,
intervertebral joint
Situated in midline, permanent, binding
cartilage and fibrocartilage
Symphysis
www.medpgnotes.com
45
OSTEOLOGY
ANATOMY
Type of joint between sacrum and coccyx
Sacrococcygeal joint
Ellipsoid joint
Examples of ellipsoid joint
First carpometacarpal joint
Examples of saddle joint
Syndesmosis
Gomphosis
Acromioclavicular joint
Synovial joint
Stability of synovial joint is
Joints between ossicles of ear
Incudomalleolar joint is an example of
Vomer sphenoidal rostrum junction
Temporomandibular joint is
Temporomandibular joint
Radioulnar joint is
Fibrous joint
Sternoclavicular joint
Upper surface of first costal cartilage
involved in sternoclavicular joint
Ankle joint is
Hinge joint
Hinge joint
Subtalar joint / talocalcaneal joint
Symphysis
Secondary cartilaginous
Wrist
Atlanto occipital joint,
metacarpophalyngeal joint, wrist
Saddle
Sternoclavicular, calcaneocuboid
Inferior talofibular
Tooth in its sockets
Plane synovial joint
Stability is inversely proportional to mobility
Inversely proportional to motility
Synovial joint
Saddle
Schindylesis
Condyloid joint
Modified hinge type synovial joint
Pivot joints
Frontoparietal suture
Synovial sellar joint
Diarthroses
Hinge joint
Ankle, elbow, interphalangeal
Elbow
Plane synovial
FORAMINA
Emissary vein is transmitted by
Sternberg canal
Sternberg canal
Foramen rotundum
Structure passing through foramen ovale
Mandibular nerve passes through
Structure passing through foramen spinosum
Middle meningeal artery enters the skull through
Foramen spinosum
Passing through jugular foramen
Anterior part of jugular foramen
Middle part of jugular foramen
Condylar canal, parietal foramen, mastoid
foramen
Located anterior and medial to foramen rotundum,
Represents persistent craniopharyngeal canal, Cause of
intrasphenoid meningocele
Located anterior and medial to foramen rotundum,
represents persistent craniopharyngeal canal, cause of
intersphenoidal meningocele
Maxillary nerve
Emissary vein , Mandibular nerve
Foramen ovale
Middle meningeal artery
Foramen spinosum
Meningeal branch of mandibular nerve, Middle
meningeal artery
9,10,11
Inferior petrosal sinus
th
th
th
9 , 10 and 11 nerve, meningeal branch of ascending
pharyngeal artery
www.medpgnotes.com
46
OSTEOLOGY
ANATOMY
Posterior part of jugular foramen
Structure NOT passing through Jugular foramen
NOT passing through jugular foramen
Foramen petrosum/canaliculus
innominatus/foramen of Arnold
Structure passing through internal auditory canal
Vertical crest in fundus of internal auditory canal
Internal acoustic meatus
Structures passing through superior orbital fissure
Nerve passing through superior orbital
fissure within annulus of Zinn
Superior orbital fissure syndrome involves
Superior orbital fissure is formed by
Does NOT pass through superior portion of superior
orbital fissure
Structure passing through infraorbital fissure
Structure does NOT pass through Inferior Orbital fissure
Passing through foramen magnum
Does NOT pass through foramen magnum
Optic foramen is situated between
Does NOT pass through optic foramen
Vidian nerve passes through
Nerve of pterygoid canal
Nerve of pterygoid canal
Pterygotympanic fissure transmits
Mental foramen located near
Mandibular foramen
Dorellos canal transmits in tip of temporal bone
Veins communicating the cavernous sinus to pterygoid
plexus pass through fossa of
Foramen Lacerum lies between
Carotid canal
Stylomastoid foramen
Structure entering through mastoid
canaliculus and exiting through
tympanomastoid fissure
Structure passing through tympanic
canaliculus
Internal jugular vein sigmoid sinus junction, emissary
vein, occipital artery
Internal Carotid artery
Hypoglossal nerve
Lesser petrosal nerve
Nerve of wrisberg, Superior vestibular nerve, Cochlear
nerve
Bills bar
Facial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve, nervus
intermedius or pars intermedia of wrisberg, labyrinthine
vessels
Trochlear nerve, Occulomotor nerve, Abduscent nerve,
Lacrimal nerve, Nasociliary nerve, Inferior ophthalmic
vein
Nasociliary nerve, occulomotor nerve,
abduscent nerve
Occulomotor nerve, Abduscent nerve, Ophthalmic
branch of Trigeminal nerve
Greater wing and lesser wing of sphenoid
Occulomotor
Zygomatic nerve
Nerve to Ciliary Ganglion
Vertebral artery, Spinal accessory nerve, Vertebral
venous plexus
Spinal cord (only lower part of medulla oblongata)
Lesser wing and Body of sphenoid
Ophthalmic nerve
Pterygoid canal
Sympathetic + greater superficial petrosal nerve
Superficial petrosal and deep petrosal
nerve
Chorda tympani, anterior tympanic
branch of maxillary artery, anterior
ligament of malleus
First premolar of mandible
Inferior alveolar vein and nerve
Abduscent nerve
Fossa Vesalius, Fossa ovale
Petrous part of Temporal bone and Sphenoid
Internal carotid artery and venous sympathetic plexus
around it
Facial nerve
Auricular branch of vagus nerve
Tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal
nerve
www.medpgnotes.com
47
HISTOLOGY
ANATOMY
RIB NOTCHING
Ribnotching
Superior rib notching
Notching of ribs
Soft tissue mass in chest with rib erosion in X ray
Does NOT cause rib notching
Blalock Taussig shunt, Pulmonary atresia with large
VSD, Aortic disruption, Neurofibromatosis, Aortic
aneurysm, Aortic obstruction, Coarctation of aorta
Hyperparathyroidism, Poliomyelitis, Marfan syndrome
AR, TOF, Thrombotic occlusion of abdominal aorta
Leukemia, Ewings sarcoma, Multiple Myeloma
Waterson Cooley shunt
HISTOLOGY
Sinuses are seen in
Sinuses are NOT seen in
Auerbach plexus present in
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Duct NOT lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
Basal layer of cell in stratified squamous epithelium
Ducts lined with stratified squamous epithelium
Non keratinized stratified squamous
epithelium
Parakeratinization
Similar kind of epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Spleen, Endocrine gland, Liver
Kidney
Colon, esophagus, stomach, small intestine
Sweat gland, Salivary gland, Pancreas
Sebaceous gland
Cuboidal columnar
Ducts of Sweat gland, salivary gland and pancreas
Cornea, mouth, tongue, pharynx,
esophagus, vagina
Non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Lung alveoli and bowman capsule
Sensory epithelium of olfactory area,
trachea, nasolabial cyst
www.medpgnotes.com
48
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Understanding Human Anatomy and PathologDocumento334 pagineUnderstanding Human Anatomy and PathologVladislav Kotov100% (1)
- Anatomy Work BookDocumento50 pagineAnatomy Work BookAmal Helal100% (7)
- Rapid Review of Embryology, First PDFDocumento137 pagineRapid Review of Embryology, First PDFmayurdadhaniya100% (1)
- Anatomy PDFDocumento1.207 pagineAnatomy PDFMustafa Kamal Bangash100% (16)
- Cardiac AnatomyDocumento46 pagineCardiac Anatomyveegeer100% (2)
- The Upper LimbDocumento100 pagineThe Upper LimbAhmed Raza KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Mnemonics (Lower Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedDocumento4 pagineAnatomy Mnemonics (Lower Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedMDreamer0% (1)
- Class Test Question Collection AnatomyDocumento20 pagineClass Test Question Collection AnatomyEindra Myat MaungNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy NotesDocumento3 pagineAnatomy NotesKaren Kaye Canlas100% (3)
- Anatomy - NotesDocumento149 pagineAnatomy - Noteshusayn12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human PhysiologyDocumento23 pagineHuman Physiologysarah anggita100% (2)
- Physiology Magdy Sabry EndocrineDocumento162 paginePhysiology Magdy Sabry Endocrineaminata kamara89% (9)
- General Physiology PDFDocumento11 pagineGeneral Physiology PDFmedpgnotes100% (4)
- Anatomy Class NotesDocumento263 pagineAnatomy Class NotesNikhil Vasan Arulmany100% (1)
- Anatomy of The SkullDocumento29 pagineAnatomy of The Skullaya abdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Human AnatomyDocumento571 pagineEssentials of Human AnatomyOniga Robert80% (5)
- GIT EmbryologyDocumento162 pagineGIT EmbryologywahyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Quizbook Volume 2 Head and NeckDocumento92 pagineAnatomy Quizbook Volume 2 Head and NeckSakhile NdlovuNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding MusclesDocumento235 pagineUnderstanding MusclesTasha Freeman100% (8)
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocumento120 pagineAnatomy Lower LimbVn Dang100% (3)
- Anatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckDocumento20 pagineAnatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckTracie YWNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential HistologyDocumento520 pagineEssential Histologyv@r0_5100% (7)
- AnatomyDocumento24 pagineAnatomydkavanagh_anatomy100% (1)
- The A To Z of Skeletal MusclesDocumento238 pagineThe A To Z of Skeletal MusclesAspenPharma99% (161)
- Stretching AnatomyDocumento3 pagineStretching AnatomyMedShareNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesDocumento25 pagineThe Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesJoanna Poshnja100% (1)
- Ankle and FootDocumento206 pagineAnkle and FootZenabNaaz100% (1)
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocumento72 pagineAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- B D Chaurasia's Handbook of General Anatomy (4th Ed)Documento276 pagineB D Chaurasia's Handbook of General Anatomy (4th Ed)iahmed300090% (80)
- Lower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletDocumento5 pagineLower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletAsif HanifNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocumento57 pagineIntroduction To Human AnatomyJomari Kilantang100% (2)
- Cutaneous Innervation of HeadDocumento4 pagineCutaneous Innervation of HeadAlexandros LazarouNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy IntroductionDocumento34 pagineAnatomy IntroductionJoanne Tolopia100% (1)
- Anatomy Class NotesDocumento57 pagineAnatomy Class NotesClinical Psychology0% (1)
- Human Musculoskeletal BiomechanicsDocumento254 pagineHuman Musculoskeletal Biomechanicsuilifteng100% (2)
- Atlas of Human AnatomyDocumento50 pagineAtlas of Human AnatomyLuis S Guillén100% (4)
- Appleton & Lange Review of Anatomy PDFDocumento157 pagineAppleton & Lange Review of Anatomy PDFherry2sw100% (2)
- Anatomy Quizbook PDFDocumento92 pagineAnatomy Quizbook PDFLipid Berger67% (3)
- Clinic Anatomy by System PDFDocumento16 pagineClinic Anatomy by System PDFAsepta Cecep0% (1)
- Muscle Flash CardsDocumento127 pagineMuscle Flash Cardsjoelh9100% (3)
- Langmans Medical EmbryologyDocumento487 pagineLangmans Medical EmbryologyJaweria Islam Khan Bangash60% (5)
- Anatomy PDFDocumento49 pagineAnatomy PDFBiswajyoti SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Weight and Dumbbell ExercisesDocumento79 pagineBody Weight and Dumbbell ExercisesshamsoudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Criterios de Manejo Trauma ColumnaDocumento88 pagineCriterios de Manejo Trauma ColumnaMamut Christian ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- PMFIAS NCERT Biology 6 12 CompilationDocumento319 paginePMFIAS NCERT Biology 6 12 Compilationtakias100% (2)
- Science Awareness For Upsc PDFDocumento196 pagineScience Awareness For Upsc PDFGirish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory SystemDocumento60 pagineRespiratory SystemShanmugam BalasubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- Organoid Culture HandbookDocumento40 pagineOrganoid Culture HandbookGabriella Panuccio100% (1)
- Sakai Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocumento47 pagineSakai Et Al-2019-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsNakarit SangsirinawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Kdigo Aki GuidelineDocumento187 pagineKdigo Aki GuidelineGoghuladheeiwy ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- The Psychic Roots of Disease: New Medicine (Color Edition) EnglishDa EverandThe Psychic Roots of Disease: New Medicine (Color Edition) EnglishValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- 9501-001-50 REV H1 Physicians GuideDocumento54 pagine9501-001-50 REV H1 Physicians GuidejimurgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of The Squat and Deadlift PDFDocumento43 pagineBiomechanics of The Squat and Deadlift PDFDRN100% (2)
- The Gist of NCERT PDF - SCIENCEDocumento154 pagineThe Gist of NCERT PDF - SCIENCESuresh GollaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT XI Biology Notes and Solutions PDFDocumento215 pagineNCERT XI Biology Notes and Solutions PDFSaurav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol.13 Human Performance and LimitationsDocumento222 pagineVol.13 Human Performance and LimitationsMostafa MohsenNessuna valutazione finora
- P160043S034CDocumento94 pagineP160043S034Cbraulio HuarachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shock – modern clinical treatment conceptsDa EverandShock – modern clinical treatment conceptsNessuna valutazione finora
- Anesthesiology PDFDocumento40 pagineAnesthesiology PDFBiswajyoti SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- HeadDocumento135 pagineHeadalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Anatomy HandoutDocumento10 pagineFunctional Anatomy HandoutpowerliftermiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Eliminate Your Low Back Pain Treatment Prevention Without Drugs, Surgery, or Chiropractic Sessions by Chopra, Dr. MonikaDocumento146 pagineEliminate Your Low Back Pain Treatment Prevention Without Drugs, Surgery, or Chiropractic Sessions by Chopra, Dr. MonikaloamfgNessuna valutazione finora
- Yoga For Knee Pain 5 Poses To Add Strength & Reduce DiscomfortDocumento6 pagineYoga For Knee Pain 5 Poses To Add Strength & Reduce DiscomfortWazzah BieNessuna valutazione finora
- Module II MCQ Exam (A)Documento8 pagineModule II MCQ Exam (A)Precious JuliusNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoas Release Party Spring 15Documento84 paginePsoas Release Party Spring 15onix200096% (24)
- Katz enDocumento71 pagineKatz enAyush MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Working With Hip Mobility (Myofascial Techniques)Documento4 pagineWorking With Hip Mobility (Myofascial Techniques)Advanced-Trainings.com100% (2)
- Muscles of The Upper and Lower LimbsDocumento67 pagineMuscles of The Upper and Lower LimbsAngel 冯晓君Nessuna valutazione finora
- NEET PG 2013 Question Paper With SolutionsDocumento2.164 pagineNEET PG 2013 Question Paper With SolutionsSK RaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Hip Assessment SRSDocumento46 pagineHip Assessment SRSSreeraj S RNessuna valutazione finora
- Glute Growth GuideDocumento29 pagineGlute Growth GuideLili FarrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System NotesDocumento6 pagineMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy Physiology 8Th Edition Marieb Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento55 pagineHuman Anatomy Physiology 8Th Edition Marieb Test Bank Full Chapter PDFninhdermotc1u100% (9)
- Program Forta 3 Saptamani 3 ZileDocumento5 pagineProgram Forta 3 Saptamani 3 ZileIoan-Alexandru CodarceaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide 1Documento12 pagineHuman Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide 1api-637418753Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4-Week Workout PlanDocumento1 pagina4-Week Workout PlanSara67% (3)
- Fernandez-Zacal Learning Center, Inc.: I. Read The Sentences Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocumento3 pagineFernandez-Zacal Learning Center, Inc.: I. Read The Sentences Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answerdanny boyNessuna valutazione finora
- Glute Guide EbookDocumento50 pagineGlute Guide EbookJustin C. King100% (3)
- Sample ExamDocumento13 pagineSample ExamJenny Mendoza VillagonzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Training: Carlos Hilado Memorial State College Physical Education 1 (Physed 1)Documento11 pagineFunctional Training: Carlos Hilado Memorial State College Physical Education 1 (Physed 1)Sunny EggheadNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy For ExerciseDocumento33 pagineAnatomy For ExerciseSarah LCNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Order and Sequencing For Corrective Exercise ProgramsDocumento10 pagineExercise Order and Sequencing For Corrective Exercise ProgramsalmaformaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spine Conditioning Program - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocumento12 pagineSpine Conditioning Program - OrthoInfo - AAOSJimmy Laporal TrésorNessuna valutazione finora
- Toaz - Info Ultimate Guide To Greater Glutes v2 Brittany Perille PRDocumento44 pagineToaz - Info Ultimate Guide To Greater Glutes v2 Brittany Perille PRZiva Li Lena100% (1)
- Sci ReportDocumento43 pagineSci ReportFaith BugtongNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoas StretchesDocumento9 paginePsoas Stretcheswalterego58Nessuna valutazione finora
- SP Thirty Day Program Guide Apr2019 Grey FINDocumento85 pagineSP Thirty Day Program Guide Apr2019 Grey FINLarissa100% (1)
- ANATOMY Multiple Choice Questions 2012Documento39 pagineANATOMY Multiple Choice Questions 2012kishorechandra100% (5)
- Fmge Jan 2023 Pyq PDFDocumento144 pagineFmge Jan 2023 Pyq PDFZainab Siddiqui100% (1)
- Chapter 28 Pelvis and Perineum PDFDocumento89 pagineChapter 28 Pelvis and Perineum PDFMACON824Nessuna valutazione finora