Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Valvular Heart Disease
Caricato da
Anonymous TVk12eX4Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Valvular Heart Disease
Caricato da
Anonymous TVk12eX4Copyright:
Formati disponibili
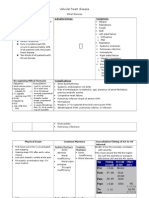
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
TRICUSPID REGURGITATION
Most common cause functional tricuspid regurgitation
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
In the absence of pHPN. TR is generally well tolerated
With pHPN cardiac output declines with manifestations of systemic venous
congestion
Neck veins are distended with prominent V waves
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Holosystolic murmur at the 4th ICS LPS is intensified by inspiration
- Carvallos sign
Prominent RV pulsations
Electrocardiogram
- usually nonspecific and RV enlargement
Radiologic findings
- enlargement of both RA & RV
Echocardiogram
- demonstrates RV dilatation and abnormalities in the tricuspid valve
- color flow Doppler estimates the severity and pulmonary artery pressure
TRICUSPID STENOSIS
generally rheumatic and more common in women
hemodynamic hallmark - diastolic pressure gradient bet the right atrium and the
ventricle
gradient of >4mmhg -systemic venous congestion
low cardiac output causes fatigue
elevated systemic venous pressure - hepatomegaly, ascitis, and anasarca
severity of these symptoms is out of proportion to the degree of dyspnea
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
giant s waves
slow Y descent
diastolic murmur heard best at the 4th ICS LPS is accentuated by
inspiration
Mueller maneuver
leg raising
amyl nitrite inhalation
squatting and isometric exercise
MANAGEMENT
TR in the absence of pulmonary hypertension usually does not require surgical
treatment
Annuloplasty - Carpentier ring or De-Vega annuloplasty
Valve replacement
PULMONIC VALVE STENOSIS
congenital - most common cause
degree of obstruction - principal determination of clinical severity
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
RV hypertrophy
prominent a wave in jugular venous pulse
systolic thrill along the upper left sternal border
ejection systolic murmur at the left upper sternal border
holosystolic murmur of TR
LABORATORY EXAMINATION
Electrocardiogram
tall right atrial P waves
Radiological findings
dilated right atrium without enlarged pulmonary artery
dilated superior vena cava
Echocardiography
diastolic doming of the leaftlets with thickening and restriction of motion
MANAGEMENT
intensive salt restriction and diuretic therapy
Surgical treatment - for severe TS with mean diastolic pressure gradient of >5mmHg
or TVA of <2 cm2
Electrocardiogram
RA D and RV hypertrophy
Chest Roentgenography
RA and RV enlargement
poststenotic dilatation of the left pulmonary artery - valvar pulmonic stenosis
dysplastic valve - thickened and immobile leaflets with hypoplasia of the
pulmonary valve annulus without post stenotic dilatation of the LPA
Cardiac catheterization
usual indication is to provide therapy for the lesion
MANAGEMENT
mild to moderate PS - generally have favorable course
percutaneous transluminal balloon valvuloplasty
initial procedure of choice
surgical relief of the obstruction
IE prophylaxis
PULMONARY REGURGITATION
dilatation of the valve ring secondary to pHPN
infective endocarditis
RV volume overload
Graham steel murmur - high-pitched, decrescendo diastolic blowing murmur along
the left sternal border
usually of little hemodynamic significance
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Aortic RegurgitationDocumento19 pagineAortic RegurgitationsunilgenextNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic RegurgitationDocumento12 pagineAortic RegurgitationSanjeet SahNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento10 pagineValvular Heart DiseaseEzyan SyaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment or Acute Renal Failure SymptomsDocumento6 pagineAssessment or Acute Renal Failure SymptomsRifa Aprillia CahyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvular Heart Disease. KulDocumento60 pagineValvular Heart Disease. KulIntan Kumalasari RambeNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart FailureDocumento20 pagineCongestive Heart FailurehuzaifahjusohNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Enzyme StudiesDocumento4 pagineCardiac Enzyme StudiesDara VinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Valve SurgeriesDocumento13 pagineValve SurgeriesShreeja SajitNessuna valutazione finora
- IHDDocumento34 pagineIHDElly Msi ProbolinggoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic EncephalopathyDocumento21 pagineHepatic EncephalopathyAnonymous n3qy0JdCgNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathDocumento6 pagineHeart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathSachin DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With DysrhythmiasDocumento19 pagineSelected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With Dysrhythmiaslanie_jecielNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocumento3 pagineCardiac CatheterizationAmir ZiadNessuna valutazione finora
- Defribrillation and CardioversionDocumento18 pagineDefribrillation and CardioversionLady Meshell CabugsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of The Patient With A Cardiac Mechanical DisorderDocumento8 pagineCare of The Patient With A Cardiac Mechanical DisorderthubtendrolmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial LinesDocumento9 pagineArterial LinesRei IrincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiomyopathy: Leonard Shaju Joisy AloorDocumento34 pagineCardiomyopathy: Leonard Shaju Joisy AloorJoisy AloorNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Stress TestingDocumento24 pagineCardiac Stress TestingRhoda Dela Torre ContrerasNessuna valutazione finora
- Intra Aortic Balloon PumpDocumento5 pagineIntra Aortic Balloon PumpZainal 'babeh' Arifin100% (1)
- Defibrillation and Cardioversion PDFDocumento12 pagineDefibrillation and Cardioversion PDFmadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesDocumento25 pagineCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesAlvin OmondiNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To The Cardiovascular Examination567 160120085414 PDFDocumento22 pagineApproach To The Cardiovascular Examination567 160120085414 PDFHNINNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 AHA Guidelines BradicardiaDocumento106 pagine2018 AHA Guidelines BradicardiaArio Richard NinaNessuna valutazione finora
- PacemakersDocumento19 paginePacemakersAswathy RCNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Catheterization and PCIDocumento75 pagineCardiac Catheterization and PCIJobelyn Tunay100% (1)
- Cardiac AsthmaDocumento12 pagineCardiac AsthmaNeupane KsabNessuna valutazione finora
- Inotropes, Excellent Article, With DosingDocumento47 pagineInotropes, Excellent Article, With DosingNavojit ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary AngiographyDocumento5 pagineCardiac Catheterization and Coronary Angiographyedem100% (1)
- Seminar On Cirrhosis of LiverDocumento9 pagineSeminar On Cirrhosis of Liverrufusprasanth_rachaproluNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationDocumento15 pagineAnaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationNaresh Dhawan100% (1)
- Cardiac EmergenciesDocumento21 pagineCardiac Emergenciesgus_lionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study On PacemakersDocumento6 pagineCase Study On PacemakersBalamuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento54 pagineValvular Heart DiseaseRommanah AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac ElectrophysiologyDocumento40 pagineCardiac Electrophysiologyashwinagrawal1995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aha Guidelines StemiDocumento94 pagineAha Guidelines StemiDika DekokNessuna valutazione finora
- EKG InterpretationDocumento63 pagineEKG InterpretationMiriam Cindy MathullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocumento97 pagineNormal Sinus RhythmNatasha LiberisNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationDocumento16 pagineCare of Patient With TPM Slide PresentationirzehronNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento12 pagineAcute Renal FailureRifa Aprillia CahyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionDocumento11 pagineDiagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionPauline Del MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocumento16 paginePulmonary Function TestsRashed ShatnawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitral StenosisDocumento17 pagineMitral Stenosispriyanka bhowmikNessuna valutazione finora
- Jugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionDocumento53 pagineJugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionJoshua JayakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Line Arterial LineDocumento13 pagineArterial Line Arterial LineLinamaria Lozano100% (1)
- Arrhythmias + Pharmacology: Mechanism of ArrhythmiaDocumento10 pagineArrhythmias + Pharmacology: Mechanism of ArrhythmiaJuliana Ching Joo LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Disorders: BY: Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MANDocumento65 pagineCardiovascular Disorders: BY: Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MANRellie Castro100% (1)
- IntroductionDocumento13 pagineIntroductionSiyara AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes, Symptoms, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis-A ReviewDocumento23 pagineCauses, Symptoms, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis-A ReviewBaharudin WahyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Pacemakers NewDocumento108 pagineCardiac Pacemakers NewAlif Fanharnita BrilianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio Vascular Assessment: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingDocumento46 pagineCardio Vascular Assessment: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingmeghanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The ABC's of Heart DiseaseDocumento78 pagineThe ABC's of Heart DiseaseChRist LumingkewasNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology of Heart in DetailDocumento101 paginePhysiology of Heart in Detailakanksha sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CycleDocumento12 pagineCardiac Cycleanupam manu100% (1)
- Stress TestDocumento2 pagineStress TestDavid GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDocumento8 pagineIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Documento28 pagineCardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Sparsh GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Types Heart Failure PDFDocumento10 pagineTypes Heart Failure PDFHannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementDocumento225 pagineAdult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementOsama Elsayed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisDocumento6 pagineBlood Gas Analysis For Bedside DiagnosisMuhamad Wirawan AdityoNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportDocumento3 pagineNURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportAkira PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionDocumento9 pagineViii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionChristian Karl B. LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- UDID What Medical Doctors May Need To KnowDocumento37 pagineUDID What Medical Doctors May Need To KnowdrhareeshNessuna valutazione finora
- DfahDocumento7 pagineDfahexpert 60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amenorrhea - Absence of Periods - ACOGDocumento7 pagineAmenorrhea - Absence of Periods - ACOGdroc ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- BioFire BrochureDocumento3 pagineBioFire BrochureETNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatrics, Geriatrics and Clinical MicrobiologyDocumento15 paginePediatrics, Geriatrics and Clinical MicrobiologySelvakumardxbNessuna valutazione finora
- PSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsDocumento8 paginePSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsAriadne MangondatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation SiliconomaDocumento24 pagineCase Presentation Siliconomaentgo8282Nessuna valutazione finora
- Speech DefectDocumento20 pagineSpeech DefectAbegail VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review 02Documento2 pagineReview 02Vicki KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan GiziDocumento11 pagineLaporan GiziEfrata MadridistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Health - Soap Note 5Documento3 pagineAdult Health - Soap Note 5api-546259691100% (3)
- The PERT Concept Q1 A Step-By-Step Approach To Managing Pulmonary EmbolismDocumento9 pagineThe PERT Concept Q1 A Step-By-Step Approach To Managing Pulmonary EmbolismntnquynhproNessuna valutazione finora
- Eczema, Immunity & The Skin Microbiome: Heidi H. Kong Dermatology Branch, CCR, NCIDocumento38 pagineEczema, Immunity & The Skin Microbiome: Heidi H. Kong Dermatology Branch, CCR, NCIrafdiaz2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutDocumento6 pagineGenetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutAlvin L. Rozier100% (3)
- Nurses ChartingDocumento2 pagineNurses ChartingdemethraNessuna valutazione finora
- Health AssessmentDocumento30 pagineHealth AssessmentWeng RamojalNessuna valutazione finora
- Panc Adenocarcinoma Recent Data and Perspective JR Delpero HPB Course 2022 V4-NuoveDocumento176 paginePanc Adenocarcinoma Recent Data and Perspective JR Delpero HPB Course 2022 V4-NuoveDiana MitreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Demystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggDocumento6 pagineDemystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggEddie CaptainNessuna valutazione finora
- Oncology NCLEX Questions Flashcards - QuizletDocumento50 pagineOncology NCLEX Questions Flashcards - QuizletGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANessuna valutazione finora
- BE FAST ED FormDocumento1 paginaBE FAST ED FormTHARHATA I JUHASANNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunologic and Allergic DiseaseDocumento49 pagineImmunologic and Allergic DiseaseFidz LiankoNessuna valutazione finora
- MINOR DISORDER IN PREGNANCY MaterialDocumento8 pagineMINOR DISORDER IN PREGNANCY MaterialAnuradha MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- WRTNG Assgnmnt Oral Health wk2Documento4 pagineWRTNG Assgnmnt Oral Health wk2bnvjNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat TeratogenikDocumento24 pagineObat TeratogenikHidayat BazeherNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal Paracentesis.Documento4 pagineAbdominal Paracentesis.Sukh Preet100% (1)
- Ovarian Cancer: A. IntroductionDocumento10 pagineOvarian Cancer: A. IntroductionBer AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- About Tattoos What Is A Tattoo?Documento2 pagineAbout Tattoos What Is A Tattoo?Çağatay SarıkayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yoga For Back PainDocumento8 pagineYoga For Back Paingiorgino100% (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDa EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (253)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (392)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (169)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyDa EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosDa Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (207)