Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2.5B TOXICOLOGY - Phetty PDF
Caricato da
Bea SamonteDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2.5B TOXICOLOGY - Phetty PDF
Caricato da
Bea SamonteCopyright:
Formati disponibili
`
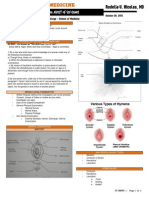
PHARMACOLOGY
2.5B ENVIRONMENTAL & OCCUPATIONAL TOXICANTS, HEAVY METALS AND CHELATORS
TOXICOLOGY
OCCUPATIONAL
Chemicals found in the workplace.
Concentration of contaminant may be virtually undetected in
water
Magnified thousands of times as the contaminant passes up
the food chain
BIOMAGNIFICATION
ENVIRONMENTAL
Deleterious impact of chemicals on living organism present as
pollutants.
BIOMAGNIFICATION IN FOOD CHAIN
Polychlorinated biphenyls
undetectable in water
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Toxic effects of chemicals and physical agents on population
and communities of living organism within a specified
ecosystem.
Phyloplankton X 1
Zooplankton X 49.2
OCCUPATIONAL TOXICOLOGY
Identifies agents
Defines safety
- Threshold limit values (TLVs)
Lays down guidelines to minimize absorption
Rainbow smelt X 416
Lake trout X 1932
Herring gulf X 49,600
water
Fish fry ???
environment
air
soil
POLLUTION
Industrialization
Technologic development
Urbanization
HAZARD
VS
Ability of agent to cause
injury
Primary consideration:
Use and exposure
RISK
Frequency of occurrence
of undesirable effects
arising from exposure.
EXPOSURE
ROUTES
Inhalation
Oral
Transdermal
DURATION
Acute - single or multiple
for 2-3 days
Industry - occupational
Chronic - occupational or
atmospheric
AGENT ORANGE VIETNAM WAR
HEALTH EFFECTS
3 million vietnamese people have been affected by Agent
Orange
Including at least 150,000 children born with birth defects
4.8 million Vietnamese were exposed to Agent Orange,
resulting in 400,000 people being killed or maimed.
POLLUTION AND POLLUTANTS
Introduction of substances into the environment that alter its
physical, chemical and biological properties in such a way that
it is harmful to living organism.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATION
Intake of a contaminant by an organism
Exceeds the latter's activity to metabolize or excrete substance
Chemical accumulates within the tissue of the organism
BIOACCUMULATION
AIR POLLUTANTS
TYPES & SOURCES OF AIR POLLUTION
Sulfur oxides
CO
Volatile organic compounds
5 pollutants - 98% of air
Particulate matter
pollution
Nitrogen oxides
Others - Lead, Hydrocarbons, Cadmium, H2S, Ozone,
Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon, Indoor air pollution
POLLUTANTS
CO - 52%
SO - 14%
Hydrocarbons - 14%
Air pollution - 98%
NO - 14%
Particulate matter - 4%
SOURCES
Transportation
Industry
Generation of electric power
Space heating
Refuse disposal
Coal combustion
CO - 52%
PROPERTIES
Colorless, tasteless, odorless and non-irritating gas
Incomplete combustion
MECHANISMS OF ACTION
CO + HB = Carboxyhemoglobin
Cannot transport oxygen
Brain and heart most affected
CLINICAL EFFECTS
Psychomotor impairment
Headache
Loss of visual acuity
Tachycardia, tachypnea, syncope & coma
Page 1 of 2
Pharmacology
Convulsions, shock and respiratory failure
TREATMENT
Administration of oxygen
2.5B ENVIRONMENTAL & OCCUPATIONAL TOXICANTS, HEAVY METALS AND CHELATORS
SO2 - 14%
PROPERTIES
Colorless, irritant gas
Combustion of sulfur - containing fossil fuels
MECHANISM OF EFFECTS
Moist membranes + SO2 -> sulfurous acid -> severe irritation
of the eyes, mucous membranes, skin
Bronchoconstriction & Pulmonary edema
TREATMENT
No specific treatment
NO2 - 14%
PROPERTIES
Brownish irritant gas
Fire and fresh silage-Silo filler's disease in farmers
Lung irritant - pulmonary edema
TREATMENT
Preventive and symptomatic
OZONE
PROPERTIES
Bluish irritant gas - occurs normally in the earth's atmosphere
SOURCES
Workplace - around high-voltage electrical equipment and
around ozone-producing devices used for air and water
purification.
Important oxidant found in polluted urban air.
Important absorbent of ultraviolet light.
CLINICAL EFFECTS AND TREATMENT
Mild exposure - URTI
Severe - Deep lung irritation - pulmonary edema
Airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation
Acute intoxication - NO treatment
SOLVENTS
HALOGENATED ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBON
CCl4
Chloroform
Methyl chloroform
Trichlorethylene
Tetrachloroethylene
Industrial solvents
Degreasing agents
Cleaning agents
USES
Tetrachloroethylene -> Impaired memory and neuropathy
Carcinogenic effect - large safety margin
TREATMENT
No specific treatment
AROMATIC HYDROCARBON : BENZENE
ACUTE EFFECTS
CHRONIC EFFECTS
CNS depression
Very serious effects
Euphoria, nausea,
Injury: Bone marrow
locomotor problems
Increase incidence of
Vertigo, headache
leukemia
Coma
TOLOUENE (METHYLBENZENE)
NO myelotoxic properties, nor associated with leukemia
CNS depressant
Organochlorine
Organophosphorous
Carbamate
Botanical
Pesticides
ORGANOCHLORINE PESTICIDES
DDT (Chlorophenothane)
Benzene hexachloride
Cycylodienes
Toxaphenes
MECHANISM OF TOXICITY
Interfere with inactivation of -> rapid repetitive firing of most
neurons
EFFECTS
CNS stimulation
Tremors and convulsion
TREATMENT
No specific treatment
PROPERTIES
Environmental toxicology
Persistent chemical
Slow degradation
Bioaccumulation in acquatic ecosystem is well documented
Once absorb in soil - do not readily desorb
ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS
Chemicals mimic, enhance, or inhibit a hormonal action
Estrogen-like or anti androgenic properties
Eg. Phytoestrogens, Mycoestrogens, Persistent organochlorine
agents such as DDT
CLINICAL EFFECTS
CNS depression
Liver injury, kidney injury
Cardiotoxicity
Page 2 of 2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Microbiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceDa EverandMicrobiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceNessuna valutazione finora
- Occupational & Environmental ToxicologyDocumento62 pagineOccupational & Environmental ToxicologyRem AlfelorNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental and Occupational ToxicantsDocumento3 pagineEnvironmental and Occupational ToxicantsEhrli CuaresmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Poisoning With Toxic GasesDocumento78 pagineProfessional Poisoning With Toxic GasesAnonymous JMnKM6KrNessuna valutazione finora
- ToxicologyDocumento28 pagineToxicologyAbdulahadNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Madhusudhana Rao, M.E., LL.B.,: Environmental Legislation & ComplianceDocumento28 pagineB. Madhusudhana Rao, M.E., LL.B.,: Environmental Legislation & Compliancekirandevi1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - PollutionDocumento232 pagineUnit 2 - PollutionHariharan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data SheetDocumento7 pagineMaterial Safety Data SheetCatalin SevastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Science and Engineering: 20BSCY201Documento17 pagineEnvironmental Science and Engineering: 20BSCY201HARSHITHA M SEC 2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigerant R 22Documento6 pagineRefrigerant R 22Anca ParaschivNessuna valutazione finora
- Moiz Naveed CE 590950: Environment Pollution (3676)Documento21 pagineMoiz Naveed CE 590950: Environment Pollution (3676)Moix KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Course SEAI&ML PanuuDocumento17 pagineAudit Course SEAI&ML PanuuPranu LondheNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbons: SourcesDocumento3 pagineHydrocarbons: Sourcesmadhangi vaithyanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Soubhagya S Asst. Professor Ece DepartmentDocumento31 pagineEnvironmental Impact Assessment: Soubhagya S Asst. Professor Ece DepartmentSoubhagya KishorNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 2B4 - Safety Data Sheet For Coshh AssessmentDocumento6 pagine19 2B4 - Safety Data Sheet For Coshh AssessmentRauf HaciyevNessuna valutazione finora
- CO-&-H2S Leading Toxic HazardsDocumento2 pagineCO-&-H2S Leading Toxic HazardsarturomaravillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet Polyurethane FoamDocumento5 pagineSafety Data Sheet Polyurethane FoamAhmed KhalifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental ChemistryDocumento17 pagineEnvironmental Chemistrytannie2512Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5a AirPollution Material, TXTDocumento7 pagine5a AirPollution Material, TXTSoumya GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Dicumyl Peroxide 1346: October 1999Documento2 pagineDicumyl Peroxide 1346: October 1999Asima AtharNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.RA 6969 HAzardous Wastes Engr - Jean BorromeoDocumento117 pagine9.RA 6969 HAzardous Wastes Engr - Jean BorromeoDyeri FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Praxair Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocumento7 paginePraxair Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company Identificationeng20072007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Activities and The EnvironmentDocumento10 pagineHuman Activities and The EnvironmentAnna Daniella LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersperse MDC220Documento4 pagineHypersperse MDC220Salah MsmlNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 0. IntroducciónDocumento16 pagineTema 0. IntroducciónGloria Garcia RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocumento5 pagineSulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDipen DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sodium CarbonateDocumento85 pagineSodium Carbonatebalaclafa100% (1)
- EC Safety Data Sheet: 1. Name of Product, Characterization and Company NameDocumento3 pagineEC Safety Data Sheet: 1. Name of Product, Characterization and Company NamemitramgopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Baker Hughes: Material Safety Data SheetDocumento5 pagineBaker Hughes: Material Safety Data SheetbayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sawdust MSDSDocumento4 pagineSawdust MSDSDandika RamdhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Msds Iron PowderDocumento5 pagineMsds Iron PowdermulyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 Environmental Pollution and Waste Management Environmental Pollution Causes, Effects and Control MeasuresDocumento16 pagineUnit-3 Environmental Pollution and Waste Management Environmental Pollution Causes, Effects and Control MeasuresMithibai FacesNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Science Module 13-16Documento41 pagineEnvironmental Science Module 13-16Ranzel SerenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Aligal MSDSDocumento7 pagineAligal MSDSsalcabesNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS PolyurethaneDocumento7 pagineMSDS PolyurethaneArif SetiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge 6351 Evs 2nd UnitDocumento21 pagineGe 6351 Evs 2nd Unitsowkarthika pNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution: Adriana Agovska, MD, PHD Department of Hygiene, Medical Ecology and Nutrition, SofiaDocumento51 pagineAir Pollution: Adriana Agovska, MD, PHD Department of Hygiene, Medical Ecology and Nutrition, SofiaTasos ZelevarisNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen MsdsDocumento7 pagineHydrogen MsdssalcabesNessuna valutazione finora
- R134A - Tetrafluoroethane (Boc Limited - NZ) : Product NameDocumento5 pagineR134A - Tetrafluoroethane (Boc Limited - NZ) : Product NameSami ThirunavukkarasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocumento6 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationOnnFuiSiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Austenal Electro Pol LiquidDocumento4 pagineAustenal Electro Pol LiquidPiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hapter AIR Pollution: Reporter: Jessica Dino May Ann BorgoniaDocumento21 pagineHapter AIR Pollution: Reporter: Jessica Dino May Ann BorgoniaTel Lorayes-VillarNessuna valutazione finora
- F1-000728 MSDSDocumento7 pagineF1-000728 MSDScolinyNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Quality:: Definitions, Characteristics, and PerspectivesDocumento37 pagineAir Quality:: Definitions, Characteristics, and Perspectives^nana^Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising PlantDocumento4 pagine2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising Planthendrik subagioNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxic GasesDocumento21 pagineToxic GasesBestariNugrahiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Envsci&EnggDocumento9 pagineModule 2 - Envsci&EnggAlistair HernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Inhalational Poisoning: Patricio, Roselene P. Ricarte, Viaka Faye Salvatus, JonnaDocumento44 pagineInhalational Poisoning: Patricio, Roselene P. Ricarte, Viaka Faye Salvatus, JonnaRose PatricioNessuna valutazione finora
- K01334 - 20181114091019 - Topic 7 Issues in Conservation - PollutionDocumento56 pagineK01334 - 20181114091019 - Topic 7 Issues in Conservation - Pollutionizz isalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution: BY: John Roland Edaño Maria Theresa Aquino Camille Cabrera Noelle Catherine Diaz Danica SalorDocumento37 pagineAir Pollution: BY: John Roland Edaño Maria Theresa Aquino Camille Cabrera Noelle Catherine Diaz Danica SalorMarvin MonterosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Invironmental ChemistryDocumento5 pagineInvironmental ChemistryGudia kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Science Reviewer.Documento8 pagineEnvironmental Science Reviewer.Althea Mae JarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxicology: Dr. M. Masoom AkhtarDocumento28 pagineToxicology: Dr. M. Masoom AkhtarMuhammad Masoom AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Pharmacotoxicology: Eman Sutrisna Departement of Pharmacology and Therapy Medical School UnsoedDocumento26 pagineBasic Pharmacotoxicology: Eman Sutrisna Departement of Pharmacology and Therapy Medical School UnsoedCharmelita ClaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Process MSDS Ims 010Documento7 pagineProcess MSDS Ims 010Noe AranelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Seminar (Chemistry 481) Persistent Organic Pollutant Management and ControlDocumento31 pagineChemistry Seminar (Chemistry 481) Persistent Organic Pollutant Management and ControlAdedun Joseph AdedayoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Propanol PDFDocumento25 pagine2 Propanol PDFjovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nax Eco 2K Metal Filler - MSDSDocumento6 pagineNax Eco 2K Metal Filler - MSDSjanakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiitjee Viii 05 Pollution of Air and Water-1Documento96 pagineFiitjee Viii 05 Pollution of Air and Water-1yashNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestDocumento4 pagine1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- MOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocumento194 pagineMOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone Marrow Failure StatesDocumento2 pagineBone Marrow Failure StatesBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Bleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocumento5 pagineBleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento6 pagine1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeDocumento2 paginePelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Documento1 pagina3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Documento84 pagineCollection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesDocumento2 pagine1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesJaybee SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1b AutopsyDocumento3 pagine1.1b AutopsyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1c Identification & Medicolegal Aspects of DeathDocumento4 pagine1.1c Identification & Medicolegal Aspects of DeathBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Semen AnalysisDocumento8 pagineSemen AnalysisBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3G Forensic Path PDFDocumento17 pagine1.3G Forensic Path PDFBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1d EvidenceDocumento2 pagine1.1d EvidenceBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Group DiscussionDocumento3 pagineSmall Group DiscussionBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningDocumento2 pagineClinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4A Intro To HemaDocumento4 pagine1.4A Intro To HemaBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1c Rdu ProcessDocumento3 pagine1.1c Rdu ProcessBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1a Prescription WritingDocumento4 pagine1.1a Prescription WritingBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionDocumento2 pagineClinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- History PEDocumento6 pagineHistory PEBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6e CopdDocumento6 pagine1.6e CopdBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaDocumento9 pagineClinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1b Clinical PharmacologyDocumento1 pagina1.1b Clinical PharmacologyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- CPC-Patho Version 6Documento20 pagineCPC-Patho Version 6Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2a PhlebotomyDocumento7 pagine1.2a PhlebotomyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Dilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographDocumento1 paginaDilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsDocumento3 pagine1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid CA Case Pres EditDocumento42 pagineThyroid CA Case Pres EditBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarcini: Caiet de PracticaDocumento3 pagineSarcini: Caiet de PracticaGeorgian CristinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labor Rules English Noi Quy Bang Tieng Anh PDFDocumento27 pagineLabor Rules English Noi Quy Bang Tieng Anh PDFNga NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- CGP Module 1 FinalDocumento19 pagineCGP Module 1 Finaljohn lexter emberadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion Exhibit 4 - Declaration of Kelley Lynch - 03.16.15 FINALDocumento157 pagineMotion Exhibit 4 - Declaration of Kelley Lynch - 03.16.15 FINALOdzer ChenmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Athena 60 Installation Manual EN 2022.07.03Documento30 pagineAthena 60 Installation Manual EN 2022.07.03joaquin.cadondonNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Inggris Narrative TeksDocumento11 pagineB. Inggris Narrative TeksDew FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- KalamDocumento8 pagineKalamRohitKumarSahuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Professional Ethical Analysis - Mumleyr 022817 0344cst 1Documento40 pagineA Professional Ethical Analysis - Mumleyr 022817 0344cst 1Syed Aquib AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- CURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaDocumento13 pagineCURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaHung LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessDocumento140 pagineEntrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessAngelica Plata100% (1)
- Chapter 3C Problem Solving StrategiesDocumento47 pagineChapter 3C Problem Solving StrategiesnhixoleNessuna valutazione finora
- 1634313583!Documento24 pagine1634313583!Joseph Sanchez TalusigNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Probability Distribution UpdatedDocumento44 pagineDiscrete Probability Distribution UpdatedWaylonNessuna valutazione finora
- Water and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceDocumento18 pagineWater and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceJoyce Marian BelonguelNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncDocumento2 pagine23 East 4Th Street NEW YORK, NY 10003 Orchard Enterprises Ny, IncPamelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact Grammar Book Foundation Unit 1Documento3 pagineImpact Grammar Book Foundation Unit 1Domingo Juan de LeónNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineeringinterviewquestions Com Virtual Reality Interview Questions Answers PDFDocumento5 pagineEngineeringinterviewquestions Com Virtual Reality Interview Questions Answers PDFKalyani KalyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystek Technology Co.,LtdDocumento35 pagineCrystek Technology Co.,LtdCésar MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento56 pagineTestFajri Love PeaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Account Statement From 1 Jan 2017 To 30 Jun 2017Documento2 pagineAccount Statement From 1 Jan 2017 To 30 Jun 2017Ujjain mpNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Documento4 pagineName: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Kartikeya ThadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CrisisDocumento13 pagineCrisisAngel Gaddi LarenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrep Bazaar Rating SheetDocumento7 pagineEntrep Bazaar Rating SheetJupiter WhitesideNessuna valutazione finora
- Project TitleDocumento15 pagineProject TitleadvikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kofax Cross Product Compatibility MatrixDocumento93 pagineKofax Cross Product Compatibility MatrixArsh RashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 (Partnerships Formation, Operation and Ownership Changes) PDFDocumento58 pagineChapter 15 (Partnerships Formation, Operation and Ownership Changes) PDFAbdul Rahman SholehNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Report On Energy Sector in GujaratDocumento48 pagineResearch Report On Energy Sector in Gujaratratilal12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Documento11 pagineAlice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Oğuz KarayemişNessuna valutazione finora
- Borer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFDocumento272 pagineBorer (2013) Advanced Exercise Endocrinology PDFNicolás Bastarrica100% (1)
- Chapin Columbus DayDocumento15 pagineChapin Columbus Dayaspj13Nessuna valutazione finora