Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Transistor As Auto Switch
Caricato da
Salmizam IzamDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Transistor As Auto Switch
Caricato da
Salmizam IzamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Teaching Apoproach Using Transistor As An Automatic
Switch.
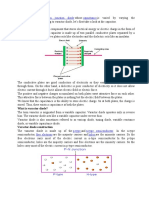
Common misconception and problem faced by students in understanding the
automatic switch transistor circuit :
( a ) When resistance of a resistor increases, current flows decreases. Thus the voltage
across the resistor decreases.
( b ) The whole transistor circuit looks complicated and difficult to understand.
Recommended Approach :
1. Start the topic by letting students explore the operation of the light controlled switch
transistor circuit using the Electronic Kits that are available in school.
2. Discuss the operation of the light controlled switch by asking the following questions
( I ) What happen to the bulb when the surrounding is dark( during the night ) ?
( ii ) What happen to the bulb when the surrounding is bright( during the day ) ?
( iii ) What will happen the the bulb if the light dependant resistor(LDR) and resistor
interchange position.
3. Teacher can start discussing the function of the LDR and fixed resistor R which are
connected in series to the battery as potential divider using the electrical circuit
below. Avoid starting discussion using the complete transistor circuit which appears to
be more complicated.
I
R
LDR
R1
R2
V1
6V
V2
Pose the following questions below to the students.
( I ) What can you say of the current I which flow through fixed resistor R and
LDR ?
( ii ) Using Ohms Law, state V1 and V2 in terms of I ,R1 and R2 respectively.
( iii) What is the total voltage for V1 + V2 ?
( iv ) If resistance of R2 is higher than R1 , compare V1 and V2
( v ) If V1 = 0.5 V, what is the voltage for V2 ?
( vi ) During the day, LDR is exposed to the sunlight, the resistance R2 decreases
and is much smaller compared to R1. Compare the voltage of V1 and V2 .
( vii ) Conversely, resistance of R2 becomes large when the surrounding is dark
during the night. What can you say of the voltage of V1 and V2 ?
4. Upon understanding the function of the LDR and fixed resistor R as potential divider
of the power source(battery). Teacher can proceed to discuss the operation of the
light controlled switch using the complete transistor circuit as shown below.
Fixed
V1
resistor
R1
Rb
6V
Ib
B
E
V2
LDR
R2
It is quite easy now for the students to understand how varying resistance R2 affects
the voltage V2 ( which is the base voltage ) and subsequently controls whether
transistor is on or off.
Students much have the prior knowledge that transistor is on when the base voltage V2 is
high enough to cause a small base current Ib flows in the base circuit. Transistor will
amplify the base current to produce a big collector current Ic to lights up the bulb M.
5. Pose the following questions to the students during discussion.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
During the day, what can you say of the resistance of LDR( R2 ) compared to R1 ?
Compare the base voltage V2 with V1 .
Is transistor On or Off ?
Repeat question ( a ) to ( c ) when the surrounding is dark.
What happen if the LDR and fixed resistor interchange position ?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basic ElectronicsDocumento18 pagineBasic ElectronicsZin Maung TunNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics: Investigatory ProjectDocumento22 paginePhysics: Investigatory ProjectabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsDa EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Ways To Test A Diode in CircuitDocumento13 pagineWays To Test A Diode in Circuitlangton mwalekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit / Project / Electronics: Electronics Project and Circuit For Students and Hobbyist. Learn by Circuit DiagramDocumento4 pagineCircuit / Project / Electronics: Electronics Project and Circuit For Students and Hobbyist. Learn by Circuit DiagramSyed Raheel AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ManualDocumento83 pagineLab ManualLucas EtienneNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide EE225 Ver1Documento6 pagineStudy Guide EE225 Ver1aonNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate: of THAKUR POLYTECHNIC (CODE:0522) Has Completed The Micro Project Satisfactorily inDocumento8 pagineCertificate: of THAKUR POLYTECHNIC (CODE:0522) Has Completed The Micro Project Satisfactorily inSaakshi MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Your Fall 2016 Motor Madness Winners: - Aaron Florian, Braden Mishler, Cole Nyffeler, Jesus Quintanilla-Cruz. - Who WinDocumento17 pagineYour Fall 2016 Motor Madness Winners: - Aaron Florian, Braden Mishler, Cole Nyffeler, Jesus Quintanilla-Cruz. - Who WinNathan KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Project InvestagtoryDocumento15 paginePhysics Project InvestagtoryprathameshrananwareNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 2Documento20 paginePresentation 2prithwikundu1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Project InvestagtoryDocumento15 paginePhysics Project InvestagtoryprathameshrananwareNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Street LightDocumento3 pagineAutomatic Street LightShilpa MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rohit Kumar XII B PHYSICSDocumento14 pagineRohit Kumar XII B PHYSICSRKNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel and Series. Sec 1Documento130 pagineParallel and Series. Sec 1Mahra AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Sensitive SwitchDocumento2 pagineLight Sensitive Switchvaibhav9428Nessuna valutazione finora
- Testing Diode CharacteristicsDocumento15 pagineTesting Diode CharacteristicsMacky Malupangue100% (1)
- Circuits Series and ParallelDocumento35 pagineCircuits Series and Parallelmike simsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento18 paginePhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMannNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento18 paginePhysics Projectabinav rajaNessuna valutazione finora
- LDR ProjectDocumento14 pagineLDR ProjectSaptak PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted by Aryan Patel Class XII ZDocumento21 pagineSubmitted by Aryan Patel Class XII Zaryan patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Assignment Questions for Class X PhysicsDocumento4 pagineElectricity Assignment Questions for Class X PhysicsPiyush YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Sensors ExDocumento6 pagineLight Sensors ExSalman AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics Solved Question BankDocumento6 pagineBasic Electronics Solved Question BankosamaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Islamic University Islamabad: Project ReportDocumento9 pagineInternational Islamic University Islamabad: Project ReportPow dowtowNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Street Light Controller Circuit Using Relays and LDRDocumento4 pagineAutomatic Street Light Controller Circuit Using Relays and LDRRavindra ParabNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangkaian Pembagi Tegangan Dan Arus: Voltage and Current Divider CircuitDocumento17 pagineRangkaian Pembagi Tegangan Dan Arus: Voltage and Current Divider Circuitali muhammad hanafiyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Street Light Control SystemDocumento10 pagineAutomatic Street Light Control SystemMahathir AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation Activity Explores LED and Zener Diode CharacteristicsDocumento8 pagineSimulation Activity Explores LED and Zener Diode CharacteristicsEmerson EspelaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS Investigatory ProjectDocumento14 paginePHYSICS Investigatory ProjectRKNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Light LuxmeterDocumento14 pagine1 Light LuxmeterHaga Ardian TariganNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring LDR Resistance with Light IntensityDocumento7 pagineMeasuring LDR Resistance with Light IntensityBlue JasmineNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment-2: Background InformationDocumento7 pagineExperiment-2: Background InformationJonmani KalitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment-2: Background InformationDocumento7 pagineExperiment-2: Background InformationMINH NGUYỄN THẾNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ElectronicsDocumento5 pagineBasic ElectronicsACAD PurposesNessuna valutazione finora
- SjhaDocumento40 pagineSjhamohit meshramNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Dependent ResistorDocumento9 pagineLight Dependent ResistorNaveen.G.SNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Circuit Basics ExplainedDocumento9 pagineDC Circuit Basics ExplainedtekellamerZ aka tekellamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptive Lighting System For AutomobilesDocumento30 pagineAdaptive Lighting System For AutomobilesDeepthi DsouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecd Lab 6Documento8 pagineEcd Lab 6Muhammad HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocumento9 paginePhysics Investigatory ProjectAdarsh P PradeepNessuna valutazione finora
- PIP Sorian0 SelfInductanceDocumento24 paginePIP Sorian0 SelfInductancetheronNessuna valutazione finora
- Clipper and Clamper Circuits: January 2012Documento23 pagineClipper and Clamper Circuits: January 2012Bus BusNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory Project On LDRDocumento22 paginePhysics Investigatory Project On LDRBabli SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoresistor, Transistor, and LED's: Prelab QuestionsDocumento14 paginePhotoresistor, Transistor, and LED's: Prelab QuestionsSubin UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- CH-7 Alternating CurrentDocumento90 pagineCH-7 Alternating CurrentAviralTNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Street Light ControllerDocumento4 pagineAutomatic Street Light ControllerMaha BuNessuna valutazione finora
- Applying Basic Electronics PrinciplesDocumento10 pagineApplying Basic Electronics PrinciplesJohn Edelbert Del MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Circuits Lab Possible Viva QuestionsDocumento18 pagineAnalog Circuits Lab Possible Viva Questionsarsp_0610198571% (14)
- Met 2Documento10 pagineMet 2Ářvíňď PřášáďNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation Activity Explores Zener Diode and LED FunctionalityDocumento8 pagineSimulation Activity Explores Zener Diode and LED FunctionalityGong BoNessuna valutazione finora
- LDR New Phy BDocumento21 pagineLDR New Phy BAnugrahan JonathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Night Lamp - PHPDocumento5 pagineAutomatic Night Lamp - PHPEmy Lou DellasNessuna valutazione finora
- Varactor Diode DefinitionDocumento6 pagineVaractor Diode DefinitionMohit BhavsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Blinking LED CircuitDocumento22 pagineBlinking LED Circuit1213 Vaibhav KothareNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSIGNMENTDocumento3 pagineASSIGNMENTElias NegashNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetism - Teacher's GuideDocumento47 pagineElectromagnetism - Teacher's GuideSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Law Topical TestDocumento2 pagineLinear Law Topical TestSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Differentiated Instruction Strategies and ExampDocumento24 pagine20 Differentiated Instruction Strategies and ExampSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Math 2012Documento2 pagineAdd Math 2012Salmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Box Problem DifferentiationDocumento3 pagineBox Problem DifferentiationSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 5 Unit 2Documento5 pagineLesson Plan 5 Unit 2nandhakumarmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra: Log Log LogDocumento1 paginaAlgebra: Log Log LogSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Physic's Paper 1 Form4-08Documento15 paginePhysic's Paper 1 Form4-08Salmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Math Form 4Documento2 pagineAdd Math Form 4Salmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionDocumento62 pagineSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionJanice Yizing91% (23)
- Add Maths F4 Pro 12012Documento2 pagineAdd Maths F4 Pro 12012Salmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- VECTORS AND MATRICESDocumento9 pagineVECTORS AND MATRICESksganNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation NotesDocumento13 pagineDifferentiation NotesMalaysiaBoleh96% (45)
- B L Ossoms Modul E The Science Ofsoapbubbles, Part1 B y Paola Rebus CoDocumento11 pagineB L Ossoms Modul E The Science Ofsoapbubbles, Part1 B y Paola Rebus CoSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability ImageDocumento18 pagineProbability ImageSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Law Practice 2: Solving Non-Linear Equations and Finding Gradients & InterceptsDocumento6 pagineLinear Law Practice 2: Solving Non-Linear Equations and Finding Gradients & InterceptsSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Mathematics Camp 2013 PDFDocumento12 pagineAdditional Mathematics Camp 2013 PDFSamsiah MustaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Law Practice Paper 2Documento4 pagineLinear Law Practice Paper 2Salmizam Izam100% (1)
- Differentiation NotesDocumento13 pagineDifferentiation NotesMalaysiaBoleh96% (45)
- Space Science GeneralDocumento9 pagineSpace Science GeneralSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 10 Physics Activities For Use in STEM Clubs: Stemclubs@brighton - Ac.ukDocumento1 paginaTop 10 Physics Activities For Use in STEM Clubs: Stemclubs@brighton - Ac.ukSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- STEP 1: Make Observations STEP 2: Come Up With A Question Based On ObservationsDocumento2 pagineSTEP 1: Make Observations STEP 2: Come Up With A Question Based On ObservationsSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Capture Penguin Coordinate Geo PDFDocumento1 paginaCapture Penguin Coordinate Geo PDFSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Build A Soda Straw Rocket: FactDocumento4 pagineBuild A Soda Straw Rocket: FactSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Clean Up The Money!: Players: 2 Materials: Game MatDocumento3 pagineClean Up The Money!: Players: 2 Materials: Game MatSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Capture Penguin Coordinate GeoDocumento1 paginaCapture Penguin Coordinate GeoSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Grab The CandyDocumento4 pagineGrab The CandySalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Aktiviti Coordinate GeometryDocumento9 pagineAktiviti Coordinate GeometrySalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressed PDFDocumento1 paginaPressed PDFSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- PressedDocumento1 paginaPressedSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5 Multivariate MethodsDocumento26 pagineCh5 Multivariate MethodsRikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmakaraka PDFDocumento46 pagineAtmakaraka PDFrohitsingh_8150% (4)
- Affidavit of DesistanceDocumento6 pagineAffidavit of Desistancesalasvictor319Nessuna valutazione finora
- Life Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessDocumento31 pagineLife Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessMichelle Casto100% (2)
- What Is Link AdaptationDocumento4 pagineWhat Is Link AdaptationAshutosh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DefenseDocumento20 pagineDefenseManny De MesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atty. Represented Conflicting Interests in Property CaseDocumento35 pagineAtty. Represented Conflicting Interests in Property CaseStella C. AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 6 - Autograph BingoDocumento1 paginaActivity 6 - Autograph Bingoapi-277504884Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enuma Elish LitChartDocumento20 pagineEnuma Elish LitChartsugarntea24Nessuna valutazione finora
- HI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Documento3 pagineHI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Abeer ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM 2 MARKSDocumento12 pagineTQM 2 MARKSMARIYAPPANNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Download Cosmetic Injection Techniques A Text and Video Guide To Neurotoxins Fillers Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocumento36 pagineHow To Download Cosmetic Injection Techniques A Text and Video Guide To Neurotoxins Fillers Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapterkerri.kite140100% (24)
- scn625 Summativeeval SarahltDocumento6 paginescn625 Summativeeval Sarahltapi-644817377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Analysis of Six Sigma Implementation Inservice OrganisationsDocumento30 pagineCase Study Analysis of Six Sigma Implementation Inservice OrganisationsMohammed AwolNessuna valutazione finora
- ENG01P001S02U00Documento14 pagineENG01P001S02U00arghasen2014100% (1)
- Capital StructureDocumento59 pagineCapital StructureRajendra MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- King Rama VDocumento3 pagineKing Rama Vsamuel.soo.en.how2324Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flowera, Fruits and SeedsDocumento66 pagineFlowera, Fruits and SeedsNikkaMontil100% (1)
- أبعاد التنمية الإجتماعية العربية في ضوء التجربة الأردنيةDocumento36 pagineأبعاد التنمية الإجتماعية العربية في ضوء التجربة الأردنيةkadhim4981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionDocumento7 pagineRock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionChad HorsleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing The NeckDocumento3 pagineAssessing The NeckAnne Joyce Lara AlbiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Property Management Agreement TemplateDocumento2 pagineProperty Management Agreement TemplatemarcelNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact Resistance Between Gas Diffusion Layer and CatalystDocumento5 pagineContact Resistance Between Gas Diffusion Layer and Catalystp.designNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Aspirin Therapy Understand The Benefits and RisksDocumento5 pagineDaily Aspirin Therapy Understand The Benefits and RisksNicholas OwensNessuna valutazione finora
- NIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceDocumento26 pagineNIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceAristide AhonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionDocumento7 pagineKinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionPrithwish Kr SutradharNessuna valutazione finora
- Webquest Biotechnology RubricDocumento2 pagineWebquest Biotechnology Rubricapi-556285637Nessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Instrumentation Engineering Solved 2013Documento22 pagineGATE Instrumentation Engineering Solved 2013Meghraj ChiniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (542)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsDa EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsDa EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Da EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemDa EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (331)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDa EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionDa Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingDa EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesDa EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDa EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowDa EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesDa EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDa EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDa EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationDa EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastDa EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (76)
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeDa EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (52)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionDa EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (10)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinDa EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersDa Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsDa EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)