Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
X X X X X X: IB Questionbank Maths SL 1
Caricato da
farahDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
X X X X X X: IB Questionbank Maths SL 1
Caricato da
farahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
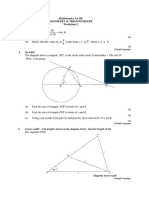
1.
(a)
d
1 d 2
ln x = ,
x = 2x
dx
x dx
(seen anywhere)
attempt to substitute into the quotient rule (do not accept product rule)
A1A1
M1
1
x 2 2 x ln x
x
x4
e.g.
correct manipulation that clearly leads to result
A1
x 2 x ln x x (1 2 ln x ) x 2 x ln x
,
, 4
x4
x4
x
x4
e.g.
g ( x ) =
(b)
1 2 ln x
x3
evidence of setting the derivative equal to zero
AG
N0
N2
(M1)
e.g. g(x) = 0, 1 2ln x = 0
ln x =
1
2
A1
x = e2
A1
[7]
2.
gradient of tangent = 8 (seen anywhere)
f(x) = 4kx3 (seen anywhere)
(A1)
A1
recognizing the gradient of the tangent is the derivative
(M1)
setting the derivative equal to 8
e.g. 4kx3 = 8, kx3 = 2
(A1)
substituting x = 1 (seen anywhere)
k=2
(M1)
A1
N4
[6]
3.
(a)
substituting (0, 13) into function
e.g. 13 = Ae0 + 3
13 = A + 3
A = 10
IB Questionbank Maths SL
M1
A1
AG
N0
(b)
substituting into f(15) = 3.49
e.g. 3.49 = 10e15k + 3, 0.049 = e15k
evidence of solving equation
e.g. sketch, using ln
ln0.049
accept
15
k = 0.201
(c)
f(x) = 10e0.201x + 3
f(x) = 10e0.201x 0.201 (= 2.01e0.201x)
(i)
A1
(M1)
A1
N2
A1A1A1
N3
Note: Award A1 for 10e0.201x, A1 for 0.201,
A1 for the derivative of 3 is zero.
(d)
(ii)
valid reason with reference to derivative
e.g. f(x) < 0, derivative always negative
R1
N1
(iii)
y=3
A1
N1
finding limits 3.8953, 8.6940 (seen anywhere)
evidence of integrating and subtracting functions
correct expression
e.g.
8.69
3.90
g ( x) f ( x)dx,
A1A1
(M1)
A1
8.69
3.90
[( x 2 + 12 x 24) (10e 0.201x + 3)]dx
area = 19.5
A2
N4
[16]
4.
(a)
(i)
1.15, 1.15
(ii)
recognizing that it occurs at P and Q
e.g. x = 1.15, x = 1.15
k = 1.13, k = 1.13
IB Questionbank Maths SL
A1A1
(M1)
A1A1
N3
N2
(b)
evidence of choosing the product rule
e.g. uv + vu
(M1)
derivative of x3 is 3x2
(A1)
2x
2
derivative of ln (4 x ) is 4 x
correct substitution
2x
x3
+ ln(4 x 2 ) 3 x 2
2
4x
e.g.
2x 4
+ 3x 2 ln(4 x 2 )
2
g(x) = 4 x
(A1)
A1
AG
N0
(c)
A1A1N2
(d)
w = 2.69, w < 0
A1A2
N2
[14]
5.
(a)
(b)
evidence of valid approach
e.g. f(x) = 0, graph
a = 1.73, b = 1.73 (a = 3 , b = 3 )
(M1)
A1A1
attempt to find max
e.g. setting f(x) = 0, graph
(M1)
c = 1.15 (accept (1.15, 1.13))
(c)
A1
attempt to substitute either limits or the function into formula
e.g. V =
V = 2.16
[ f ( x)]
c
IB Questionbank Maths SL
N3
]
2
dx, x ln(4 x ) ,
1.149...
N2
M1
y dx
A2
N2
(d)
valid approach recognizing 2 regions
e.g. finding 2 areas
(M1)
correct working
e.g.
1.73...
f ( x)dx +
(A1)
1.149...
f ( x)dx;
1.73...
f ( x)dx +
1.149...
f ( x)dx
area = 2.07 (accept 2.06)
A2
N3
[12]
6.
(a)
evidence of using the product rule
M1
f (x) = ex(1 x2) + ex(2x)
A1A1
x
Note: Award A1 for e (1 x ), A1 for e (2x).
f (x) = ex(1 2x x2)
AG
N0
(b)
y=0
A1
N1
(c)
at the local maximum or minimum point
(ex(1 2x x2) = 0)
f (x) = 0
(M1)
1 2x x2 = 0
(M1)
r = 2.41 s = 0.414
(d)
A1A1 N2N2
f(0) = 1
A1
gradient of the normal = 1
A1
evidence of substituting into an equation for a straight line
correct substitution
(M1)
A1
e.g. y 1 = 1(x 0), y 1 = x, y = x + 1
x+y=1
(e)
(i)
AG
intersection points at x = 0 and x = 1 (may be seen as the limits) (A1)
approach involving subtraction and integrals
fully correct expression
(e (1 x ) (1 x ) ) dx ,
1
e.g.
(ii)
N0
area R = 0.5
1
0
f ( x ) dx
(M1)
A2
N4
A1
N1
(1 x ) dx
0
[17]
IB Questionbank Maths SL
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Christina Latham-Koenig Clive Oxenden: Paul Seligson With Jane HudsonDocumento94 pagineChristina Latham-Koenig Clive Oxenden: Paul Seligson With Jane HudsonNatalia KonkolniakNessuna valutazione finora
- IB DerivativesDocumento66 pagineIB DerivativesCamila Velasco RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- (Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Documento146 pagine(Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Keya SanghviNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Transformations and VectorsDocumento3 pagineUT Transformations and Vectorsmaju mundurNessuna valutazione finora
- SL Linear Functions Paper 2Documento10 pagineSL Linear Functions Paper 2dfrtgfrtgfNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Ibsl QsDocumento7 pagineCalculus Ibsl QsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Review MSDocumento51 pagineCalculus Review MSAKILA PNessuna valutazione finora
- Math IB Revision CalcusDocumento56 pagineMath IB Revision Calcusmykiri79100% (1)
- 2 Exam Paper - IB SL MAth - Algebra and Functions - QuadraticsDocumento18 pagine2 Exam Paper - IB SL MAth - Algebra and Functions - QuadraticsYahya HaririNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Tukar Unit - PjiDocumento6 pagineLatihan Tukar Unit - PjisaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Name - Chapter 4 - Functions Review 1Documento4 pagineName - Chapter 4 - Functions Review 1Terence AnquandahNessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneous Equations 3 VariablesDocumento4 pagineSimultaneous Equations 3 VariablesCaroliny JetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Review Packet NovemberDocumento23 pagineCalculus Review Packet NovemberagwenexusNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations - Word Problems - 1step MCQ AllDocumento6 pagineEquations - Word Problems - 1step MCQ AllKevin HolcombNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFDocumento293 pagineRevision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFAnonymous yjLUF9gDTSNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 2 QsDocumento5 pagineCalculus 2 QsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision 9709 Paper 1Documento12 pagineRevision 9709 Paper 1api-25887606Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical InductionDocumento5 pagineMathematical InductionTU YUZE TU BILLY (4L27)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Further Trigonometry - QBDocumento12 pagineFurther Trigonometry - QBKYNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 15 Trigonomeertric FunctionsDocumento32 pagineModule 15 Trigonomeertric Functionsbakaraz7523027Nessuna valutazione finora
- 24 Transformation of Curves DONEDocumento31 pagine24 Transformation of Curves DONEABDULLAH SHAHZADNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Simultaneous Equations MajuDocumento3 pagine4 Simultaneous Equations Majujalrizal7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Implicit DifferentiationDocumento2 pagineImplicit DifferentiationAlicia TerrazasNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry & Trigonometry AA HL W1Documento3 pagineGeometry & Trigonometry AA HL W1anish.goel.4720Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 Fractions: Answer The QuestionsDocumento3 pagineGrade 7 Fractions: Answer The QuestionsDaniel TrencheskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation Optimization ProblemsDocumento49 pagineDifferentiation Optimization ProblemsGeorgette DNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformations - Mixed Questions: Image. RotationDocumento6 pagineTransformations - Mixed Questions: Image. RotationJoel SohNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 HSSolutionDocumento16 pagine2019 HSSolutionrizky rajendra anantadewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18 I Number Bases ENHANCEMENTDocumento14 pagineChapter 18 I Number Bases ENHANCEMENTadibahazNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Documento9 pagineProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions - 1 Mark Each: Maths Assignment Chapter 1 To 7Documento7 pagineMultiple Choice Questions - 1 Mark Each: Maths Assignment Chapter 1 To 7api-233604231Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2016-2018 VCAA - Matrices - SolutionsDocumento38 pagine2016-2018 VCAA - Matrices - SolutionsEmily LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambiguous TrianglesDocumento4 pagineAmbiguous TrianglesMaureen GalinganNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Documento32 pagineIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1ibrahim fadelNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex-Number FM 9231Documento37 pagineComplex-Number FM 9231BorisNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiplication WorksheetsDocumento10 pagineMultiplication WorksheetsVimala Devi100% (1)
- MATHS T :NUMBERS & SETSDocumento1 paginaMATHS T :NUMBERS & SETSlimsiewthiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 1 Expansion of BracketsDocumento1 paginaAlgebra 1 Expansion of BracketsPatriciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - Hyperbolic FunctionsDocumento15 pagine01 - Hyperbolic FunctionsshahulNessuna valutazione finora
- EER4 Notes PDFDocumento6 pagineEER4 Notes PDFChien Manh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With CalculatorDocumento28 pagine2nd Practice Test 2 Levels 6-8 - With Calculatorwong chee shengNessuna valutazione finora
- Created by Neevia Docuprinter LT V6.0: AlgebraDocumento3 pagineCreated by Neevia Docuprinter LT V6.0: AlgebraMaths Home Work 123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Solving With Quadratic EquationsDocumento12 pagineProblem Solving With Quadratic Equationselizagaming352Nessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On Remainder Theorm: Leading Institute For Banking, Railway, SSCDocumento2 pagineQuestions On Remainder Theorm: Leading Institute For Banking, Railway, SSCNivrutti TamboliNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On Ages.37Documento37 pagineProblems On Ages.37makwana86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Guide Aiming For Grade 5Documento81 pagineRevision Guide Aiming For Grade 5Khin Kyi Thar SweNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated Pure 2 Practice QuestionsDocumento20 pagineUpdated Pure 2 Practice QuestionsABDULLAH SHAHZADNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Math SequencesDocumento3 pagineIB Math SequencesSaumyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 2 PERAK SMKMethodist (Acs) Ipoh - MATHS QADocumento5 pagine2014 2 PERAK SMKMethodist (Acs) Ipoh - MATHS QASK100% (2)
- Primary-3 SIN 2017Documento12 paginePrimary-3 SIN 2017Thuy NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Math C4 PracticeDocumento53 pagineMath C4 PracticeMoustafa SohdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Documento29 pagineMathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Kevin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet Powers, Roots and Logarithms 2020-2021 PDFDocumento2 pagineWorksheet Powers, Roots and Logarithms 2020-2021 PDFDonkingLobusNessuna valutazione finora
- NSMTeacher'sResource Class7Documento223 pagineNSMTeacher'sResource Class7Nasir MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul 4 Simultaneous EquationsDocumento8 pagineModul 4 Simultaneous Equationshasnitajb100% (1)
- GCSE Maths - EquationsDocumento50 pagineGCSE Maths - EquationsPrinceShalomNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Paper 3 Practice MSDocumento47 pagineMath Paper 3 Practice MSRaahish KalariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math SL End of Year Review AnswersDocumento51 pagineMath SL End of Year Review AnswersAmanda Tan100% (2)
- X X X X Y: 1 Arcsin D DDocumento4 pagineX X X X Y: 1 Arcsin D Dapi-108235015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Ibsl MsDocumento12 pagineCalculus Ibsl MsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Globalization BMDocumento13 pagineGlobalization BMfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Ibsl QsDocumento7 pagineCalculus Ibsl QsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Ibsl MsDocumento12 pagineCalculus Ibsl MsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 2 QsDocumento5 pagineCalculus 2 QsfarahNessuna valutazione finora
- M1 PPT 1CDocumento35 pagineM1 PPT 1CMarvin CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- JavaScript Book Without Projects Code v1Documento84 pagineJavaScript Book Without Projects Code v1yeechienNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 1Documento10 pagineProject 1Mishal almusawiNessuna valutazione finora
- MQL 5Documento5.994 pagineMQL 5Andreas Von Schelzen100% (1)
- Gaming Theory - Study NotesDocumento51 pagineGaming Theory - Study Notesbarakkat72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Programming Module 1Documento3 pagineComputer Programming Module 1Jess VituallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bellman Ford Algorithm PDFDocumento15 pagineBellman Ford Algorithm PDFSayednowroz SayedyNessuna valutazione finora
- Image Caption Generator Using Deep Learning: Guided by Dr. Ch. Bindu Madhuri, M Tech, PH.DDocumento9 pagineImage Caption Generator Using Deep Learning: Guided by Dr. Ch. Bindu Madhuri, M Tech, PH.Dsuryavamsi kakaraNessuna valutazione finora
- OOP Assignment #5: FriendDocumento1 paginaOOP Assignment #5: FriendMohammed Fadhl AlbadwiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 ProgramsDocumento9 pagine11 ProgramsSushila KrishniaNessuna valutazione finora
- CA - Bharathiar University - Practical ScheduleDocumento1 paginaCA - Bharathiar University - Practical ScheduleOur educational ServiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Solving Agents: Blind and Informed SearchesDocumento23 pagineProblem Solving Agents: Blind and Informed SearchesJohnwilliam PNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Bike SystemDocumento62 pagineElectric Bike Systemshreestationery2016Nessuna valutazione finora
- HTTP - App - Utu.ac - in - Utuexmanagement - Exammsters - Syllabus - CS4015-Essentials of Advanced Object-Oriented ProgrammingDocumento2 pagineHTTP - App - Utu.ac - in - Utuexmanagement - Exammsters - Syllabus - CS4015-Essentials of Advanced Object-Oriented ProgrammingOmprakash ChandrakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Assignment of PythonDocumento21 pagineAnswer Assignment of PythonRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Support Vector Machines: Andrew W. Moore Professor School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon UniversityDocumento65 pagineSupport Vector Machines: Andrew W. Moore Professor School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon UniversityKyuudaimeNessuna valutazione finora
- C, Java, SQL 1Documento128 pagineC, Java, SQL 1dhana raj nakkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Documento305 pagineXii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Arun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- jModelTest 2 Manual v0.1.11Documento27 paginejModelTest 2 Manual v0.1.11mitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Informed Search and ExplorationDocumento6 pagine4 Informed Search and ExplorationI CETNessuna valutazione finora
- M.E. Cse (Ai&ml)Documento63 pagineM.E. Cse (Ai&ml)CBSE-Bhavana SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- RSLogix 500 - 12.00.01 (Released 12 - 2018)Documento6 pagineRSLogix 500 - 12.00.01 (Released 12 - 2018)Everton PodencianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Algorithms For Message-Passing Systems-1Documento517 pagineDistributed Algorithms For Message-Passing Systems-1Luis BelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Programming in JavaDocumento26 pagineFundamentals of Programming in JavanighatNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 2 Project (Max Area)Documento1 paginaCourse 2 Project (Max Area)mishi19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Few Shot Prompt Static AnalysisDocumento12 pagineFew Shot Prompt Static AnalysisAsif HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Set 2.3: One-Sided Limits: FX, FX and FX, IfDocumento3 pagineExercise Set 2.3: One-Sided Limits: FX, FX and FX, IfValentino Leo SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1221 Question PaperDocumento2 pagine1221 Question PaperSaurabh BodkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab3 String FunctionsDocumento7 pagineLab3 String FunctionsSarah SonaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen Java Programmer IDocumento116 pagineExamen Java Programmer IRicardo Bautista Silva0% (1)