Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cytoplasm Histo
Caricato da
Darwin CruzDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cytoplasm Histo
Caricato da
Darwin CruzCopyright:
Formati disponibili
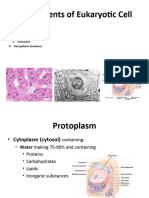
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
CELL CYTOPLASM
CELLS are the basic structural and functional
units, the smallest living parts of the body.
Animal cells are eukaryotic, with distinct
membrane bound nuclei surrounded by cytoplasm
containing many membrane-bound organelles.
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
200 cell types all derived from the zygote (the
single cell formed from the union of an oocyte
and spermatozoa)
The zygote undergoes cell division to form a
mass of cells called blastomere that specialize
and eventually give rise to all tissue types
The specialization process is called cell
differentiation
- Synthesize specific proteins
- Change shape
- Acquire specific functions
Cellular functions in specialized cells:
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 1 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Movement - muscle cells and other contractile
cells
Form adhesive and tight junctions between cells
- epithelial cells
Synthesize and secrete components of the
extracellular matrix - fibroblasts, cells of bone
and cartilage
Convert physical and chemical stimuli to action
potential - neurons and sensory cells
Synthesis and secretion of enzymes - cells of
digestive glands
Synthesis and secretion of mucous substances mucus gland cells
Synthesis and secretion of steroids - adrenal
gland, testis and ovary cells
Ion transport - cells of the kidney and salivary
gland cells
Intracellular digestion - macrophages and white
blood cells
Metabolite absorption - cells lining the intestines
The cell is composed of two basic parts:
cytoplasm & nucleus.
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 2 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Plasma membrane (plasmalemma) defines the
external limit of the cell and separates the
cytoplasm from the extracellular environment
- Contains proteins called integrins that are
linked to both cytoplasmic cytoskeletal
filaments and ECM components; allows
constant exchange of influences
The cytoplasm is composed of a fluid
component called cytosol in which
metabolically active structures, the organelles
are found
The shape and motility of cells is determined by
the components of the cytoskeleton
Inclusions are cytoplasmic structures that
contain deposits of carbohydrates, lipids or
pigments.
PLASMA MEMBRANE
Limiting membrane composed of
phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins and
oligosaccharides covalently linked to
phospholipid and protein molecules
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 3 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Acts as a selective barrier that regulates the
passage of certain materials into and out of the
cell and facilitates transport of specific
molecules.
- Keeps ion content of cytoplasm constant
7.5-10 nm thick
Membrane phospholipids consist of two nonpolar (hydrophobic) long chain fatty acids
linked to a charged polar (hydrophilic) head
group
Organized into a double layer (bilayer) with the
hydrophobic chains towards the middle and
hydrophilic polar heads directed outward to
contact with water
Cholesterol molecules insert among
phospholipid fatty acids modulating fluidity and
movement of the membrane
Proteins are of two groups:
- Integral proteins are directly incorporated
within the lipid bilayer; may span the
membrane from one side to the other, thus
also called transmembrane proteins
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 4 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
- Peripheral proteins loosely attached to one
membrane surface
The carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins and
glycolipids project from the external surface of
the plasma membrane
- Constitute components of molecules called
receptors that participate in cell adhesion,
recognition and response to protein
hormones
Membrane proteins are synthesized in the
rough endoplasmic reticulum, modified and
completed in the Golgi apparatus, and
transported in vesicles to the cell surface
Glycocalyx is a carbohydrate rich region of the
external cell surface ; role in cell recognition
and attachment to other cells & extracellular
molecules
Membrane Transport
1.Passive diffusion- through ion channels
2.Active transport- via ion pumps using ATP
3.Endocytosis - bulk uptake of material across
the plasma membrane; involves folding and
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 5 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
fusion of membranes to form vesicles which
enclose the material transported
- Phagocytosis - "cell eating"; vacuole is
called phagosome
- Fluid phase endocytosis/ Pinocytosis - "cell
drinking"; most vesicles fuse with
lysosomes; in other cells, like capillary
lining cells, vesicles move to the opposite
side of the cell membrane and release their
contents outside the cells (transcytosis)
- Receptor mediated endocytosis - transport
for protein hormones; binds to a receptor
and then aggregates in regions called
coated pits that is invaginate forming
coated vesicles
4. Exocytosis - cytoplasmic vesicle fuses with
the plasma membrane resulting in the release of
its contents to the extracellular space
Signal Reception and Transduction
Cells need to communicate with one another to
regulate development into tissues, to control
their growth and division, and to coordinate
their functions
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 6 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Signals may pass directly from cell to cell
through gap junctions
Soluble extracellular signaling molecules (ex.
hormones, neurotransmitters) only bind to
specific receptors found on target cells
MITOCHONDRIA
Membrane-enclosed organelles with enzyme
arrays specialized for aerobic respiration and
production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
which contains energy stored in high-energy
phosphate bonds
Glucose is converted anaerobically to pyruvate
in the cytoplasm (glycolysis) ; pyruvate goes
into the mitochondria and oxidized to CO2 and
H2O releasing ATP and heat
Elongated but constantly changing in shape
Number is dependent on the cell's energy needs
On LM, seen as discrete eosinophilic organelles
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 7 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
On TEM, is seen to have two membrane layers
separating two compartments, the inner matrix
and a narrow intermembrane space
- The outer membrane is sieve-like containing
numerous transmembrane proteins called
porins
- The inner membrane is folded forming
cristae that projects into the matrix;
impermeable to ions
- Matrix contains enzymes that oxidizes
pyruvate and molecules that provide
electrons for the respiratory /electron
transport chain
The matrix also contains a small circular
chromosome of DNA, ribosome, mRNA and
tRNA
RIBOSOMES
Small electron dense particles composed of 4
segments of rRNA and 80 different proteins;
mitochondrial ribosomes are smaller and
contain fewer constituents
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 8 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
- RNA is synthesized in the nucleus, proteins
synthesized in the cytoplasm
For protein synthesis
Numerous ribosomes are found on mRNA as
polyribosomes / polysomes
- The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA
determines the amino acid sequence of the
protein synthesized
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Network of intercommunicating channels and
sacs formed by a continuous membrane which
encloses a space called cisterna
In some ER, polyribosomes cover the outer
membrane surface
Rough ER (RER)
- Prominent in cells specialized for protein
secretion ex. pancreatic acinar cells,
fibroblasts, plasma cells
- With polyribosomes on its outer membrane
Smooth ER (SER)
- Do not have polyribosomes
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 9 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
- Contains enzymes for the synthesis of
phospholipid molecules of cell membranes,
steroid synthesis, enzymes for
detoxification of noxious substances
- Also sequesters and release Ca++ in muscle
cells (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
GOLGI APPARATUS
Packages, concentrates and stores proteins
synthesized in the RER
Composed of smooth membranous saccules
Proteins and products produced by cells are
stored in secretory vesicles or granules until its
release by exocytosis signaled by a metabolic,
hormonal or neural message
LYSOSOMES
Are sites of intracellular digestion and turnover
of cellular components
Membrane limited vesicles with 40 different
hydrolytic enzymes (proteases, nucleases,
phosphatases, sulfatases, phospholipids)
Abundant in phagocytic cells
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 10 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Material that enters the cell by endocytosis is
digested when lysosomes fuse with the
phagosome or pinocytic vesicle
Indigestible material is retained in vacuoles
called residual bodies
- Residual bodies can accumulate and are
called lipofuscin granules
Also removes non functional organelles and
excess cytoplasmic structures by autophagy
PROTEASOMES
Function to degrade denatured and
nonfunctional polypeptides; removes proteins
no longer needed by the cell
PEROXISOMES or MICROBODIES
Oxidize specific potentially toxic organic
substrates (alcohol, drugs) by removing
hydrogen atoms that is transferred to molecular
oxygen producing hydrogen peroxide which in
turn is broken down by catalase
CYTOSKELETON
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 11 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Determines the shape of cells, for movement of
cells, organelles and vesicles
Consists of microtubules, microfilaments (actin
filaments) and intermediate filaments
Microtubules
Fine tubular structures in the cytoplasm, cilia
and flagella
Composed of the protein tubulin
Role in formation and maintenance of cell
shape, intracellular transport of organelles and
vesicles, and acts as base for centrioles, cilia
and flagella
Microfilaments (Actin filaments)
Contractile activity of cells results from
interaction between actin and myosin
Responsible for changes in cell shape during
endocytosis, exocytosis and cell locomotion,
and movement of cell organelles
Intermediate filaments
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 12 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
Four major groups:
- Keratins /cytokeratins - found in all
epithelial cells, nails, horns, feathers,
scales; strengthen the tissue and provide
protection against ion and water loss
- Vimentin - found in mesenchymal cells
derived from the middle layer of the embryo;
desmin is found in muscle cells; glial
fibrillation acidic protein (GFAP) is found in
astrocytes
- Neurofilaments - found in neurons
- Lamins - form a structural framework for the
nuclear membrane
INCLUSIONS
Composed mainly of accumulated metabolites
and are often transitory components of the
cytoplasm
Fat droplets are prominent in adipocytes, liver
cells and adrenal cortical cells
Glycogen granules found mainly in liver cells
Lipofuscin granules golden brown bodies
present in many cells; accumulate with age in
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 13 of 14
CYTOPLASM
Jsgyu 2015
stable non-dividing cells (neurons, cardiac
cells); material derived from residual bodies
after lysosomal digestion
JessicaSocorroGaboyaYu,MD
Page 14 of 14
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Cell: and Cellular OrganellesDocumento70 pagineThe Cell: and Cellular OrganellesKunda JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.cell 1Documento67 pagine4.cell 1Raymond LundaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells: General ZoologyDocumento71 pagineCells: General ZoologyAzaleaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell & Its OrganelleDocumento66 pagineCell & Its OrganellerookieNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocumento60 pagineChapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyMarcos AlbaridaNessuna valutazione finora
- chapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYDocumento54 paginechapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYCza Mae ArsenalNessuna valutazione finora
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento24 pagineGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNessuna valutazione finora
- Hist of Cell-Organelles 2022Documento45 pagineHist of Cell-Organelles 2022betelhema71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure SeranDocumento4 pagineEukaryotic Cell Structure SeranLeah Jane MalinaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Human CellDocumento24 pagineBasics of Human Cellananya girishbabuNessuna valutazione finora
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento23 pagineGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal CellsDocumento17 pagineAnimal CellsJhan SasisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure FunctionDocumento43 pagineCell Structure Functioneishawajid75Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - The Cell - Organelles, Nucleus, Inclusions and DivisionDocumento58 pagine02 - The Cell - Organelles, Nucleus, Inclusions and DivisionMartha Orendu Oche AttahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure & Function 2022Documento43 pagineCell Structure & Function 2022Kavita MahaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocumento52 pagineMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physiology by BrownDocumento51 pagineGeneral Physiology by BrownuzohchukwuebukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocumento27 pagineLecture 3 - Cell Structure & Functionlazysadoon09Nessuna valutazione finora
- The CellDocumento24 pagineThe CellTyra Joyce Revadavia100% (1)
- Subcellular ComponetDocumento70 pagineSubcellular ComponetMcdonald AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell: By: Kinza ChaudhariDocumento16 pagineThe Cell: By: Kinza ChaudhariChris GayleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DR Fasiha Hussain Biochemistry DemonstratorDocumento37 pagineCell DR Fasiha Hussain Biochemistry DemonstratorAqsa ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryotic Cells - RuahDocumento16 pagineEukaryotic Cells - RuahruahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells: Components Structure and FunctionDocumento45 pagineCells: Components Structure and FunctionJada HartNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Taxonomy: Ma. Concepcion A. Maico, RN, Man, Ed.DDocumento46 pagineCell Structure and Taxonomy: Ma. Concepcion A. Maico, RN, Man, Ed.DIconMaicoNessuna valutazione finora
- NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESDocumento39 pagineNUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESolawandeilo123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Junction 2Documento90 pagineCell Junction 2sohail shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell ConstituentsDocumento39 pagineCell ConstituentsMilky YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- S 13 Lect 2Documento35 pagineS 13 Lect 2Anonymous fbXIfToSNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Day 1Documento50 pagineThe Cell Day 1Abegail Ashley PenoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - The Cell and The Epithelium LectureDocumento82 pagine2 - The Cell and The Epithelium Lecturegodara28pNessuna valutazione finora
- CELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Documento103 pagineCELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Allan Q VenusNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell StrucutreDocumento40 pagineCell StrucutreJeevitha VanithaNessuna valutazione finora
- HistologeDocumento62 pagineHistologe89sar2365Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Structure, Functions of The CellDocumento76 pagineThe Cell Structure, Functions of The CellCharles SsekawuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure & MembraneDocumento24 pagineCell Structure & MembraneAbhishek Singh ChandelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pengantar Biologi SelDocumento81 paginePengantar Biologi SeldiesNessuna valutazione finora
- TR-1 BioenglishDocumento11 pagineTR-1 BioenglishReza maulana AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell PhysiologyDocumento31 pagineCell PhysiologyJulie Calo PugiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Notes in Histology LecDocumento8 pagineAdditional Notes in Histology LecJISOO KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell UltrastructureDocumento47 pagineCell UltrastructureEugenia Migranova100% (1)
- Structure and Function of Cell: Presented by Miss - Robinsini.F 4 Year BSC Nursing Hosmat College of NursingDocumento29 pagineStructure and Function of Cell: Presented by Miss - Robinsini.F 4 Year BSC Nursing Hosmat College of NursingJoshua SpotifyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytology (Cell Biology)Documento86 pagineCytology (Cell Biology)Osakuni OlaoluwakitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocumento25 pagineReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3.Documento11 pagineLecture 3.rahaf.khalid226Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Cells & TissuesDocumento35 pagineChapter 3 Cells & TissuesKaye CorNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureDocumento32 pagine1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureRabiatul AdawiyyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and PhysiologyDocumento29 pagineCell Structure and PhysiologyZaid AbdulqadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch05 LectureDocumento58 pagineCh05 LectureGeorge Livingston GrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioc 211 Complete NotesDocumento158 pagineBioc 211 Complete NotesKevin KipropNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellDocumento77 pagine2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellalfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells, Tissues, Glands and Memranes - LECTURE ANATOMYDocumento198 pagineCells, Tissues, Glands and Memranes - LECTURE ANATOMYlouradelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell, Tissues, Chemistry of Life: V O2Abdvq4M84Documento63 pagineCell, Tissues, Chemistry of Life: V O2Abdvq4M84ROMEL RIMANDONessuna valutazione finora
- Biology ObjectivesDocumento12 pagineBiology ObjectivesNicholas OwNessuna valutazione finora
- Biokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Documento74 pagineBiokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Rizky NNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Part 1Documento38 pagineCell Part 1Fatih BedirhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFDocumento73 pagine2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFMuhammad Danial HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocumento8 pagineAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Cell AnatomyDocumento56 pagineHuman Cell Anatomysanthiyasandy100% (3)
- CPD FAQs 62918 PDFDocumento24 pagineCPD FAQs 62918 PDFHaru LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Blood TypeDocumento1 paginaA Blood TypeDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Health Information System: Crispinita A. Valdez Director, Information Management ServiceDocumento22 paginePhilippine Health Information System: Crispinita A. Valdez Director, Information Management ServiceJuly AlliveNessuna valutazione finora
- Widely Used by 5000+ Doctors, Hospitals and Healthcare FacilitiesDocumento2 pagineWidely Used by 5000+ Doctors, Hospitals and Healthcare FacilitiesDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento36 pagineChemical BondingDarwin Cruz100% (1)
- Mycology Intro NotesDocumento7 pagineMycology Intro NotesDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Merchant of VeniceDocumento9 pagineThe Merchant of VeniceDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperance AwardeesDocumento7 pagineTemperance AwardeesDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmo 14 S 2006Documento73 pagineCmo 14 S 2006John Terrence M. RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Class Jokes and HumorDocumento5 pagineMath Class Jokes and HumorDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Histopath LabDocumento11 pagineHistopath LabFatima Ong75% (4)
- Chapter 11Documento30 pagineChapter 11Darwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- English 210Documento2 pagineEnglish 210Darwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- BeowufDocumento10 pagineBeowufDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cc1 Amino AcidsDocumento8 pagineCc1 Amino AcidsDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Class Jokes and HumorDocumento5 pagineMath Class Jokes and HumorDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- BS in Medical Technology in The Philippine1Documento5 pagineBS in Medical Technology in The Philippine1Darwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring VolumeDocumento37 pagineMeasuring VolumeDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- PipettesDocumento37 paginePipettesDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Use PipettesDocumento1 paginaHow To Use PipettesDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chapter9 EscabarteDocumento30 pagineChapter9 EscabarteDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- HistologyDocumento14 pagineHistologyDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin of The Holy RosaryDocumento2 pagineOrigin of The Holy RosaryDarwin CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 355 Exam 1 Study GuideDocumento2 pagineBiology 355 Exam 1 Study GuideNgoc Minh NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 9 Science Chapter 5Documento27 pagineNCERT Exemplar For Class 9 Science Chapter 5Vidhan PanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation About CellsDocumento39 paginePresentation About Cellsharfiyanto100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocumento11 pagineEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA To ProteinsDocumento9 pagineDNA To ProteinsGAVIRAJ ENNessuna valutazione finora
- ScanDocumento32 pagineScanIka S NurroyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Bacteriology: David K. NgunjiriDocumento69 pagineIntroduction To Bacteriology: David K. NgunjiriFrancis ChegeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chloroplast DNA - WikipediaDocumento40 pagineChloroplast DNA - WikipediaARCHANA SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lehninger Ch26Documento81 pagineLehninger Ch26AMAN KUMAR SINGH100% (1)
- 2-Intro RNA and Protein - UploadDocumento52 pagine2-Intro RNA and Protein - UploadYuting ZhengNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein MetabolismDocumento18 pagineProtein MetabolismAbdul RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 13-2 Ribosomes and Protein SynthesisDocumento17 pagine13-2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesisapi-2699623300% (1)
- Biotech Module 1 1Documento49 pagineBiotech Module 1 1Janine CallanganNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture (Antibiotics) PDFDocumento97 pagineLecture (Antibiotics) PDFAnonymous FMCCRgvNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Question For Gpat or Niper Jee ExamDocumento6 paginePharmacology Question For Gpat or Niper Jee ExamraghvendradhakadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2Documento4 pagineDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2tifqbfgig100% (2)
- Chapter 4 - Cellular MetabolismDocumento6 pagineChapter 4 - Cellular Metabolismpatricia_sheepNessuna valutazione finora
- GeneticsDocumento55 pagineGeneticsJonathan Carlisle CheungNessuna valutazione finora
- M.SC Bio Chemistry Syllabus2016 17Documento29 pagineM.SC Bio Chemistry Syllabus2016 17QwertyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Control of ProteinDocumento43 pagineGenetic Control of ProteinGabriela ZahiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento83 pagineMolecular Basis of InheritanceKeerthi Sagar100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNADocumento53 pagineNucleic Acids - DNA and RNATom Anthony TonguiaNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 161 QuizletDocumento25 pagineBS 161 QuizletKaushik SridasyamNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP-01 - Cell The Unit of Life CORRECTEDDocumento3 pagineDPP-01 - Cell The Unit of Life CORRECTEDSiazzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Documento10 pagineBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNessuna valutazione finora
- RNA Structure and PropertyDocumento64 pagineRNA Structure and Propertystevensb055Nessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Ii. Subject MatterDocumento6 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7: Ii. Subject Matterpinky señaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science Lesson 13 The Structure and Properties of MatterDocumento17 paginePhysical Science Lesson 13 The Structure and Properties of MatterJustin BirdNessuna valutazione finora
- Review:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachDocumento4 pagineReview:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachIndrani GoswamiNessuna valutazione finora
- The EMBO Journal - 2022 - Han - Gut Colonization by Bacteroides Requires Translation by An EF G Paralog Lacking GTPaseDocumento20 pagineThe EMBO Journal - 2022 - Han - Gut Colonization by Bacteroides Requires Translation by An EF G Paralog Lacking GTPasesethNessuna valutazione finora