Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
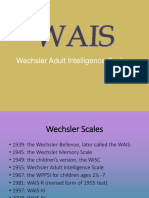
Wais-3 Interpretation Verbal
Caricato da
Incopelusas NoemaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Wais-3 Interpretation Verbal
Caricato da
Incopelusas NoemaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Interpreting the WAIS-III VERBAL SUBTESTS
Verbal Subtests
VOCABULARY
Student gives verbal
definition for words
presented in a list
and pronounced by
administrator
SIMILARITIES
Student tells how 2
items, presented
orally, are the same
(house and store
buildings)
ARITHMETIC
Progressively more
complex math word
problems are
presented orally.
Student calculates in
head and responds
orally.
TIMED TEST
Abilities Measured
Auditory perception understanding single words
Verbal comprehension and expression
Acquired knowledge
Degree of abstract thinking
Learning ability (Correlates most highly with academic success)
Long-term memory
Language development
Auditory perception understanding simple words in pairs
Verbal comprehension and expression
Fluid intelligence new problem solving abilities
Degree of abstract thinking
Distinguishing essential from nonessential details
Verbal reasoning
Categorical thinking
Intellectual flexibility ability to see new connections
Auditory perception of complex verbal items
Mental alertness Attention, focus, concentration
Working memory short-term auditory memory
Verbal comprehension
Acquired knowledge in math
Sequential processing
Processing speed working under time pressure
Ability to tolerate school activities
WAIS-III Interpretation-Verbal EDU.doc
Average Score = 10 in each subtest. Scores below 8 show significant deficits
J. Kirst based on Essentials of WAIS-III Assessment by Kaufman & Lichtenberger, 1999
Notes
Affected by cultural opportunities
Affected by English proficiency
Related to reading experience
Related to school learning
Low score indicates difficulty
understanding and/or defining
words; difficulty in settings
requiring verbal communication
Affected by overly concrete
thinking
Affected by limited language
experiences at home
Affected by English proficiency
Related to reading experience
Low score indicates difficulty
understanding relationships
between words or ideas
Affected by distractibility
Affected by test or math anxiety
Related to math experience
Low score indicates difficulty in
settings requiring student to listen
to and process detailed
information and/or difficulty with
basic math
3/5/07
Interpreting the WAIS-III VERBAL SUBTESTS
Verbal Subtests
INFORMATION
Student verbally
answers factual oral
questions (Who was
Charles Lindbergh?
On what continent is
Bolivia? How many
inches in a yard?)
COMPREHENSION
Student verbally
answers reasoning
questions presented
orally (Why should
some foods be
cooked? Why do
cities need garbage
collection? What
does the grass is
always greener on
the other side of the
fence mean?)
LETTER-NUMBER
SEQUENCING
Student hears lists
of letters & numbers,
reorders them, and
verbally repeats
(7-N-4-R becomes
4-7-N-R)
Abilities Measured
Auditory perception of complex verbal information
Verbal comprehension and expression
Acquired knowledge
Long-term memory
U.S. cultural knowledge
Range of general factual knowledge
Academic abilities
Alertness to environment Intellectual ambitiousness
Notes
Affected by cultural opportunities
Affected by English proficiency
Related to reading experience
Related to school learning
Affected by anxiety
Affected by acquired brain injuries
Low score indicates difficulty
recalling or expressing factual info
Auditory perception of complex verbal information
Verbal comprehension
Common sense
Understanding cause-effect
Acquired knowledge ability to evaluate & use past experience
Reasoning
Expression of thoughts and ideas
Social judgment social intelligence
Knowledge of conventional standards of behavior
Intellectual flexibility ability to verbalize reasons for common
events, ability to understand proverbs
Affected by cultural awareness
Shows development of
conscience or moral sense
Affected by overly concrete
thinking
Requires stable, emotionally
balanced attitude
Shows social-adaptive functioning
Low score indicates difficulty
understanding or responding
appropriately to everyday
situations requiring logic.
Auditory perception of simple words single letters & numbers
Working memory short-term auditory memory
Fluid intelligence ability to reorder information
Visualization
Sequential processing
Learning ability - Ability to develop new strategies on demand
Planning ability
Mental alertness Attention, focus, concentration
Frustration tolerance
Mental manipulation (reordering items before repeating)
Affected by distractibility
Affected by persistence giving
up
Affected by anxiety
Affected by acquired brain injuries
Low score indicates difficulty
attending to, processing, and/or
recalling isolated pieces of info
(i.e., taking orders in restaurant)
WAIS-III Interpretation-Verbal EDU.doc
Average Score = 10 in each subtest. Scores below 8 show significant deficits
J. Kirst based on Essentials of WAIS-III Assessment by Kaufman & Lichtenberger, 1999
3/5/07
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Wais 3 Interpretation PerformanceDocumento2 pagineWais 3 Interpretation PerformanceIncopelusas Noema100% (2)
- WISC IVInterpOutlineDocumento7 pagineWISC IVInterpOutlineUche AnekeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Interpretive Report For WISC IVDocumento14 pagine1 Interpretive Report For WISC IVdr rajesh AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Benton Visual Retention TestDocumento53 pagineBenton Visual Retention TestRin Sua100% (1)
- Key Words: Neuropsychological Evaluation, Standardized AssessmentDocumento20 pagineKey Words: Neuropsychological Evaluation, Standardized AssessmentRALUCA COSMINA BUDIANNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix A A.1: WAIS IV Interpretive Worksheet 1Documento40 pagineAppendix A A.1: WAIS IV Interpretive Worksheet 1ClinPsyNessuna valutazione finora
- WAIS IV in Forensic PsychologyDocumento17 pagineWAIS IV in Forensic Psychologyrupal arora100% (2)
- Unlocking The Mistery of WISC-IVDocumento49 pagineUnlocking The Mistery of WISC-IVClaudia SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Wais LoveDocumento13 pagineWais LoveRabia SajjadNessuna valutazione finora
- WISC-IV Subtest DescriptionsDocumento2 pagineWISC-IV Subtest DescriptionsPUÑOYLETRANessuna valutazione finora
- Wais RDocumento17 pagineWais Rmhrizvi_12100% (1)
- Administration and Scoring of Verbal Components of WaisDocumento13 pagineAdministration and Scoring of Verbal Components of WaisAli Haider0% (1)
- 5 Raven's Standard Progressive Matrices™ (SPM)Documento1 pagina5 Raven's Standard Progressive Matrices™ (SPM)VINEET GAIROLA100% (1)
- 16 PF Competency Report (Sample)Documento49 pagine16 PF Competency Report (Sample)Rory CharlestonNessuna valutazione finora
- WaisDocumento5 pagineWaisLeanne Moreno100% (1)
- Raven's Standard Progressive Matrices AssessmentDocumento2 pagineRaven's Standard Progressive Matrices AssessmentJomay Pardillo75% (4)
- Wais Workin Memory NumbersDocumento10 pagineWais Workin Memory Numberspola osamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Picture Arrengement WaisDocumento60 paginePicture Arrengement WaisAbshar ParamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Administration and Scoring of the WAIS-IV Intelligence TestDocumento11 pagineAdministration and Scoring of the WAIS-IV Intelligence Testrupal arora50% (2)
- WJ Wiat Ktea ComparisonDocumento5 pagineWJ Wiat Ktea ComparisonAirNessuna valutazione finora
- Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IIIDocumento24 pagineWechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IIIPriscila FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- WAIS IV BrochureDocumento6 pagineWAIS IV BrochureArda TessaNessuna valutazione finora
- WISC IV Handout PDFDocumento121 pagineWISC IV Handout PDFvaluat100% (1)
- WISC-IV Introductory HandoutDocumento14 pagineWISC-IV Introductory HandoutTarekNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample ReportDocumento12 pagineSample Reportapi-342059544100% (1)
- Benton VRT PDFDocumento134 pagineBenton VRT PDFabc123-1100% (1)
- WISC IV WIAT IIInterpretiveParentDocumento4 pagineWISC IV WIAT IIInterpretiveParentAmelia AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuropsychological AssessmentDocumento6 pagineNeuropsychological AssessmentAkhwand Saulat100% (1)
- The Wechsler Adult Intelligence ScaleDocumento8 pagineThe Wechsler Adult Intelligence ScaleRimsha AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Career Clusters Interest Survey Generates Personalized Career RecommendationsDocumento6 pagineCareer Clusters Interest Survey Generates Personalized Career RecommendationsSikandar AmanNessuna valutazione finora
- WAIS Lecture On Assessment ScoringDocumento17 pagineWAIS Lecture On Assessment ScoringYork Hong100% (3)
- Wiat-Ii ReportDocumento7 pagineWiat-Ii Reportapi-290668891Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wechsler Adult Intelligence ScalesDocumento20 pagineWechsler Adult Intelligence ScalesUkhtSameehNessuna valutazione finora
- WISC-III Testing Protocols ExplainedDocumento24 pagineWISC-III Testing Protocols ExplainedleonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Bookmatter IntellectualDisabilityDocumento22 pagine2013 Bookmatter IntellectualDisabilityPriyanka AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Tat - Scors ManualDocumento37 pagineTat - Scors ManualMikeFinn100% (1)
- Norms For The Stroop Color-Word Interference Test and The TowerDocumento17 pagineNorms For The Stroop Color-Word Interference Test and The Towerlaura4dapNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Interpretation of the WAIS-III and WMS-IIIDa EverandClinical Interpretation of the WAIS-III and WMS-IIIValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The H-T-P personality testDocumento10 pagineThe H-T-P personality testjonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Interpretive Report PDFDocumento28 pagineSample Interpretive Report PDFTakashi AokiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kwest Wais-IvDocumento2 pagineKwest Wais-Ivapi-464058787Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tat ReportDocumento14 pagineTat Reportmarriumemaan582Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wiat III ReportDocumento3 pagineWiat III ReportMaricris Cuadrado75% (4)
- Wechsler Memory Scale, Third Edition, India (Wms-Iii)Documento1 paginaWechsler Memory Scale, Third Edition, India (Wms-Iii)NANDHINI BNessuna valutazione finora
- WISC-IV 20adm ChecklistDocumento20 pagineWISC-IV 20adm ChecklistJay Sun100% (2)
- Wechsler Intelligence Scales: History and DevelopmentDocumento4 pagineWechsler Intelligence Scales: History and DevelopmentBhanu Mati100% (1)
- Wisc Report No IdentityDocumento10 pagineWisc Report No Identityapi-290117367Nessuna valutazione finora
- WAIS SUBTEST MATERIAL REFERENCE India PDFDocumento27 pagineWAIS SUBTEST MATERIAL REFERENCE India PDFVINEET GAIROLANessuna valutazione finora
- LD-Practice Guidelines - India 2011 PDFDocumento48 pagineLD-Practice Guidelines - India 2011 PDFnesumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test de Bender & KoppitzDocumento16 pagineTest de Bender & Koppitz4gen_7Nessuna valutazione finora
- WISCDocumento24 pagineWISCAhmad Irtaza AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Template Psychological Evaluation (Confidential) Name: Date of Birth: Chronological Age: Parents: Grade: Date of Assessment: Date of ReportDocumento6 pagineReport Template Psychological Evaluation (Confidential) Name: Date of Birth: Chronological Age: Parents: Grade: Date of Assessment: Date of ReportMarl Vincent Madronero100% (1)
- Lecture 15 - The Wechsler Intelligence ScalesDocumento42 pagineLecture 15 - The Wechsler Intelligence ScalesKresna Surya WNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of TAT and Other Storytelling AssessmentsDa EverandEssentials of TAT and Other Storytelling AssessmentsNessuna valutazione finora
- WISC-IV Advanced Clinical InterpretationDa EverandWISC-IV Advanced Clinical InterpretationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Essentials of Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (SB5) AssessmentDa EverandEssentials of Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (SB5) AssessmentValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- HCPC Course Information FormDocumento8 pagineHCPC Course Information FormKamal JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- School Monitoring & Evaluation Plan AdjustmentDocumento24 pagineSchool Monitoring & Evaluation Plan AdjustmentKlaris ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Coping with Stress and Maintaining Mental HealthDocumento5 pagineCoping with Stress and Maintaining Mental HealthMavelle FamorcanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocal Anatomy Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineVocal Anatomy Lesson Planapi-215912697Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 04 Test BankDocumento82 pagineChapter 04 Test Bankbiubiu BIUNessuna valutazione finora
- Sti CollegeDocumento9 pagineSti Collegejayson asencionNessuna valutazione finora
- Daina's ResumeDocumento1 paginaDaina's ResumeDaina CleekNessuna valutazione finora
- LS Academic Calendar SY2020-2021 As of Aug 15 2020Documento4 pagineLS Academic Calendar SY2020-2021 As of Aug 15 2020Karen F. SoNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance-Based AssessmentDocumento2 paginePerformance-Based AssessmentJingleNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2009 Nursing Practice 1Documento9 pagineJune 2009 Nursing Practice 1Karl Gabriel BonifacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng 327 (A Survey of Applied Linguistics)Documento6 pagineEng 327 (A Survey of Applied Linguistics)debbiebraham21Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Kirkova-Naskova JFL SecondlanguagepronetcDocumento19 pagine2019 Kirkova-Naskova JFL SecondlanguagepronetcLorena ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- HUMSS Grade 11 Weekly Home Learning PlanDocumento8 pagineHUMSS Grade 11 Weekly Home Learning PlanDaisy LabasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis Front of The Class Movie - Anita Dan Anitia - PBI 5ADocumento2 pagineAnalysis Front of The Class Movie - Anita Dan Anitia - PBI 5AAnitazu 10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Monitoring, Evaluation and Adjustment (SMEA) of Plans: Quarter 1Documento81 pagineMonitoring, Evaluation and Adjustment (SMEA) of Plans: Quarter 1Pevi VirtudazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asca Lesson Plan - Stress Management 2Documento4 pagineAsca Lesson Plan - Stress Management 2api-284032620Nessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON PLAN Blockbuster 1 - StorytimeDocumento4 pagineLESSON PLAN Blockbuster 1 - StorytimeRadu NanNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 36 automation interview questionsDocumento58 pagineTop 36 automation interview questionsHamelNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Expectations Class Expectations:: R. Palacios Cahsee Prep School Year 2008-2009Documento4 pagineCourse Expectations Class Expectations:: R. Palacios Cahsee Prep School Year 2008-2009Mr. PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Behavior Problems in The ClassroomDocumento2 pagineCommon Behavior Problems in The ClassroomJaycel Abrasado DaganganNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7Documento2 pagineModule 7ANGEL ROY LONGAKITNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational Learning Dimensions TheoryDocumento24 pagineOrganizational Learning Dimensions TheoryOana CaragațeNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 4th QRTRDocumento2 pagineDaily Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 4th QRTRJPades Point88% (16)
- CHAPTER 4 Teaching ProfessionDocumento25 pagineCHAPTER 4 Teaching ProfessionAldrin Cagnaan SatiniamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment BrochureDocumento2 pagineAssessment Brochureapi-453717811Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Generation Z Learns Better PDFDocumento11 pagineHow Generation Z Learns Better PDFJosh A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parables Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineParables Lesson PlanpghsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test 26Documento8 paginePractice Test 26Thu HiềnNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical ExpositionDocumento13 pagineAnalytical Expositionulfatun azizahNessuna valutazione finora
- School Hekasi Action Plan Sy 2014-2015Documento2 pagineSchool Hekasi Action Plan Sy 2014-2015Sherwin Dulay100% (1)