Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
IGCSE Bio
Caricato da
Majid Dardas0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
175 visualizzazioni5 pagineBy: Majid Dardas
Biology Research
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoBy: Majid Dardas
Biology Research
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
175 visualizzazioni5 pagineIGCSE Bio
Caricato da
Majid DardasBy: Majid Dardas
Biology Research
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
BIOLOGY
REASEARCH
Majid Dardas
Uses of Aspirin
Majid Dardas
Aspirin, or acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is a salicylate drug,
and is generally used as an analgesic (something that
relieves pain without producing anesthesia or loss of
consciousness) for minor aches and pains, to reduce fever
(an antipyretic), and also as an anti-inflammatory drug.
Your doctor may direct you to take a low dose of aspirin to
prevent blood clots. This effect reduces the risk of stroke and
heart attack. If you have recently had surgery on clogged
arteries (such as bypass surgery, carotid endarterectomy,
coronary stent), your doctor may direct you to use aspirin
in low doses as a blood thinner to prevent blood clots.
When should you not use aspirin?
You should not use aspirin if you have a bleeding disorder such as hemophilia, a
recent history of stomach or intestinal bleeding, or if you are allergic to an NSAID
(non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) such as Advil, Motrin, Aleve, Orudis,
Indocin, Lodine, Voltaren, Toradol, Mobic, Relafen, Feldene, and others.
Do not give this medication to a child or teenager with a fever, flu symptoms, or
chicken pox. Salicylates can cause Reyes syndrome, a serious and sometimes
fatal condition in children.
Therefore the uses of aspirin are:
1) As an analgesic (something that relieves
pain without producing anesthesia or loss of
consciousness)
3) As an antipyretic (to
reduce fever)
4) As a blood thinner (to
prevent blood clot)
2) As an anti-inflammatory drug (inflammation
is when the body becomes reddened,
swollen, hot and often painful.
5) To treat angina (chest
pain)
Angioplasty
Majid Dardas
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of
heart disease. It is the leading cause of death in the United
States in both men and women.
CAD happens when the arteries that supply blood
to heart muscle become hardened and narrowed.
This is due to the buildup of cholesterol and other
material, called plaque, on their inner walls. This
buildup is called atherosclerosis. As it grows, less
blood can flow through the arteries. As a result, the
heart muscle cant get the blood or oxygen it needs.
This can lead to chest pain (angina) or a heart attack.
Most heart attacks happen when a blood clot suddenly
cuts off the hearts blood supply, causing permanent
heart damage.
Over time, CAD can also weaken the heart muscle and contribute to heart
failure and arrhythmias. Heart failure means the heart cant pump blood well
to the rest of the body. Arrhythmias are changes in the normal beating rhythm
of the heart.
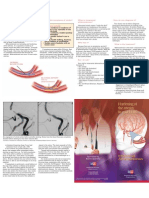
Angioplasty is a procedure to restore blood flow through the artery. You have
angioplasty in a hospital. The doctor threads a thin tube through a blood
vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has
a tiny balloon on the end. When the tube is in place, the doctor inflates the
balloon to push the plaque outward against the wall of the artery. This widens
the artery and restores blood flow.
Doctors may use angioplasty to:
Reduce chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart
Minimize damage to heart muscle from a heart attack
Many people go home the day after angioplasty, and are able to return to
work within a week of coming home.
By-Pass Surgery
Majid Dardas
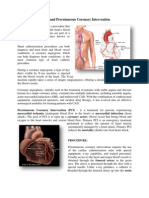
Another way to treat coronary artery disease is by a by-pass surgery. During
a bypass surgery, a blood vessel is removed or redirected from one area
of the body and placed around the area or areas of narrowing in order to
bypass the blockages and restore blood flow to the heart muscle. This
vessel is called a graft.
These substitute blood vessels can come from your chest, legs, or arms.
Theyre safe to use because there are other pathways that take blood to and
from those tissues. The surgeon will decide which graft(s) to use depending
on the location of your blockage, the amount of blockage and the size of
your coronary arteries.
Before your surgery you will get general anesthesia. You will be asleep
(unconscious) and pain-free during surgery. Once you are unconscious, the
heart surgeon will make an 8 - 10-inch surgical cut in the middle of your
chest. Your breastbone will be separated
to create an opening. This allows your
surgeon to see your heart and aorta, the
main blood vessel leading from the heart to
the rest of your body.
Most people who have coronary bypass
surgery are connected to a heart-lung
bypass machine, or bypass pump.
Your heart is stopped while you are
connected to this machine.
This machine does the work of your
heart while your heart is stopped for
the surgery. The machine adds oxygen
By-Pass Surgery
Majid Dardas
To create the bypass graft:
1) The doctor will take a vein or artery
from another part of your body and uses
it to make a detour (or graft) around the
blocked area in your artery. Your doctor
may use a vein, called the saphenous
vein, from your leg.
3) A blood vessel in your chest, called
the internal mammary artery (IMA), can
also be used as the graft. One end of
this artery is already connected to your
aorta. The other end is attached to your
coronary artery.
2) To reach this vein, a surgical
cut will be made along the inside
of your leg, between your ankle
and groin. One end of the graft
will be sewn to your coronary
artery. The other end will be
sewn to an opening made in
your aorta.
4) Other arteries can also be used
for grafts in bypass surgery. The
most common one is the radial
artery in your wrist.
After the graft has been created, your breastbone will be closed with wires.
These wires stay inside you. The surgical cut will be closed with stitches.
This surgery can take 4 to 6 hours. After the surgery, you will be taken to the
intensive care unit.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Final Case Study - CADDocumento109 pagineFinal Case Study - CADPatricia Marie Buenafe100% (1)
- Case Study Sa Nutrition-1Documento7 pagineCase Study Sa Nutrition-1Hazel Sumulong GumapacNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Website Questions Frcem Sba Frcem ResourcesDocumento4 pagineSample Website Questions Frcem Sba Frcem ResourcesmtogooNessuna valutazione finora
- Mi DrugsDocumento5 pagineMi DrugsKing Nehpets AlczNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento9 pagineCoronary Artery DiseaseMariquita Buenafe100% (1)
- What Is Heart Bypass SurgeryDocumento10 pagineWhat Is Heart Bypass SurgeryVanitha AlagarsamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento21 pagineMyocardial InfarctionAAMIR NAWAZNessuna valutazione finora
- Describe The Management of Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction (Lecture)Documento5 pagineDescribe The Management of Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction (Lecture)KesyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Disease and Heart Bypass SurgeryDocumento3 pagineHeart Disease and Heart Bypass SurgeryAuladi Lubis ∑Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Heart AttackDocumento12 pagineWhat Is A Heart AttackAlia MaisarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)Documento4 pagineAtrial Septal Defect (ASD)gitanoviiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment For AisDocumento3 pagineTreatment For AisXentur XenNessuna valutazione finora
- Saywan Ziyad Yusif-CABGDocumento14 pagineSaywan Ziyad Yusif-CABGCapitan SaywanNessuna valutazione finora
- Beating Surgery FinalDocumento17 pagineBeating Surgery FinalSimon JosanNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart FailureDocumento3 pagineHeart FailureSudhir ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lovesh Final PresentationDocumento63 pagineLovesh Final PresentationLovesh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment: Ischemic StrokeDocumento4 pagineTreatment: Ischemic StrokeGopi KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Artery DiseaseDocumento8 paginePeripheral Artery DiseasemainehoonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lovesh PresentationDocumento58 pagineLovesh PresentationLovesh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocumento11 pagineCoronary Heart DiseaseZaryna TohNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Coronary Bypass Surgery Is An Open-Heart Surgery, You MightDocumento17 pagineCoronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Coronary Bypass Surgery Is An Open-Heart Surgery, You MightNuzhat FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Attack Risk Factors: Non-Coronary Artery Disease Causes of Heart Attack May Also Occur, These IncludeDocumento12 pagineHeart Attack Risk Factors: Non-Coronary Artery Disease Causes of Heart Attack May Also Occur, These IncludeHazwan AkmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Stent For LifeDocumento6 pagineStent For LifeAbrar KhafagaNessuna valutazione finora
- CABGDocumento41 pagineCABGJasmin Jacob100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento22 pagineChapter 1 - The Cardiovascular SystemHoa LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathologies Affecting Blood VesselDocumento11 paginePathologies Affecting Blood VesselroselynroukayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and TreatmentDocumento6 pagineCarotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and TreatmentVijay Baskar SNessuna valutazione finora
- A Stroke RecoveryDocumento2 pagineA Stroke Recoverymanjukumard2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- C P P C P P: Ardiology Atient AGE Ardiology Atient AGEDocumento4 pagineC P P C P P: Ardiology Atient AGE Ardiology Atient AGEsatish_vsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mi TreatmentDocumento24 pagineMi TreatmentAradhanaRamchandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Atriclip OverviewDocumento14 pagineAtriclip Overviewmohamed ghedanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Living With Congestive Heart Failure CHF 4Documento28 pagineLiving With Congestive Heart Failure CHF 4Soror RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocardial RevascularizationDocumento3 pagineMyocardial Revascularizationapi-610954065Nessuna valutazione finora
- CT 089106Documento7 pagineCT 089106dr_dinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDDocumento11 pagineAcyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDFenita Renny DinataNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: UnderstandingDocumento24 pagineCoronary Artery Bypass Surgery: UnderstandingNurArsitaPebruatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocumento9 pagineCoronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary Interventionellaine0024100% (2)
- AngioplastyDocumento2 pagineAngioplastysubirghosh1100% (1)
- Cardiac Catheterization: Why It's DoneDocumento3 pagineCardiac Catheterization: Why It's DoneRania S. HamdanNessuna valutazione finora
- DX Dan TX StrokeDocumento8 pagineDX Dan TX StrokeFirmansah SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento3 pagineCoronary Artery DiseaseMarta Luquez RNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento23 pagineMyocardial InfarctionNishaThakuri100% (1)
- What Is Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento3 pagineWhat Is Acute Coronary SyndromeMa Ceres P SisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Procedure in Cardiogenic ShockDocumento2 pagineMedical Procedure in Cardiogenic ShocksamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Ischemic StrokeDocumento9 pagineTreatment of Ischemic Strokeka 66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interventional Cardiology and SurgeryDocumento19 pagineInterventional Cardiology and SurgeryDEV NANDHINI RNessuna valutazione finora
- ThibodeauDocumento3 pagineThibodeauapi-532080282Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study For Myocardial InfarctionDocumento4 pagineCase Study For Myocardial InfarctionGabbii CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart DiseaseDocumento38 pagineHeart DiseaseDr.Sunil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Documento11 pagineDiagnosis: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Ferdinand VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- NORBE BSN4A Midterm Activity 1Documento2 pagineNORBE BSN4A Midterm Activity 1Marlo Dañez NorbeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Cardiac Heart Surgery V4Documento32 pagine2016 Cardiac Heart Surgery V4B Prashant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AngioplastyDocumento45 pagineAngioplastym maskNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocumento25 pagineCardiac CatheterizationQueeny Anne ApilNessuna valutazione finora
- PTCADocumento51 paginePTCAJasmin Jacob100% (1)
- Consent Carotid StentingDocumento13 pagineConsent Carotid StentingAbhinav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Symptoms: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocumento6 pagineSymptoms: by Mayo Clinic StaffIvan HalimNessuna valutazione finora
- 15A ArteryDocumento72 pagine15A Arterypavi7muruganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- ArtherosclerosisDocumento23 pagineArtherosclerosistanyagargNessuna valutazione finora
- Ischemia Is An Insufficient Supply of Blood To An Organ, Usually Due To A Blocked ArteryDocumento7 pagineIschemia Is An Insufficient Supply of Blood To An Organ, Usually Due To A Blocked ArteryharryNessuna valutazione finora
- Angioplasty, (Stent Dilatation) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandAngioplasty, (Stent Dilatation) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 9700 s12 Ms 23 (-21)Documento7 pagine9700 s12 Ms 23 (-21)Majid DardasNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 s16 Ms 21 (-14)Documento7 pagine9700 s16 Ms 21 (-14)Majid DardasNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 s14 Ms 23 (-5)Documento9 pagine9700 s14 Ms 23 (-5)Majid DardasNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 s16 Ms 21 (-14)Documento7 pagine9700 s16 Ms 21 (-14)Majid DardasNessuna valutazione finora
- HyperkalemiaDocumento9 pagineHyperkalemiaFabdul RaufNessuna valutazione finora
- B.8 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in OxygenationDocumento11 pagineB.8 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in OxygenationSOLEIL LOUISE LACSON MARBASNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Diagnosa ICD-ICDX Rawat Jalan - CompressedDocumento245 pagineLaporan Diagnosa ICD-ICDX Rawat Jalan - Compressedendang lestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsDocumento17 pagineFluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsA.Nessuna valutazione finora
- CF4FRIDocumento11 pagineCF4FRIJERWIN TIBIGNessuna valutazione finora
- Merritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleDocumento75 pagineMerritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleChelsea ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- PNLE II For Community Health Nursing and Care of The Mother and ChildDocumento20 paginePNLE II For Community Health Nursing and Care of The Mother and ChildASDF ASDFNessuna valutazione finora
- Neorev - Emergencias Quirúrgicas Abdominales en NeoDocumento10 pagineNeorev - Emergencias Quirúrgicas Abdominales en NeoLuis Ruelas SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 - Elbokl - Severe Caffeine Intoxication Treated With HemodialysisDocumento4 pagine2021 - Elbokl - Severe Caffeine Intoxication Treated With Hemodialysisamanda lssNessuna valutazione finora
- The Lancet JournalDocumento2 pagineThe Lancet JournalAleaAVKNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic - Characters and Affinities of DipnoiDocumento11 pagineTopic - Characters and Affinities of Dipnoihj100% (1)
- Physio - Chapter 37Documento4 paginePhysio - Chapter 37Regina Ysabel SartagudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q - A PharmacologyDocumento9 pagineQ - A PharmacologyYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nle - High-Risk PregnancyDocumento113 pagineNle - High-Risk Pregnancytachycardia01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vasopressors For ShockDocumento21 pagineVasopressors For ShocknugrahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Cardiovascular SystemDocumento3 pagineNotes On Cardiovascular Systemmohamed waleedNessuna valutazione finora
- Physio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 5Documento4 paginePhysio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 5Roland Calipayan Jr.0% (1)
- Surgical Atrial Appendage 2022Documento5 pagineSurgical Atrial Appendage 2022吳醫師Nessuna valutazione finora
- Broncho-Pulmonary SegmentsDocumento29 pagineBroncho-Pulmonary SegmentsArbin PanjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocumento2 pagineDirection: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answerariel agos100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and The Cardiovascular System Vascular Repair and Regeneration As A Therapeutic TargetDocumento26 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and The Cardiovascular System Vascular Repair and Regeneration As A Therapeutic TargetAndreea MoalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento36 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiamomodou s jallowNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Examination of Gastrointestinal SystemDocumento34 pagineClinical Examination of Gastrointestinal SystemDivya Rajendran100% (1)
- NCM of Clients With Endocrine DisordersDocumento24 pagineNCM of Clients With Endocrine DisordersArgee Alonsabe100% (1)
- Internal Medicine OSCE MindmapsDocumento21 pagineInternal Medicine OSCE MindmapsCheru TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- PerindoprilDocumento5 paginePerindoprilEsther Afrianti SagalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q - A Random 14Documento6 pagineQ - A Random 14Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Anatomy: DR - Raja'a Al-Adhami (2) January 28, 2021 The SkinDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Anatomy: DR - Raja'a Al-Adhami (2) January 28, 2021 The Skinscort cherNessuna valutazione finora