Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Asthma Drugs Clinical Pharmacology
Caricato da
crystalsheCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Asthma Drugs Clinical Pharmacology
Caricato da
crystalsheCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Clin Pharm Asthma Drugs
Study online at quizlet.com/_1xtwci
inhaled
corticosteroids direct
MOA
inhibit (cytokine-induced)
production of inflammatory proteins
2.
pharm agents causing
ASA, Beta blockers
3.
physical triggers
cold air, exercise
4.
physiologic triggers
(4)
stress, GERD, URI, rhinitis
factors influencing
dev/exp - host
genetic, gender, obesity
6.
inflam cells in asthma
mast, eosino/baso/neutrophils,
platelets, TH2
7.
mediators
histamine
LTE
Kinins, endothelin, prosanoids
8.
diagnosis
>12% reversibility or increase in
FEV1 of 200c
9.
obstructive pattern
reduced FEV1/FVC ratio w/ albuterol
10.
restrictive pattern
reduced FVC (normal ratio) w/
albuterol
11.
methacholine
challenge
bronchoprovocative test;
20% or more decrease in FEV1
12.
Severe asthmatic
episode - ABG
pH down
paCo2 down
pa02down
HCO3 way down
1.
5.
13.
sputum
eosinophils, charcot-leyden crystals,
inc IgE
14.
chest xray
inc AP diam, dark (translucent)
fields, depressed/flat diaphragm
15.
Step 1 - 4; symptom
freq
1; <2x per week
2; > 2x per week
3; daily
4; continual
21.
mast cells
filled w/ basophil granules
22.
short acting beta agonists
relax smooth muscle,
inc airflow in 30 sec; DOC for
attacks
23.
indicates inadequate
control
> 1 canister/mth SABA
24.
dosing positive response is
200 ml increase or 12%
increase in FEV1
25.
Beta2 agonists SE
tremor
heart palps
hypokal
O2 sat reduction
26.
SABAs - ALPMT
(short goats on alp
mountains)
Albuterol
Levalbuterol
Pirbuterol
Metaproterenol
Terbutaline
27.
dosing levalbuterol
(Xopenex) - only R
isomer/active
half of racemic albuterol - 0.63
mg, 1.25 mg (3X cost)
28.
LABAs - AFAS
Albuterol ER
Formoterol
Aformoterol,
Salmeterol,
29.
LABA's considerations
not monotherapy;
only if cannot be controlled
otherwise
shortest duration & taper off
30.
LABAs - COPD only
Formoterol
Aformoterol
31.
combo LABA &
corticosteroids (3)
Symbicort, Dulera, Advair
32.
Symbicort
Formoterol & Budesonide
33.
Advair
Salmeterol & Fluticasone
16.
Zone mgmnt
green/yellow/red
patient self monitoring system
34.
Dulera
Formoterol & Mometasone
(asthma only)
17.
asthma classifications
allergic, exercise induced, nocturnal
35.
Dulera
18.
non drug treatment,
avoid triggers & treat
aggravating
allergies, GERD, rhinitis, viral RI
combo LABA & steroid for
asthma only
36.
inhaled corticosteroids
direct MOA
inhibit cytokine (induced
prod of pro-inflamm proteins)
19.
drug types for asthma
(6)
beta agonists, corticosteroids, mast
cell stabilizers, LTE modifiers,
theophylline, anti IgE ab's
37.
inhaled corticosteroids
indirect MOA (4)
20.
Beta 2 agonists MOA
G-protein receptors activates
adenylyl cyclase/cAMP - >
intercellular Ca ->
bronchodiliation & mast cell
stabilization
alter m-RNA prod
suppress inflam
produce anti-inflam mediator
increase B2 receptors,
decrease mucous
38.
mild asthma - once a day
inhaled steroid options
budesonide
ciclesonide
mometasone furoate
39.
corticosteroids
SEs
thrush; hypergly
adrenal suppress
osteoporosis
elev WBC
52.
cromolyn (intal) - class
nedocromil (tilade)
mast cell stabilizer
(no inherent bronchodilation)
53.
cromolyn MOA
blocks Cl channels
blocks histamine release from
mast cells
54.
cromolyn SE
bad taste; GI
55.
Montelukast (Singulair) class
Zafirlukast (Accolate)
LTE receptor antagonists
56.
Zileuton (zyflo) - class
LTE receptor antagonists
5-lipoxygenase inhibitor reduces synthesis
57.
Zileuton (zyflo) interaction
inhibits metabolism of
theophylline & warfarin
(increases levels)
58.
LTE antagonists - not
indicated for
acute attacks
blockade adenosine receptors
59.
Montelukast vs Zafirlukast
Montelukast more favorable;
can be used in kids 2-5 yrs
Ca+ released from sarcoplasm
60.
Ipratropium - class
antimuscarinic (atropine - like)
61.
Ipratroprium - indication
quick relief; additive to beta
agonists
62.
Omalizumab (xolair) - class
IgE antibody inhibitor
63.
Omalizumab MOA
binds IgE on mast
cells/basophils; prevents
release
64.
Omalizumab - indication
persistent, mod-severe
allergic asthma not controlled
on oral steroids
65.
Omalizumab dosage
every 2-4 weeks; half-life 26
days
66.
Omalizumab concern
very expensive
67.
Omalizumab dosage based
on
IgE serum levels -but 1+ yr
post treat
68.
Omalizumab SE
HA
injection site rxn
URI arthralgia
69.
MOA of Omalizumab
(Xolair)?
Inhibits binding of IgE to the
high affinity IgE receptor on
surface of mast cells and
basophils
70.
Which type of patient
should use Omalizumab
(Xolair)?
Patient with moderate-severe
persistant allergic asthma not
controlled by inhaled steroids
71.
When prescribing Inhibitors
of IgE antibodies, what
should the dosing be based
on?
IgE serum levels and body
weight
40.
corticosteroids dosing therapy
oral or IV "burst" therapy
41.
corticosteroids
dosing strategy
long term
step down: after controlled
dec 25% every 2 wks (8wks min)
42.
methylxanthines
include
caffeine, theophylline, theobromine
43.
methylxanthine indication
adjuvant to inhaled steroids
alt to LABA to control nocturnal
symptoms
methylxanthines
MOA (3)
phosphodiesterase inhib, inc CAMP->
inhibits LTE broncho/vasodilate, cardiac
stim, vasodilate
44.
45.
theophylline SE's 7 NITSCHA
N/V
insomnia
tremors
seizures
confusion
HA
arrhyth
46.
theophylline concern
narrow therapeutic window; monitor
conc
47.
theophylline interaction
is a Cyp 450 substrate; many interactions
theophylline CYP450
interaction
causes
inhibitors inhibit liver metabolism;
increase Theo levels
inducers enhance ......cause decreased
Theo
theophylline avoid CY450
INHIBITORS
(inhibited hide
FACE Very well)
Fluvoxamine
Amiodarone
Cipro
Erythromycin
Verapamil
theophylline avoid CY450
INDUCERS
(PCPR - induce
halluc)
Phenytoin
Phenobarbital
CBZ
Rifampin
theophylline disease state
interactions
smoking, hyperthy - dec Theo
CHF, liver disease - inc Theo
48.
49.
50.
51.
72.
T/F: Inhibitors of IgE antibodies are cost
effective for the patient
False: They are about $600 per 1 150mg. vial
73.
Intermittent Asthma - Step 1 Tx
SABA as PRN
74.
Intermittent Asthma - Step 1, w/ mod/sev viral
inf Tx
SABA PRN
short course systemic steroids
75.
mild persistent asthma - Step 2 Tx
daily long term control
inhaled steroids or (cromolyn or nedocromil)
Zafirlukast or zileuton in adults (12+YOA)
76.
mod persistant asthma - Step 3 Tx
increased inhaled steroids or
add LABA or
add nedocromil
77.
mod persistant asthma - Step 3 not controlled
Tx
increase to high dose inhaled steroids
add LABA (servent or theophylline)
78.
severe persistent asthma - Step 4 Tx
Add oral systemic steroids
monitor closely
79.
LABA black box warning
inc risk for asthma-related deaths; only for uncontrolled (w/ inhaled corticosteroid
or 2+ maintenance meds)
80.
Acute asthma exacerbation; FEV1 or PEF < 50% Tx
O2 90-95% sat
inhaled SABA or cont albuterol
oral systemic steroids (prednisone)
anti-cholinergics (never alone)
81.
which drugs specifically not recommended for
acute asthma
methylxanthine/theophylline
mucolytic
sedation
abx
82.
aggressive hydration in acute asthma
not reco'd adults; maybe infants/children
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- NCLEX-RN Exam Prep 2024-2025: 500 NCLEX-RN Test Prep Questions and Answers with ExplanationsDa EverandNCLEX-RN Exam Prep 2024-2025: 500 NCLEX-RN Test Prep Questions and Answers with ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cvs (Diuretics)Documento2 pagineCvs (Diuretics)CatNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs For AsthmaDocumento3 pagineDrugs For AsthmaMelissa Deso MillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarcoidosis: Dr. Col. Vishal MarwahaDocumento26 pagineSarcoidosis: Dr. Col. Vishal MarwahaSreekrishnan TrikkurNessuna valutazione finora
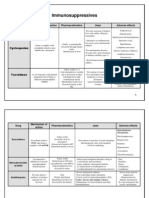
- 1 - Immuno Tables1Documento4 pagine1 - Immuno Tables1Urugonda VenumadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Status Examination Medical StudentsDocumento23 pagineMental Status Examination Medical StudentseurocoupeNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Medicine OSCE Dr. Rebeca HoilettDocumento20 pagineFamily Medicine OSCE Dr. Rebeca HoilettFatma El FaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma DrugsDocumento1 paginaAsthma DrugskakuNessuna valutazione finora
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDocumento17 pagineFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: OxygenationDocumento37 pagineCase Studies On Major Concepts: OxygenationJek Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematologic DisordersDocumento32 pagineHematologic DisordersQuolette ConstanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Week-2 Mental Status ExaminationDocumento23 pagineWeek-2 Mental Status ExaminationSaud TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocumento65 pagineAntiepileptic DrugsZarish IftikharNessuna valutazione finora
- Case History M.SCDocumento10 pagineCase History M.SCRaksha RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory AssessmentDocumento43 pagineRespiratory AssessmentLui Andrei AnilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Description of The Patient & Instructions To SimulatorDocumento7 pagineDescription of The Patient & Instructions To SimulatorCindy WongNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Major Veins of The BodyDocumento26 pagine3-Major Veins of The BodyTJPlayz100% (1)
- Medical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Documento377 pagineMedical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Benyamin KhalevNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of PlacentaDocumento5 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of PlacentaAmuNessuna valutazione finora
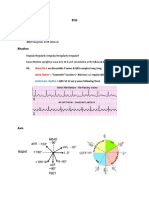
- ECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalDocumento11 pagineECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalJonathan DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Viral DrugsDocumento6 pagineAnti Viral DrugskakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune System Docs 2019Documento13 pagineImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion For ChildrenDocumento5 pagineTransfusion For ChildrenKristine Mae AbrasaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Edition All NeuroDocumento92 pagine7th Edition All NeuroCrystal LynaeNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Fluid ChartDocumento2 pagineIV Fluid Chartbenny christantoNessuna valutazione finora
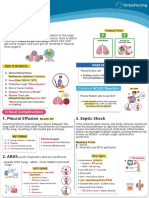
- Pneumonia: 1. Pleural Effusion 3. Septic ShockDocumento1 paginaPneumonia: 1. Pleural Effusion 3. Septic ShockTrisha VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest Pain Chest Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamDocumento1 paginaChest Pain Chest Pain: Focused History Focused Physical ExamdocNessuna valutazione finora
- Hem-Onc: AnswerDocumento3 pagineHem-Onc: AnswerAman Raj KNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2Documento4 pagineMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2TrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Documento3 paginePain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Ryan TurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteDocumento2 pagineDrugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteyukariNessuna valutazione finora
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocumento28 pagineAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine DisordersDocumento5 pagineEndocrine DisordersBilly Ray VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoimmune Diseases: Henry O. Ogedegbe, PHD., C (Ascp) SC Department of EhmcsDocumento47 pagineAutoimmune Diseases: Henry O. Ogedegbe, PHD., C (Ascp) SC Department of EhmcsGalih Putra RanggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocumento22 pagineFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsDocumento2 pagine50 Most Commonly Prescribed Medications1stsgtwife4055Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2a Haematology Saq QuestionsDocumento12 pagine2a Haematology Saq QuestionskamaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Diuretic DrugsDocumento2 pagineDiuretic DrugsEngku ElisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocumento5 paginePharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNessuna valutazione finora
- GI Signs and SymptomsDocumento40 pagineGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Blood ProductsDocumento11 pagine4 Blood ProductsGampa VijaykumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocumento2 pagineImmune System Review Questionsapi-524061079Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisorderDocumento50 pagineAssessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisorderZanida ZainonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39Documento94 pagine1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39hamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiDocumento8 pagineImmunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiHamad Alshabi100% (1)
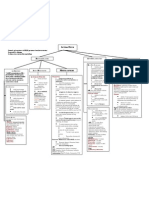
- Concept Map Week 2Documento2 pagineConcept Map Week 2Ashley ChristensenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sympathomimetic Agents: CLIN. PHARM (Dr. Salvador) Asthma 05 SEPT 2017Documento3 pagineSympathomimetic Agents: CLIN. PHARM (Dr. Salvador) Asthma 05 SEPT 2017Seff Causapin100% (1)
- Valvular Heart DseDocumento8 pagineValvular Heart DseJane Pineda CuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal Swelling + AscitesDocumento29 pagineAbdominal Swelling + AscitesDevina CiayadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesDocumento11 pagineDisease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesSara AshurstNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Unconscious PatientDocumento23 pagineApproach To Unconscious Patienttantw880% (1)
- Anatomy Ospe PDFDocumento25 pagineAnatomy Ospe PDFrizki ardiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic and NephriticDocumento27 pagineNephrotic and Nephritictam meiNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Medicine VivasDocumento9 pagineInternal Medicine Vivasponcus payNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma GI CardsDocumento16 paginePharma GI CardsDoctorsHangout.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Disoreder of PerceptionDocumento36 pagineDisoreder of PerceptionUmar Khan100% (1)
- Self-Bullying: What to do when the bully is YOU!Da EverandSelf-Bullying: What to do when the bully is YOU!Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optimal Life: Essentials of AsthmaDa EverandOptimal Life: Essentials of AsthmaNessuna valutazione finora
- FIrstAidCLerkship EM DiagnosticsDocumento3 pagineFIrstAidCLerkship EM DiagnosticscrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- OSCE Stop - Lecture Long HistoryDocumento18 pagineOSCE Stop - Lecture Long HistorycrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- Lange Current Emergency Medicine - GI Bleed ChapterDocumento3 pagineLange Current Emergency Medicine - GI Bleed ChaptercrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Provider Manual 2015 NotesDocumento5 pagineACLS Provider Manual 2015 Notescrystalshe93% (14)
- Packrat Cardio QuestionsDocumento63 paginePackrat Cardio Questionscrystalshe100% (1)
- Bates Thorax Lungs With TermsDocumento4 pagineBates Thorax Lungs With Termscrystalshe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology LymphomaDocumento4 paginePathophysiology LymphomacrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjuncts Quiz 1: Study Online atDocumento5 pagineAdjuncts Quiz 1: Study Online atcrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Facts For Electrolyte AnalysisDocumento3 pagineQuick Facts For Electrolyte AnalysiscrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Neck Infections Obstructive Airway Disease FactsDocumento17 pagineHead Neck Infections Obstructive Airway Disease FactscrystalsheNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidneys Fluid Regulation ElectrolytesDocumento10 pagineKidneys Fluid Regulation Electrolytescrystalshe100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY-1st BatchDocumento27 pagineDRUG STUDY-1st BatchCanny CańasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanDocumento9 pagineCardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanjikookNessuna valutazione finora
- Health 8Documento319 pagineHealth 8Anngela Arevalo BarcenasNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF TextDocumento3 paginePDF TextYogita PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Programme Guide Certificate in Community Health (BPCCHN) - CompressedDocumento120 pagineProgramme Guide Certificate in Community Health (BPCCHN) - CompressedChakrapani ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 4 Hand Washing and Ppe - CincoDocumento3 pagineWeek 4 Hand Washing and Ppe - CincoShecana Rose CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessments: What They Are, Why They're Important and How To Complete ThemDocumento5 pagineRisk Assessments: What They Are, Why They're Important and How To Complete ThemAL Hazm National ProjectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Aconitum Ferox - Blue AconiteDocumento2 pagineAconitum Ferox - Blue Aconitejcoppala4476100% (1)
- A Simplified List of All Protocols - HubermanLabDocumento2 pagineA Simplified List of All Protocols - HubermanLabMorten NessNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Elements Qi GongDocumento1 pagina5 Elements Qi GongBill HonakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubungan Kejadian Dismenore Dengan Asupan Fe (Zat Besi) Pada Remaja PutriDocumento5 pagineHubungan Kejadian Dismenore Dengan Asupan Fe (Zat Besi) Pada Remaja Putriashar hariyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.02 Medicina Clínica PDFDocumento100 pagine3.02 Medicina Clínica PDFCristina Maite Chacon AmayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phoenix, Arizona: Principles To Guide Zoning For Community Residences For People With DisabilitiesDocumento44 paginePhoenix, Arizona: Principles To Guide Zoning For Community Residences For People With Disabilitiesdan-304518Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cyclo ThermDocumento24 pagineCyclo ThermProtantagonist91% (11)
- The Bethesda System For Reporting Cervical Cytolog PDFDocumento359 pagineThe Bethesda System For Reporting Cervical Cytolog PDFsurekhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka - 2pusssDocumento6 pagineDaftar Pustaka - 2pusssMuhammad ShodiqinNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Class 9 Political Science Chapter 6 YouTube Lecture HandoutsDocumento5 pagineNCERT Class 9 Political Science Chapter 6 YouTube Lecture Handoutsarjun anjana anjanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acupuncture With Manual and Electrical Stimulation For Labour Pain: A Two Month Follow Up of Recollection of Pain and Birth ExperienceDocumento9 pagineAcupuncture With Manual and Electrical Stimulation For Labour Pain: A Two Month Follow Up of Recollection of Pain and Birth ExperiencejayaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICAO Manual Doc 9984 1st Edition Alltext en Published March 2013Documento54 pagineICAO Manual Doc 9984 1st Edition Alltext en Published March 2013Disability Rights Alliance67% (3)
- MSDS RBD Palm Olein cp10Documento4 pagineMSDS RBD Palm Olein cp10sugitra sawitaNessuna valutazione finora
- MRU-QMS-HSE-Form - JSA - Geotechnical Drilling & Geotechnical Field Investigation - Rev00Documento11 pagineMRU-QMS-HSE-Form - JSA - Geotechnical Drilling & Geotechnical Field Investigation - Rev00AditNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing 2 4yDocumento10 pagineNursing 2 4yGCON KURNOOLNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypomochlion Aided Reduction For Sub-Condylar FracturesDocumento2 pagineHypomochlion Aided Reduction For Sub-Condylar FracturesshyamNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsDocumento8 pagine02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsKenneth TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Mosquito Repellent Devices-Problems and Prospects: August 2018Documento6 pagineUse of Mosquito Repellent Devices-Problems and Prospects: August 2018Cyrus Ian LanuriasNessuna valutazione finora
- Carlton Hubbards ResumeDocumento2 pagineCarlton Hubbards Resumeapi-662079150Nessuna valutazione finora
- Effectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionDocumento10 pagineEffectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionAbdel Hadi KanjNessuna valutazione finora
- DHCDocumento2 pagineDHCLiaqat Ali KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- ISSLDocumento58 pagineISSLsufiNessuna valutazione finora
- AbDocumento5 pagineAbapi-466413302Nessuna valutazione finora