Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Irjet V2i288
Caricato da
MagibalanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Irjet V2i288
Caricato da
MagibalanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 02 Issue: 02 | May-2015
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
Static and dynamic behavior of Jute reinforced epoxy composites with
and without Silicon Di oxide as epoxy modifier: A Review
Vikas S Hoysala1, Dr Kiran Kumar.P2, Prof T. Madhusudhan3
1Mechanical
Department, M.Tech student, Machine Design, SJBIT, Bangalore, India.
Department, Professor, SJBIT, Bangalore, India.
3Mechanical Department, H.O.D, SJBIT, Bangalore, India.
---------------------------------------------------------------------***--------------------------------------------------------------------2Mechanical
Abstract- In recent days many of the researchers are
attracted to the natural fibers due to their potential to
replace synthetic fibers in many primary applications
(wind turbine blades, beams etc.) and unique
properties such as low density, good specific properties
compared to synthetic fiber. In this present work
similar attempt is made to study the effect of Silicon Di
oxide as filler on the dynamic behavior of the jute fiber
reinforced epoxy composites, so that we can go a step
closer in replacing synthetic fibers by natural fibers in
primary applications. The dynamic behavior of the
material refers to the natural frequency, damping and
mode shapes of the material. The dynamic behavior is
obtained for Jute epoxy woven composites with filler
and without filler and they are compared. SiO2 or silica
is selected as secondary reinforcement or filler as it is
easily available and also increases the flexural and
tensile modulus of the FRP composites.
Key Words: Composite materials, Dynamic behavior,
silicon dioxide, primary applications, Natural fibers.
1. INTRODUCTION
A composite is when two or more different materials are
combined together to create a material having unique and
superior properties, which is impossible to get from
individual materials. The constituents are combined at
macroscopic level and are not soluble in each other. One
constituent is called as Matrix phase and the other is called
Reinforcing phase. When designed properly, the new
combined material exhibits better strength than would
each individual material. The composites can be classified
based on the reinforcing and the matrix materials. They
strength of these natural fiber reinforced composites are
also influenced by the resin and secondary reinforcing
phase used.
2015, IRJET.NET- All Rights Reserved
1.1 Reinforcing Phase
Reinforcing phase may be in form of fibers or flakes or
particulates. Considering fiber reinforcement, natural
fibers and synthetic fibers are one of the divisions of the
reinforcing phase of the composites. As the name indicates
that these natural fibers are available in nature either
from plant or animals (EX: bark of a tree or wool from
sheep).They have good specific properties than synthetic
fibers thus making it very good competitors for the
synthetic fibers. Further they are bio degradable and can
easily be disposed. India and Bangladesh are one of the
larger producers of Jute. They are peeled from the bark of
the plant and then washed and dried in air; jute is one of
the major plant fibers which can be used for various
applications when used as composite material.
1.2 Matrix
This is one of the important parts of FRP composites. It is
used to hold the fibers together and form a strong bond
with each other. The matrix phase used is mostly
thermosetting in nature. Matrix phase consists of a resin
and a hardener, addition of this hardener causes the resin
to cure and become hard thus making it a rigid material.
The curing of the composites depends on the hardener
used (High temperature curing or room temperature
curing)
1.3 Secondary Reinforcing Phase
These are also called as filler materials used to improve
the strength in the composite materials. They improve the
mechanical properties of the composite material, thus
obtaining a material required for a particular application.
1.4 Dynamic Behavior
Dynamic behavior of the material is defined by 3
parameters natural frequency, mode shapes and damping
factor. Natural frequency is the frequency at which a
system tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving or
damping force. At a particular frequency the dynamic
Page 480
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 02 Issue: 02 | May-2015
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
response of the plates or the structure is high and then it
decreases, again at some particular higher frequency the
same response is obtained, these keeps on continuing. The
frequencies at which dynamic response of the structures
are maximum are called as the natural frequencies and
these different natural frequencies of the same material
represent different modes of vibration.
Damping is the property of the material to resist
oscillations or vibrations.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
The use of natural fibers is increasing due to its unique
properties. They are easily available and can easily be
used as the reinforcing phase without much processing
compared to synthetic fibers and have good specific
properties.
Reliability of the composites were investigated by
Manuel Chiachio, et al,[1] wherein they focused on
reliability based design and safety factor calibration,
where reliability calculations are crucial. Thus, a
composite can be used for wide range of applications.
A research has been carried by P. Parandaman et
al,.[2] and has analyzed the effect of the retrofitted FRP
composites structures with concrete beams to provide
good performance. The thickness of the FRP material used
is 6mm thick. FRP materials used are GFRP, CFRP and
KFRP. The performance of the retrofitted beam with FRP
increases than without retrofitting.
Dipl. Phys. Michael Karus, et al.,[3] has
surveyed the use of natural fibers in automotive sectors
and have found that demand is increasing day by day. We
can also see the importance of compression molded parts.
Major automotive suppliers make the most substantial
contribution to the use of natural fibers for composites.
For the future, one can expect other models in other
vehicle segments and means of transport (e.g. small cars,
trucks, trains), as well as in other European countries, to
be fitted with natural fiber press-molded parts.
Anin Memon,et al.,[4] has carried out
experimental work on fabrication of jute reinforced
composite using compression molding. Impregnation
quality and dispersion of fiber bundle were increased with
increasing the molding temperature, as molding
temperature increased the tensile strength reduced due to
the deterioration of jute fiber. Thus, molding temperature
affects the mechanical properties of the jute fibers. It also
depends on the resin used.
Md. Rashnal Hossain.et al.,[5] has studied
behavior of environment friendly jute epoxy laminated
composite due to its superior specific properties
compared to manmade synthetic fibers like glass, Kevlar,
asbestos, etc. The developed composites were
characterized by tensile and three point bend tests.
Experimental results revealed that the tensile properties
of the developed composites are strongly dependent on
the tensile strength of jute fibers.
2015, IRJET.NET- All Rights Reserved
Another research conducted by A. Ticoalu, et
al,[6] has highlighted that natural fibers are suitable for
load bearing materials such as roofs and beams. If the
materials have tensile strength more than 50Mpa they can
be used in roofs. Furthermore, for infrastructure
applications where the use of synthetic fibers is not
suitable, natural fibers can be a suitable substitute. Jute
mats reinforced composites have been used for trenchless
rehabilitation of underground drain pipes and water
pipes. Availability of fibers is also an important parameter
for mass production.
G.M. Arifuzzaman Khan, et al.,[7] has conducted
mechanical properties of woven jute fabric reinforced
poly(L-lactic acid) composites. Woven jute composites in
warp and weft directions presented superior mechanical
properties than non-woven jute fabric (NWJF) composites.
The influence of woven structure and direction on the
properties such as tensile, flexural and impact properties
was investigated. Finally, it can be concluded that PLLA
based woven jute fabric composites might be a good
alternate of synthetic fiber composites and are suitable for
high load bearing applications.
Vivek Mishra et al,.[8] has carried out an
investigation on bi directional jute fiber, a natural fiber
abundantly available in India. The minimum and
maximum void content are in neat epoxy and 12 wt. %
fiber loading specimens respectively. It is also found from
the study that the void content decreases with the increase
in fiber loading. The hardness, tensile properties and
impact strength of the jute-epoxy composites increases
with the increase in fiber loading. Flexural strength and
inter-laminar shear strength are greatly influenced by the
void content.
Ajith Gopinath et al, [9] has investigated and
compared the mechanical properties of woven jute fiber
with both epoxy and polyster resin. The prepared
composites were tested to study the mechanical
properties of the composite such as tensile, flexural,
impact strength and hardness. The jute reinforced epoxy
composite exhibited better mechanical properties than
Jute-polyester composite.
Darshil U. Shah et al,.[10] has investigated the
use of flax fiber in rotor blade and has compared it with
glass fiber rotor blade. Flax fibers are 10%lighter than the
glass fiber. It is also concluded that flax is a potential
structural replacement to E-glass for similar composite
small wind turbine blade applications. However flax fibers
are very expensive (almost 3 times than that of E-glass
fibers).
Another research has been successfully carried
out by S.Prabhakaran et al, [11] on vibrational behavior
of natural fibers. When the composites are used in higher
applications, dynamic loads acts on the composites
causing vibrations, this further causes the micro cracks to
grow and further leads to failure. Hence, vibrational
behavior of the materials is of utmost importance. The
vibrational behavior of the Flax and glass fibers are
Page 481
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 02 Issue: 02 | May-2015
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
compared and is found that flax fiber reinforced
composites have 51.03% higher vibration damping than
the glass fiber reinforced composites.
A study conducted by Andrzej K. Bledzki et al,
[12] have tabulated the values of different plant fibers and
compared it with glass fibers. The tensile strength and the
Youngs modulus of the synthetic fibers are visibly much
higher than that of the natural fibers. However, the
difference in the specific values of synthetic and natural
fiber, most important with respect to applications, is not
as great. Jute and flax have similar and better mechanical
properties compared to other natural fibers .Further the
jute fibers are less dense than flax.
In this work experimental investigation is carried
out by K. Senthil Kumar, et al [13] on free vibration
characteristics of short sisal fiber (SFPC) and short banana
fiber (BFPC) polyester composites and is found that 50:50
ratio of resin and fiber volume fraction gives good result.
Further length of the fibers is also considered. Damping
nature of the fibers is also studied.
The investigation carried on mechanical
properties, odor emission and structure properties of
abacca, jute and flax fibers by A. K. Bledzki et al, [14]
reveals that jute is found to have superior tensile and
flexural modulus than the other two.
Nattakan Soykeabkaew et al,.[15] has
successfully prepared starch-based batters incorporating
jute, flax fibers inside a hot mold. Compared to flax, jute
had more reinforcing effect (observed from the SEM
photographs) than flax fibers.
Based on the survey carried out by government of
India [16]. The availability of jute fiber is more than flax
fibers (.5 million tons). Global production (2.5 million
tons) of jute is more than any other natural fiber (except
cotton).More importance of developing jute composites
should be considered.
According to M.Sivapragash et al. [17] plant
fiber (jute) has been found to be a versatile material for
application in rural areas to high tech applications. Use of
these fibers saves environment and also reduces the
energy consumption which is required in processing manmade fibers. It is also coated that more research has to be
carried out on the natural fibers to avoid any set back
during the finalization from lab scale to commercial level.
Further modifying the resin by an appropriate
modifier or filler can increase the mechanical properties of
the composite materials. Ramesh K. Nayak, et al. [18] has
modified the epoxy matrix by Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2 micro
particles in glass fiber/epoxy composite to improve the
mechanical properties. It is observed that mechanical
properties like inter lamina shear strength, flexural
strength and modulus are more in case of SiO2 modified
epoxy composite compare to other micro modifiers.
Impact strength is more in case of Al2O3.
The addition of SiO2 increased the tensile, flexural
strength and hardness of glass epoxy composite as
investigated by Ramesh Chandra yadav, et al. [19].
2015, IRJET.NET- All Rights Reserved
Silicon Di Oxide is added to the composite based on the
weight of the epoxy (0%, 5%, 10% etc.).As the filler
content increased the Youngs modulus also increased,
even flexural modulus also increased up to 10%of the filler
content and after 10% the flexural modulus decreased.
Hence the filler percentage selected should be within 10%
of the weight of the epoxy.
A research carried is out by Sharayu U.
Ratnaparkhi, et al. [20] on dynamic behavior by
fabricating a glass epoxy composite of thickness less than
7mm. The Resin: Fiber ratio is 50:50.The length of the
specimen used is 25cm.
3. CONCLUSIONS
The reviews show that there is lot of research work going
on in natural fibers due to the increasing demand of the
environmental friendly composite materials and also for
their dynamic behavior. The following may be concluded
based on this review.
Natural fibers have good specific properties than
synthetic fibers which are used in applications
Jute availabity is high in India and thus can be
used for mass production.
Woven jute fibers have good strength than nonwoven jute fibers and can be used for load
carrying applications. It can also be used in
primary applications
Epoxy resin is better choice of resin to be used.
Usually when the materials are used for higher
applications many dynamic loads acts on the
structures these loads are very different from the
static loads, thus various parameters are to be
considered while analyzing these structures, and
the important parameters are vibrational
behavior, damping characteristics. The unwanted
vibrations cause the micro cracks to grow within
the material and thus leading to failure.
As the Sio2 increases the tensile and flexural
modulus, investigations have to be carried out to
improve the dynamic behavior of the composites.
Damping is also important parameter as it offers
resistance to vibration. So, effect of SiO2 on
damping is also important.
Dynamic behavior of composites is very
important when they are used in primary
applications. However the research on effect of
filler materials on Dynamic behavior is still at its
beginning.
Dynamic characteristics depend on many
parameters such as fiber orientation, fiber volume
fraction etc. it also depends on mechanical
properties such as youngs and flexural modulus.
Page 482
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 02 Issue: 02 | May-2015
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors sincerely thank and acknowledge the support
provided by the principal and management of SJBIT
Bangalore.
[10]
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
Manuel Chiachio, Juan Chiachio, Guillermo Rus
Reliability In Composites A Selective Review And
Survey Of Current Development Dept. Structural
Mechanics and Hydraulic Engineering, University
of Granada. Composites: Part B 43 (2012) 902
913
P. Parandaman and M. Jayaraman, Finite Element
Analysis Of Reinforced Concrete Beam Retrofitted
With Different Fiber Composites Department of
Mechanical Engineering, Velalar College of
Engineering & Technology, Erode, Tamil Nadu,
India
Dipl. Phys. Michael Karus, Dr. rer. pol. Markus
Kaup und Dipl. Econ. Sven Ortmann, Use Of
Natural Fibres In Composites In The German And
Austrian Automotive Industry Market Survey
2002: Status, Analysis and Trends
Anin Memona, Asami Nakaib Fabrication And
Mechanical Properties Of Jute Spun Yarn/Pla
Unidirection Composite By Compression Molding,
Department of Advanced Fibro-Science, Kyoto
Institute of Technology,Matsugasaki, Sakyo-ku,
Kyoto, 606-8585, JAPAN
Md. Rashnal Hossain, Md. Aminul Islam, Aart Van
Vuurea, Ignaas Verpoest Tensile Behavior Of
Environment Friendly Jute Epoxy Laminated
Composite, 5th BSME International Conference
on Thermal Engineering
A. Ticoalu, T. Aravinthan & F. Cardona A Review
Of Current Development In Natural Fiber
Composites For Structural And Infrastructure
Applications Centre of Excellence in Engineered
Fiber Composites, University of Southern
Queensland Toowoomba, Australia
G.M. Arifuzzaman Khan, M. Terano , M.A. Gafur, M.
Shamsul Alam , Studies On The Mechanical
Properties Of Woven Jute Fabric Reinforced Poly(LLactic Acid) Composites, Journal of King Saud
University Engineering Sciences (2013)
Vivek Mishra , Sandhyarani Biswas Physical And
Mechanical Properties Of Bi-Directional Jute Fiber
Epoxy Composites Chemical, Civil and Mechanical
Engineering Tracks of 3rd Nirma University
International
Conference
on
Engineering
(NUiCONE 2012) Procedia Engineering 51 ( 2013
) 561 566
Ajith Gopinatha, Senthil Kumar.Mb, Elayaperumal,
Experimental Investigations On Mechanical
2015, IRJET.NET- All Rights Reserved
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
Properties Of Jute Fiber Reinforced Composites
With Polyester And Epoxy Resin Matrices
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Anna
University,Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India-600025
Darshil U. Shah, Peter J. Schubel, Mike J. Clifford,
Can Flax Replace E-Glass In Structural
Composites? A Small Wind Turbine Blade Case
Study Polymer Composites Group, Division of
Materials, Mechanics and Structures, Faculty of
Engineering, The University of Nottingham,
Nottingham
S.Prabhakarana, V. Krishnaraj, M. Senthil kumar,
R. Zitoune Sound And Vibration Damping
Properties Of Flax Fiber Reinforced Composites
Department
of
Robotics
&
Automation
Engineering, PSG College of Technology,
Coimbatore-641004, India. Procedia Engineering
97 ( 2014 ) 573 581
Andrzej K. Bledzkia,, WenyangZhang , Andris
Chateb Natural-Fibre-Reinforced Polyurethane
Microfoams, Composites Science and Technology
61 (2001) 24052411
K. Senthil Kumar, I. Siva , P. Jeyaraj, J.T. Winowlin
Jappes, S.C. Amico, N. Rajini Synergy Of Fiber
Length And Content On Free Vibration And
Damping Behavior Of Natural Fiber Reinforced
Polyester Composite Beams Materials and Design
56 (2014) 379386 science direct
A. K. Bledzki, A. A. Mamun, O. Faruk, Abaca Fibre
Reinforced Pp Composites And Comparison With
Jute And Flax Fibre Pp Composites Institut fr
Werkstofftechnik,
Kunststoffund
Recyclingtechnik,
University
of
Kassel,
Mnchebergstrasse ,Kassel, Germany
Nattakan Soykeabkaew, Pitt Supaphol, Ratana
Rujiravanit, Preparation And Characterization Of
Jute- And Flax-Reinforced Starch-Based Composite
Foams Polymer Processing and Polymer
Nanomaterials Research Unit, The Petroleum and
Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University,
Soi Chula 12, Phyathai Road, Pathumwan,
Bangkok 10330, Thailand
Ministry of textiles Government of India.
M.Sivapragash, Testing The Vibrational Behaviour
Of Jute Fiber Based Sandwich Composite
Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil, Thuckalai,
Tamilnadu, India.
Ramesh K. Nayak , Alina Dasha and B.C.Ray,
Effect Of Epoxy Modifiers (Al2o3/Sio2/Tio2) On
Mechanical Performance Of Epoxy/Glass Fiber
Hybrid Composites, 3rd International Conference
on Materials Processing and Characterization
(ICMPC 2014) Procedia Materials Science 6 ( 2014
) 1359 1364 www.sciencedirect.com.
Ramesh Chandra yadav, An Investigation Of
Mechanical And Sliding Wear Behavior Of Glass
Page 483
[20]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395 -0056
Volume: 02 Issue: 02 | May-2015
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite With And
Without Addition Of Silica department of
mechanical engineering AL-flash school of
engineering and technology Faridabad India
Sharayu U. Ratnaparkhi, S.S. Sarnobat Vibration
Analysis of Composite Plate Department of
Production Engineering, D.Y. Patil College of
Engineering, Pune, India. International Journal of
Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
BIOGRAPHIES
Vikas S Hoysala, completed his BE
in mechanical engineering from
City Engineering college ,
Bangalore and currently pursuing
his M.Tech in Machine Design
from SJBIT Bangalore, Karnataka.
His area of interest is in
composite
materials
and
vibrational behavior of materials.
Emailid: vikashoysala@gmail.com
Dr. Kiran Kumar P, is having 18
years of experience in industry
and academics. He has published
many journal papers and also
presented paper in various
national
and
internationl
conferences. His area of interest
includes radiation curing of
materials
and
polymer
composites and design of
experiments .Presently he is
working as a professor at SJBIT,
Bangalore.
Prof. T Madhusudhan is a faculty
serving as a head of the
department
of
mechanical
engineering department SJBIT,
has a vast experience in
engineering
academics.
His
special interest are automobile
systems, polymer composites,
renewable energy sources
and dynamics of machine.
2015, IRJET.NET- All Rights Reserved
Page 484
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Building Technology (ALE Review 1)Documento1 paginaBuilding Technology (ALE Review 1)Jehan MohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- NCSEA - Seismic Design of Large Wood Panelized Roof Diaphragms in Heavy Wall Buildings (John Lawson) 6-15-17Documento150 pagineNCSEA - Seismic Design of Large Wood Panelized Roof Diaphragms in Heavy Wall Buildings (John Lawson) 6-15-17leandro_pimenta_240% (1)
- Ventilation Requirements For Indoor Pools: Technical FeatureDocumento9 pagineVentilation Requirements For Indoor Pools: Technical FeaturetasabajcNessuna valutazione finora
- DsDocumento28 pagineDsArié WibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastick WeldDocumento35 paginePlastick WeldsuronocaturatmojoNessuna valutazione finora
- Day LightingDocumento30 pagineDay LightingRachana GoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Regulations For RoadsDocumento14 pagineTechnical Regulations For RoadsAlexe FloreaNessuna valutazione finora
- 14.gi Conduit BecDocumento4 pagine14.gi Conduit BeckailasamvvNessuna valutazione finora
- 65 Series Lubricated OmDocumento12 pagine65 Series Lubricated Omalex_alfonso9407Nessuna valutazione finora
- Air Handling Unit (DDC 02)Documento8 pagineAir Handling Unit (DDC 02)Anonymous qOBFvINessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Information: The Stelrad You Know and So Much MoreDocumento2 pagineTechnical Information: The Stelrad You Know and So Much MoreSunnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthDocumento5 pagineTutorial - 1-Design For Static and Fatigue StrengthSouradeepBhattacharya50% (2)
- 07 Genpurp Mooring - QXD 27/1/12 12:48 PM Page 1Documento9 pagine07 Genpurp Mooring - QXD 27/1/12 12:48 PM Page 1Daniel0010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Stations G1950: Guardian EquipmentDocumento2 pagineSafety Stations G1950: Guardian Equipmenteisenbarger5607Nessuna valutazione finora
- CIDECT 2 - Structural Stability of Hollow SectionsDocumento58 pagineCIDECT 2 - Structural Stability of Hollow SectionsClaudio AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- JFK Airport, UsaDocumento8 pagineJFK Airport, UsadivugoelNessuna valutazione finora
- York Air Cooled Screw Liquid Chillers (Style G)Documento120 pagineYork Air Cooled Screw Liquid Chillers (Style G)Braun-installations100% (1)
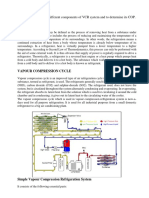
- To Understand Different Components of VCR System and To Determine Its COPDocumento6 pagineTo Understand Different Components of VCR System and To Determine Its COPMohit MinzNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM D6049 03 - Standard Test Method For Rubber Property - Measurement of The Viscous and Elastic Behavior of Unvulcanized Raw Rubbers and Rubber Compounds by Compression Between Parallel Plates PDFDocumento9 pagineASTM D6049 03 - Standard Test Method For Rubber Property - Measurement of The Viscous and Elastic Behavior of Unvulcanized Raw Rubbers and Rubber Compounds by Compression Between Parallel Plates PDFAndre Rodriguez SpirimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 MasonryDocumento81 pagineChapter 2 MasonryNabin MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Br. No. PierDocumento33 pagineBr. No. PierAnish ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- WCD Densopol Tapes - IfU 2020Documento5 pagineWCD Densopol Tapes - IfU 2020Makamu Max Las MokgaoganyiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 CuDocumento7 pagine2 CuilieoniciucNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Design Approach For Geogrid Base ReinforcementDocumento3 pagineBasic Design Approach For Geogrid Base ReinforcementTrader RedNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 1 - Pavement Materials and ConstructionDocumento32 pagineClass 1 - Pavement Materials and Constructionlohit12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bit DesignDocumento42 pagineBit DesignAli AbukhzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical Properties of ADIDocumento1 paginaTypical Properties of ADIutkuNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat ExchangersDocumento66 pagineHeat ExchangerssafwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A435Documento3 pagineAstm A435Alberto PavanNessuna valutazione finora
- p355n NH Nl1 Nl2 TubesDocumento4 paginep355n NH Nl1 Nl2 Tubesado31Nessuna valutazione finora