Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Water Quality Management of Swimming Pool PDF
Caricato da
Madhan RajDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Water Quality Management of Swimming Pool PDF
Caricato da
Madhan RajCopyright:
Formati disponibili
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Water Quality Management
of Swimming Pools
Prof. Rajendrakumar V. Saraf
INTRODUCTION
A growing number of people throughout the world use Swimming pools. India is no exception.
Exponentially increasing population, changing lifestyles, rising health consciousness and
better incomes have given rise to a large swimming pool industry. These days swimming
pools are nding a place in:
Residences (Single homes/ Apartments/ Villas/ Townships)
Educational institutions
Sports complexes
Spas
Water Parks
Special pools for physically challenged
Pools for Animals(Equine/ Dolphin)
Diving pools
to name a few.
Consequent to unchecked pollution, natural water bodies such as Village ponds, Lakes and
Rivers are fast losing their appeal as places where one could swim safely. As a result even
farmhouses with natural water bodies in them tend to have modern swimming pools these
days as a common feature.
DECEMBER 2012 14
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
A swimming pool is no longer just a piece of
architecture. It involves various techniques and
requires a multi-disciplinary approach for a
comprehensive design. There are many ways of
designing a swimming pool and the Pool industry
offers many schemes to meet most situations for
the investors benet. Swimming pool designers,
contractors and operators have preferences or
prejudices for one system or another. While
aesthetics and pool sizing can be dependent on
individual requirements, site characteristics and
economics; safety considerations will have to be
of the highest priority without any compromises.
A Swimming Pool is either rectangular or of any
free shape. Free shape tanks are generally used
for resort and leisure pool complexes. Generally,
rectangular tanks are preferred for learners and
purposes of competitions.
A tank is normally constructed in either RCC or
brickwork. After water proong, glazed ceramic
tiles or glass tiles are xed on the inner surface of
the tank.
Dimension of pool
The dimensions for the pool are based on the
Cage of Safety for the appropriate category of
diving. The Cage of Safety is a body of water
within the pool into which it is safe to dive from
the deck or the diving board. The prole of a pool
may be of any shape or size provided it contains
minimum dimension of the Cage of Safety. Basic
requirements for pool dimensions depend on its
type and usage.
WATER IN SWIMMING POOL
Water is the most important part of a swimming
pool. Earlier practice was to fill it with fresh
water and use until such time the water was
visibly dirty. The pool was then drained and
refilled with fresh water. Each swimmer
entering the pool contaminates water with
microbes, inorganic and organic compounds,
sweat, saliva, perspiration, cosmetics, and
excretory products of the body. Further, dust,
leaves and flowers from the surrounding
environment pollute pool water. This makes
water unsafe and turbid, as it promotes
microbial and algal growth rapidly. Infection
of many water borne diseases due to water
contamination in poorly operated swimming
pool cannot be ruled out. Since the entire body
of the swimmer comes in contact with water,
water quality in the swimming pool is most
important from the health aspect and has to be
considered during designing and installing of
the swimming pool. Consequently, filtration
systems with recirculation were introduced
to continue using the same water for longer
periods. Water in a pool is filtered, disinfected,
and recycled to accepted pool water standards.
Only make up water is added to compensate
water loss due to evaporation, suction sweeping
of pool and backwashing of filter.
Therefore, it is essential to have an efcient
design of water circulation, and treatment system
incorporating disinfection of water.
WATER CIRCULATION IN POOL
Contaminated water along with floating scum
and solids overflows from the pool and is led to
the filtration system. There are different types
of overflow systems. Water is also drawn from
the bottom of the pool at the deepest point.
Overflow of the water plays an important
role in maintaining water quality in the pool.
Some of the typical overflows from the pool are
shown in Figure-1. Overflowing water from the
pool either goes to the balancing tank or to the
bucket strainer. Leaves and hair are trapped
in the strainer. Water from balancing tank or
strainer is pumped to the Pressure Sand Filter.
Suspended solids and turbidity are removed
in the filter. Filtered water is disinfected and
returned to the pool. Fully treated water enters
the pool through the nozzles at bottom or in
sidewalls. Inlet and outlet of water in the pool
are to be designed to ensure that the filtered
disinfected water replaces water at any corner
in a designed turnover time. Typical water
filtration and circulation system for water are
shown in Figure-2.
DECEMBER 2012 15
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Turnover Time
Pool becomes polluted at different rates
depending on the usage and swimmers.
Generally, water becomes turbid very fast at
shallow depth because more people wash off
more dirt in less amount of water. An old and
practical guide to decide the capacity of the
filter is to reduce one hour from the pools
turnover time for each foot depth of water.
Now, turnover time is decided on the basis of
dust loading. It varies from 10 hour for very
light loading in deep water to 10 minutes for
extreme loading to beach shallow all within
the same pool. To maintain the desired quality
of water in the pool, total volume of water in
the pool shall be passed through the filter and
circulated in given time called as turnover time.
It is defined as below:
Total Volume of Water
in Pool (cu.m.)
Turnover time (hr) = ---------------------------------Filtration Rate cu.m./hr
Selection of the correct turnover time for the
pool will guarantee the design, water clarity
and quality even at peak bathing loads. General
recommended turnover time in hours for different
pools is as below:
Paddling or intensive learner, shallow pools
Teaching & Play pools
Public & Hotels with intensive use
School, Olympic/International Competition
Community
Clubs and Private intensive usage
Residential pool
Diving Deep side, light & private usage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Filtration System
The lter deals with particulate matter. It strains
out suspended solids to sub-micron size to
maintain clarity of water. It neither removes
dissolved solids nor deals with micro-organisms.
Filtration combined with disinfection keeps
water:
Clear and non-toxic
Odourless and tasteless
Free of bacteria and algae
Balanced to prevent corrosion and scale
formation
DECEMBER 2012 16
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
The working capacity of a lter is the amount
of dirt it can hold without blocking or passing
more than, say 10-micron size particle in a given
time. The rate of ltration is the ow of water
that passes through the lter to achieve specied
degree of clarication in a given turnover time.
Due consideration shall be given to the following
factors that inuence ltration such as:
High bathing loads
Heating of pool water
Covering the pool
Blown algae and dust falling on the surface of pool
Mineral found in water itself
Generally, pressure sand lters of medium (25
cu.m./sq.m./hr) and high (50 cu.m./sq.m./
hr) loading rate are used. Other lters, such
as Cartridge lter, Pre-coat lter and Vacuum
Diatomaceous lter are also used. Various
swimming pool lter manufacturers claim the
ltration rate for their lter models. However, it
is commonly observed that these rates are not on
realistic grounds, therefore causes malfunctioning
of the pool system.
Other Pool Cleaning Equipments
Once heavy dust and the dead algae settle down
on the bottom of the pool, it cannot be removed
by ltration. Therefore, a device called as
Suction Sweeper is used. It has a Suction Head
provided with a brush and a Vacuum/Suction
Hose. The Suction Sweeper pumps water along
with dust out of the pool. Water is either wasted
or recycled to the lter. Nylon brushes are also
used to clean and scrub off the algal growth on
the tiles.
DISINFECTION
Once a swimmer enters the pool, his/her entire
body gets in contact with pool water. Therefore,
pool water must be as good as, if not better than
the water we drink. It has to be clearer than
drinking water and should have a palatable
disinfectant. Water shall always stay fresh even
though every swimmer is adding contaminants
repeatedly and adding to bacterial pollution.
Each bather can introduce about 600 million
microbes at first plunge. Followings are
essential requirements for disinfectant for the
pool:
DECEMBER 2012 17
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Action of Chlorine as disinfectant
When chlorine is added to pool water, the following
reactions take place:
Neutralises the pollutants present in the pool
water
Reacts with sunlight, heat and agitation
Combines with nitrogenous impurities to form
chloramines (Combined Chlorine)
Remains as residual chlorine for disinfection
and algae control over a design period.
Shall be potent enough to destroy microorganisms rapidly to prevent transmission
from one swimmer to another
Adequate disinfectant residual in the water at
all times
Shall be nontoxic to swimmer without any toxic
byproducts
Shall not contribute bad taste/odour
Shall not accumulate in pool to reach to the
harmful level
A satisfactory disinfection system with efcient
ltration stops infection; prevents algae formation;
eliminates taste and odours; controls scaling and
corrosion in water; makes water crystal clear; gives
sparkling appearance; and keeps the pool always
safe for the swimmer. Different disinfectant
products and systems are available in the market
and can be categorized as below:
Chlorine gas and chlorine compounds
Halogen other than chlorine
Ozonization
Metal ion generators
Alternative disinfection systems and chemicals
1. Chlorination
Chlorine can be introduced to swimming pool
water by the use of the following:
Chlorine Gas
Sodium Hypochlorite solution
Calcium Hypochlorite powder
Lithium Hypochlorite granules/tablets
Chloroisocyanurate granules/tablets
Electrolytic Hypochlorite generators
The Residual Chlorine in water can be measured as
free, combined and total chlorine. It plays a major
role in eliminating the chances of transmitting
infection to fellow swimmer. Free Chlorine is
a strong disinfectant, almost odourless and
immediately kills micro-organisms. Combined
Chlorine is a poor disinfectant, has pungent smell
and causes irritation to eyes and takes few hours
to act. As guidelines, Free Residual Chlorine
should be three times more than the Combined
Residual Chlorine. It ensures immediate action
and a long-lasting action for safe water. It also
overcomes eye irritation, odour and algal growth.
The practice of break point or super-chlorination
to the level of 5 mg/l, Residual Chlorine destroys
chloramines and reduces the Combined Chlorine
level.
Residual Chlorine exists in water, mainly as
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and less effective
Hypochlorite (OCl) ions. Action of disinfectant
ions depends on the pH level. For example, even
mild acid pH (6.5) will speed up the disinfection
process and also corrosion. Too alkaline pH (more
than 7.5) will nullify compound properties and
increase dosing rates just to deal with ordinary
contamination. Most favourable pH is mild
alkaline (7.1-7.3) above the neutral.
A comparison of three forms of Chlorine i.e.
Chlorine gas, liquid Chlorine and dry Chlorine is
given in the Table-1:
Dry Chlorine - Lithium Hypochlorite
It is granulated bleaching powder, packed in
bags, having 30% available Chlorine and pH
7-8. It is totally soluble in water. It is safe, can be
easily stored and handled, and can be added to
pool directly. It is more expensive and not easily
available in India. It adds 65% of binder to pool
total dissolved solids.
DECEMBER 2012 18
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Table-1 : Comparison of different forms of Chlorine
Details
Chlorine Gas
Liquid Chlorine
Dry Chlorine
Technical Name
Chlorine
Sodium Hypochlorite
Calcium
Hypochlorite
Physical &
chemical
Properties
Green, pungent gas.
2.5 times heavier than air.
pH: Acidic
Liquid
Alkaline. pH:12-13
Dry powder.
pH: 11-12
Storage
Liqueed gas in cylinder
(100 kg). Long shelf life
Liquid stored in cans, short
shelf life
Powder stored in bags. Long
shelf life if packed properly
Available
Chlorine
100%
5 to 10%. Rest is alkali and
water.
30 to 70%. Rest is either
insoluble or soluble Calcium salts
Disinfection
Power
Highly effective
It disperses easily and acts
rapidly
Very effective disinfectant
Feeding Device
Requires failsafe,
sophisticated feeding
(Vacuum Feed/Pressure
Feed) arrangements
By gravity or through simple
dosing pump.
Flow can be immediately
measured and dozing can be
proportionate to water ow.
It is partly soluble in water and
cannot be dozed directly to
pool. As a general practice, it
is dispersed in water and clear
superant is dozed.
Handling/ Risks
Dangerous if not handled
properly. Requires special
storage facilities and stringent precautions. No more
recommended in west on
safety grounds.
Requires careful handling and
highly dangerous if crosscontaminated with acid
Safe to handle. Generates dust
when dry and sludge when
wet. It is a strong oxidizing
agent with potential safety
hazards, highly combustible
with oil, sawdust, organic
materials and solvents, etc.
Manpower
Trained manpower to
handle dozing devices and
emergency situation caused
due to Chlorine leakage
Semi-skilled
Semi-skilled
Additional
chemicals to be
added
Soda ash to maintain
alkalinity
Hydrochloric Acid to adjust pH Hydrochloric Acid to adjust
pH
Side effects
Wet Chlorine is corrosive
for all metals. Lowers pH
of water due to acid formation.
Increases Chloride
level. Burns eyes and skin.
Bleaches costumes if added
in high concentration into
pool water
Increase in pH, total dissolvent, and chlorides. Acid is to
be added to adjust the pH to
neutral. Chloride accumulation
needs careful inspection.
Application
All types of water and pool Medium and smaller pools.
In hard water it causes precipitates and deposits on pool
walls.
Very good for soft water. In
hard water, causes precipitates
and deposits on pool walls.
Cost
Lowest cost per kg of Chlo- Costlier than Chlorine gas, has
rine and disinfectant
overall high performance cost
and requires efcient and guaranteed supply services.
Economical
DECEMBER 2012 19
In hard water, it causes precipitates and deposits on pool
walls and scale formation in
pipelines. It may clog lter,
feeder or cloud hard waters.
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Chlorocyanurates
Cyanuric acid is used to reduce Chlorine loss
in the outdoor pools. Cyanuric acid shields
decomposition of Hypochlorous Acid from ultraviolet light. It facilitates the presence of chlorine
in water for longer duration. Recommended dozes
are from 25 to 100 PPM maximum. Cyanuric acid
is a powder having pH 3-5. To be effective, a level
of 30-mg/l cyanuric acid should be maintained in
water. Handling of Cyanuric acid is difcult due
to its pungent smell and irritation to eyes. Its use is
not yet popular in India. Cyanuric Acid combines
with Chlorine to form following compounds
called Cyanurates Chlorine.
Sodium dichloroc Stabilized powder or
yanurate & Potassium granules 60% available
dichlorocyanurate
chlorine, pH 6-7,
effective, self stabilizing
disinfectant readily &
completely soluble
Sodium trichlorois-
Stabilized powder
ocyanuric acid or tablet,
90% available chlorine
Chloroisocynurates provide their own Cyanuric
Acid. When these compounds are used as
disinfectants, the level of Cyanuric Acid in the
pool water should not be normally allowed
to exceed 200 mg/l, however in exceptional
circumstances, it may be allowed to rise to
400 mg/l. Pool can be operated with higher
free Chlorine residual (2 mg/l). It should be
increased to at least 2.5 mg/l when Cyanuric
Acid level exceeds 100 mg/l.
Chloroisocynurates are very effective; readily and
completely soluble; and self-stabilizing agents.
They have long storage life; can be conveniently
handled; powerful and ideal in bright sunlight;
also very effective in hard water. There is no
need of a feeding device, as it can be added
directly to the pool. Chloroisocynurates are more
expensive, and slow down kill rate of Chlorine.
Dozing continually raises Cyanuric Acid level.
They are incompatible with any contamination
or any other Chlorine. Further, periodic super
chlorination of pool water is required. Binder
presence can cause algal bloom and slow down
destruction. It is highly susceptible to hazardous
contamination in store. Due to slow action, algae
may grow in the pool.
Electrolytic Chlorination
In the Electrolyzer, current is passed through the
anode and cathode in the salt solution, which is a
good conductor of electricity, thus electrolyzing the
salt solution. This results in Chlorine (Cl) gas being
produced at the anode, while Sodium Hydroxide
(NaOH) and Hydrogen (H2) gas are produced at
the cathode. The Chlorine further reacts with the
Hydroxide to form Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl).
The solution generated has a pH value between
8 to 8.5, and a maximum equivalent Chlorine
concentration of less than 8 g/l. It has very long
shelf life which makes it suitable for storage. Using
onsite Sodium Hypochlorite generator, 4.5 kg of
salt and 4 KWH of power are required to produce
1kg equivalent of chlorine. Hydrogen gas must
be vented suitably and safely to the atmosphere
outside the building. It is most suitable for stable
bathing loads. Electrodes last for 2 to 3 years.
2. Halogens Other than Chlorine
(a) Bromine
Bromine is also a member of the halogen group of
element and its reactions in pool water are almost
similar to that of Chlorine. Both free Bromine as
Hypobromous Acid and the combined forms as
Bromamines are effective bactericides, viricides,
algaecides and oxidizers of organic matter.
Unlike Chlorine and Chloramines, free Bromine
and Bromamine cannot co-exist other than
momentarily so only small combined residual
is necessary for a strong disinfecting property.
Breakpoint reaction with Bromine at pool water
pH levels (7.3-7.8) reaches almost instantaneously
in the presence of even slight excess of Bromine.
Bromination offers faster kill rates and fewer side
effects. Residual remains longer and is dissipated
slower by sunlight. Bromination is very effective
at pH 7.8. A pH adjustment is required but to
a less extent. Bromamines are not as irritating
as chloramines. Even at 1-2 ppm, bromination
odours are not greatly noticeable. Bromine is
an excellent algaecide and a 3-ppm super dose
invariably helps in eliminating algae growth.
Generally, the side effects are not as difcult to
control as for Chlorine. It makes bromination
more economical than chlorine. Besides,
dispensing systems are not under pressure like
Chlorine gas, so liquid bromination is less likely
to be a ventilation hazard. Due to difculty in
availability of liquid and dry Bromine in India,
bromination is not yet practised in India. Liquid
Bromine and Bromochlorodimethylhydantoin
DECEMBER 2012 20
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
tablets in dry form are used for Bromine treatment
of pool water.
Liquid Bromine : Water is bubbled through
Bromine liquid for dozing. Equipment is relatively
economical and simpler to operate. It is nasty to
handle and as obnoxious as Chlorine, similar risk
to operator and bather from dangerous fumes. It
attacks all metal, therefore it is stored in glass, glass
reinforced plastic or plastics fail safe containers.
Dry Bromine Tablet : It is safer and more
convenient but still more expensive and not yet
widely available. Bromine residual in the range of
2-4 mg/l for private pool and 4-6 mg/l for public
pool shall be maintained. Dimethylhydantoin
remains in water after the treatment. The
Department of Environment recommends that the
level of dimethylhydantoin should not exceed 200
mg/l. (1).
(b) Iodine
It is stable and safe to handle, and can be
easily stored. It can be dispensed into pool
water easily and economically. Iodamines are
not formed and algaecide support is required.
Most modern algaecide are incompetent with
iodine, therefore intermittent super chlorination
is necessary. Iodine ion is not an effective
bactericide. It doesnt contribute taste or odour
to pool water and, therefore doesnt cause eye
irritation. However, iodine ion can be converted
into molecular iodine with chlorine and can be
reused for several times.
It attacks most of the metal, but other side
reactions are less than the chlorine. Greenish tint
is noticeable between 2-5 ppm at pH 7.5. Difculty
can be experienced in maintaining the required
and total concentration. Not popularly used in
abroad and not at all in India.
3. Ozone
Ozone gas is manufactured by an expensive
sophisticated system. It is unstable and an
allotropic form of oxygen, where third atom
readily detaches to become a powerful oxidizing
agent. It is 10 to 20 times more powerful than
chlorine to inactivate bacteria, viruses, cysts and
spores, removes colour, taste and smell. It is fast
acting, very effective, non selective and does not
produce unwanted byproducts common with
other oxidants. A slight excess of ozone in pool
water produces a redox potential + 800 V @ pH
7.5 and destroys bacteria within few seconds.
Since ozone has short half-life and decomposes
rapidly, it must be generated at site by the ozone
generators.
Ozone is dozed to the pool either directly to the
circulation system or into small portion of water
passing through a circulation system. Ozonization
of water is without and with deozonization system.
In the rst system, ozone is dozed in such a way
that the level of ozone remaining in the water,
when re-entering the pool, does not exceed 0.05
mg/l. In the second system, 0.8 to 1.0 mg/l ozone
is dosed into the water and a contact period of 1
to 2 minutes is provided. After the contact period,
ozone is completely removed by passing water
through deozonizing medium (activated carbon)
before returning to pool. To ensure residual
disinfectant in pool water, ozone has to be used
in conjunction with chlorine. Normally 0.2 to 0.3
ppm chlorine with marginal hypochlorination is
sufcient because all oxidizable organic matter is
already been oxidized.
Ozone is a dangerous chemical in the air and
highly corrosive to metals. Approximately 1
ppm of ozone induces headache and tightness in
DECEMBER 2012 21
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
the chest. To a more graving situation, 20 ppm
nearly kills. Discharge tubes must be kept efcient
to prevent runaway cost of ozone production.
Ozonator system should include safety alarms
to operate at 0.1 ppm. Continuous dry airow
ensures quick removal of ozone and prevents
any moisture build up in the pools humid
atmosphere. An Ozonator is costly and takes
major share of the pool cost. Further, addition of
deozonization system plus chlorine dozing and
controlling system exaggerates the costing of
ozonator. It is yet to become popular for Indian
swimming pool.
4. Metal Ion Generators
Metal Ion Generators are electrolytic devices
installed into the pool circulation system. These
devices introduce silver and copper ions into the
pool water. Silver and copper ions are known
for bactericidal effect. There are number of such
systems available in the market, which are based
on the same principle, however their design
and practical conditions vary. For example,
certain but not all generators are used with
secondary form of disinfectant such as chlorine.
It makes it difcult to standardize operation of
a metal generator. For Indian pools, secondary
disinfectant is must to counteract heavy organic
load in the pool.
5. Alternative Disinfection Systems & Chemicals
(a) Ultraviolet Light
Ultraviolet light is a potent disinfectant to
ensure 100% sterilization. UV lamps can be
placed with 100 mm of maximum water ow
depth. Also, fast turnover is must. It does not
provide any residual disinfectant and does not
oxidize organic matter in pool. Therefore, it is
to be used only in conjunction with secondary
disinfectant that shall be maintained always at
the desired level. Initial cost of equipment is
high and operation cost is low. It may be suitable
only for small family pool.
(b) Organic Biocides
Organic biocide is a synthetic organic microbiocide
and algaecide, safe and stable; offers long-term
residual, clear, tasteless and non-odourous, nonbleaching and neutral pH. It is incompatible with
chlorine, therefore chlorine is to be removed and
pH is to be adjusted to 7.5 before its application.
Recommended dose varies from 10 to 50 ppm. It
fails to produce crystal clear bright water. Water
may become greenish when pH is not neutral.
They do not have oxidizing properties and
therefore are normally to be used along with an
oxidizing agent.
(c) Chlorine Dioxide
Soluble chlorine dioxide is produced by
automatically drawing solution of sodium chlorite
and hydrochloric acid solution from two different
containers by the following reaction:
5NaClO2+ 4HCl = 4ClO2+ 5NaCl + 2H2O
Often some chlorine is produced. It has no taste,
no smell, offers no eye or skin irritation, can be
easily and safely used. A minimum of 0.1 ppm
residual is required with 0.3 acceptable. A trained
personnel is required to operate.
There are many alternatives tried for disinfection.
However, chlorine and its compounds are used in
most of the swimming pools for its cost, availability
and simplicity.
Algae Control
Algae growth is most undesirable in pool due
to safety risks, aesthetic look and also as it
imparts bad taste and odour to the pool water.
Following are the common forms of algae in the
pool water :
a. Suspended growth - pool water is greenish or
milky and causes chocking of lter that
ultimately needs more backwashing
b. Attached growth on to the wall - making pool
surface slippery and ugly
c. Black algae patches rmly attached to the pool
wall (especially it grows between the joints of
the tiles) as a result of symbiotic relationship of
algae with fungi.
Algae contain chlorophyll and other pigments
to make use of solar energy, and need nitrogen,
carbon hydrogen, oxygen and sunlight for growth
in pool water. Algae spores exist in the air all the
time. A low pH is conducive to algae growth, and
a rising pH indicates that algae are growing fast in
pool. Pool water becomes greenish and clarity of
water diminishes. There are many causes for algal
bloom in pool water; some of them can be listed as
below to understand means of algal control.
DECEMBER 2012 22
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
a. Intense sun light and warm weather
b. Poor ltration and longer turnover time
c. Poor water circulation causing dead spots in
the pool where disinfectant level is zero
d. Inadequate disinfectant
e. Addition of nitrogen and organic impurities
by bathers and surrounding environment, and
from chemical compound binders present in
some of the disinfectants
Proper disinfectant level, monitoring pool water
quality, regular backwashing of lter, running
the lter for given turnover time, regular suction
sweeping, cleaning of pool walls and better
hygienic conditions etc., are preventive measures
to avoid algal growth in pool. Intermittent
super-chlorination or addition of oxidizing
agent removes or breaks down nitrogenous and
organic impurities that deny ever present algae
the opportunity to thrive. Shock chlorination
deters quite severe attack however for black algae
it may require large quantity of chlorine and
blocks the lter due to dead organism. Copper
sulphate wipes out algae but causes black stains.
Mercury compounds are active but accumulate
dangerously. Quats are excellent to control but the
dose excess than 50 ppm causes froth and foam
in the pool water. Many synthetic algaecides are
available in the market. However care has to be
taken in the selection of algaecide and its doses
to ensure that there is no adverse and toxicity
effect on the swimmer. It is always better to avoid
usage of these unknown chemicals. Strict control
and vigilance is must to avoid algal growth in the
pool, otherwise in a severe algal bloom, pool is to
be emptied, cleaned and relled again with fresh
water.
Pool Water Quality
Pool water quality is dened by physical,
chemical, bacteriological and biological standards.
Specications of Indian Standards and SPATA for
swimming pool water are given in Table-1. The
maintenance of these standards is very essential
to ensure health and comfort of bathers, and to
minimize the risk to cause damage to the pool
ttings and the equipments. Parameters like pH,
clarity, alkalinity, hardness and desired doses
of disinfectant etc play important role to get the
desired quality of water.
Operation & Maintenance
No matter how beautiful the shape of a pool, the
type of system selected and whether manually or
automatically operated, water quality of a pool
is nally decided by the pool operator. Only a
trained and qualied pool operator shall operate
the pool. However, it is not normally so. Often, the
operator adds chemicals to the pool water without
having understood the chemical characteristics
and the after effects. For example, to control the
algae and to have blue tint to the water, a dose of
copper sulfate to the level of 10 ppm is added to
the pool, which is toxic if ingested.
Table 1 : Quality Standards for Water Quality for Swimming Pool
Sr. No.
Characteristic
IS: 3328-1965 (2)
SPATA 1990 (3)
i)
Ph
7.5 to 8.5
7.2 to 7.8
ii)
Total alkalinity (as CaCO3), mg/l
50 to 500
100 to 200
iii)
Aluminum (as Al), mg/l, Max
0.1
iv)
Total residual chlorine, mg/l
(a) At inlet
(b) At outlet
0.5 Max
0.2 Max
0.5-2.0
(Depends on type of
disinfectant used)
v)
Oxygen absorbed in 4 hour at 27 oC, mg/l, Max
1.0
vi)
Total hardness
50 to 500
Less than 400
> 200/ml
>10/100 ml
>100/ml
Nil
vii)
Sulphate
viii)
Bacteriological
(a) Standard plate count
(b) Coliform organisms, MPN index
ix)
Clarity
Clear & colourless
Deepest part shall be
clearly visible, free from
suspended matter
x)
Odour
Absent
Absent
DECEMBER 2012 23
INDIAN PLUMBING TODAY COVER STORY
Conclusion
Swimming pool is not a simple water tank to be
lled with water. In designing a pool, problems
associated with water must be clearly understood.
A proper water circulation system to eliminate
dead spots in the pool, correct turnover time, right
type of ltration system and the most suitable
disinfectant and its adequate dose, regular
monitoring of water quality can assure sparkling,
crystal clear and safer than drinking water in
swimming pool. The system shall be always userfriendly. The operator should know the preventive
and control measures. IPT
References
1. The Treatment & Quality of Swimming Pool Water,
Department of Environment, National Water Council, U.K.
2. Indian Standards Quality Tolerance for Water For Swimming
Pool, Bureau of Indian
3. SPATA Standards for Swimming Pool Vol. & Vol. 2,
Swimming Pool & Allied Trade Association Ltd, U.K.
4. SPATA Standards for Swimming Pools Water & Chemicals,
Swimming Pool & Allied Trade Association Ltd, U.K.
5. John Daves, Handbook Design & Planning of Swimming
Pool, The Institute of Swimming Pool Engineers, U.K.
Editorial Note: The Indian Plumbing Association (IPA)
and the International Association of Plumbing and
Mechanical Ofcials India (IAPMO- I) have jointly
published the Uniform Swimming Pool Code India 2011
which may be referred to for additional information on
Swimming Pool Designs.
Prof. R. V. Saraf is the Founder Chairman of Viraj
Envirozing India Pvt. Ltd., a Pune-based company
providing one window solution to environment. He
has done M.Sc. in Biochemistry; AMIE in Chemical
Engineering; and M.Sc. in Environmental Control
Engineering & Resource Utilisation from UK.
He has 40 years of experience with more than 1000 successful projects to his
credit, including 300 swimming pools. He is a Life Fellow of the Institution of
Engineers India and a Life Member of Indian Association of Environmental
Management. He can be contacted at watersgs@vsnl.net
DECEMBER 2012 24
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Koi Pond BeginnersDocumento20 pagineKoi Pond BeginnersjackNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: How Do We Clean Polluted Water?Documento15 pagineLesson Plan: How Do We Clean Polluted Water?Tarun MattaparthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips of Fountain Design Part 1 - 3 - Blog of Fountain Design and Water ShowsDocumento3 pagineTips of Fountain Design Part 1 - 3 - Blog of Fountain Design and Water ShowsAnh Đức NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pool Water ChemistryDocumento34 paginePool Water ChemistryRoman MangalindanNessuna valutazione finora
- BIONICS - DR - Parameswari. PHD Agri., Bionics Enviro Tech, NanozymeDocumento26 pagineBIONICS - DR - Parameswari. PHD Agri., Bionics Enviro Tech, NanozymeK SASIKUMAR100% (1)
- Air Reverse OsmosisDocumento12 pagineAir Reverse Osmosisirdawan100% (2)
- Lab DI Water Systems Guide - Filtration, RO, Resin Filters ExplainedDocumento6 pagineLab DI Water Systems Guide - Filtration, RO, Resin Filters ExplainedHaidee Che RizminNessuna valutazione finora
- Chillers - CatalogDocumento2 pagineChillers - Catalogdéborah_rosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Industrial WastewaterDocumento42 pagineTreatment of Industrial WastewaterchanlalNessuna valutazione finora
- Drinking Water SolutionsDocumento16 pagineDrinking Water SolutionsLiviu SomesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Advanced Water Treatment Using Microbubbles - Pan Li - 2006Documento149 pagineDevelopment of Advanced Water Treatment Using Microbubbles - Pan Li - 2006cristian muozNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Paper "Advanced Water Treatment"Documento1 paginaReaction Paper "Advanced Water Treatment"CharisseElaineDionisioNessuna valutazione finora
- Wastewater IrrigationDocumento28 pagineWastewater IrrigationZindai WazirNessuna valutazione finora
- 500 LPH UF Plant BOQDocumento6 pagine500 LPH UF Plant BOQSimbu ArasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Filter - BrochureDocumento4 paginePressure Filter - BrochureLTE002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Filtration Process DescriptionDocumento4 pagineFiltration Process DescriptionJoy Das MahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- MEMBRANE PROCESSES: FILTRATION, APPLICATIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONDocumento35 pagineMEMBRANE PROCESSES: FILTRATION, APPLICATIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONArie Ikhwan SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Cum - DayDocumento5 pagine10 Cum - DayAbhijit MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Algal Origin and DiversityDocumento18 pagineAlgal Origin and DiversityArunchand RayarothNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems of Drinking Water in Rural AreaDocumento14 pagineProblems of Drinking Water in Rural AreaRoumyadeep ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Swimming Pool Sanitation Conservation FlourideDocumento9 pagineSwimming Pool Sanitation Conservation FlourideHarshal SabaneNessuna valutazione finora
- محاضرات امدادات المياه - الكورس الاولDocumento146 pagineمحاضرات امدادات المياه - الكورس الاولمحمد حيدر هاشم زبون100% (1)
- Importance of Water ConservationDocumento1 paginaImportance of Water ConservationYuvraj KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enpro Project ReportDocumento51 pagineEnpro Project ReportYadav VirendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Digestion Water TreatmentDocumento2 pagineAdvance Digestion Water TreatmentRashesh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Asws Reverse Osmosis PlantDocumento7 pagineAsws Reverse Osmosis PlantEngenharia MecânicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tube Settler Application in 40 CharactersDocumento10 pagineTube Settler Application in 40 CharactersIlu SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Philips UV Technology BrochureDocumento16 paginePhilips UV Technology BrochurevaglohrdNessuna valutazione finora
- Antioxidant Activity of Some Morrocan Hydrosols PDFDocumento9 pagineAntioxidant Activity of Some Morrocan Hydrosols PDFSmail FreeManNessuna valutazione finora
- Production of Single Cell Protein From Orange PeelDocumento5 pagineProduction of Single Cell Protein From Orange PeelHarish Kasam100% (1)
- Swimming Pool Water Treatment Basics B1i1 enDocumento7 pagineSwimming Pool Water Treatment Basics B1i1 enMislav PerinNessuna valutazione finora
- CVEN9857 - Wastewater Treatment 1Documento29 pagineCVEN9857 - Wastewater Treatment 1onlynameNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3 Arvia Water TreatmentDocumento24 pagineExperiment 3 Arvia Water TreatmentBrendaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Sand FiltrationDocumento16 pagineRapid Sand FiltrationNurul ShafinazNessuna valutazione finora
- SVI AnalysisDocumento2 pagineSVI AnalysisenviroashNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorine Dosing PumpDocumento24 pagineChlorine Dosing PumpByron HisseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Is A Water Purification Process That Uses ADocumento12 pagineReverse Osmosis (RO) Is A Water Purification Process That Uses Amulenga lubemba100% (1)
- Microfiltration 141003025053 Phpapp01Documento8 pagineMicrofiltration 141003025053 Phpapp01Aminatu JuriahNessuna valutazione finora
- SCP as Dietary Supplement: Neutraceutical SurveyDocumento20 pagineSCP as Dietary Supplement: Neutraceutical SurveyStephen MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Treatment Process - Objectives & Methods of Water Treatment ProcessDocumento5 pagineWater Treatment Process - Objectives & Methods of Water Treatment ProcesstefovNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Overview of Drinking Water TreatmentDocumento36 pagine02 Overview of Drinking Water TreatmentCharlie CB PortnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Research: Wisconsin Department of Natural ResourcesDocumento20 pagineResearch: Wisconsin Department of Natural ResourcesFrancoGarbarinoRiffoNessuna valutazione finora
- Southern Peel Common 2008Documento6 pagineSouthern Peel Common 2008mrjimmyjamNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Treatment Plant: MD - ShamsuzzamanDocumento11 pagineSewage Treatment Plant: MD - Shamsuzzamanapi-3701567100% (3)
- DesignDocumento3 pagineDesigntata_77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disinfection Methods for Water TreatmentDocumento6 pagineDisinfection Methods for Water TreatmentAriff JasniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra Pure WaterDocumento6 pagineUltra Pure Watergauravgarg115Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stages Water Treatment ProcessDocumento2 pagineStages Water Treatment Processglo lipaodNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikDocumento6 pagineField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, NashikMarmik Javare100% (1)
- Water Treatment Plant With RO For Mineral Water Rahul VKDocumento13 pagineWater Treatment Plant With RO For Mineral Water Rahul VKRahul Khedkar100% (1)
- Reverse Osmosis State of The Art in IndonesiaDocumento16 pagineReverse Osmosis State of The Art in IndonesiachrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimum Design of Reverse Osmosis System Under Different Feed Concentration and Product SpecificationDocumento11 pagineOptimum Design of Reverse Osmosis System Under Different Feed Concentration and Product SpecificationPatricio LeonardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Package Type STPDocumento4 paginePackage Type STPjeykumar.BalannairNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Cell Protein Production A Review PDFDocumento12 pagineSingle Cell Protein Production A Review PDFseharNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua BaseDocumento8 pagineAqua BasejpfamiliabNessuna valutazione finora
- Treating Water Through Coagulation, Sedimentation, Filtration and DisinfectionDocumento21 pagineTreating Water Through Coagulation, Sedimentation, Filtration and DisinfectionGani AbdilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Drinking Water Sludge Recovery Feb 2011Documento2 pagineDrinking Water Sludge Recovery Feb 2011Fernando GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- No-Fluff Swimming Pool Maintenance Guide for Beginners: Easy Steps to Maintain Water Chemistry, Eliminate Algae and Keep Your Pool SparklingDa EverandNo-Fluff Swimming Pool Maintenance Guide for Beginners: Easy Steps to Maintain Water Chemistry, Eliminate Algae and Keep Your Pool SparklingNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Piping Design Basis DocumentDocumento25 pagineStandard Piping Design Basis DocumentMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- DR014 LAB Feedwater-Suctionline Pipe Routing RequirementsDocumento4 pagineDR014 LAB Feedwater-Suctionline Pipe Routing RequirementsMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- DR008 - Earthing of PipingDocumento3 pagineDR008 - Earthing of PipingMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel PhaseDocumento174 pagineSteel PhasechopkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Spring SupportsDocumento12 pagineVariable Spring SupportsMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSYS TutorialDocumento44 pagineANSYS Tutorialsauravc88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens piping slope requirementsDocumento4 pagineSiemens piping slope requirementsMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Ut Referance NotesDocumento164 pagineUt Referance NotesRaja BoopathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Aspects of Steam GeneratorsDocumento12 pagineDesign Aspects of Steam GeneratorsMadhan Raj100% (1)
- DR008 - Earthing of PipingDocumento3 pagineDR008 - Earthing of PipingMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Cleaning ProcedureDocumento6 pagineAcid Cleaning ProcedureMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Floating ProcedureDocumento5 paginePiping Floating ProcedureMadhan Raj50% (2)
- ANSYS TutorialDocumento44 pagineANSYS Tutorialsauravc88Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of Standards: Si - No Description Drawing NoDocumento2 pagineList of Standards: Si - No Description Drawing NoMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- BoilerDocumento29 pagineBoilerMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Trunnion Calculation 0193 - 001Documento9 pagineTrunnion Calculation 0193 - 001Madhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Outokumpu Duplex Stainless Steel Data SheetDocumento12 pagineOutokumpu Duplex Stainless Steel Data SheetbayumahardikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lump MassDocumento10 pagineLump Masspkshrawal1976Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDocumento41 pagineShell and Tube Heat Exchanger DesignAhmad Budiman100% (2)
- M 120Documento40 pagineM 120ilkinNessuna valutazione finora
- Black Liquor Recovery - How Does It WorkDocumento7 pagineBlack Liquor Recovery - How Does It Workmancini10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design Calc Saud It SampleDocumento25 pagineDesign Calc Saud It SampleglazetmNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Drying of PulpsDocumento8 pagine10 Drying of PulpsMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Black Liquor Recovery - How Does It WorkDocumento7 pagineBlack Liquor Recovery - How Does It Workmancini10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Boilers PDFDocumento5 pagineTypes of Boilers PDFJosé RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Code for Public Swimming PoolsDocumento18 pagineSafety Code for Public Swimming PoolsAditi Bansal100% (5)
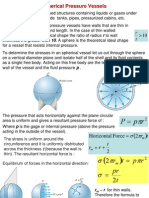
- Pressure VesselDocumento32 paginePressure VesselYonjon SubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration Control of A Traveling Suspended SystemDocumento8 pagineVibration Control of A Traveling Suspended SystemMadhan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Quality Management of Swimming Pool PDFDocumento11 pagineWater Quality Management of Swimming Pool PDFMadhan Raj100% (1)
- Swimming Pool DesignDocumento49 pagineSwimming Pool Designcashlover100% (1)
- Metatron AustraliaDocumento11 pagineMetatron AustraliaMetatron AustraliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessDocumento7 pagineEvoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessKenny AlphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Apola Ose-Otura (Popoola PDFDocumento2 pagineApola Ose-Otura (Popoola PDFHowe JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsDocumento14 pagine13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsWillSmathNessuna valutazione finora
- Restructuring ScenariosDocumento57 pagineRestructuring ScenariosEmir KarabegovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Otis, Elisha Graves REPORTDocumento7 pagineOtis, Elisha Graves REPORTrmcclary76Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 WORD White Paper TemplateDocumento4 pagine2009 WORD White Paper Templateomegalpha777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jharkhand VAT Rules 2006Documento53 pagineJharkhand VAT Rules 2006Krushna MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- ESS 4104 AssignmentDocumento9 pagineESS 4104 AssignmentSamlall RabindranauthNessuna valutazione finora
- Mech Course HandbookDocumento20 pagineMech Course Handbookbrody lubkeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Modulo InglesDocumento8 pagineModulo InglesJames Mosquera GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- REBECCA SOLNIT, Wanderlust. A History of WalkingDocumento23 pagineREBECCA SOLNIT, Wanderlust. A History of WalkingAndreaAurora BarberoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ramesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesDocumento11 pagineRamesh Dargond Shine Commerce Classes NotesRajath KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Short EssayDocumento3 pagineShort EssayBlue PuppyNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 1Documento2 pagineCase Study 1Diana Therese CuadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Challan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFDocumento1 paginaChallan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFsaleem_hazim100% (1)
- Chrome Settings For CameraDocumento6 pagineChrome Settings For CameraDeep BhanushaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocumento25 pagineCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Music Forms ExplainedDocumento11 pagineClassical Music Forms Explainedcorinna_harrison100% (1)
- Soal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISDocumento59 pagineSoal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISsdn6waykhilauNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Estate Marketing Agent Registration Form: Important InstructionsDocumento7 pagineReal Estate Marketing Agent Registration Form: Important InstructionsAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- DDAL05-02 The Black RoadDocumento45 pagineDDAL05-02 The Black Roadlpokm100% (1)
- SWSP6033 00 2022T3 V1.0-1Documento14 pagineSWSP6033 00 2022T3 V1.0-1ayman.abaidallah1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Documento57 pagineMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Shabanito GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ra 1425 Rizal LawDocumento7 pagineRa 1425 Rizal LawJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoNessuna valutazione finora
- 8086 ProgramsDocumento61 pagine8086 ProgramsBmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaflet STP2025 LightDocumento2 pagineLeaflet STP2025 LightNoel AjocNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 Fourier Series & Integral: 2130002 - Advanced Engineering MathematicsDocumento143 pagineUnit-2 Fourier Series & Integral: 2130002 - Advanced Engineering MathematicsDarji DhrutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Geller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Documento27 pagineGeller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Miguel AntónioNessuna valutazione finora
- The Voice of PLC 1101Documento6 pagineThe Voice of PLC 1101The Plymouth Laryngectomy ClubNessuna valutazione finora