Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Microbiology Practical Exam Notes
Caricato da
Tovin NguyenTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Microbiology Practical Exam Notes
Caricato da
Tovin NguyenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Practical exam
1.Culture media
1.1 Blood agar: 6 bacteria
1.2. Chocolate agar: 2 bacteria
1.3. Eosin-methylen blue agar: 4 bacteria
1.4. Nutrient agar: 4 bacteria
1.1. Blood agar
-hemolysis: not complet (biliverdin
green)
-hemolysis: complet (clear zone)
1.1.1. -hemolytic streptococci
alfa-hemolytic streptococci (colourless colonies, with green zone)
Differentiation (only theoretical):
Bile
Optochin S
Mice
BEA
Heat resistance
(56 oC, 30 min)
pathogenicity
S. pneumoniae
E. faecalis
Viridans group
1.1.2. -hemolytic streptococci
-hemolytic streptococci (colourless colonies, clear zone)
Differentiation (theoretical only):
Group
Bacitracin S
CAMP test
S. pyogenes
S. agalactiae
1.1.3. Non-hemoytic streptococci
E. faecalis
E. faecalis (colourless, non-hemolytic zone)
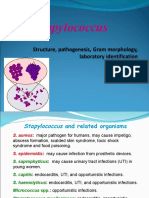
1.1.4. S. aureus
1-2 mm diameter, beta-hemolytic zone, yellow-gold pigment.
1.1.5. CNS (coagulase negative staphylococci)
S. epidermidis novobiocin S, S. saprophyticus novobiocin R.
1-2 mm diameter, white (grayish) colonies, without hemolysis
Differentiation of staphylococci and streptococci (theoretical only):
microscopical
katalase
pigment
hemolysis
size of colonies
picture
test
production
staphylococci
grape-like
or -
1-2 mm diameter
streptococci
chain/pair
, , or -
very small (point)
1.1.6. B. cereus
causative agent of food poisoning
1-2 cm diameter, flat, gray, dry colonies with beta-hemolysis
1.2. Chocolate agar
X (hem) and V (NAD) factors are free. H. influenzae and N. meningitidis, N. gonorrhoeae
may grow only on chocolate medium. On this agar only alfa-hemolysis may observed. (beta
never!)
Theoretical quisteion: satellite phenomenon (H. influenzae may grow on blood agar with S.
aureus) int he beta-hemolytic zone of S. aureus (the X and v factors will be free int he
hemolytic area)
1.2.1. Alfa-hemolytic streptococci
alfa-hemolytic streptococci
1.2.2. H. influenzae
colourless colonies, special smell
1.3. Eosin-methylen blue agar
Lactose positive: blue (pink) colonies
Lactose negative: colourless
1.3.1. E. coli
Dark blue dry colonies with metallic sheen. Lactose positive.
1.3.2. Klebsiella pneumoniae
Blue or pink mucoid colonies (lactose positive).
Differentiation between E. coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
Indol
Methyl Red
Voges-Proskauer
Citrate
Motility
E. coli
K. pneumoniae
1.3.3. Proteus mirabilis or Proteus vulgaris
colourless (lactose negative colonies), oxidase negative
lactose
motility
H2S
oxidase
phenylalanin- deaminase
urease
Salmonella
Proteus
1.3.4. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
colourless (lactose negative), oxidase positive
1.4. Nutrient agar
No hemolysis! It is suitable for detection of pigment production, or swarming.
1.4.1. S. aureus
1-2 mm diameter. yellow-gold pigment
1.4.2. Coagulase-negatv staphylococcusok (CNS)
1-2 mm diameter white or gray colonies
1.4.3. Proteus mirabilis or Proteus vulgaris
swarming, very bad smell
1.4.4. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
green pigment (diffusion onto agar), fruity smell
2. Microscopical investigation
Stained preparations should check with immersion oil (white ring).
8 slide: 6 Gram stained, 1 methylen-blue stained, 1 Ziel-Neelsen stained.
Ziehl-Neelsen
4 Gram-positive (blue or
purple)
methylen blue
2 Gram-negative (pink)
Gram positive cocci: 3
grape like: staphylococcus
chain: streptococcus
pair: S. pneumoniae
Gram positive long rods:eg. Bacillus spp.
Gram-negative cocci: eg. Neisseria spp.
Gram-negative short rods: eg. E. coli
staphylococcus
(grape like)
streptococcus
(chain)
S. pneumoniae
(diplococcus)
2.
Helminths
1.: Ascaris lumbricoides (20-25 cm, roundworm, geohelminth, larva migration into the lung)
2. Taenia solium (3-5 m pork tape worm, hermaphroditic, number of the branches of the
uterus < 10)
3. Taenia saginata (7-10 m beef tape worm, hermaphroditic, numebr of the branches of the
uterus > 15)
4. Enterobius vermicularis (1 mm, roundworm pinworm, most frequent in Hungary among
children, perianal itching)
5. Fasciola hepatica (3-5 cm liver fluke, hermaphroditic)
6. Diphyllobotrium latum (13 m fish tape worm, hermaphroditic, 2 intermidiate hosts, loss of
B12 vitamin, megaloblastic anemia, rosette like uterus)
1.
4.
3.
5.
2.
4.
6.
4. Collection of the specimen
Hemoculture bottles
It is important to obtain at least 3 specimens (with at least 30 min. between the specimens).
The specimens should be preferably taken before fever spikes (during chills). If possible,
both aerobic and anaerobic bottles should be used (3x 2 bottles, altogether). The site of
venipuncture and the plug of the bottle containing the medium must be properly disinfected.
The amount of blood injected to the bottle should be about 10 % of the liquid medium
(usually 10 ml/ bottle, for chlidren less, approximately 2-3 ml into specific Pedi bottle).
Pedi bottle
Keep the specimen under conditions recommended by the manufacturer of the medium (room
temperature or 37 oC).
Uricult:
A midstream specimen taken preferably in the morning, after thorough celaning of the
external genital area.
Keep and transport it at room temperature (native urine at + 4 oC)
Feces (stool:
Keep and transport it at room temperature.
Pus, bile ear, eye etc. transport medium:
Keep and transport it up to 24-48 hours at room temperature.
Liquor (central spinal fluid, CSF):
Collect the CSF by sterile lumbar punction into sterile tube. The site of lumbar puncture must
be properly disinfected. Keep and transport it up to 1 h at room temperature or 37 oC (except
suspected Listeria monocytogenes, at 4 oC)
Sputum
The sputum taken preferably int he morning after the tooth washing. Keep and transport it up
to 1 h at room temperature.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Gram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Documento45 pagineGram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Charmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- CNS Microbiology MeningitisDocumento26 pagineCNS Microbiology MeningitisSaransh GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteriology SummaryDocumento38 pagineBacteriology SummaryMohsen HaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- High Yield - Bacteriology ChartsDocumento9 pagineHigh Yield - Bacteriology ChartsAmirsalar EslamiNessuna valutazione finora
- CLS 400 - Test 4 (Extra Credit)Documento8 pagineCLS 400 - Test 4 (Extra Credit)McNeeseInsiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Microbiology Exam Revision: Slide Spots CollectionDocumento40 paginePractical Microbiology Exam Revision: Slide Spots Collectionعلي الكوافيNessuna valutazione finora
- Tietz's Applied Laboratory MedicineDa EverandTietz's Applied Laboratory MedicineMitchell G. ScottValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Dams Lastlook Microbiology PDFDocumento27 pagineDams Lastlook Microbiology PDFChauhan Monika100% (1)
- Taking Home Examination Provides Insights into BiostatisticsDocumento9 pagineTaking Home Examination Provides Insights into BiostatisticsUsran Ali BubinNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento32 pagineAntibiotic ResistanceEmine Alaaddinoglu100% (2)
- Clinical Microbiology BacteriologyDocumento25 pagineClinical Microbiology BacteriologyMunish DograNessuna valutazione finora
- Yeast Invasion of Male's Central Nervous SystemDocumento9 pagineYeast Invasion of Male's Central Nervous SystemRomie SolacitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Parasitology - FullDocumento30 pagineMedical Parasitology - FullJesse Osborn100% (2)
- Saudi Council ExamDocumento23 pagineSaudi Council ExamFarooq MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Fluids (Post Lab)Documento56 pagineBody Fluids (Post Lab)Dorothy Silva-JameroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ain Shams University - Clinical Pathology Ain ShamsDocumento182 pagineAin Shams University - Clinical Pathology Ain ShamsRowaa SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Lab Technician AasDocumento2 pagineMedical Lab Technician AasAnonymous t5TDwdNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-200review of Microbiology and Immunology (PDFDrive) - 1-200Documento201 pagine1-200review of Microbiology and Immunology (PDFDrive) - 1-200Jamila ridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Medical MicrobiologyDocumento40 pagineMicrobiology Medical MicrobiologyAngelic khanNessuna valutazione finora
- General Microbiology Questions-2 PDFDocumento36 pagineGeneral Microbiology Questions-2 PDFAntar Inenigog67% (3)
- 3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationDocumento18 pagine3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationFatihah JahsmiNessuna valutazione finora
- IM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitDocumento12 pagineIM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitCzara DyNessuna valutazione finora
- ABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesDocumento9 pagineABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesRichard SiahaanNessuna valutazione finora
- IVMS - General Pathology, InflammationDocumento94 pagineIVMS - General Pathology, InflammationMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gram staining characteristics and morphologies of common enteric bacteriaDocumento4 pagineGram staining characteristics and morphologies of common enteric bacteriakris0% (1)
- HematologyDocumento5 pagineHematologyIvy Jan OcateNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology - ParasitologyDocumento34 pagineMicrobiology - ParasitologySasi DharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Fungal DrugsDocumento2 pagineAnti-Fungal Drugssarguss14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mycology ReviewDocumento9 pagineMycology ReviewChristine NazarenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vision - Micro PicturesDocumento53 pagineVision - Micro Picturessk100% (1)
- Microbiology MMV-Sample-MCQsDocumento8 pagineMicrobiology MMV-Sample-MCQsMuhammad AttiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Graff's Textbook of Routine Urinalysis and Body Fluids, 2010, Lillian A. Mundt, Kristy ShanahanDocumento20 pagineGraff's Textbook of Routine Urinalysis and Body Fluids, 2010, Lillian A. Mundt, Kristy ShanahanAnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Diagnosis of Painful Genital LesionsDocumento7 pagineDifferential Diagnosis of Painful Genital LesionsKyra KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Documento3 pagineBest Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Danielle SangalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Paps SmearDocumento51 paginePaps SmearCatherine MerillenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Leukaemoid Reaction Lecture by DRDocumento35 pagineLeukaemoid Reaction Lecture by DRapi-273068056100% (1)
- Microbiology - Bacteria TableDocumento3 pagineMicrobiology - Bacteria TableJerry G100% (2)
- Summary of Diagnostic BacteriologyDocumento45 pagineSummary of Diagnostic Bacteriologyomaromran100% (3)
- Practical 4 Staphylococci PresentationDocumento24 paginePractical 4 Staphylococci PresentationPatrisha BuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Documento13 pagineMicrobiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Jessica MalinNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliDocumento31 pagineAerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliCagar Irwin TaufanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Blood DonationDocumento55 pagineChapter 8 Blood DonationCHALIE MEQUNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Fast StainingDocumento4 pagineAcid Fast Stainingchaudhary TahiraliNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Bethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytopathologyDocumento6 pagine2017 Bethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytopathologyLuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Infectious Diseases and the Immune SystemDocumento88 pagineOverview of Infectious Diseases and the Immune SystemAhimsa MartawigunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathomechanisms of InfectionDocumento44 paginePathomechanisms of InfectionMardhisemNessuna valutazione finora
- Robert O'Connor University College Dublin: Show Details / Rate ItDocumento10 pagineRobert O'Connor University College Dublin: Show Details / Rate Itmusatii0% (1)
- CLINPATH Finals ReviewerDocumento28 pagineCLINPATH Finals ReviewerVon HippoNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiphospholipid SyndromeDocumento6 pagineAntiphospholipid SyndromeOm Lakhani100% (1)
- Clinical-Microscopy Must KnowsDocumento61 pagineClinical-Microscopy Must KnowsMonique BorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical HistoryDocumento167 pagineMedical HistoryPragya Saran100% (1)
- Correctly: IncorrectlyDocumento70 pagineCorrectly: IncorrectlyDjdjjd Siisus100% (1)
- Generalov-II - Medical Microbiology Virology Immunology - Pt-2 - 2016 PDFDocumento392 pagineGeneralov-II - Medical Microbiology Virology Immunology - Pt-2 - 2016 PDFMohammad YasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Neoplasia Exam ReviewDocumento37 pagineNeoplasia Exam ReviewSaWera AsGhar100% (1)
- Microbiology Quiz: Answer All Questions in Two Minutes To Win A Lollypop!Documento13 pagineMicrobiology Quiz: Answer All Questions in Two Minutes To Win A Lollypop!SwaraNessuna valutazione finora
- BRS Microbiology Flash-CardsDocumento500 pagineBRS Microbiology Flash-CardsAmirsalar Eslami100% (1)
- My Loving Parents and Teachers Medical NotesDocumento38 pagineMy Loving Parents and Teachers Medical NotesGoL Di100% (1)
- Typhidot TestDocumento3 pagineTyphidot TestHisyam IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandSenior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoonoses: Skin Infection Resembling ErysipelasDocumento1 paginaZoonoses: Skin Infection Resembling ErysipelasTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Treponema Pallidum: Transplacental (Intrauterin)Documento2 pagineTreponema Pallidum: Transplacental (Intrauterin)Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- S Mannitol Salt Agar Selective For Salt-Tolerant StaphylococciDocumento9 pagineS Mannitol Salt Agar Selective For Salt-Tolerant StaphylococciTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Internal Elastic Lamina of Primarily Medium and Large Sized ArteriesDocumento2 pagineThe Internal Elastic Lamina of Primarily Medium and Large Sized ArteriesTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- B29 - Generalised Anxiety Disorder, Mixed Anxiety-Depressive DisorderDocumento2 pagineB29 - Generalised Anxiety Disorder, Mixed Anxiety-Depressive DisorderTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth and Development in InfancyDocumento2 pagineGrowth and Development in InfancyTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth and Development in InfancyDocumento2 pagineGrowth and Development in InfancyTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical exam 1.Culture media: α-hemolytic streptococciDocumento14 paginePractical exam 1.Culture media: α-hemolytic streptococciTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers For Practice ECGDocumento2 pagineAnswers For Practice ECGTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Vasculitis by VinhDocumento4 pagineVasculitis by VinhTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Prescriptions - DOTE 2018Documento2 pagineDermatology Prescriptions - DOTE 2018Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- 5A - Acute Left Ventricular FailureDocumento1 pagina5A - Acute Left Ventricular FailureTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth and Development in InfancyDocumento2 pagineGrowth and Development in InfancyTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoulder Dystocia: McRobert's Manoeuvre for DeliveryDocumento1 paginaShoulder Dystocia: McRobert's Manoeuvre for DeliveryTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 12 MyocarditisDocumento2 pagineTopic 12 MyocarditisTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- DOTE - Pharmacology II Drugs ListDocumento24 pagineDOTE - Pharmacology II Drugs ListTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology of The LiverDocumento2 paginePharmacology of The LiverTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Preventive TopicsDocumento28 paginePreventive TopicsTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology, 2nd Semester - Sollas NotesDocumento224 paginePharmacology, 2nd Semester - Sollas NotesTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Minus 92Documento8 pagineHeart Minus 92Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Minus 92Documento8 pagineHeart Minus 92Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic #1 of Pathology FinalDocumento2 pagineTopic #1 of Pathology FinalTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathological Cardiac ExcitabilityDocumento3 paginePathological Cardiac ExcitabilityTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Charactersitic Feature: Whirled' Pattern: Psammoma BodyDocumento3 pagineCharactersitic Feature: Whirled' Pattern: Psammoma BodyTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Theory - Week 1 PT 2Documento3 pagineAnatomy Theory - Week 1 PT 2Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Histopatho 1st SemesterDocumento8 pagineHistopatho 1st SemesterTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Instruments Classification and Techniques"TITLE"Guide to Common Surgical Tools and Procedures" TITLE"Overview of Basic Surgical Procedures and InstrumentationDocumento66 pagineSurgical Instruments Classification and Techniques"TITLE"Guide to Common Surgical Tools and Procedures" TITLE"Overview of Basic Surgical Procedures and InstrumentationTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- I Am But A Flower PoemDocumento1 paginaI Am But A Flower PoemTovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Theory - Week 1 PT 1Documento1 paginaAnatomy Theory - Week 1 PT 1Tovin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Emily Act 3 GraficoDocumento13 pagineEmily Act 3 Graficoemily lopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing Family Nursing AssessmentDocumento2 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Family Nursing AssessmentRy LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Dof Omm Ss Skirting Sk-02Documento8 pagineDof Omm Ss Skirting Sk-02Ideal DesignerNessuna valutazione finora
- Business-Process Integration: Supply-Chain Management 2.0 (SCM 2.0)Documento8 pagineBusiness-Process Integration: Supply-Chain Management 2.0 (SCM 2.0)nidayousafzaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Slimline: Switch Disconnector Fuse, SR 63-630 ADocumento46 pagineSlimline: Switch Disconnector Fuse, SR 63-630 AЕвгений МатвеевNessuna valutazione finora
- A 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFDocumento4 pagineA 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFأسامة وحيد الدين رمضانNessuna valutazione finora
- Angel FishDocumento1 paginaAngel FishWilla CrowellNessuna valutazione finora
- Global POVEQ NGADocumento2 pagineGlobal POVEQ NGABonifaceNessuna valutazione finora
- FINA 7A10 - Review of ConceptsDocumento2 pagineFINA 7A10 - Review of ConceptsEint PhooNessuna valutazione finora
- Tax Invoice: New No 30, Old No 24 Bhagirathi Ammal ST, T Nagar, Chennai 600017 CIN: U74900TN2011PTC083121 State Code: 33Documento1 paginaTax Invoice: New No 30, Old No 24 Bhagirathi Ammal ST, T Nagar, Chennai 600017 CIN: U74900TN2011PTC083121 State Code: 33golu84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Guide for lemonPOS POS SoftwareDocumento4 pagineInstallation Guide for lemonPOS POS SoftwareHenry HubNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual For Master Researchpproposal - ThesisDocumento54 pagineManual For Master Researchpproposal - ThesisTewfic Seid100% (3)
- Corporate Citizenship, Social Responsibility, Responsiveness, and PerformanceDocumento27 pagineCorporate Citizenship, Social Responsibility, Responsiveness, and Performanceguru2k9100% (1)
- Ashok LeylandDocumento4 pagineAshok Leylandsodhiseema100% (1)
- Gen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseDocumento26 pagineGen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseAhmed Khodja KarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Joou No Gohoubi - Tate No Yuusha No Nariagari 288869 Doujin - EdoujinDocumento25 pagineJoou No Gohoubi - Tate No Yuusha No Nariagari 288869 Doujin - Edoujinaura.nazhifa10020% (1)
- How COVID-19 Affects Corporate Financial Performance and Corporate Valuation in Bangladesh: An Empirical StudyDocumento8 pagineHow COVID-19 Affects Corporate Financial Performance and Corporate Valuation in Bangladesh: An Empirical StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Com II Year Economics Previous Year QuestionsDocumento11 pagineB. Com II Year Economics Previous Year QuestionsShashiMohanKotnalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Populist Movement (Anant)Documento7 paginePopulist Movement (Anant)Siddhi JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Saturn Engine Compression Test GuideDocumento7 pagineSaturn Engine Compression Test GuideManuel IzquierdoNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual With FAQs - Sales Invoice For Petrol PumpsDocumento10 pagineUser Manual With FAQs - Sales Invoice For Petrol PumpsRavindra MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- All India CW Pricelist Wef 01.05.2021Documento6 pagineAll India CW Pricelist Wef 01.05.2021Sameer PadhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical and Social Dimensions of Science and TechnologyDocumento26 pagineEthical and Social Dimensions of Science and TechnologyKlester Kim Sauro ZitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Install CH340 driver for ArduinoDocumento8 pagineInstall CH340 driver for Arduinosubbu jangamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramic Tiles Industry Research ProjectDocumento147 pagineCeramic Tiles Industry Research Projectsrp188Nessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsDocumento28 pagineDerivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsElle PaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Return On Marketing InvestmentDocumento16 pagineReturn On Marketing Investmentraj_thanviNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic FertilizerDocumento2 pagineOrganic FertilizerBien Morfe67% (3)
- Currency Exchnage FormatDocumento1 paginaCurrency Exchnage FormatSarvjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Eslit-Vinea-LA 03 Task #1-4Documento11 pagineEslit-Vinea-LA 03 Task #1-4darkNessuna valutazione finora