Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chemistry Bridging Course Lecture Notes
Caricato da
NDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemistry Bridging Course Lecture Notes
Caricato da
NCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Monday, January 25, 2016
Lecture #1: Atomic Structure
Thomsons atomic model:
PLUM PUDDING
Rutherford, Ernest:
Discovered the atomic nucleus 100 years ago.
Gold foil experiment. So far, it was known that electrons
could be separated from the atom. So by logic, there must
have been positive particles to counteract. Determined that
alpha particles were equivalent of Helium nucleus (mass, no.
of electrons, neutrons). Fired alpha particles into a container,
allowing them to accumulate, placing high charge through and
seeing the spectrum produced.
Showed that the spectrum produced from alpha particles were
same as those from helium.
Fired alpha particles at a thin gold foil (0.5 microns thick).
Most went straight through, hitting a curved detecting screen.
Small amount actually hitting screen: Most particles went
straight through, few deflected, very few greatly deflected.
Like howitzer shells bouncing off of tissue paper
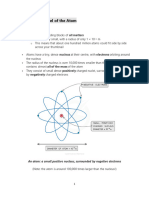
Conclusion: That there must be a lot of empty space between
gold atoms.
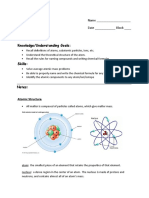
Small, dense, positively charged nucleus.
Number of protons didnt always correspond with weight of
atom. Leading to neutrons.
Chadwick:
Discovered Neutron. In 1932, observed that beryllium exposed
to bombardment by alpha particles released an unknown
radiation that ejected protons from nuclei of various
substances. He interpreted this radiation as being of particles
of mass approximately equal to that of the proton but without
electrical charge. I.e. Neutrons.
---------------------- Electron mass: 1/1800
Proton/electron mass: 1 (Charge: +/-1)
Size in atoms:
Atom: 1
Nucleus: 1/10,000
Proton: 1/100,000
Quark/electron: 1/100,000,000
12 <- Mass Number
C
6 <- Atomic Number (Z)
6 protons/electrons, 6 neutrons.
The number of protons defines an element.
Isotopes: Remember that the number of protons defines an
element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have
the same number of protons, but a different number of
neutrons.
Regular hydrogen protium has no neutrons. Heavy
hydrogen, deuterium (as in heavy water), has 1 neutron.
Tritium has 2 neutrons.
Calculation of relative atomic mass:
Relative Atomic mass is the average mass of all the isotopes
of that element compared to 1/12 the mass of Carbon-12 12
C, 12.011.
6
Carbon in a lump of coal is a combination of Carbon isotopes.
Mostly Carbon-12, a little Carbon-13, and even less Carbon-14.
12.011 calculated by (98.89 x 12 + __ x 13 + __ x 14)/100
Out of every 100 atoms 90.92 are 10Ne, 0.26 are 21Ne, and
8.82 are 22Ne.
Average = (90.92 x 20 + 0.26 x 21 + 8.82 x 22)/100
= 20.179 = 20.18
Ans is in 3 sig figs = 20.2
Periodic table:
Starting point: Mendeleevs 1869 periodic table, with vertical
periods and horizontal groups. Followed by his 1871 periodic
table.
http://www.ptable.com interactive P.T.
Ionization energy ->
Electron affinity ->
Atomic radius <Atomic radius v
Electron affinity, Ionization energy ^
Nonmetallic character to the top right, metallic to the
bottom left.
Ions
If an atom loses one or more electrons, you will have a
positively charged ion. This is a CATION, BECAUSE IT IS
ATTRACTED TO THE NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF THE SYSTEM,
CALLED THE CATHODE.
IF AN ATOM GAINS ONE OR MORE ELECTRONS, YOU WILL HAVE
A NEGATIVELY CHARGED ION. THIS IS CALLED AN ANION,
BECAUSE IT IS ATTRACTED TO THE NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF
THE SYSTEM, WHICH IS CALLED THE ANODE.
Two ions are isoelectronic if they have the same number of
electrons. Na+ is isoelectronic with Ne, which is also
isoelectronic with F-. They all have the same number of
electrons.
Tutorial #1: Atomic Structure
All elements may lose or gain electrons to achieve the noble
gas configuration, or magic number (such as 10, 18, 36, 54).
Group number: combining capacity
With loss of electrons, an atom becomes a +ve cation.
With gain of electrons, an atom becomes a ve anion.
With electrostatic attraction between cations and anions,
compounds are formed.
E.g. Na+ & Cl- form compound NaCl by an ionic bond (which is
essentially, electrostatic attraction).
Metals lose electrons, Non-metals gain electrons.
Metals -> cations,
Non-metals -> anions
Metalloids/semi-metals
There are no tri-atomic gases. E.g. of tetraatomic: P4. The rest
are known as polyatomic.
Bromine is liquid at room temperature.
Allotropes: Different arrangement of atoms.
E.g. Carbon: diamond, graphite
Properties change with allotropes. E.g. graphite can conduct
electricity but diamond cannot.
Think of atomic number in relation mostly to protons. So
where Oxygen gains 2 electrons, the atomic number of 8 is
thought of to remain the same.
Iso -> same.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- What Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsDocumento22 pagineWhat Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsCaleb MukaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic StructureDocumento55 pagineAtomic StructureNikolai Matthew BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Atomic Structure QSDocumento51 pagine1.1 Atomic Structure QSakilNessuna valutazione finora
- Isotopes of Pennium LabDocumento3 pagineIsotopes of Pennium Labapi-312554801Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phet Contribution 3459 6801Documento208 paginePhet Contribution 3459 6801Idrus Prakota100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Atom, Molecule & Ions: Presented byDocumento46 pagineFundamentals of Atom, Molecule & Ions: Presented byMai Nguyễn ThịNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Atomic StructureDocumento31 pagineChemistry Atomic StructureApex InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Term: Grade 9 ScienceDocumento70 pagineSecond Term: Grade 9 Sciencecaeameko:)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic StructureDocumento55 pagineAtomic StructureBhuwan GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Midterm Practice TestDocumento24 pagineChemistry Midterm Practice TestClara BetancourNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Da EverandAn Introduction to Physics (Material Science Metallurgy)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesDa EverandThe Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Module 1-3Documento5 pagineChem Module 1-3John CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry: Quarter 1Documento26 pagineGeneral Chemistry: Quarter 1Jacko Leno100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocumento9 pagineAtomic StructurehenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole and Atomic ModelDocumento73 pagineMole and Atomic ModelApeksha MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes 2 - Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocumento6 pagineNotes 2 - Atoms and Atomic Theoryochiengjoseph122Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocumento7 pagineCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Be Sure To Read The Law of Definite Proportions and Multiple ProportionsDocumento6 pagineBe Sure To Read The Law of Definite Proportions and Multiple ProportionsMahdi MiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure 1Documento15 pagineAtomic Structure 1animenba07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 General Chemistry PDFDocumento29 pagineUnit 1 General Chemistry PDFchuchu maneNessuna valutazione finora
- For Other Uses, See .: Atom (Disambiguation)Documento2 pagineFor Other Uses, See .: Atom (Disambiguation)Hana SpahicNessuna valutazione finora
- 1ST CHAPTER Long Questions Basic Concept PDFDocumento50 pagine1ST CHAPTER Long Questions Basic Concept PDFAnonymous 6HADGUEXDNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryDocumento52 pagineElectronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryNAM TRƯƠNG HOÀINessuna valutazione finora
- Helium Atom: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocumento2 pagineHelium Atom: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchWYNNessuna valutazione finora
- 2025 Syllabus Chapter 02 Atomic StructureDocumento74 pagine2025 Syllabus Chapter 02 Atomic StructureNate ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.radiometry and DosimetryDocumento17 pagine10.radiometry and DosimetryAchraf RabadiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6988chemistry Unit 1 RevisionDocumento10 pagine6988chemistry Unit 1 RevisionNicola NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic StructureDocumento17 pagineAtomic StructureAvel Xyphus N. MaravillaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE101 - Class 03 (Chapter 2)Documento44 pagineCHE101 - Class 03 (Chapter 2)Mst. Meherin Jahan 2011229642Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Atomic StructureDocumento47 pagineChapter 4 Atomic StructureJulius Erick EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of AtomDocumento7 pagineStructure of AtomMera FunportalNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of The Atom Class 9Documento11 pagineStructure of The Atom Class 9JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and Their Styructure Chapt4Documento57 pagineAtoms and Their Styructure Chapt4Manoy KolokoyNessuna valutazione finora
- C6a Atoms and Elements Chem WebsiteDocumento25 pagineC6a Atoms and Elements Chem Websiteapi-261462856Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Nuclear AtomDocumento25 pagineThe Nuclear Atomnaazim mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and Their StructureDocumento57 pagineAtoms and Their StructureJan Edzel IsalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of The Atom: Atomic ModelsDocumento14 pagineStructure of The Atom: Atomic ModelsShrinivasan HariprasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Atomic StructureDocumento8 pagineChapter 4 Atomic StructureVishal GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocumento14 pagineNuclear Physics NotesJonathan ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure: Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocumento3 pagineAtomic Structure: Dalton's Atomic TheoryRohan PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Note For EJUDocumento18 pagineNote For EJUmr.draungnaingwinNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAP4 AtomicStructureDocumento34 pagineCHAP4 AtomicStructureJex AsupardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Chapter 2Documento102 pagineChemistry Chapter 2Stephanie Palomares LevitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of AtomDocumento3 pagineStructure of AtomabiramirajalaksmiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTDocumento4 pagine3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTRoldan Delapa PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento58 pagineChemashwin.sp.004Nessuna valutazione finora
- As Physics NotesDocumento43 pagineAs Physics Notesleelakdd108100% (1)
- Chapter 02 Atomic StructureDocumento62 pagineChapter 02 Atomic StructureJishen ZhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Theory 1Documento3 pagineAtomic Theory 1Husen HasenNessuna valutazione finora
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocumento49 pagineL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of AtomsDocumento4 pagineStructure of AtomsAtanu SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and IonsDocumento13 pagineAtoms and IonsYousuf Al ManjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear PhysicsDocumento54 pagineNuclear PhysicsSuhaan HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Documento20 pagine(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Trishia Mae Gregorio BelenNessuna valutazione finora
- Punjab Boards 11th Class Chemistry Book English Medium 6368075084588991190 PDFDocumento583 paginePunjab Boards 11th Class Chemistry Book English Medium 6368075084588991190 PDFGulshairNessuna valutazione finora
- AtomDocumento32 pagineAtommcmusbixNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocumento55 pagineNuclear Physics Notesmsukwa.cheyoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Physics NotesDocumento93 pagineA Level Physics NotesAdam BaldwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsslive-XI-chem-2. Atomic Structure PDFDocumento12 pagineHsslive-XI-chem-2. Atomic Structure PDFGautham GrimaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 11 Unit 7 PPT 1 HebdenDocumento27 pagineChem 11 Unit 7 PPT 1 HebdenMarina XuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Documento13 pagineUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1Da EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Heidelberg Science Library) M. F. O'Dwyer, J. E. Kent, R. D. Brown (Auth.) - Valency-Springer-Verlag New York (1978)Documento262 pagine(Heidelberg Science Library) M. F. O'Dwyer, J. E. Kent, R. D. Brown (Auth.) - Valency-Springer-Verlag New York (1978)fionna andesonNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Science (SHS) - Q2 - Mod10 - DIfferent Methods in Determining The Sge of Rocks - v2Documento19 pagineEarth Science (SHS) - Q2 - Mod10 - DIfferent Methods in Determining The Sge of Rocks - v2Emer Perez80% (5)
- US Army Medical Course MD0803-100 - General ChemistryDocumento117 pagineUS Army Medical Course MD0803-100 - General ChemistryGeorges100% (1)
- A-Encyclopedia of Solid Earth GeophysicsDocumento24 pagineA-Encyclopedia of Solid Earth GeophysicsJuan Diego NiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Nuclear Physics - 3 Modes of Radioactive Decay and Types of RadiationDocumento41 pagineBasic Nuclear Physics - 3 Modes of Radioactive Decay and Types of RadiationphooolNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE - 3AF, 3BF, 3AM, 3CM MID-TERM Question Spring-2020 PDFDocumento2 pagineCSE - 3AF, 3BF, 3AM, 3CM MID-TERM Question Spring-2020 PDFscribd2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Class 11Documento26 pagineAtomic Structure Class 11Milan AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocumento16 pagineCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationiSean1337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 127 Exam 1 06Documento11 pagineChem 127 Exam 1 06Glitch172Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alpha, Beta, and Gamma RadiationDocumento5 pagineAlpha, Beta, and Gamma RadiationMalaya Kumar BhoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Class 11 Part 2Documento161 pagineChemistry Class 11 Part 2maupravin1230% (1)
- Physics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THDocumento48 paginePhysics 200 Question Mission 100 Class 12 THNARENDER YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Reaction ReviewDocumento3 pagineNuclear Reaction ReviewSeyi Martins ObandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sas8 STM-005Documento5 pagineSas8 STM-005mayasNessuna valutazione finora
- Preuniversity Chemistry CourseDocumento179 paginePreuniversity Chemistry CoursepapaioasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Documento16 pagineCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11dxD.T.C.dxNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology Global 10th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology Global 10th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFwaterycobstone.yg9zl100% (10)
- Yusuf ChemistryDocumento95 pagineYusuf ChemistryLAVTOLNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Supplementary Exercise Microscopic World I (Question)Documento147 pagine2 Supplementary Exercise Microscopic World I (Question)RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 (Worksheet)Documento7 pagineChapter 4 (Worksheet)Abdullah AlthaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Sheet (Narayana) Goyal SirDocumento65 pagineAtomic Structure Sheet (Narayana) Goyal SirKassandra0% (1)
- List of Physics Terms: Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionDocumento11 pagineList of Physics Terms: Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionazlinabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 9th Edition Anderson Test Bank PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 9th Edition Anderson Test Bank PDFmabelbevisgr2100% (14)
- PHET Build An AtomDocumento4 paginePHET Build An AtomJake100% (1)