Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
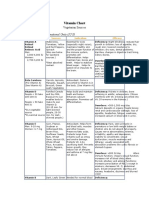
Vitamin/ Mineral Source Indication Efficacy Claims
Caricato da
halo35Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Vitamin/ Mineral Source Indication Efficacy Claims
Caricato da
halo35Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Vitamin/ Mineral
Source
Vitamin A, Retinol, Men: 3
Liver, fortified Milk (Retinol form see
000 IU, Women: 2 700 IU, , ,
below for Carotene sources.)
,,,
Indication
Efficacy
Claims
Eyes ( Night Vision), Skin, Hair,Bones, Teeth, Immune System,
Liver,Reproductive Organs, Pregnancy & Lactation
Deficiency: Night blindness; reduced hair growth in children; loss of
apetite; dry, rough skin; lowered resistance to infection; dry eyes.,
Overdose: Headaches; blurred vision; fatigue; diarrhea; irregular
periods; joint and bone pain; dry, cracked skin; rashes; loss of hair;
vomiting, liver damage,
Assists body in ridding
environmental pollutants
The antioxidant properties
of this nutrient may be a
factor in reducing the risk
of certain forms of cancer.
Alfalfa sprouts, Avocado, Bannana, Bee
Beta Carotene, (Pro-Vitamin pollen, Brocolli, Cayenne pepper, Carrots
Antioxidant. Converted to Vitamin A in the body. (See Vitamin A)
Yellow orange fruit, Garlic, Squash,
A), (See Vitamin A),
Broccoli, Green & Yellow Vegetables
Vitamin D, Men: 100 IU,
Women: 100 IU, , , ,
Vitamin E, Men: 9-10 mg,
Women: 6-7 mg, , , ,
Egg Yolk, Milk, Exposure to sun enables
body to make its own Vitamin D., Cod
liver Oil, Salmon, seeds, lemongrass,
dandelion root, alfalfa sprouts, avocado,
garlic, greens leafy
Corn or Cottonseed Oil, Butter, Brown
Rice, Soybean Oil, Vegetable oils such as
Corn, Cottonseed or Soybean, Nuts
Wheat Germ.
Green Vegetables, Liver, also made by
intestinal bacteria.
Vitamin K, None
established., Estimated at
0.03 mcg/kg,
Water Soluble Vitamins are
not stored in the body and
should therefore be
consumed daily.
Vitamin B1, Thiamine, Men: Sunflower Seeds, Pork, whole and
enriched Grains, dried Beans., kelp,
0.8 1.3 mg, Women: 0.8
dates, garlic, parsley, wild rice,
mg, , , , , ,
watercress, wheatgrass
Vitamin B2, Riboflavin, Men: Liver, Milk, Spinach, enriched Noodles,
Mushrooms., alfalfa sprouts, apple ,
1.3 1.6 mg, Women: 1.1
apricot, avocado, dates, figs, garlic, kelp,
mg, ,, , , ,
parsley, wild rice rosehips, seeds
Vitamin B3, Niacin, Men: 16- Mushrooms, Bran, Tuna, Chicken, Beef,
Peanuts, enriched Grains., rice brown,
23 mg, Women: 14-16 mg,
wild , alfalfa, almonds, apricots,
Niacin is converted to
chamomile, figs, garlic, nuts
niacinamide in the body.,
Abundant in animal tissues, whole grain
Vitamin B5, Pantothenic
cereals and legumes., alfalfa, almonds,
Acid, Men: 2.5 mg, Women:
avocado, broccoli, honey faw, oats,
2.5 mg,
oranges, peas, seeds, soybeans, walnuts
Animal protein foods, Spinach,, Broccoli,
Vitamin B6, Pyridoxine,
Bananas, alfalfa, bell pepper, beets,
Men: 1.8 mg, Women: 1.5
cantaloupe, greens, lemon, nuts,peas,
mg, , , , ,
sprouts, veggies green, , , , , , ,
Found almost exclusively in animal
Vitamin B12,
products, alfalfa, beans, dulse, garlic,
Cyanocobalamin, Men: 2
Korean, Siberian ginseng, klep, nuts,
mcg, Women: 2 mcg, ,
seeds,
Cheese, Egg, Yolk, Cauliflower, Peanut
Butter, alfalfa sprouts, banana , beans,
Biotin, 60 mcg, , , , ,
fruits, grains, nuts ,brown rice, seeds,
soybeans
Folic Acid (Folacin), Men:
180-220 mg, Women: 160190 mg, ,
Green, leafy vegetables, Orange Juice,
organ Meats, Sprouts.
Vitamin C, Ascorbic Acid,
Citrus Fruits, Strawberries, Broccoli,
Men: 40 mg, Women: 30 mg,
Green Peppers
,
Minerals in organic products
essential for body functions.
Teeth & Bones, Immunity, Enhances calcium & phosphorus absorption.,
Deficiency: Rickets in children; bone softening in adults; osteoporosis.,
Regulates mineral absorption, Stabilizes nervous system & heart, Normal Overdose: Calcium deposits in organs; fragile bones; renal and
blood clotting,
cardiovascular damage., , , , ,
Antioxidant. Helps form red blood cells, muscles and other tissues.
Preserves fatty acids., Reproduction, Lacation, RBC protection, Wounds,
Prevention blood clots,
Needed for normal blood clotting.
Deficiency: Rare, seen primarily in premature or low birth weight babies The antioxidant properties of
or children who do not absorb fat properly. Causes nerve abnormalities., this nutrient may be a factor
in reducing the risk of certain
Overdose: Unknown., , , , ,
forms of cancer
Deficiency: , Defective blood coagulation., Overdose: Jaundice in
infants.,
Carbohydrate metabolism, Muscle coordination., Proper nerve function.,
VIP consistent growth in children, Helps with Stress, Stabilizes appetite by
improving digestion and assimilation of nutrients, Fertility & Lactation,
Provides Energy, Mental attitude , focus & concentration,
Needed for metabolism of all foods and the release of energy to cells.
Essential to the functioning of Vitamin B6 and Niacin., RBCs & antibodies,
Vision, Skin, nails , hair, Stress,
Deficiency: , Anxiety; hysteria; depression; muscle cramps; loss of
appetite; in extreme cases beriberi (mostly in alcoholics)., Overdose: ,
Unknown, although excess of one B vitamin may cause deficiency of
others., , , , , ,
Needed in many enzymes that convert food to energy. Helps maintain a
healthy digestive tract and nervous system. In very large doses, lower
cholesterol (large doses should only be taken under the advice of a
physician).
Deficiency: , In extreme cases, pellagra, a disease characterized by
dermatitis, diarrhea and mouth sores., Overdose: , Hot flashes; ulcers;
liver disorders; high blood sugar and uric acid; cardiac arrythmias, ,
Deficiency: Cracks and sores around the mouth and nose; visual
problems., Overdose: See Vitamin B1, , , ,
Converts food to molecular forms. Needed to manufacture adrenal
hormones and chemicals that regulate nerve function., Wounds, Adrenals, Deficiency: , Unclear in humans., Overdose: , See Vitamin B,
Produced in the body by the beneficial bacteria in the intestines,
Protein metabolism and absorption, Carbohydrate metabolism., Helps
form red blood cells., Promotes nerve and brain function., Skin , Teeth,
muscles , nerves, Antibodies, RBCs, Balance of Sodium & Phosphorus,,
Balance of Sodium & Potassium,
Deficiency: , Anemia, irritability, patches of itchy, scaling skin;
convulsions., Overdose: , Nerve damage., , , , ,
Deficiency: , Pernicious anemia; nerve damage. (Note: Deficiency rare
Builds genetic material. Helps form red blood cells., Growth, Energy, RBC
except in strictvegetarians, the elderly or people with malabsorption
s, Concentration, memory , balance,
disorders.), Overdose: , See Vitamin B1., ,
Needed for metabolism of glucose and formation of certain fatty acids.
Essential for proper body chemistry., Formation RNA & DNA, Food into
energy, Prevent exhaustion, Muscle pain, Helps prevent baldness,
Deficiency: , Seborrhicdermatitis in infants. Rare in adults, but can be
induced by consuming large amounts of egg whites anorexia, nausea,
vomiting, dry scaly skin., Overdose: , See Vitamin B1, , ,
Essential for the manufacture of genetic material as well as protein
metabolism and red blood cell formation, Brain Function, RBCs,
Circulation,
Deficiency: Impaired cell division; anemia; diarrhea; gastrointestinal
upsets., Overdose: Convulsions in epileptics. May mask pernicious
anemia (see Vitamin B12 deficiency)., , ,
Antioxidant. Helps bind cells together and strengthens blood vessel walls.
Helps maintain healthy gums. Aids in the absorption of iron., Collagen,
Deficiency: Muscle weakness, bleeding gums; easy bruising. In extreme
Connective Tissue, Bones, Teeth,, Natural laxative, Formation of
cases, scurvy., Overdose: Loose bowls, , , ,, ,
adrenalin,, ,
Adequate amounts of this
nutrient in the firststage of
pregnancymay reduce
the risks of neural tube
birth defects., , , ,
The antioxidant properties of
this nutrient may be a factor
in reducing the risk of certain
forms of cancer. May reduce
the effects of the common
cold., ,
Calcium, Men: 800 1000
mg, Women: 700-800 mg, ,
Milk, Yogurt, Cheese, Sardines, Broccoli, Bones & Teeth, Muscle & Nerve Function, Blood Clotting, Activates
Turnip Greens.
enzymes needed to convert food to energy,
Chromium
Beets, cardamom, cloves, dulse, garlic,
kelp, mushrooms, wheatgrass, onions
Copper, 2-3 mg, , , , , ,
Liver and other organ Meats, Seafoods,
Nuts and Seeds., pomegranates, prunes,
green veggies , parslety , peas, raisins,
grains, almonds , avocado
Liver, lean Meats, Kidney beans,
enriched Bread, Raisins., alfalfa sprouts,
Iron , (Elemental), Men: 8-10 almonds, apricot, asparagus, beets,
cherries, dates, figs, grains, grteens,
mg, Women: 8-13 mg, , ,
lentils , parsley, peacans, pistachio nuts,
seeds, swiss chard, walnut, Note: Oxalic
acid in spinach hinders iron absorption., ,
Spinach, Beef Greens, Broccoli, Tofu,
Magnesium, Men: 230 250
Popcorn, Cashews, Wheat Bran,
mg, Women: 200 210 mg, ,
coconut, dates, figs, beets, avocado,
,,,,,,
honey raw,
Tea, whole Grains and Cereal products
are the richest dietary sources. Adequate
amounts are found in Fruits and
Vegetables.
The concentration in food varies
depending on the environment in which
Molybdenum, 0.15-0.3 mg, , the food was grown. Milk, Beans, Breads
and Cereals contribute the highest
amounts.
Phosphorus, Men: 1000 mg, Chicken Breast, Milk, Lentils, Egg Yolks,
Nuts, Cheese
Women: 850 mg (3-6 g),
Manganese, 2-5 mg, , ,
Potassium, Men: 40-80
mmol, Women: 40-80 mmol
(3-6 g),
Selenium, 0.05-0.2 mg, ,
Peanuts, Bananas, Orange Juice, Green
Beans, Mushrooms, Oranges, Broccoli,
Sunflower Seeds.
Adequate amounts are found in Seafood,
Kidney, Liver and other meats. Grains
Sodium
Zinc, Men: 12 mg, Women:
9 mg, ,
Oysters, Shrimp, Crab, Beef, Turkey,
whole Grains, Peanuts, Beans.
Glucose to Energy, Metabolism of amino acids ( building blocks of
proteins) and fats, ,
Proteins involved in growth, Nerve function, Energy release, Enzymes for
Iron metabolism ( ceruplasmin ( ferroxidase I) and ferroxidase II),
Antioxidant, Regulation of gene expression, Component of
severalenzymes, including on needed to make skin, hair and other
pigments. Stimulates iron absorption. Needed to make red blood cells,
connective tissue and nerve fibres.,
Essential for making hemoglobin, the red substance in blood that carries
oxygen to body cells, Most iron is stored in bone marrow that makes blood
cells, If there is not enough in the body , it goes to the bone marrow
reserves. If this iron stored in the bone marrow is low, RBCs dont form
properly, they are smaller than usual ( microcytosis) and fewer, , , ,
Activates enzymes needed to release energy in body. Needed by cells for
genetic material and bone growth., Low calcium, Low serum potassium,
Retention of sodium, Low circulating levels of parathyroid hormone,
Muscular tremors, spasms, Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, personality
changes, Alkalinity, Lung & Brain Function, Aids digestion,
Deficiency: Muscle cramps, Brain function, Rickets in children;
osteomalacia (soft bones) and osteoporosis in adults., Overdose:
Constipation, Kidney Stones, calcium deposits in body tissues. Hinders
absorption of iron and other minerals., , ,
Deficiency: Glucose intolerance or insulin resistance hyperglycemia,
Raised serum lipids & weight changes, Overdose: Hinders bodys
absorption of calcium.,
Minerals in organic products
essential for body functions.
Deficiency: , Anemia that is unresponsive to iron therapy but corrected
by copper, Low WBCs thus lower immunity, Rare in adults. Infants may
develop a type of anemia marked by abnormal development of bones,
nerve tissue and lungs., Overdose: , Liver disease; vomiting; diarrhea, ,
Deficiency: , Skin pallor; weakness; fatigue; headaches; shortness of
breath, difficulty concentrating, brittle nails, cracked lips , Overdose: ,
Constipation, Type II diabetes ( J of A Medical Assn), Toxic buildup in
liver and in rare instances the heart,
Deficiency: Nausea, irritability, muscle weakness; twitching; cramps,
cardiac arrhythmias., Overdose: Nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure,
nervous system disorders., Warning:Overdose can be fatal to people
with kidney disease., , , , , , , ,
Deficiency: , Impaired growth, reproduction, skeletal system, glucose
tendon and bone structure., Wound healing, Metabolism of carbohydrates, tolerance, altered carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, Overdose: Caution
Antioxidant
amino acids & cholesterol, Thyroid hormones,
may be toxic at high doses Generally results from inhalation of
manganese containing dust or fumes, not dietary ingestion., ,
Component of enzymes needed in metabolism. Helps regulate iron
storage.
Deficiency: Unknown in humans., Overdose: , Gout-like joint pain.,
With calcium builds bones and teeth. Needed for metabolism, body
chemistry, nerve and muscle function
Deficiency: (Rare) Weakness; bone pain; Anorexia., Overdose: Hinders
bodys absorption of calcium., ,
Helps maintain regular fluid balance. Needed for nerve and muscle
function.
Deficiency: Nausea, anorexia, muscle weakness, irritability. (Occurs
most often in persons with prolonged diarrhea.), Overdose: , Rare.,
Antioxidant. Interacts with Vitamin E to prevent breakdown of fats and
body chemicals
Acid neutralizer, Proper fx of muscles and nerves, Prevents clotting,
Enhances digestion,
Necessary element in more than 100 enzymes that are essential to
digestion and metabolism
Deficiency: Unknown in humans., Overdose: , Finger nail changes, hair
loss,
Deficiency: , Maybe related to low blood pressure, Overdose: , May
elevate blood pressure,
Deficiency: , Slow healing of wounds; loss of taste; retarded growth and
delayed sexual development in children., Overdose: , Nausea, vomiting;
diarrhea; abdominal pain; gastric bleeding,
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MOST Assign1 VitaminsDocumento6 pagineMOST Assign1 VitaminsbubblingbrookNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocumento6 pagineVitamin and Mineral Chartsellitt ngNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and Minerals ChartDocumento4 pagineVitamins and Minerals ChartAhwen 'ahwenism'100% (2)
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocumento4 pagineVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel KairupanNessuna valutazione finora
- MCHN Week 1november-18Documento46 pagineMCHN Week 1november-18cyrilperry1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin ChartDocumento5 pagineVitamin ChartHimNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and Minerals READINGDocumento5 pagineVitamins and Minerals READINGXimena Lucia Grandez BreñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and minerals - essential nutrientsDocumento3 pagineVitamins and minerals - essential nutrientsAsha ShanthakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Vitamins ?Documento91 pagineWhat Are Vitamins ?muhammad amjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 6 VITAMINSDocumento36 pagineTopic 6 VITAMINSnaem nadzriNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins & Minerals Chart: Functions, Food Sources & RDADocumento6 pagineVitamins & Minerals Chart: Functions, Food Sources & RDAfarhanyazdaniNessuna valutazione finora
- L PDFDocumento51 pagineL PDFMs RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento4 pagineVitaminsHemanth KokaNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento18 pagineVitaminshitesh_tilala100% (1)
- Vitamins & Supplements: Vitamins and Their Functions and SourcesDocumento18 pagineVitamins & Supplements: Vitamins and Their Functions and Sourceshitesh_tilalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity Management: UNIQUE PAPER CODE: 12555261Documento26 pagineObesity Management: UNIQUE PAPER CODE: 12555261Dhritiraj KalitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micronutrients 2020Documento44 pagineMicronutrients 2020Arsyi ZahwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hindi ch-1 Q-ADocumento9 pagineHindi ch-1 Q-AmahipalNessuna valutazione finora
- Alex Q. Carodan Jr. Maed-TemDocumento20 pagineAlex Q. Carodan Jr. Maed-TemMistekee MaramagNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins: Wendy Matte Stephanee Potts Jennifer Sulak Allie WalkerDocumento94 pagineVitamins: Wendy Matte Stephanee Potts Jennifer Sulak Allie WalkerEllenArominNessuna valutazione finora
- Do You Really Need a MultivitaminDocumento41 pagineDo You Really Need a MultivitaminEve TinirnacNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento95 pagineVitaminscaksonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition AssignmentDocumento17 pagineNutrition Assignmentabel_kayel100% (2)
- Vitamins A, B, C, D - Functions, Sources, DeficienciesDocumento18 pagineVitamins A, B, C, D - Functions, Sources, DeficienciesdedefreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- W10 Water, Vitamins & MineralsDocumento37 pagineW10 Water, Vitamins & MineralsHowell YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Mineral Chart - Nutrient Chart - Minerals in Fruits and Veget..Documento6 pagineMineral Chart - Nutrient Chart - Minerals in Fruits and Veget..travi95Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 & 3 - Overview of NutrientsDocumento84 pagineWeek 2 & 3 - Overview of Nutrientsامل الهوسهNessuna valutazione finora
- XII-Ch-2 - Sports and NutritionDocumento10 pagineXII-Ch-2 - Sports and NutritionSwati Sagarika NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Water, Vitamins & MineralsDocumento38 pagineWater, Vitamins & MineralsmalaitamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient - Daily Amount Needed Information Fruit Sources Vegetable Sources Nut SourcesDocumento10 pagineNutrient - Daily Amount Needed Information Fruit Sources Vegetable Sources Nut SourcesGopal PodderNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition: Presented By: Group 3Documento54 pagineNutrition: Presented By: Group 3Leona CentenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesDocumento4 pagineVitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesKevin Carl A. CorpuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Needed For Vision, Healthy Skin and Mucous Membranes, Bone and Tooth Growth, Immune System HealthDocumento3 pagineNeeded For Vision, Healthy Skin and Mucous Membranes, Bone and Tooth Growth, Immune System HealthMonhannah Calimbol Sumapal LimbutunganNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Documento5 pagineUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Documento5 pagineUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNessuna valutazione finora
- VITAMINS AND SUPPLEMENTS: AN OVERVIEWDocumento94 pagineVITAMINS AND SUPPLEMENTS: AN OVERVIEWFerdauza TupasNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E and KDocumento60 pagineFat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E and Kanisha2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- TengG WBfinalDocumento119 pagineTengG WBfinalGary TengNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Nutritional Requirements for ChildrenDocumento7 pagineDaily Nutritional Requirements for ChildrenDeepa SelvakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nu Tri en 1Documento8 pagineNu Tri en 1Nur AsiahNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento4 pagineVitaminsVikram SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: VitaminsDocumento3 pagineVitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: Vitaminsjenny gallegosNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins in Human BodyDocumento3 pagineVitamins in Human BodyJawad AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Daily Energy NeedsDocumento27 pagineThe Importance of a Balanced Diet for Daily Energy NeedsNigel Subhash BakkerNessuna valutazione finora
- MineralsDocumento2 pagineMineralsStacy WinterNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins & Vitamin Containing DrugsDocumento20 pagineVitamins & Vitamin Containing DrugsFarjana Islam Aovi20% (5)
- Vitamin and MineralDocumento41 pagineVitamin and MineralMADE ARY SARASMITANessuna valutazione finora
- The Food Cop: Vitamin and Mineral GuideDa EverandThe Food Cop: Vitamin and Mineral GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- A Functional Approach: Key Vitamins and Minerals for Bone, Blood and Antioxidant HealthDocumento15 pagineA Functional Approach: Key Vitamins and Minerals for Bone, Blood and Antioxidant HealthEunbi J. ChoNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Vitamins & NutrientsDocumento8 pagineEssential Vitamins & NutrientsPritamveer SirviNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins 1Documento1 paginaVitamins 1peru1975Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient - Daily Amount Needed Informati On Fruit Sources Vegetab Le Sources Nut/Grain Sources Meat/Pro Tein Sources Legum e Source SDocumento13 pagineNutrient - Daily Amount Needed Informati On Fruit Sources Vegetab Le Sources Nut/Grain Sources Meat/Pro Tein Sources Legum e Source SRaja DhanasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient - Estimated Amounts Needed: CalciumDocumento32 pagineNutrient - Estimated Amounts Needed: CalciumKashyap AddepallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrisi Utama & Kebutuhan: DR - Brain Gantoro, M.Gizi, SPGKDocumento100 pagineNutrisi Utama & Kebutuhan: DR - Brain Gantoro, M.Gizi, SPGKIntan RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 6Documento14 pagineCSO Olympiad Book For Class 6harnil trivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin and Mineral TABLEDocumento1 paginaVitamin and Mineral TABLEHibozoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrisi Utama & Kebutuhan MakananDocumento101 pagineNutrisi Utama & Kebutuhan MakananMochammad Fariz AmsalNessuna valutazione finora
- DeLaTorreB WB13Documento123 pagineDeLaTorreB WB13Bryan De La TorreNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-1 Essential NutrientsDocumento22 pagineUNIT-1 Essential Nutrientsblessy kurianNessuna valutazione finora
- List of + Positive WordsDocumento11 pagineList of + Positive Wordshalo35Nessuna valutazione finora
- VertigoDocumento2 pagineVertigohalo35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ford Sierra 0903-WD Wire DiagramDocumento47 pagineFord Sierra 0903-WD Wire Diagramhalo35100% (1)
- Curve: Mass (KG) Velo (KM/H) Radius (MT) Enter Values in White Boxes 10296.97Documento79 pagineCurve: Mass (KG) Velo (KM/H) Radius (MT) Enter Values in White Boxes 10296.97halo35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic AerodynamicsDocumento48 pagineBasic Aerodynamicshalo35100% (1)
- Digestive System PDFDocumento179 pagineDigestive System PDFBesmir NezhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Questions For Form Five Students That Can Lead For Their Excel in SPMDocumento14 pagineBiology Questions For Form Five Students That Can Lead For Their Excel in SPMZati Mohd RazibNessuna valutazione finora
- PANCREATIC JUICE FUNCTIONS AND REGULATIONDocumento28 paginePANCREATIC JUICE FUNCTIONS AND REGULATIONfdafasfa100% (1)
- Disease Prevention in Shrimp - Nutriad - Animal Feed AdditivesDocumento8 pagineDisease Prevention in Shrimp - Nutriad - Animal Feed AdditivesSuprapto NsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comprehensive Guide To Managing AutismDocumento89 pagineA Comprehensive Guide To Managing Autismapi-3696876100% (4)
- CSEC Biology - Digestion TestDocumento3 pagineCSEC Biology - Digestion TestTamicka Bonnick100% (4)
- In PDFDocumento106 pagineIn PDFTrinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Bloog Group AB+ Diet ChartDocumento3 pagineBloog Group AB+ Diet ChartChetan Sharma100% (9)
- Faecal AnalysisDocumento83 pagineFaecal AnalysisJoseph SabidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem1. revisionSLDocumento84 pagineSem1. revisionSLRawanMazen SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayurvedic Treatments and Natural Yogic RemediesDocumento72 pagineAyurvedic Treatments and Natural Yogic RemediesMario Garcia AnteloNessuna valutazione finora
- San Gabriel Science Exam ReviewDocumento3 pagineSan Gabriel Science Exam ReviewLester Eslava Orpilla82% (97)
- DR Clark Purity Kidney Cleanse DirectionsDocumento4 pagineDR Clark Purity Kidney Cleanse DirectionsrolickaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Science 3rd & 4th Quarter Exam - FinalDocumento6 pagine8 Science 3rd & 4th Quarter Exam - FinalAbe Estrada EnanoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Complete Guide to DigestionDocumento44 pagineThe Complete Guide to DigestionsunielgowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE STUDY of AGE With Moderate DehydrationDocumento24 pagineCASE STUDY of AGE With Moderate DehydrationAnne Monique Moran Ongjoco100% (4)
- Fish Physiology - 3Documento11 pagineFish Physiology - 3Anonymous 7Ih46sNessuna valutazione finora
- THOR3 14 Week ProgramDocumento28 pagineTHOR3 14 Week Programkmivanov100% (2)
- June 2019 QP - Paper 1B Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocumento32 pagineJune 2019 QP - Paper 1B Edexcel Biology IGCSEmantieNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade X: Introducing Yourself and OthersDocumento14 pagineGrade X: Introducing Yourself and Othersuswatun karimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hard Copy Sublingual FinalDocumento7 pagineHard Copy Sublingual FinalRaya Ibarra LumogdangNessuna valutazione finora
- Basti KarmukataDocumento31 pagineBasti KarmukataAkshataNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiments 11 15 NotesDocumento16 pagineExperiments 11 15 NotesJoshuel MontecilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Arvind Academy: Mode of NutritionDocumento20 pagineArvind Academy: Mode of Nutritionrohan thakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-7th To 8th GoingDocumento4 pagineClass-7th To 8th GoingManasNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Digestive System (5th)Documento14 pagine4 Digestive System (5th)Catherine JeaneNessuna valutazione finora
- National Vocationaltraining Institute: Testing DivisionDocumento64 pagineNational Vocationaltraining Institute: Testing DivisionAvoryi Juliana100% (1)
- Digestive System ExplainedDocumento4 pagineDigestive System Explainedjuswa coralNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural planning and environmental factors notesDocumento52 pagineAgricultural planning and environmental factors notesWarren564Nessuna valutazione finora