Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Theory
Caricato da
Prashant SharmaCopyright
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoTheory
Caricato da
Prashant SharmaCoupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
Theory
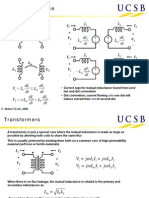
Coupled Circuits:
Consider 2 coils L1 and L2,
Let currents i1 and i2 flowing through coil 1 and 2 respectively.
Consider a case, when current i1 is flowing through coil 1 and current i2
is equal to zero in the second coil. Due to this flux 1 is produced in coil
1.
As both the coils are sufficiently close to each other, part of this flux 1
links with the second coil and due to mutual induction an emf is induced
in second coil.
The emf induced in first coil due to self inductance is given by,
V 1 = L1
i2 = 0
The emf induced in coil 2 due to mutual induction is given by,
V2 = M
i2 = 0
Similarly consider a case when the current i2 is flowing in coil 2 and
current i1 is equal to zero in coil 1.
Coupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
Theory
The emf induced in coil 2 due to self inductance is given by,
V 2 = L2
i1 = 0
Now if both the current i1 and i2 are flowing in coil 1 and 2 respectively
we can say that,
V 1 = L1
V 2 = L2
+M
+M
-----(1)
-----(2)
In terms of dependent sources, we can represent the above 2
equations as follows,
Now let's consider a case when the dots are placed at the opposite
ends in the 2 coils as shown in figure,
When both the currents i1 and i2 are flowing in coil 1 and 2 respectively
we can write the total EMF induced in coil 1 and 2 as follows,
2
Coupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
V 1 = L1
V 2 = L2
-M
Theory
-M
This can be expressed in terms of dependent sources as,
REMEMBER THIS:
Rule1: When both the current (i1 in coil 1 and i2 in coil 2) are entering a
leaving the coils at the dotted terminals, the sign of M term (mutual
inductance) will be same as the sign of L term (self inductance).
Example:
In figure 1 both the current i1 and i2 are entering the coil 1 and 2
respectively through dotted terminals.
So here, as per the Rule 1 the sign of M term will be same as the sign
of L term.
Therefore we get,
V 1 = L1
V 2 = L2
+M
+M
-----(1)
-----(2)
Sign of M term is same as sign of L1 term in equation 1 and same in
equation 2, sign of M term is same as sign of L2 term.
But the QUESTION arises,
3
Coupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
Theory
HOW TO DETERMINE THE SIGN OF L TERM?
Guys we are deciding the sign of M term according to the sign of L
term.
Now let's learn how to get the sign of L term.
Let's find out sign of L term in this figure.
Here in coil 1 the current i1 enters through the positive terminal of input (v1). So
the sign of L1 term is positive.
Same is the case with coil 2, i2 enter through positive end of the input.
So the sign of L2 term is positive.
Here, the current i1 coil 1 enters through negative terminal of input (v1),
so the sign of L1 term is Negative.
While in coil 2, current i2 enters through positive terminal of input (v2),
so the sign of L2 term is positive.
Example on Rule1:
4
Coupled Circuits
V1 = -L1
Coupled Circuits
V 2 = -L2
-M
Theory
-M
Rule 2:
If one current is entering through the dotted terminal while other current
leaving at the dotted terminal, the sign of M term will be opposite of that
of L term.
Example:
1)
V 1 = L1
V 2 = L2
-M
-M
2)
Coupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
V1 = -L1
V2 = L2
+M
-M
Theory
Q) HOW TO CONNECT THE DEPENDENT SOURCES IN THE
CIRCUIT?
Refer the following figures.
1)
2)
3)
Coupled Circuits
Coupled Circuits
4)
Theory
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsDa EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- 4 Mutual InductanceDocumento3 pagine4 Mutual Inductanceapi-27307515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterDa EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic CK TsDocumento23 pagineMagnetic CK TsAbdullah1021Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Elec Chapter FourDocumento17 pagineBasic Elec Chapter FourNebiyou KorraNessuna valutazione finora
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 3B: Quantum Mechanics Part TwoDa EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 3B: Quantum Mechanics Part TwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IV) (IV) : (Chapter 9)Documento35 pagineSinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IV) (IV) : (Chapter 9)Phan Phuong NgocNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec3 PDFDocumento11 pagineLec3 PDFARIJIT ROYNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Coupled CircuitsDocumento5 pagineMagnetic Coupled CircuitsAmitava Biswas100% (2)
- Induced Emf PDFDocumento4 pagineInduced Emf PDFVenkata SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenna & Wave PropogationDocumento4 pagineAntenna & Wave PropogationAditya SamavedulaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ideal TransformerDocumento2 pagineThe Ideal TransformerGabriel KaundaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.magnetically Coupled CircuitDocumento38 pagine3.magnetically Coupled CircuitRamanjaneyulu Anji YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitDocumento38 pagineMagnetically Coupled CircuitAlfred MoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 32 InductanceDocumento25 pagineChapter 32 InductancePriyadarsini TinagharanNessuna valutazione finora
- L1 - 1 MagCC - PPSXDocumento14 pagineL1 - 1 MagCC - PPSXmageedNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocumento53 pagineMagnetically Coupled Circuitsmohsensharifi787980Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Additional) Self - Mutual InductancesDocumento10 pagine(Additional) Self - Mutual InductancesBT21EE017 Gulshan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Documento82 pagineSyllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Hassan SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cir2 Lect 5 Magnetically Coupled Circuits UpdatedDocumento22 pagineCir2 Lect 5 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Updatedsuresh270Nessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceDocumento37 pagineEEE 1002 Module 8 Self and Mutual InductanceGnanavignesh RNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Dot ConventionDocumento2 pagineRules of Dot ConventionPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Main Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocumento17 pagineJEE Main Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadVineela SuthakaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit+14 Electromagnetic+Induction+and+Alternating+Currents PDFDocumento17 pagineUnit+14 Electromagnetic+Induction+and+Alternating+Currents PDFSanket PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Theory Part - 2 Tutorial - 8-1-13Documento13 pagineCircuit Theory Part - 2 Tutorial - 8-1-13dcsekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Self and Mutual InductancesDocumento10 pagineSelf and Mutual InductancesBT21EE017 Gulshan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- TransformersDocumento5 pagineTransformersYsdlv PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Receiving Antennas: 1 Equivalent Circuit Model of A Radio LinkDocumento7 pagineReceiving Antennas: 1 Equivalent Circuit Model of A Radio LinkTalianaAlarcónNessuna valutazione finora
- LitarDocumento7 pagineLitarMohd Rizal Abdul HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Power Systems: RT Watt Sec. in Case of An Inductor LI CVDocumento1 paginaFundamentals of Power Systems: RT Watt Sec. in Case of An Inductor LI CVragupaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocumento3 pagineElectro Magnetic Inductionadnankhannomanpathan100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission Line Switching Overvoltages - November - 2011Documento26 pagineTransmission Line Switching Overvoltages - November - 2011Sabeeh HasnainNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformers and Turns Ratio Version 1Documento3 pagineTransformers and Turns Ratio Version 1Shreeyash ChandgudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Assigment of Capastor & InductorDocumento24 pagineAssigment of Capastor & Inductorp pakistanNessuna valutazione finora
- (Fig. 1.1) (Fig. 1.2) Built Around A Ring-Shaped Core (Fig. 1.3)Documento7 pagine(Fig. 1.1) (Fig. 1.2) Built Around A Ring-Shaped Core (Fig. 1.3)Калоян ТотевNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternating Current CircuitsDocumento10 pagineAlternating Current CircuitsElvis ArguellesNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Chapter 32Documento58 paginePC Chapter 32ultimuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Mutual InductanceDocumento15 pagine1 Mutual InductanceMarco MarchesiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bucking Coils Produce Energy Gain2Documento6 pagineBucking Coils Produce Energy Gain2KONSTANTINOS TOMAZISNessuna valutazione finora
- Current ElectricityDocumento112 pagineCurrent Electricitysavita patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 1 Basic PrinciplesDocumento24 pagineLect 1 Basic PrincipleshumnaharoonNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Mutual InductanceDocumento54 pagine01 Mutual InductanceyahyeNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC313 Lab#2Documento6 pagineELEC313 Lab#2Ali MoharramNessuna valutazione finora
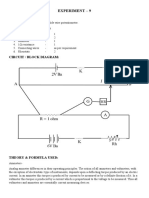
- Experiment - 9: Objective: Apparatus RequiredDocumento4 pagineExperiment - 9: Objective: Apparatus RequiredAditya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical CircuitsDocumento9 pagineElectrical Circuitsمسلم محمودNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric CurrentDocumento19 pagineElectric CurrentSai MNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 02Documento21 pagineLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Physics HW11Documento18 pagineMastering Physics HW11siow26100% (1)
- Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitDocumento13 pagineSirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsitقويه TasmanNessuna valutazione finora
- TransfrormerDocumento91 pagineTransfrormerArial96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity:-: Chapter - 3Documento26 pagineCurrent Electricity:-: Chapter - 3Mohit SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 2Documento35 pagineChap 2far remNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceDocumento8 pagineInternal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- Fisdas2 Inductance 4201419040Documento16 pagineFisdas2 Inductance 420141904040 Dani Firmansyah KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Emi AcDocumento6 pagineEmi ActhinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
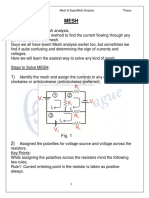
- Network Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryDocumento5 pagineNetwork Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento3 pagineTheoryPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento5 pagineTheoryPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Analysis: Krichoff's LawsDocumento2 pagineNetwork Analysis: Krichoff's LawsPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Dot ConventionDocumento2 pagineRules of Dot ConventionPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento5 pagineTheoryPrashant Sharma100% (1)
- Ladder & Non Ladder NetworksDocumento6 pagineLadder & Non Ladder NetworksPrashant Sharma100% (1)
- 4) Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocumento4 pagine4) Maximum Power Transfer TheoremPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Theorems: 1) Superposition TheoremDocumento7 pagineNetwork Theorems: 1) Superposition TheoremPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Realization of RL Functions:: Points To Keep in MindDocumento2 pagineRealization of RL Functions:: Points To Keep in MindPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento5 pagineTheoryPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction & Types of NnetworksDocumento4 pagineIntroduction & Types of NnetworksPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento7 pagineTheoryPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laplace Transform & It'S ApplicationDocumento2 pagineLaplace Transform & It'S ApplicationPrashant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- BPE4000 - CAB Benning PDFDocumento154 pagineBPE4000 - CAB Benning PDFbata88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded SystemsDocumento5 pagineEmbedded SystemsjascnjNessuna valutazione finora
- APOIDDocumento12 pagineAPOIDTiberiu ComsaNessuna valutazione finora
- GisgrndDocumento125 pagineGisgrndPremNessuna valutazione finora
- X Series InterconnectGuide Non-IR CompressorsDocumento48 pagineX Series InterconnectGuide Non-IR CompressorsDipak SatavNessuna valutazione finora
- Ark Flash - PracticalDocumento3 pagineArk Flash - PracticalmiguelpaltinoNessuna valutazione finora
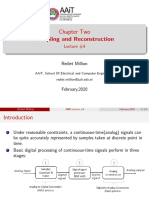
- Chapter Two Sampling and Reconstruction: Lecture #4Documento22 pagineChapter Two Sampling and Reconstruction: Lecture #4yohannes woldemichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Type B Ground-Fault Protection On Adjustable Frequency Drives PDFDocumento6 pagineType B Ground-Fault Protection On Adjustable Frequency Drives PDFRajuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 01 18 34 31 InsulatorsDocumento4 pagine2016 01 18 34 31 InsulatorsAnonymous p4GdtQpNessuna valutazione finora
- Sharplcd13 15 20s1u2Documento59 pagineSharplcd13 15 20s1u2Melvin MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ciena DWDMDocumento143 pagineCiena DWDMVictor HugoNessuna valutazione finora
- MS For The CCTV Installation and TerminationDocumento28 pagineMS For The CCTV Installation and Terminationwaaji snapNessuna valutazione finora
- EAMCDocumento149 pagineEAMCvspd2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- OpenDSS Custom ScriptingDocumento8 pagineOpenDSS Custom ScriptingHassan Ali Al SsadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing QuantumDocumento332 pagineDigital Signal Processing QuantumSudhir MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- 011 Chapter 9Documento10 pagine011 Chapter 9xiaomiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7H0011X0 W&C Tech Handbook Sec 07 PDFDocumento19 pagine7H0011X0 W&C Tech Handbook Sec 07 PDFJohn ElyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mira 3 User ManualDocumento23 pagineMira 3 User ManualCenk ErdincNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum of Ms in Avionics EngineeringDocumento34 pagineCurriculum of Ms in Avionics EngineeringUfi70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Batumi Alternate Firmware GuideDocumento1 paginaBatumi Alternate Firmware GuidefumezdunhillNessuna valutazione finora
- On A/C All: Wiring Diagram ManualDocumento4 pagineOn A/C All: Wiring Diagram ManualatrflyerNessuna valutazione finora
- SM5ce - V3 SawDocumento9 pagineSM5ce - V3 SawBryan DixNessuna valutazione finora
- S32K DSDocumento85 pagineS32K DSResham ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- 417-01 Exterior Lighting: Stop and Reverse LampsDocumento11 pagine417-01 Exterior Lighting: Stop and Reverse Lampsolyga mgolNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Project PDFDocumento18 paginePhysics Project PDFNidhi Porwal60% (10)
- 3A, 28V, 925Khz Step-Down Converter: The Future of Analog Ic TechnologyDocumento13 pagine3A, 28V, 925Khz Step-Down Converter: The Future of Analog Ic TechnologyGabriel GodoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1N4001S - 1N4007S: FeaturesDocumento2 pagine1N4001S - 1N4007S: FeaturesselocaNessuna valutazione finora
- Symphony Maintenance and Technical Guide 1907555 PDFDocumento36 pagineSymphony Maintenance and Technical Guide 1907555 PDFRicha Potdar50% (4)
- Airpods Pro 2gen BE03405288 InfoDocumento8 pagineAirpods Pro 2gen BE03405288 InfoZMENEZES2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance - Electrical Switch Contact PDFDocumento24 pagineGuidance - Electrical Switch Contact PDFdenny yusufNessuna valutazione finora