Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Focus Economics Grade 10 Exam Practice Book
Caricato da
Mmapontsho TshabalalaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Focus Economics Grade 10 Exam Practice Book
Caricato da
Mmapontsho TshabalalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CAPS
Economics
m
a
e
x
c
E
i
t
ac
Pr
Focus_Exam Practice Book_COVER_Economics_Gr10.indd 2
k
o
o
10
e
d
a
r
G
2011/09/02 3:17 PM
Economics Tests.pdf 1 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST ONE
Marks: 60
QUESTION 1
Choose the correct term in brackets. Write only the term next to the question number (1.11.4)
in your answer book.
1.1
(Micro-economics/Macro-economics) examines economy-wide phenomena such as
unemployment, national income, economic growth and inflation.
(2)
1.2
The theory of price determination is an example of a topic study in (microeconomics/macro-economics).
(2)
1.3
To say, income tax in South Africa is an unfair system of taxation, is an example of a
(normative/positive) statement.
(2)
1.4
To say, interest rates in South Africa are below 10%, is an example of a
(normative/positive) statement.
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 2
List the THREE basic economic questions.
[6]
QUESTION 3
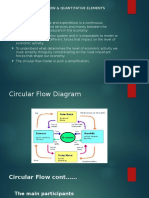
Draw and label a circular flow diagram to show how firms, households and the government
interact in an open economy.
[18]
Economics Tests.pdf 2 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
QUESTION 4
Study the diagram below and then answer the questions that follow.
4.1
Identify the missing parts (labelled AD) in the diagram above.
(8)
4.2
Explain whether the above diagram represents an open or closed economy.
(4)
Economics Tests.pdf 3 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
4.3
Use the figures in the table below to calculate the value of aggregate spending in the
economy.
Areas of spending
Symbols
Aggregate spending
Consumption spending
R140 million
Investment spending
R20 million
Government spending
R90 million
Imports
R40 million
Exports
R10 million
(8)
[20]
QUESTION 5
Choose the correct term in brackets. Write only the term next to the question number (5.15.4)
in your answer book.
5.1
During a recession in the business cycle, there is an increase in the rate of
(unemployment/economic growth).
(2)
5.2
During a boom in the business cycle, there is (a depreciation/an appreciation) of the
local currency.
(2)
5.3
Technological advances which improve productivity levels will generally lead to an
economic (recession/boom).
(2)
5.4
During an economic (boom/recession), there is an increase in the real value of goods
and service produced.
(2)
[8]
[TOTAL: 60 marks]
Economics Tests.pdf 4 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST TWO
Marks: 70
QUESTION 1
Various possible answers are provided for each of the following questions. Write the letter only
of the correct answer next to the relevant question number.
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
Which of the following factors would lead to an increase in the demand for DVDs?
A
A decrease in the price of DVDs.
An increase in the supply of DVDs.
A decrease in the price of DVD players.
A decrease in the supply of DVDs.
(2)
Which of these statements best describes the law of demand?
A
When the supply of a product increases the demand will increase.
When the price of a product increases the quantity demanded will decrease.
When the price of a product increases the quantity demanded will increase.
If consumer incomes increase there will be an increase in demand for a product.
(2)
Suppose there is a very effective advertising campaign for a particular good. The effect
of this, ceteris paribus, will be:
A
a shift along the demand curve up and to the left.
a shift along the demand curve down and to the right.
a shift in the position of the demand curve up and to the right.
a shift in the position of the demand curve down and to the left.
(2)
A shows what can be produced when using the factors of production in the most
efficient way possible.
A
balance of payments account
market equilibrium curve
production possibility curve
graph depicting the intersection of a demand curve and a supply curve.
4
(2)
Economics Tests.pdf 5 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
Suppose there is an increase in the demand for a good. This, will ceteris paribus, lead
to
A
a decrease in the equilibrium price and quantity of the good.
an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity of the good.
an increase in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of
the good.
a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of
the good.
(2)
Suppose there is an increase in the supply of a good. This, will ceteris paribus, lead
to
A
a decrease in the equilibrium price and quantity of the good.
an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity of the good.
an increase in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of
the good.
a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of
the good.
(2)
Suppose that the demand and supply of a product increase simultaneously. This, will
ceteris paribus, lead to
A
an increase in the market price.
a decrease in the market price.
an increase in the equilibrium quantity.
a decrease in the equilibrium quantity.
(2)
Suppose that unfavourable weather conditions affect the supply of apples in South
Africa. The effect of this, ceteris paribus, will be:
A
a shift along the supply curve up and to the right.
a shift along the supply curve down and to the left.
a shift in the position of the demand curve down and to the right.
a shift in the position of the demand curve up and to the left.
(2)
Economics Tests.pdf 6 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
1.9
Which of the following statements best describes the law of supply?
A
When the demand for a product increases the supply decreases.
When the demand for a product decreases the supply decreases.
When the price of a product increases the quantity supplied increases.
When costs of production increase the supply of a product will decrease.
(2)
[18]
QUESTION 2
List any THREE functions of a market.
[6]
QUESTION 3
Study the figures below:
Quantity
15
Fixed Cost
250
Variable cost
500
Using the above figures, calculate:
3.1
Total costs
(2)
3.2
Average Costs
(4)
3.3
Average Variable costs
(4)
3.4
If the total cost for 25 units is R350 and the total cost for 30 units is R550, calculate the
Marginal cost.
(6)
[16]
QUESTION 4
List THREE characteristics of an imperfect market.
[6]
Economics Tests.pdf 7 7/2/2011 4:09:25 PM
QUESTION 5
Choose the correct term in brackets. Write only the term next to the question number (5.15.4)
in your answer book.
5.1
Value-added tax (VAT) is an example of (a direct/an indirect) tax.
(2)
5.2
(Subsidies/direct taxes) are provided to both consumers and producers.
(2)
5.3
(Subsidies/welfare grants) enable firms to supply a greater quantity of a good or
service, thus lowering the market price.
(2)
5.4
If the state imposes a price ceiling (maximum price), it ensures that the price of the
good remains (below/above) a certain level.
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 6
Use a diagram to analyse the effect of an indirect tax on a good or service.
[TOTAL: 70 marks]
[16]
Economics Tests.pdf 8 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST THREE
Marks: 50
QUESTION 1
Various possible answers are provided for each of the following questions. Write the letter only
of the correct answer next to the relevant question number.
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
In the economic history of South Africa, the of economic development was
characterised by subsistence farming and bartering.
A
pre-colonial era
agricultural phase
agricultural mining phase
industrial development phase.
(2)
During the of economic development in South Africa, the VOC bought slaves from
India, East Indies and Madagascar to work on their commercial farms and to work as
gardeners, builders and carpenters.
A
pre-colonial era
agricultural phase
agricultural mining phase
industrial development phase.
(2)
The first bank notes were issued in South Africa
A
in the early 1700s.
in the late 1700s.
before 1700.
after 1800.
(2)
The first bank to be established in South Africa was
A
a private bank which only took deposits.
a government-controlled bank which only took deposits.
a private bank which lent people money to purchase land.
a government-controlled bank which lent people money to purchase land.
8
(2)
Economics Tests.pdf 9 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
1.5
The is defined as that proportion of the population, which is between 16 and 65 years
of age and has the potential to be employed.
A
labour force participation rate
economically-active population
rate of unemployment
labour absorption rate.
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 2
Choose an appropriate description from COLUMN B to match the concept in COLUMN A. Write
only the letters (AH) to indicate your choice next to each question number (2.12.8) in your
answer book.
COLUMN A
COLUMN B
2.1
Characteristic of the traditional stage
of economic development in Europe
The establishment of towns and the
emergence of travelling merchants
2.2
Characteristic of the transitional
stage of economic development in
Europe
Industrial Revolution
2.3
Characteristic of the take-off stage of
economic development in Europe
A severe lack of economic freedom
and no specialisation of labour
2.4
Characteristic of the stage of
economic maturity in Europe
Formation of labour unions
2.5
Characteristic of the period of mass
production in the economic
development of Europe
Approximately from 1200 to 1700
2.6
The duration of the transitional
period of economic development in
Europe
Mercantilism
2.7
The duration of the take-off period of
economic development in Europe
Approximately from 1700 to 1900
2.8
The duration of the period of
economic maturity in Europe
Approximately from 1000 to 1200
[16]
9
Economics Tests.pdf 10 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 3
List the THREE most important characteristics of the pre-colonial era of economic development
in South Africa.
[6]
QUESTION 4
List ONE item which was commonly used to barter with in Africa, prior to the introduction of
notes and coins.
[2]
QUESTION 5
Choose the correct term in brackets. Write only the term next to the question number (5.15.4)
in your answer book.
5.1
Population growth leads to (an increase/a decrease) in the supply of labour.
(2)
5.2
The difference between the birth rate and death rate is called the (infant mortality
rate/natural growth rate).
(2)
5.3
Population growth leads to (an increase/a decrease) in the demand for consumer
goods.
(2)
5.4
Urbanisation is the process whereby the population of urban areas
(decreases/increases) as the result of migration.
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 6
Choose the correct term in brackets. Write only the term next to the question number (6.16.4)
in your answer book.
6.1
Since 1970, the unemployment rate in South Africa has steadily (increased/decreased).
(2)
6.2
The unemployment rate is the percentage of the (total/economically-active) population
that is actively looking for work, but is unable to find employment.
(2)
6.3
Population growth leads to (an increase/a decrease) in the supply of labour.
(2)
6.4
Population growth leads to (an increase/a decrease) in the aggregate demand for
consumer goods.
(2)
[8]
[TOTAL: 50 marks]
10
Economics Tests.pdf 11 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST FOUR
Marks: 60
QUESTION 1
Various possible answers are provided for each of the following questions. Write the letter only
of the correct answer next to the relevant question number.
1.1
1.2
1.3
When people are temporarily unemployed because they are moving between jobs, they
form part of unemployment figures.
A
seasonal
frictional
structural
cyclical.
(2)
If the demand for labour increases, there will be
A
an increase in the wage rate, but a decline in the level of employment.
an increase in both the wage rate and the level of employment.
a decrease in the wage rate and an increase in the level of employment.
a decrease in both the wage rate and the level of employment.
(2)
Suppose both the demand for and supply of labour were to increase. This, would ceteris
paribus, most certainly lead to
A
an increase in the wage rate.
an increase in the level of employment.
a decrease in the wage rate.
a decrease in the level of employment.
(2)
[6]
11
Economics Tests.pdf 12 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 2
Choose an appropriate description from COLUMN B to match the concept in COLUMN A. Write
only the letters (AH) to indicate your choice next to each question number (2.12.8) in your
answer book.
COLUMN A
COLUMN B
2.1
Labour unions
A group set up within an organisation to
settle disputes between employers and
employees
2.2
Workplace forums
Assists with disputes, which could not be
resolved within an organisation
2.3
Bargaining councils
A group of workers from a specific sector,
who organise themselves to promote their
social, economic and political goals
2.4
Commission for Conciliation,
Mediation and Arbitration
(CCMA)
Legislation, which seeks to protect the
rights of individuals in the workplace and
promote collective bargaining
2.5
Labour courts
A body responsible for regulating labour
practices and ensuring compliance with
the Labour Relations Act
2.6
Basic Conditions of
Employment Act
Legislation which seeks to promote the
employees physical well-being
2.7
Labour Relations Act
Sets out minimum terms and conditions for
employment
2.8
Occupational Health and
Safety Act
A collection of employees within a
business who meet to discuss labour
issues at work
[16]
12
Economics Tests.pdf 13 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 3
Critically discuss the factors which contribute to high unemployment figures in South Africa.
[16]
QUESTION 4
List any THREE examples of legislation in South Africa, which seek to promote labour relations
and workers rights.
[6]
QUESTION 5
Explain the difference between the Labour Relations Act and the Basic Conditions of
Employment Act.
[TOTAL: 60 marks]
13
[16]
Economics Tests.pdf 14 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST ONE MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
macro-economics
(2)
1.2
micro-economics
(2)
1.3
normative
(2)
1.4
positive
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 2
2
What , how , and for whom to produce?
[6]
QUESTION 3
3
[18]
14
Economics Tests.pdf 15 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 4
4.1
A: Business enterprises
B: Households
C: Households receive income (wages, salaries, rent and interest)
D: Taxes
(8)
4.2
The diagram shows a closed economy , because there is no foreign sector .
(4)
4.3
Y = C + I + G + X M
Y = R140 million + R20 million + R90 million + R10 million R40 million
Y = R220 million
(8)
[20]
QUESTION 5
5.1
unemployment
(2)
5.2
an appreciation
(2)
5.3
boom
(2)
5.4
boom
(2)
[8]
[TOTAL: 60 marks]
15
Economics Tests.pdf 16 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST TWO MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
(2)
1.2
(2)
1.3
(2)
1.4
(2)
1.5
(2)
1.6
(2)
1.7
(2)
1.8
(2)
1.9
(2)
[18]
QUESTION 2
2
Brings buyers and sellers together .
Allocates resources .
Allows prices and quantities to be negotiated .
[6]
QUESTION 3
3
Worked answer
3.1
Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost
Total Cost = 250 + 500
Total Cost = 750
3.2
Average Costs = Total Costs / Quantity
Average Costs = 750 / 15
Average Costs = 50
3.3
Average Variable Costs = Variable Costs / Quantity
Average Variable Costs = 500 / 15
Average Variable Costs = 33.3
3.4
Marginal Costs = change in Total costs / change in Quantity
Marginal Costs = (550 350) / (30 25)
Marginal Costs = 200 / 5
Marginal Costs = 40
16
[16]
Economics Tests.pdf 17 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 4
4
Any THREE of the following:
A single supplier ()
Products are not homogenous (similar / identical) ()
The seller is protected from competition no free competition ()
Companies are given the rights to be the only operators in a country ()
[6]
QUESTION 5
5.1
indirect
(2)
5.2
subsidies
(2)
5.3
subsidies
(2)
5.4
below
(2)
[8]
17
Economics Tests.pdf 18 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 6
6
Mark allocation for diagram
The above diagram shows how imposing an indirect tax shifts the supply curve up and to
the left (in effect decreasing the supply of the good ). This leads to a decrease in
the quantity of the good being produced and an increase in the market price .
[16]
[TOTAL: 70 marks]
18
Economics Tests.pdf 19 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST THREE MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
(2)
1.2
(2)
1.3
(2)
1.4
(2)
1.5
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 2
2.1
(2)
2.2
(2)
2.3
(2)
2.4
(2)
2.5
(2)
2.6
(2)
2.7
(2)
2.8
(2)
[16]
QUESTION 3
3
Any THREE of the following:
The country was inhabited by the Khoi-San and African tribes ().
Subsistence farming was the norm although some barter took place (using skins,
livestock, food, pottery, tobacco and metal objects) ().
Ivory and gold were traded (sometimes with individuals from other countries) ().
In 1652, a Dutch shipping company (the VOC), established a halfway port and
refreshment station in the Cape ().
19
[6]
Economics Tests.pdf 20 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 4
4
Any ONE of the following:
cattle ()
sheep ()
goats ()
[2]
indigenous grain ()
QUESTION 5
5.1
increase
(2)
5.2
natural growth rate
(2)
5.3
an increase
(2)
5.4
increases
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 6
6.1
increased
(2)
6.2
economically-active
(2)
6.3
an increase
(2)
6.4
an increase
(2)
[8]
[TOTAL: 50 marks]
20
Economics Tests.pdf 21 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
Grade 10
ECONOMICS
PRACTICE TEST FOUR MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
(2)
1.2
(2)
1.3
(2)
[8]
QUESTION 2
2.1
(2)
2.2
(2)
2.3
(2)
2.4
(2)
2.5
(2)
2.6
(2)
2.7
(2)
2.8
(2)
[16]
QUESTION 3
3
In South Africa, the following factors contribute to unemployment:
Declining demand for consumer goods, which leads to a decreased demand for
labour
Increased mechanisation and a shift to capital-intensive production techniques ,
which leads to a decrease in the demand for labour
Trade unions which drive up wage rates , and decreases the demand for
labour
An oversupply of skilled labour
Rapid population growth
A lack of investment , which results in a lack of new business opportunities and
employment opportunities
21
[16]
Economics Tests.pdf 22 7/2/2011 4:09:26 PM
QUESTION 4
4
Labour Relations Act
Basic Conditions of Employment Act
Occupational Health and Safety Act
[6]
QUESTION 5
5
The Labour Relations Act sets out to protect the rights of individual workers by
providing a mechanism for collective bargaining and the resolution of disputes .
This Act seeks to promote consultation in the workplace . This is different from the
Basic Conditions of Employment Act, which also seeks to promote individual workers
rights , but does so by stipulating certain standards and limits to protect
workers, for example, from working long hours or being paid unfairly . Both Acts
prevent exploitation, but in different ways .
[TOTAL: 60 marks]
22
[16]
Maskew Miller Longman (Pty) Ltd
Forest Drive, Pinelands, Cape Town
Ofces in Johannesburg, Durban, King Williams Town, Polokwane, Bloemfontein, representatives in
Makeng and companies throughout southern and central Africa.
website: www.mml.co.za
Maskew Miller Longman (Pty) Ltd 2011
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of the copyright holder.
Every effort has been made to trace the copyright holders of material produced in this title. We would
like to apologise for any infringement of copyright so caused, and copyright holders are requested to
contact the publishers in order to rectify the matter.
First published in 2011
ISBN 978-0-636-12975-7
www.mml.co.za
Focus_Exam Practice Book_COVER_Economics_Gr10.indd 1
2011/09/02 3:17 PM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- IGCSE ECONOMICS: Factor PaymentsDocumento2 pagineIGCSE ECONOMICS: Factor Paymentskbafna28100% (1)
- Mathsclinic Smartprep GR10 Eng V1.1Documento36 pagineMathsclinic Smartprep GR10 Eng V1.1Ebrahim Rayned100% (1)
- Unit 1 Business Activity WorksheetDocumento3 pagineUnit 1 Business Activity WorksheetLeticia Corbellini100% (1)
- Examiner Tips For IGCSE Economics 0455 FINALDocumento4 pagineExaminer Tips For IGCSE Economics 0455 FINALbookaholic404890% (10)
- Price Elasticity of Supply ExplainedDocumento8 paginePrice Elasticity of Supply Explained梁楚欣100% (1)
- Elasticity WorksheetDocumento4 pagineElasticity WorksheetHamza Bin ZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Business Worksheet (Paper 1) - Chapter 6 To 9Documento6 pagineA Level Business Worksheet (Paper 1) - Chapter 6 To 9Phuong DaoNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE ECONOMICS: Spending, Saving and BorrowingDocumento2 pagineIGCSE ECONOMICS: Spending, Saving and Borrowingkbafna28100% (3)
- Igcse Economics NotesDocumento6 pagineIgcse Economics NotesMunni Chetan0% (1)
- Business Studies - Objective Part - Section 1Documento64 pagineBusiness Studies - Objective Part - Section 1Edu TainmentNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Business NotesDocumento119 pagineAS Business NotesLuke Smith81% (27)
- A Level Business Studies Question BankDocumento3 pagineA Level Business Studies Question Bankoalevels100% (10)
- Microeconomics Igcse EconomicsDocumento212 pagineMicroeconomics Igcse Economicspranav100% (2)
- O Level Economics SyllabusDocumento17 pagineO Level Economics SyllabusMehreen KhurshidNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Documento32 pagine100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Hassan Asghar100% (4)
- Forms of Ownership Guide for Grades 10 & 12Documento32 pagineForms of Ownership Guide for Grades 10 & 12shreeshail_mp6009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Economics For O.LevelsDocumento86 pagineSimple Economics For O.LevelsthugnatureNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Economics Exam QuestionsDocumento1 paginaIGCSE Economics Exam QuestionsEllie HousenNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Studies HomeworkDocumento10 pagineBusiness Studies Homeworkapi-248004746100% (1)
- Caps SP Technology GR 7-9Documento88 pagineCaps SP Technology GR 7-9Mmapontsho Tshabalala100% (8)
- 2.1 Economic Systems: Igcse /O Level EconomicsDocumento13 pagine2.1 Economic Systems: Igcse /O Level EconomicsJoe Amirtham0% (1)
- A'Level Ecos NotesDocumento342 pagineA'Level Ecos NotesBeckham T MaromoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge-Igcse & O-Level-Eco-WorkbookDocumento81 pagineCambridge-Igcse & O-Level-Eco-WorkbookEllie HousenNessuna valutazione finora
- CIE IGCSE Unit 3.3 - Workers - Occupations, Earnings and The Labour Market - Miss PatelDocumento19 pagineCIE IGCSE Unit 3.3 - Workers - Occupations, Earnings and The Labour Market - Miss PatelJingyao HanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ib Economics Review Questions MacroeconomicsDocumento6 pagineIb Economics Review Questions Macroeconomicsapi-196719233Nessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Economics WB Answers Screen Optimised PDFsDocumento40 pagineIGCSE Economics WB Answers Screen Optimised PDFscthiruvazhmarbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Economic ProblemDocumento21 pagineBasic Economic ProblemMamta LalwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Economics Synoptic Revision Mats Vol1 SampleDocumento6 pagineA Level Economics Synoptic Revision Mats Vol1 SampleanusuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Bs NotesDocumento19 pagineO Level Bs NotesKush GurbaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme of Work S4.S5.S6 ECONOMICSDocumento41 pagineScheme of Work S4.S5.S6 ECONOMICSNdayishimiye Raymond83% (6)
- Mankiw Econ Class Lecture Slides & Test Bank Ch 1-10Documento1 paginaMankiw Econ Class Lecture Slides & Test Bank Ch 1-10Anonymous 7CxwuBUJz33% (29)
- Business Studies QuizDocumento2 pagineBusiness Studies QuizSamanthaYau100% (3)
- Chapter 6 Motivating WorkersDocumento5 pagineChapter 6 Motivating WorkersSamanthaYau100% (2)
- Principles of EconomicsDocumento27 paginePrinciples of EconomicsAqil Siddiqui100% (2)
- Demand and Elasticity WorksheetDocumento4 pagineDemand and Elasticity Worksheethuxayn100% (1)
- Accounting Grade 11 Term 3 Week 4 - 2020Documento6 pagineAccounting Grade 11 Term 3 Week 4 - 2020adriana espinoza de los monterosNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE ECONOMICS: Basic Economic ProblemDocumento2 pagineIGCSE ECONOMICS: Basic Economic Problemkbafna2883% (12)
- Essay PlanDocumento5 pagineEssay PlanΜιχάλης Θεοχαρόπουλος100% (2)
- IGCSE Economics: Introduction to EconomicsDocumento16 pagineIGCSE Economics: Introduction to EconomicssilNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Sample QuestionsDocumento11 pagineIntroduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Sample Questionsecobalas7100% (1)
- Economics MYP - Subject BriefDocumento1 paginaEconomics MYP - Subject BriefJulius DennisNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel As Unit 1Documento202 pagineEdexcel As Unit 1rishamsaif100% (1)
- PPC-Explaining Micro & Macro IssuesDocumento9 paginePPC-Explaining Micro & Macro IssuesChing Yi0% (2)
- Incomplete Record - QuestionDocumento4 pagineIncomplete Record - QuestionChandran Pachapan100% (3)
- Ten Ways To Improve Your Evaluation Skills and Marks For A2 EconomicsDocumento9 pagineTen Ways To Improve Your Evaluation Skills and Marks For A2 EconomicsJim Riley86% (7)
- Complete Business Studies For Cambridge IGCSEDocumento2 pagineComplete Business Studies For Cambridge IGCSEEllenZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Econ 101Documento164 pagineMicroeconomics Econ 101Alphá Kídd100% (1)
- IGCSE Economics GuideDocumento44 pagineIGCSE Economics GuideWayne Wy40% (5)
- Business Studies IGCSE - Unit 1. Chapter 3. Forms of Business Org PDFDocumento8 pagineBusiness Studies IGCSE - Unit 1. Chapter 3. Forms of Business Org PDFNadine Salah El-DinNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Economics Exam Chapters 1Documento7 pagineAP Economics Exam Chapters 1Dani WashingtonNessuna valutazione finora
- 55 IB Economics Worksheets Pack SSISe551871-UnlockedDocumento13 pagine55 IB Economics Worksheets Pack SSISe551871-UnlockedJack Cariaso100% (2)
- Economics Revision Notes For OlevelDocumento114 pagineEconomics Revision Notes For OlevelJeelan Haroon Jay Jay76% (17)
- IGCSE Accounting All Mark Scheme 2002 Summer 2018Documento1.453 pagineIGCSE Accounting All Mark Scheme 2002 Summer 2018Muhammad Arif100% (2)
- Commerce NotesDocumento73 pagineCommerce NotesAgrippa MungaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Economics Fall 2002 Review #3Documento18 paginePrinciples of Economics Fall 2002 Review #3Kalen CarneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam - 2019 SpecialDocumento12 pagineFinal Exam - 2019 SpecialLiz zzzNessuna valutazione finora
- CAT 2-Fundamentals of EconomicsDocumento7 pagineCAT 2-Fundamentals of Economicstrevor.gatuthaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Fall FinalsDocumento12 pagine2019 Fall FinalsmeganyaptanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam1 Review QuestionsDocumento3 pagineExam1 Review QuestionsOpen ThedorNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics Midterm Exam KeyDocumento8 pagineMacroeconomics Midterm Exam Keyshush10Nessuna valutazione finora
- TextbookDocumento58 pagineTextbookMmapontsho Tshabalala0% (1)
- Economic Concepts Principles and Market Dynamics - With Track ChangesDocumento109 pagineEconomic Concepts Principles and Market Dynamics - With Track ChangesMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Impacts of Economic VulnerabilityDocumento2 pagineImpacts of Economic VulnerabilityMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Plans Summary of Grade 10 Annual Teaching Plan Term 1 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10Documento19 pagineTeaching Plans Summary of Grade 10 Annual Teaching Plan Term 1 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10Mmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Activity The Setting of EconomicsDocumento1 paginaClassroom Activity The Setting of EconomicsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Economic (Business) CyclesDocumento3 pagineCauses of Economic (Business) CyclesMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Setting of Economics Within The FieldDocumento1 paginaThe Setting of Economics Within The FieldMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Activity Human RightsDocumento1 paginaClassroom Activity Human RightsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Promotion or Violation of Human Rights and The EnvironmentDocumento2 paginePromotion or Violation of Human Rights and The EnvironmentMmapontsho Tshabalala100% (1)
- Changes in Economic GrowthDocumento6 pagineChanges in Economic GrowthMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocumento3 pagine6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesPradeep KurupNessuna valutazione finora
- Aggregate Supply and Aggregate DemandDocumento4 pagineAggregate Supply and Aggregate DemandMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Analysis of South Africa's National IncomeDocumento2 pagineAn Analysis of South Africa's National IncomeMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACTIVITY 1 Unpacking of EconomicsDocumento1 paginaACTIVITY 1 Unpacking of EconomicsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Economic ParticipantsDocumento2 pagineThe Economic ParticipantsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Processes, Production, Consumption, ExchangeDocumento3 pagineBasic Processes, Production, Consumption, ExchangeMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor Market and Production MarketDocumento43 pagineFactor Market and Production MarketMmapontsho Tshabalala100% (1)
- The Relation of Economics To Other SciencesDocumento1 paginaThe Relation of Economics To Other SciencesMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of EconomicsDocumento33 pagineMethods of EconomicsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Caps SP Technology GR 7-9Documento88 pagineCaps SP Technology GR 7-9Mmapontsho Tshabalala100% (8)
- WEEKLY Lesson Plan COMF 511Documento3 pagineWEEKLY Lesson Plan COMF 511Mmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Term 1 Circular Flow (Presentation)Documento5 pagineTerm 1 Circular Flow (Presentation)Mmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week5-6: Circular Flow & Quantitative ElementsDocumento4 pagineWeek5-6: Circular Flow & Quantitative ElementsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understand: Macroeconomics Microeconomics Economic Pursuits Economic IssuesDocumento2 pagineUnderstand: Macroeconomics Microeconomics Economic Pursuits Economic IssuesMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Term 2 Week 1-3:dynamic of MarketsDocumento17 pagineTerm 2 Week 1-3:dynamic of MarketsMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blog ActivitiesDocumento3 pagineBlog ActivitiesMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Term 1 Test Section ADocumento4 pagineTerm 1 Test Section AMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 7 - 8Documento6 pagineWeek 7 - 8Mmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan COMF 511 DAILYDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan COMF 511 DAILYMmapontsho TshabalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus Economics Grade 10 Exam Practice BookDocumento24 pagineFocus Economics Grade 10 Exam Practice BookMmapontsho Tshabalala100% (8)
- Chapter 5 Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocumento41 pagineChapter 5 Elasticity and Its ApplicationeiaNessuna valutazione finora
- First Things First (1964 & 2000)Documento5 pagineFirst Things First (1964 & 2000)MarinaCórdovaAlvésteguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ais FormsDocumento2 pagineAis FormsChris LampleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Charter: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Delivery SystemDocumento2 pagineProject Charter: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Delivery SystemcamanjarresvNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume - J.P. DubeyDocumento5 pagineResume - J.P. DubeyRanjana DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Innovation Policymakers in Vietnam GIPA Scoping StudyDocumento31 pagineUnderstanding Innovation Policymakers in Vietnam GIPA Scoping StudyChrist KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Structure of Accounting 1: Chapter OneDocumento15 pagineBasic Structure of Accounting 1: Chapter OneSeid KassawNessuna valutazione finora
- TTSL All India SiteDetailsDocumento28 pagineTTSL All India SiteDetailssavan anvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- SBLC Monetizing MOUDocumento9 pagineSBLC Monetizing MOUDinni Resa75% (4)
- Bartertrade - Io - WhitepaperDocumento41 pagineBartertrade - Io - WhitepaperRandall FlaggNessuna valutazione finora
- MM Elec 2Documento17 pagineMM Elec 2juliesa villarozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 10-3 Unit 1.4 Worksheet - Sales 2018-19 W - KEYDocumento8 pagineMath 10-3 Unit 1.4 Worksheet - Sales 2018-19 W - KEYBob SmynameNessuna valutazione finora
- General Motors Company S Marketing Mix 4Ps AnalysisDocumento4 pagineGeneral Motors Company S Marketing Mix 4Ps AnalysisSugandha DasNessuna valutazione finora
- RFP for AIIMS Guwahati Executing AgencyDocumento32 pagineRFP for AIIMS Guwahati Executing AgencyAmlan BiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Question: You Are An Antenna Engineer and You Are Asked To DesignDocumento1 paginaQuestion: You Are An Antenna Engineer and You Are Asked To DesignOscar GómezNessuna valutazione finora
- Request For Permanent WorkDocumento2 pagineRequest For Permanent WorkNirmal BandaraNessuna valutazione finora
- FM SMN 01 Memorandum of Agreement 1Documento5 pagineFM SMN 01 Memorandum of Agreement 1MineNessuna valutazione finora
- PRIA FAR - 016 Share-Based Payments (PFRS 2) Notes and SolutionDocumento4 paginePRIA FAR - 016 Share-Based Payments (PFRS 2) Notes and SolutionEnrique Hills RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- FDI Advantages DisadvantagesDocumento4 pagineFDI Advantages DisadvantagesRaja Ahsan TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Question AnswersDocumento2 pagineInterview Question AnswersSushilSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CosmoEye BrandbookDocumento104 pagineCosmoEye BrandbookJakub PiaszczyńskiNessuna valutazione finora
- 12) United States Patent: Funge Et ADocumento20 pagine12) United States Patent: Funge Et ANose NoloseNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circular Flow of Economic ActivityDocumento4 pagineThe Circular Flow of Economic ActivityMaria Trecia ExchaureNessuna valutazione finora
- MARINE SERRE-Roshni DhandabaniDocumento63 pagineMARINE SERRE-Roshni DhandabaniRoshniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lundstrom Sectional Bookcases - 1921Documento42 pagineLundstrom Sectional Bookcases - 1921Dan MarrNessuna valutazione finora
- (4 Marks) : Page 1 of 2Documento2 pagine(4 Marks) : Page 1 of 2Saiful IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- ST STDocumento2 pagineST STmukinduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Bobcat Compact Excavator E16 Operation Maintenance Manual 6989423Documento14 pagineBobcat Compact Excavator E16 Operation Maintenance Manual 6989423andrewshelton250683psa100% (67)
- DMS (Next Gen Dealer Management Systems DMS)Documento13 pagineDMS (Next Gen Dealer Management Systems DMS)Ulfa AkhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratika CVDocumento2 pagineRatika CVKushal BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora