Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PEDIA - Acquired Heart Disease
Caricato da
Stephen Pilar PortilloDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PEDIA - Acquired Heart Disease
Caricato da
Stephen Pilar PortilloCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PEDIATRICS
Acquired heart disease
MARIVIC MOTILLA-ESGUERRA, MD
Objectives
1. To know the different acquired heart diseases
2. To know the etiology of acquired heart diseases
3. To know the pathophysiology of acquired heart diseases
4. To know the management acquired heart diseases
Bacterial Agents in Pediatric Infective Endocarditis
COMMON: NATIVE VALVE OR OTHER CARDIAC LESIONS
Viridans group streptococci (S.mutans, S. sanguis, S. mitis)
Staphylococcus aureus
Group D streptococcus (enterococcus) (S.bovis, S. faecalis)
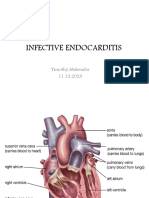
CHD vs. normal heart
Infective Endocarditis
a microbial infection of the endocardial (endothelial) surface of
the heart.
Native or prosthetic heart valves
Endocarditis also can involve septal defects
The mural endocardium
Intravascular foreign devices
intracardiac patches
surgically constructed shunts
intravenous catheters.
UNCOMMON: NATIVE VALVE OR OTHER CARDIAC LESIONS
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Coagulase-negative staphylococci
Coxiella burnetii (Q fever)
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Brucella
Chlamydia psittacli
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia pneumoniae
Legipnella
Bartonella
HACEK group
Streptobacillus moniliformis
Pasteurella multocida
Campylobacter fetus
Culture negative (6% of cases)
PROSTHETIC VALVE
Microorganisms
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus aureus
Viridans group streptococcus
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Serratia marcescens
Diphtheroids
Legionella species[*]
HACEK group[]
Fungi[]
Pre-existing congenital/acquired heart disease
Pressure gradient turbulence
tissue damage
fibrin / platelet adherence
TRANSCOM | BEDIMANS MD|1
PEDIATRICS
Acquired heart disease
lysosomal granules release
hydrolytic enzymes
Laboratory Diagnosis
Clinical and Laboratory Findings in Patients with IE
Clinical
Finding
Frequency
++++
+++
Fever
Non-specific symptoms (myalgia,
arthralgia, headache, malaise)
Heart murmur (new or changing)
++
Heart Failure
Petechiae
Embolic phenomena
Splenomegaly
Neurologic Findings
Osler nodes, Janeway lesions,
Roth spots, splinter hemorrhages
Legend:
++
++
++
++
++
+
++++
very common
++ infrequent
+++
in most cases
+ rare
Finding
Frequency
Positive blood culture (off antibiotics)
++++
Elevated acute phase reactants
++++
Anemia
+++
Hematuria
+++
Presence of rheumatoid factor
++
Leukocytosis
++
Legend:
++++
very commom
+++
in most cases
++
Infrequent
rare
Clinical Features
Laboratory
New or changing murmurs are usually heard
- Frequent auscultation is essential
Patients with suspected embolic events are candidates for
serial echo to localize vegetations and to define changes that
may occur with time
Splenomegaly may be present in a majority of instances
when the disease has been present for weeks or months
Neurologic findings are present in 20% of children and may
simulate the picture of an abscess, infarct or aseptic
meningitis
Blood Culture most valuable tool
Collection of 2 or 3 samples over a 24 hr period is adequate
in most cases
Acute phase reactants are elevated
ESR only minimally elevated (as the disease progresses ,
the ESR will increase)
- remain elevated for some time even after documented
bacteriologic cure
Immune complexes or Rheumatoid factor
Anemia common, particularly in long standing infection
May be hemolytic or may represent anemia of chronic
disease
Microscopic or macroscopic hematuria represents renal
embolization or nephritis
Leukocytosis is not a consistent finding but is more
common in acute IE
Antibodies against techoic acid and cell wall peptidoglycan in
severe staphylococcal infection may be present
2D-Echocardiography
A negative echocardiogram does not rule out endocarditis
More helpful in children with normal cardiac anatomy or
with isolated valvar abnormalities in children with more
complex congenital anomalies
Duke Major Criteria : oscillating intracardiac mass or
vegetation, an annular abscess, prosthetic valve partial
dehiscence, and new valvular regurgitation
DIAGNOSIS: Duke criteria
Major:
(+) blood culture
Evidence of endocarditis on echocardiography
A. Positive echocardiogram for IE defined as:
i. Oscillating intracardiac mass on valve or supporting
structures, in the path of regurgitant jets, or an implanted
material in the absence of an alternative anatomic explanation or
ii.Abscess, or
iii.New partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve or
B. New valvular regurgitation (worsening or changing of preexisting
murmur)
Minor criteria
Predisposition: predisposing heart condition or intravenous drug use
Fever: temperature > 38.0 C (100.4 F)
Vascular phenomena: major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary
infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival
hemorrhages, and Janeway lesions. Immunologic phenomena:
glomerulonephritis, Osler's nodes, Roths spots and rheumatoid
TRANSCOM | BEDIMANS MD|2
PEDIATRICS
Acquired heart disease
MARIVIC MOTILLA-ESGUERRA, MD
factor. Microbiological evidence: positive blood culture but does not
meet a major criterion as noted above or serological evidence of
active infection with organism consistent with IE. Echocardiographic
findings: consistent with IE but do not meet a major criterion as
noted above Excludes single positive cultures for coagulasenegative staphylococci, diphtheroids, and organisms that do not
commonly cause endocarditis.
2 major criteria or 1 major and 3 minor criteria or 5 minor criteria
PROGNOSIS AND COMPLICATIONS
Heart failure-mitral and aortic valve
Myocardial abscess and toxic myocarditisArrhythmias
Systemic emboli
2 Major
1 Major + 2 Minor
Diseases of the myocardium
Cardiomyopathies
Diseases of the myocardium
primary vs. secondary
Classification:
Dilated
Hypertrophic
Restrictive
Pulmonary embolism VSD TOF
mycotic aneurysms
rupture of a sinus of Valsalva, obstruction of a valve
secondary to large vegetations, acquired VSD, and heart
block as a result of involvement (abscess) of the conduction
system.
meningitis, osteomyelitis, arthritis, renal abscess, and
immune complexmediated glomerulonephritis.
TREATMENT(Back page)
Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic Fever:
An auto immune disease preceded by GABS
Generalized disease affecting all the connective tissues of
the body
Characterized by periods of exacerbation
Commonly affects 6-15 years old
Diagnostic Criteria
Major Criteria
1. Arthritis
2. Carditis
3. Erythema Marginatum
4. Subcutaneous nodules
5. Chorea
Minor Criteria
Clinical
Fever
Arthralgia (joint pains w/o objective findings)
Pericarditis
Constrictive pericarditis
Accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space
Tamponade
Diagnosis
TRANSCOM | BEDIMANS MD|3
PEDIATRICS
Acquired heart disease
Clinical Manifestations
Precordial pain- sharp, stabbing pain radiating to the Left
shoulder and back
Friction rub
Pulsus paradoxus - caused by the normal slight decrease in
systolic arterial pressure during inspiration. With cardiac
tamponade, this normal phenomenon is exaggerated,
probably because of decreased filling of the left side of the
heart with the inspiratory phase of respiration.
Diagnosis
Echocardiogram
ECG
o Low voltage QRS
o T wave inversion
o Electrical alterna
AHA Guideline 2008
Prophylactic regiments for dental, oral, or respiratory tract , procedures
Agents
Standard oral prophylaxis
Unable to take oral medications
Amoxycillin
Regimen (single dose 30-60min before
procedure)
50 mg/kg p.o. (max 2 g)
Ampicillin or
Cefazolin or ceftriaxone
50 mg/kg IM/IV(max2g)
50 mg/kg IM/IV (max1g)
Clindamycin or
Cephalexin a or
Azithromycin or clarithromycin
20 mg/kg (max 600 mg)
50 mg/kg (max 2 g)
15 mg/kg (max 500 mg)
Penicillin allergic-oral regimen
Penicillin allergic and unable to take oral
medication
Clindamycin
or
20 mg/kg IV (max 600 mg)
Cefazolin a
50 mg/kg IM/IV(max 1g)
a Cephalosporins should not be used in individuals with immediate-type hypertensivity reaction (urticaria, angioedema, or anaphylaxis) to
penicillins.
TRANSCOM | BEDIMANS MD|4
PEDIATRICS
Acquired heart disease
MARIVIC MOTILLA-ESGUERRA, MD
Recitation:
Acquired Heart Disease
1. Kawasaki
2. Mitral Valve Prolapse
3. Rheumatic Heart Disease
4. Pericarditis
5. Cardiac tamponade
TRANSCOM | BEDIMANS MD|5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Infective Endocarditis.... MshembaDocumento39 pagineInfective Endocarditis.... MshembaTimothy Casmiry MshembaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ug Infective Endocarditis SubmitDocumento49 pagineUg Infective Endocarditis SubmitAhmed FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoDocumento37 pagine2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoLobna ElkilanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Documento45 pagineInfective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Rapid MedicineNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Infective Endocarditis (2)Documento37 pagineLecture Infective Endocarditis (2)Johnson OlawaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento45 pagineInfective EndocarditisReem 10Nessuna valutazione finora
- New-Infective EndocarditisDocumento30 pagineNew-Infective Endocarditisزياد سعيدNessuna valutazione finora
- Acquired Heart DiseaseDocumento76 pagineAcquired Heart DiseaseBirhanu ShiferawNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro - CVS InfectionsDocumento55 pagineMicro - CVS InfectionsMahmoud hilmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTDocumento21 pagineAnak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTAnastasia PinkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocumento67 pagineInfective Endocarditis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDr. Rajesh PadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento50 pagineInfective EndocarditisIsaac ayobamiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8. Infections of the Cardiovascular System 2024Documento46 pagine8. Infections of the Cardiovascular System 2024aguilarjanicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology of CVSDocumento44 pagineMicrobiology of CVSsultan khabeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento45 pagineInfective Endocarditissathish LakshmananNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocarditisDocumento38 pagineEndocarditiseviherdiantiNessuna valutazione finora
- ENDOCARDITISDocumento7 pagineENDOCARDITIS46 MalsawmtluangiNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 EndocarditeleDocumento2 pagine28 Endocarditelecristian241Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatic Valvular DiseaseDocumento28 pagineRheumatic Valvular DiseaseBenallouaminaNessuna valutazione finora
- S Infective EndocarditisDocumento24 pagineS Infective EndocarditisMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento68 pagineInfective EndocarditisDr. Rajesh PadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial EndocarditisDocumento5 pagineBacterial EndocarditisAMOS MELINessuna valutazione finora
- Disease of Endocardium, Myocardium and PericardiumDocumento54 pagineDisease of Endocardium, Myocardium and PericardiumadystiNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento37 pagineInfective EndocarditisBiruk WorkuNessuna valutazione finora
- INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTDocumento13 pagineINFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTIbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento57 pagineInfective EndocarditisRika FitriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clot Expands: Deformity/injury To The EndocardiumDocumento2 pagineClot Expands: Deformity/injury To The EndocardiumJynrose Kaye GulpanyNessuna valutazione finora
- IM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseDocumento4 pagineIM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseLucyellowOttemoesoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis: Fever, Murmur, Roth's SpotsDocumento10 pagineInfective Endocarditis: Fever, Murmur, Roth's SpotsShrests SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento5 pagineInfective Endocarditismustafa malvi100% (1)
- Endocarditis Blok 10Documento50 pagineEndocarditis Blok 10Dena Paramita RustandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sbe in ChildrenDocumento42 pagineSbe in Childrengrim reaperNessuna valutazione finora
- Microorganisms Related To Cardiac Infections: Ramlan SadeliDocumento39 pagineMicroorganisms Related To Cardiac Infections: Ramlan SadeliPriya GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9) Infective Endocarditis (IE)Documento3 pagine9) Infective Endocarditis (IE)Aris PaparisNessuna valutazione finora
- MYOCARDITIS PPT NewDocumento27 pagineMYOCARDITIS PPT Newsanta_pangaribuan_1100% (2)
- 8.29.06 Staphlococcal BacteremiaDocumento41 pagine8.29.06 Staphlococcal BacteremiaVaibhav KaroliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral MyocarditisDocumento42 pagineViral MyocarditisAlishba AtifNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis: Hariprasad KDocumento28 pagineInfective Endocarditis: Hariprasad KHari Prasad K100% (1)
- Infective Endocardits: Dr. Abhay Kumar MODERATOR-Dr. Rajesh KumarDocumento42 pagineInfective Endocardits: Dr. Abhay Kumar MODERATOR-Dr. Rajesh KumarAbhay BarnwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio - InfectiveDocumento13 pagineCardio - InfectiveHgiel100% (1)
- AaaaDocumento57 pagineAaaaandreva8Nessuna valutazione finora
- 0002 Infectious Diseases of The HeartDocumento35 pagine0002 Infectious Diseases of The Heartmblanco.dchNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvular Heart Disease: Cardiology Division, Medical Faculty Diponegoro UniversityDocumento46 pagineValvular Heart Disease: Cardiology Division, Medical Faculty Diponegoro UniversityChacha TasyaNessuna valutazione finora
- PericarditisDocumento52 paginePericarditissanjivdasNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs RJ Endoc EnglishDocumento62 pagineCurs RJ Endoc EnglishArleen MatincaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 - Invefctive EndocarditiesDocumento71 pagine9 - Invefctive EndocarditiesMahmoud OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Miocardite Si CMPDocumento108 pagineMiocardite Si CMPStefan ChirilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional LetterTemplateDocumento4 pagineProfessional LetterTemplateMax MustermannNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis WORDDocumento24 pagineInfective Endocarditis WORDHashmithaNessuna valutazione finora
- PathologyDocumento28 paginePathologyakkashamrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento66 pagineInfective Endocarditistummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (4)
- CVS 5 PDFDocumento24 pagineCVS 5 PDFafaq alismailiNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis Case ReportDocumento40 pagineInfective Endocarditis Case Reportliu_owen17100% (1)
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento18 pagineInfective EndocarditisSam100% (1)
- (Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesDocumento26 pagine(Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesJustin Ng SincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Infectious EndocarditisDocumento4 pagineInfectious EndocarditisKhalid Mahmud Arifin100% (1)
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento12 pagineInfective EndocarditisYoulin KohNessuna valutazione finora
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocumento14 pagineEPI Vaccines HandoutsStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- DENGUE Clinician GuideDocumento8 pagineDENGUE Clinician GuideLuis Alfredo LaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2B Safe Motherhood Program & Women's Health PDFDocumento11 pagine1.2B Safe Motherhood Program & Women's Health PDFStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Medicine Topics on Gifted Children, Special Needs, Adolescent and Senior HealthDocumento6 pagineFamily Medicine Topics on Gifted Children, Special Needs, Adolescent and Senior HealthStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Documento160 pagineWHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Jason MirasolNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Fmchiii Air Pollution, Housing and Noise PollutionDocumento8 pagine6-Fmchiii Air Pollution, Housing and Noise PollutionStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating TheatreDocumento26 pagineOperating TheatreStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- MseDocumento6 pagineMseStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Quality ManagementDocumento2 pagineWater Quality ManagementStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 FMCH III Universal Health CareDocumento2 pagine2 FMCH III Universal Health CareStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2a Disorders of The Optic NerveDocumento7 pagine1.2a Disorders of The Optic NerveStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Aplied Nutrition CancerDocumento17 pagineAplied Nutrition CancerStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob - Renal and Urinary Tract DisordersDocumento5 pagineOb - Renal and Urinary Tract DisordersStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric CardiologyDocumento9 paginePediatric CardiologyStephen Pilar Portillo100% (1)
- Aml, CMPD (CML, Et, PV, Im) and AllDocumento12 pagineAml, CMPD (CML, Et, PV, Im) and AllStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Hema CoverageDocumento1 paginaHema CoverageStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Discuss The Users of Financial Information Internal UsersDocumento6 pagineDiscuss The Users of Financial Information Internal UsersStephen Pilar PortilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Anesthesia Guide for Mitral Stenosis PatientDocumento67 pagineAnesthesia Guide for Mitral Stenosis PatientNamithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective EndocarditisDocumento68 pagineInfective Endocarditisjake lipovetskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocumento91 paginePart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Evaluation and Treatment in PediatricsDocumento86 paginePerioperative Evaluation and Treatment in Pediatricsmedpedshospitalist100% (2)
- KEMH Guidelines On Cardiac Disease in PregnancyDocumento7 pagineKEMH Guidelines On Cardiac Disease in PregnancyAyesha RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- ArtigoDocumento17 pagineArtigoGisele CanelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of ComplicationsDocumento52 pagineInfective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complicationsmmbire@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Class EssaysDocumento6 pagineSocial Class Essaysolylmqaeg100% (2)
- Abdominal Pain: (Everyone's Favorite!)Documento13 pagineAbdominal Pain: (Everyone's Favorite!)Emily EresumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infectious Diseases of The HeartDocumento84 pagineInfectious Diseases of The HeartHarold DiasanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdDocumento330 pagineHandbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdPedro Jose Ramos Cabrera100% (2)
- Referat EndocarditisDocumento25 pagineReferat EndocarditisNadya Hasna Rasyida DANessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis: Fever, Murmur, Roth's SpotsDocumento10 pagineInfective Endocarditis: Fever, Murmur, Roth's SpotsShrests SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wallet Card Prevention of Infective (Bacterial) EndocarditisDocumento2 pagineWallet Card Prevention of Infective (Bacterial) EndocarditisAline Caroline SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis-An EssayDocumento12 pagineAntibiotic Prophylaxis-An EssayGokul RamakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Infective Endocarditis1Documento50 pagineInfective Endocarditis1Eman ShNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 36: Inflammatory and Structural Heart Disorders Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionDocumento12 pagineChapter 36: Inflammatory and Structural Heart Disorders Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionKrishna RamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology and Pathogenesis of Infective Endocarditis in Native Heart ValvesDocumento8 paginePathology and Pathogenesis of Infective Endocarditis in Native Heart ValvesIrina TănaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Notes On Internal Medicine (TZTM)Documento255 paginePractical Notes On Internal Medicine (TZTM)Aung Zaya KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDocumento45 pagine2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient evaluation and surgical placement of dental implantsDocumento109 paginePatient evaluation and surgical placement of dental implantsCounselor Optimus EduconNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Assessment ANSWERS (MCQ)Documento15 pagineSelf-Assessment ANSWERS (MCQ)Maria OnofreiNessuna valutazione finora
- Osler VS JanewayDocumento7 pagineOsler VS JanewaytanjxNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial EndocarditisDocumento14 pagineBacterial EndocarditisSubhanAnwarKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro - CVS InfectionsDocumento55 pagineMicro - CVS InfectionsMahmoud hilmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Review Essay ExampleDocumento8 pagineBook Review Essay Exampletxmvblaeg100% (2)
- Pharm Cvs McqsDocumento30 paginePharm Cvs McqsSoodn Kang Soodn100% (3)
- Inflamatory Heart DiseaseDocumento42 pagineInflamatory Heart DiseaseChalie MequanentNessuna valutazione finora
- MOST IMPORATANT ONE LINERS Compiled by Medicinosis Magnus 2Documento18 pagineMOST IMPORATANT ONE LINERS Compiled by Medicinosis Magnus 2VAIBHAV SHARMA- 122Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Infective EndocarditisDocumento54 pagine2015 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Infective EndocarditisFernando Muñoz SolteroNessuna valutazione finora