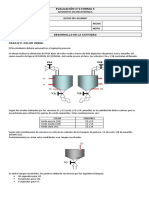
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Manual de Calculadora Ti 89
Caricato da
Anonymous yQo37BGgzlDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Manual de Calculadora Ti 89
Caricato da
Anonymous yQo37BGgzlCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
MANUAL DE LOS PROGRAMAS DE
ECUACIONES DIFERENCIALES
LAPLACE E INVERSA DE LAPLACE
FOURIER E INVERSA DE FOURIER
PARA LAS CALCULADORAS
VOYAGE 200
TI-89 TITANIUM
Autor: Estos programas y sus respectivos manuales fueron credos por el Danes Lars
Frederiksen
Adecuados por ABAK CALCULADORAS: Estos programas se acceden desde un nuevo
men creado en la pantalla HOME, ahora los programas corren aun si se debe reiniciar la
calculadora.
MENU DE MATEMATICAS:
Su calculadora debe tener instalado el men de matemticas, desde la pantalla HOME
presione la tecla diamante (verde) y el nmero 5 y vera la siguiente pantalla:
NOTA: Si su calculadora no tiene este men debe acercarse a la oficina de ABAK
CALCULADORAS para su actualizacin, para nuestros clientes fuera de
Bucaramanga por favor contctenos por el MSN para enviarle la respectiva
actualizacin.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
1. ECUACIONES DIFERENCIALES, LAPLACE E INVERSA DE LAPLACE
Ingrese al men de matemticas, escoja la opcin de
clculo y presione el cursor derecho.
Escoja ECUACIONES DIF LAPLACE INV.LAPLACE y
presione la tecla [ENTER].
El programa realiza una comprobacin interna y carga la
pantalla de trabajo.
Cuando desee ver una respuesta en toda la pantalla
solo debe seleccionar la respuesta y presionar F2.
Como se hace?: Utilice el siguiente ejemplo que esta
cargado en el programa, en la ventana F5 (Ejemp)
seleccione el ejemplo 3 para que se ejecute.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Cuando se termine de calcular la ecuacin diferencial
seleccinela (cursor arriba) y presione la tecla F2,
estando en la pantalla de visualizacin puede utilizar
los cursores para desplazarse de forma rpida por la
respuesta, para salir solo presiona la tecla ESC.
Si la opcin de visualizacin (F2) no esta activada o no
funciona debe cargar nuevamente los parches, para
esto desde HOME presiona las teclas diamante y 4
escoge la opcin PARCHES Y UTILIDADES DE
MEMORIA y la subopcin REINSTALAR LOS
PARCHES.
Cuando quiera salir del programa solo debe
presionar la tecla F6 y la tecla [ENTER].
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
TEXTO EN INGLES ORIGINAL DEL AUTOR
Differential equation solver
SlvD
This solver will find the solution to most common differential equations.
The methods the program is using can basically be split up in two types:
Reducing the order, recognising the equation type and solving using formulas.
o Separable equations
o Linear first order equations
o Bernoulli's equations
o Exact equations
o Homogeneous equations
Linear, (non)homogeneous and Euler or Cauchy equations are solved using either Laplace or a
general solution method, which has no name. These methods can solve any equation of
mentioned types only limited by the calculators ability to handle the result.
o Linear, homogeneous 1-9th order equations
o Linear, nonhomogeneous 1-9th order equations
o Euler or Cauchy 1-9th order equations
NOTE: TI-89/TI-92+ can solve single differential equation with an order<3.
Syntax for solver:
SlvD(equation, independent var, dependent var)
SlvD({equation, t0, y(t0), y(t0), y(t0), y(t0), ......}, independent var, dependent var)
The result when solving without initial conditions will contain constants with the name cc1-cc9,
which are arbitrary constants.
Following constant names is reserved for the program and may not be used in equations or
initial conditions: cc1-cc9 and all constants with two or more characters starting with a Greek
char.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Equation:
A derivative of a function is written: 'prefix'+name+order. The default prefix is the letter 'd', but
storing another letter in the variable "dif/prefix" will change it. The order can be a number from
1-9.
Example where the function name is y:
y is written "y"
y is written "dy" or "dy1"
y is written "dy2"
y is written "dy3"
...
...
y''''''''' is written "dy9"
Initial conditions
t0 is the initial time for all conditions
y(t0) is the wanted result if solution is evaluated to time t0
y(t0) is the wanted result if solution is differentiated and evaluated to time t0
...
Examples of solving equations without initial conditions.
Example 1: solving a linear first order equation
On the command line write:
slvd(dy+sin(t)*y=t^2,t,y)
Result on the home screen:
Where cc1 is an arbitrary constant.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Example 2: Linear, nonhomogeneous third order equation
On the command line write:
slvd(dy3+dy2+dy+y=tan(t),t,y)
Result on the home screen:
Example 3: general solutions to Linear, nonhomogeneous second order equations.
On the command line write:
slvd(dy2+a*dy+b*y=r(x),x,y)
Result:
NOTA: PUEDE VER LA RESPUESTA EN PANTALLA COMPLETA SELECIONANDOLA Y
PRESIONANDO LA TECLA F2
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Examples of solving equations with initial condition.
Example 1: separable equation
On the command line write:
slvd({y*t*dy+ (y)=0,5,3}, t, y)
Result on the home screen:
Example 2: third order linear equation
On the command line write:
slvd({dy3+12*dy2+36*dy=0 0, 3, 1, -7}, t, y)
Result:
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Check solutions from SlvD
Chk
Verifying the solutions from SlvD by inserting them into the original equation. It can only verify
a solution, if it can isolate the dependent variable. If there is more than one solution, then it
will only verify the first solution it finds.
This function can check many solutions, but not all. The solution may be too complex to that it
is possible to isolate the dependent variable or the solutions may be so big that the calculator
runs out of memory when trying to insert the solution in the equation. In the complex case the
only way to check the result may be to manually try to isolate the dependent variable and
insert the found solution in to the equation. In the case where the solution is to big for the
calculator to handle it may be necessary to us one of the math programs to PCs to check the
result.
Syntax:
Chk(equation, independent var, dependent var, solution from SlvD)
Chk({equation, t0, y(t0), y'(t0), ...}, independent var, dependent var, solution from SlvD)
Return: solution from SlvD inserted in the original equation.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Simultaneous differential equation solver
SimultD
Solving multiple simultaneous differential equations. The Principe in this function is, first it will
transform the equations in to the Laplace-domain and second it solves the equations as a
system of linear equations, third it transforms the solutions back to the time-domain (see
Laplace/iLaplace for further information about Laplace-transformation).There are very few
rules to obey when using SimultD. First, there has to be an equal number of equations and
unknown variables. Second, the variable has to be a function of the type f(var). Equations do
not need to be of same order. In Principe SimultD can solve any number of simultaneous
differential/integral equations of any order or mixture of different orders, if there are a
sufficient number of equations. The only limitation is the size of the calculator's memory (if it is
a very complex solution, it can run out of memory). Following constant names is reserved for
the program and may not be used in equations or initial conditions: 's' and all constants with
two or more characters starting with a Greek char.Heaviside/Dirac delta functions may be
used in equations (see Laplace/iLaplace for further information).
Syntax:
SimultD([equation1;equation2;...], [f1(var),f1(0),f1'(0),..;f2(var), f2(0),f2'(0),..;f3(var).. ])
equation1;
Differential/Integral equations separated by ';. A derivative of a
equation2;.....
function is written: d(f(x),x,n) where "d()" is the normal
differentiation function on the calculator and 'n' is the order.
Integrals of a function is written: f(x),x) or d(f(x),x,-n). Where
() is the calculators normal integral-function.
f1(var), f1(0),
Functions to solve for and belonging initial conditions separated
f1(0),....
by ';'.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Example 1:
Solve for t>=0 the first-order simultaneous differential equation
Initial conditions x=2 and y=1 at t=0
First store the equations in a variable:
[d(x(t),t)+d(y(t),t)+5*x(t)+3*y(t)=e^(-t); 2*d(x(t),t)+d(y(t),t)+x(t)+y(t)=3] ->m1
Result:
To solve the equations on the command line write:
SimultD(m1, [x(t),2;y(t),1])
Result on the home screen:
NOTA: NO OLVIDE CUANDO TENGA EN PANTALLA RESPUESTAS MUY
GRANDES (EN HORIZONTAL O EN VERTICAL) PRESIONAR LA TECLA F2
PARA VISUALIZARLA EN PANTALLA COMPLETA Y UTILIZAR EL CURSOR
DE LA CALCULADORA PARA NAVEGAR EN LA RESPUESTA.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Laplace transform
Laplace
Function, which will perform Laplace transformation.
Following constant names is reserved for the program: all constants with two or more
characters starting with a Greek char.
Syntax: Laplace(f(var), var)
f(var) Can be almost any expression, which have a Laplace
transform.
Var
Is the name of the variable to transform normally 't', but
can be any name.
Special transforms:
Unit step function (Heaviside function):
Laplace(u(t - a),t) = e^(-a*s)/s
Dirac delta function:
Laplace( (t - a),t) = e^(-a*s)
Functions/derivatives of functions: only f(var)
Laplace(d(f(t - a),t,2),t) = s^2*f(s)-s*f0-f1
You can get 'delta' by pressing 'green diamond' + G + D on TI-92.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Example 1: Find the Laplace transform of sin(t)^2
On the command line write:
Laplace(sin(t)^2,t)
Result on the home screen:
Example 2: Find the Laplace transform of cos(t)*u(t-4)
On the command line write:
Laplace(cos(t)*u(t-4),t)
Result on the home screen
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Inverse Laplace transform
iLaplace
Function, which will perform Inverse Laplace transformation.
Following constant names is reserved for the program: all constants with two or more
characters starting with a Greek char.
This is a special inverse Laplace function, designed to use in connection with solving of
differential equations or equal. It does NOT return Dirac Delta or Heaviside functions. If there
is a need for those use the inverse Laplace function from Laplace89/Laplace92.
Syntax: iLaplace(F(var), var):
F(var) can be any proper fraction.
var
is the name of the variable to transform normally 's', but
can be any name.
This function cannot transform integrals.
Special transforms:
It can transform all functions, which does NOT have a point in which it goes against infinity.
The result of the transformation will be wrong, if the function does not obey this rule.
Examples of special function, which can be transformed:
sin(f(s))/g(s) (sinus does in no point goes against infinity)
cos(f(s))/g(s)
exp(s^n)/g(s) where n={1,2,3,4....}
...
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Examples of special function, which can NOT be transformed:
tan(f(s))/g(s) (limit(tan(f(s)),f(s),pi/2+n*2pi)=infinity)
arctan(f(s))/g(s)
ln(f(s))/g(s)
exp(1/s^n)/g(s)
...
Example 1:
On the command line write:
iLaplace(b/((s+a)^2+b^2),s)
Result on the homescreen:
Example 2:
Write on the command line:
iLaplace(e^(s^2)/(s+5)^2,s)
Result on the home screen:
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
2. FOURIER E INVERSA DE FOURIER
Ingrese al men de matemticas, escoja la opcin
de clculo y presione el cursor derecho.
Escoja FOURIER INVERSA DE FOURIER y
presione la tecla [ENTER].
El programa realiza una comprobacin interna y
carga la pantalla de trabajo.
Cuando quiera salir del programa solo debe
presionar la tecla F6 y la tecla [ENTER].
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
TEXTO EN INGLES ORIGINAL DEL AUTOR
Fourier
Function: Fourier(f(var), var ,mode)
Transforms the expression "f(var)" from time domain to
cyclic/angular frequency domain (Fourier). This function
has the ability in the most occasions to perform
symbolical transformations, but not in all. It depends on the type of transform.
Parameters
Description
f(var)
Can be any expression, which have a Fourier transform.
var
Is the name of the variable to transform normally 't', but can be any
undefined variable name.
mode=1
f(var) F(w) result in angular frequency, (a)complex evaluated.
mode=2
f(var) F(w) result in angular frequency, (b)no evaluation.
mode=3
v(var) V(f) result in cyclic frequency, (a)complex evaluated.
mode=4
v(var) V(f) result in cyclic frequency, (b)no evaluation.
Complex evaluated; means that the result will be in the calculators complex format (exp(i*w)
will be rewritten to cos(w)+i*sin(w)).
No evaluation; is a special format, where the calculators complex 'i' will be replaced with the
letter 'i'. The results in this format will be exponential functions instead of sine and cosine. The
letter 'i' in the results of Fourier is the same as the complex 'i' and can always be replaced
with it.
The letter 'i' and 'complex i' will be interpreted as equal.
The expression may contain constants of any kind except constants containing the letter 's'.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Special transforms:
Unit step function (Heaviside function):
Definition:
1 for t a
u (t a ) =
0 for t < a
Fourier(u(t - a),t,2 ) = ( w) +
Fourier(u(t - a),t,4 ) =
(f )
2
1
wi
1
ai w
2 i f e i f a
Dirac delta function:
Definition:
1 for t = a
0 for t a
(t a ) =
fourier ( (t a ), t ,2) =
e aiw
1
fourier ( (t a ), t ,4) = i f a 2
(e
)
You can get the char by pressing + G + D on a V200. On a TITANIUM press + ( + D.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Signum function:
Definition:
1 for t a
signum(t-a) =
-1 for t < a
Fourier(signum(t - a), t,2) =
Fourier(signum(t - a), t,4) =
2
wi
1
i a w
i f (e i f a )
The special functions can be used in all expressions.
Some examples:
Fourier(cos(5 t), t,1) = (w - 5) + (w + 5)
(w - 5) (w + 5)
1
1
+
+
Fourier(cos(5 t) u(t), t,1) = i
2
2
2 (5 + w) 2 (w 5)
Fourier(1/(t - 1), t,1) = 2 i e w u ( w)
Fourier (sin(3 t ) / t , t ,4) =
u (3 / 2 + f ) u ( f 3 / 2)
2
2
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
iFourier
Function: iFourier(F(var), var ,mode)
Transforms the expression "F(var)" from
cyclic/angular frequency domain to time domain
(inverse Fourier). This function has the ability in the
most occasions to perform symbolical transformations, but not in all. It depends on the type of
transform.
Parameters
Description
F(var)
Can be any expression, which has an inverse Fourier transform.
var
Is the name of the variable to transform normally 'w' or f, but can be any
undefined variable name.
mode=1
F(w) f(t) from angular frequency to time, (a)complex evaluated.
mode=2
F(w) f(t) from angular frequency to time, (b)no evaluation.
mode=3
V(f) f(t) from cyclic frequency to time, (a)complex evaluated.
mode=4
V(f) f(t) from cyclic frequency to time, (b)no evaluation.
Complex evaluated; means that the result will be in the calculators complex format (exp(i*w)
will be rewritten to cos(w)+i*sin(w)).
No evaluation; is a special format, where the calculators complex 'i' will be replaced with the
letter 'i'. The results in this format will be exponential functions instead of sine and cosine. The
letter 'i' in the results of inverse Fourier is the same as the complex 'i' and can always be
replaced with it.
The letter 'i' and 'complex i' will be interpreted as equal.
The expression may contain constants of any kind except constants containing the letter 's'.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Special transforms:
Unit step function (Heaviside function):
Definition:
1 for w a
u ( w a) =
0 for w < a
iFourier(u(w - a),w,2 ) =
( t )
2
e iat
+
2 i t
e iat
iFourier(u(f - a),f,4 ) = (t ) +
i t
Dirac delta function:
Definition:
1 for w = a
0 for w a
( w a) =
e iat
ifourier ( ( w a), w,2) =
2
ifourier ( ( f a ), f ,4) = (e iat ) 2
You can get the char by pressing + G + D on a V200. On a TITANIUM press + ( + D.
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Signum function:
Definition:
1 for w a
signum(w-a) =
-1 for w < a
iFourier(signum(w - a),t,2 ) =
e iat
i t
2 e iat
iFourier(signum(f - a),t,4 ) =
i t
The special functions can be used in all expressions.
Some examples:
iFourier (u (w + 1) u (w 1), w,1) =
sin(t )
t
t u ( t )
t
iFourier (1 / (w + 1)^ 2, w,2) =
e it
2 e it
sin(5 t )
iFourier ( (w + 5) + (w 5), w,1) =
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Eval
Function: eval(f(var))
f(var) can be any expression containing Heaviside, Dirac delta or Signum functions.
This function will replace u(var), (var), signum(var) with a equivalent when-functions. The
letter 'i' will be replaced with the
'complex i'.
Example: eval(u(t-a))=when(t-a>=0, 1,0)
To obtain a numerical result from a function containing special functions
eval(f(var))|var=value
Plot
Program: Plot(f(var),var,type)
This program will graph functions containing Heaviside, dirac delta or
signum. It will not change the setting of the calculator and it is therefore up to you to manage
the window settings.
Parameters
Description
f(var)
Any function containing Heaviside, Dirac delta or Signum
var
Variable to plot
type 0-2
Type of graph
type=0
Plot the function f(var)
type=1
Plot the amplitude abs(f(var))
type=2
Plot phase
angle(f(var))
CENTRO COMERCIAL ACROPOLIS OFICINA 108
www.abacocalc.galeon.com abakcalculadoras@hotmail.com
TEL: (7)6412088 Fax: (7)6445553
Celular: 3005707077
Bucaramanga
Example:
Plot(u(t)-u(t-4),t,0)
plots a pulse
Example:
Plot the amplitude of a complex function
plot(f(var),var,1)
Plot the phase
plot(f(var),var,2)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Evaluacion2F3 EMTDocumento2 pagineEvaluacion2F3 EMTPedro Ignacio Ramirez MenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solución de Sistema de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en ScilabDocumento2 pagineSolución de Sistema de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en ScilabNanfer Perea0% (2)
- Texto Guia RESIS 1Documento136 pagineTexto Guia RESIS 1ALEX FRANCISCO CABRERA VANEGAS100% (1)
- Manual Tecnico JunkersDocumento56 pagineManual Tecnico Junkersel mariatxi100% (1)
- Electricidad Basica VW PDFDocumento104 pagineElectricidad Basica VW PDFjrrodrigueza280% (5)
- Electro 1Documento18 pagineElectro 1Antonio Cruz Sanabria100% (1)
- Curvas de Deshidratacion de AlimentosDocumento33 pagineCurvas de Deshidratacion de AlimentosAndres Anthony RosasNessuna valutazione finora
- Metodo Generales de NodosDocumento3 pagineMetodo Generales de NodosDiego Jimenez AcuñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lvsim Simulador Gratituido PasosDocumento1 paginaLvsim Simulador Gratituido Pasosroberto cuellarNessuna valutazione finora
- Planificación de Sistemas de Distribución PDFDocumento78 paginePlanificación de Sistemas de Distribución PDFDiego MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario de Dennis G Zill EcuacionesDocumento86 pagineSolucionario de Dennis G Zill EcuacionesAlejandro Amaya100% (1)
- Apuntes de Calculo Multivariable PDFDocumento99 pagineApuntes de Calculo Multivariable PDFPatty100% (1)
- FluidosDocumento5 pagineFluidosTatianaValentinaOrdoñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Resumen de Caracteristicas Del Pic 16f887Documento25 pagineResumen de Caracteristicas Del Pic 16f887PEdro CarvajalNessuna valutazione finora
- Por UnidadDocumento19 paginePor UnidadAnonymous W1QQcbA4sWNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab4 RegulaciónDocumento5 pagineLab4 RegulaciónMaria Camila Cala100% (1)
- T751Documento272 pagineT751nicolásNessuna valutazione finora
- Despacho Económico de Centrales TermicasDocumento6 pagineDespacho Económico de Centrales TermicasMontañez EverNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento7 pagineEcuaciones DiferencialesFernando de la CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios PropuestosDocumento64 pagineEjercicios PropuestosBorja Alvarez OlmosNessuna valutazione finora
- Diego Heidy TodoDocumento11 pagineDiego Heidy TodoDIEGO ALEJANDRO OLAYA BLANCONessuna valutazione finora
- Teoria EjerciciosDocumento15 pagineTeoria Ejerciciospromec2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practica 6. Terminada 3.0Documento24 paginePractica 6. Terminada 3.0Luis Eduardo VázquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo de Teoria de RedesDocumento2 pagineTrabajo de Teoria de Redesjhon fran alvarado suarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Listado4-CALCULO VECTORIALDocumento3 pagineListado4-CALCULO VECTORIALGuillermo Araya HuertaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sucesiones y Series InfinitasDocumento24 pagineSucesiones y Series InfinitasAdam GreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Documento Completo .Pdf-Pdfa PDFDocumento311 pagineDocumento Completo .Pdf-Pdfa PDFBorisParedesNessuna valutazione finora
- Aplicaciones A Flujo de Calor en Estado EstacionarioDocumento2 pagineAplicaciones A Flujo de Calor en Estado EstacionarioAlex IrxNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformaciones LinealesDocumento8 pagineTransformaciones LinealesKEVIN MARIÑONessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Capitulo 1 - 2021 1Documento88 pagine03 Capitulo 1 - 2021 1Jhunior Jhonatan Ramírez CarranzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistemas en CascadaDocumento6 pagineSistemas en CascadaBrandon TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario ELECTRONICA DE POTENCIA 2Documento7 pagineFormulario ELECTRONICA DE POTENCIA 2Daniel LudeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lugar de RaicesDocumento28 pagineLugar de RaicesKarlos Antonio Salinas MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemario 3 Sobretensiones TemporalesDocumento2 pagineProblemario 3 Sobretensiones TemporalesJoseph FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios LagrangeDocumento1 paginaEjercicios LagrangeEsteban RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingenieria de IluminacionDocumento1 paginaIngenieria de IluminacionRonal LyonNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculo de Flujo de PotenciaDocumento26 pagineCalculo de Flujo de PotenciaRazi SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Despiece PDFDocumento1 paginaDespiece PDFHugo Fernandez CeronNessuna valutazione finora
- Prueba de Rigidez Dielectrica 1Documento8 paginePrueba de Rigidez Dielectrica 1Roberto Jimenez DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- CortacircuitosDocumento8 pagineCortacircuitosoncemunicipalNessuna valutazione finora
- ++evaluación Virtual #1, ES-545, FISMA (Autoguardado)Documento19 pagine++evaluación Virtual #1, ES-545, FISMA (Autoguardado)willy huarcayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pruebas y Curvas Caracteristicas de Un Motor Trifasico de InduccionDocumento9 paginePruebas y Curvas Caracteristicas de Un Motor Trifasico de InduccionJeff Torres CaroNessuna valutazione finora
- PC2 - SOLUCIONARIO-Analisis de Corriente AlternaDocumento7 paginePC2 - SOLUCIONARIO-Analisis de Corriente AlternaTacit BladeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagrama Unifilar - F PDFDocumento4 pagineDiagrama Unifilar - F PDFJuanda FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Zbarra y YbarraDocumento4 pagineZbarra y YbarraINONessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad No. 4 Proyecto Con Transistores BJT Y FETDocumento2 pagineActividad No. 4 Proyecto Con Transistores BJT Y FETSergio Alexander PARRA GERENANessuna valutazione finora
- Convocatoria para Concurso de Robótica Seguidor de Linea UTHHDocumento3 pagineConvocatoria para Concurso de Robótica Seguidor de Linea UTHHEmigdio Velasco PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuacion de LaplaceDocumento43 pagineEcuacion de LaplaceCarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesion 10Documento4 pagineSesion 10Jeraldine Wook Torre FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Tipos de Planos ElectricosDocumento1 paginaTipos de Planos Electricosalex597Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bayas Guachanama Poveda 2019aDocumento10 pagineBayas Guachanama Poveda 2019aEduardo CoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas Esfuerzos en VigasDocumento36 pagineProblemas Esfuerzos en VigasjrgrimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Disposición Física Vertical de Las Subestaciones Eléctricas A La IntemperieDocumento3 pagineDisposición Física Vertical de Las Subestaciones Eléctricas A La IntemperieANDRES FELIPE TOBAR ALVAREZ100% (1)
- 2da Practica Procesos ManfDocumento6 pagine2da Practica Procesos ManfRonal LyonNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica3 EL AMPLIFICADOR NO INVERSORDocumento4 paginePractica3 EL AMPLIFICADOR NO INVERSORNelson JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 5Documento1 paginaTarea 5DamacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas de Reduccion para Integrales PDFDocumento9 pagineFormulas de Reduccion para Integrales PDFed_mendez_17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Matematica Basica II 2016 I PDFDocumento2 pagineMatematica Basica II 2016 I PDFJose Luis Soto DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Aisladores de SuspensionDocumento6 pagineAisladores de SuspensionEDUARDO MAYORGA100% (1)
- Guía de Ejercicios 1 Analisis Numerico IPAC 2018Documento8 pagineGuía de Ejercicios 1 Analisis Numerico IPAC 2018juan carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Flujo SecuencialDocumento33 pagineFlujo SecuencialBrezhney G Rosario ANessuna valutazione finora
- CLASE 2 FISICA CUARTO AÑO I MOMENTO CorregidaDocumento8 pagineCLASE 2 FISICA CUARTO AÑO I MOMENTO CorregidaOtilio CaraballoNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica 1Documento35 paginePractica 1Anthonny Jors Rodas CorreaNessuna valutazione finora
- CU00907C Redondear Dos o Mas Decimales Java Precision Errores BigdecimalDocumento8 pagineCU00907C Redondear Dos o Mas Decimales Java Precision Errores BigdecimalMauro VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 1 - La Salvacion - LibritoDocumento8 pagineDiscipulado 1 - La Salvacion - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 0 - Introduccion - LibritoDocumento6 pagineDiscipulado 0 - Introduccion - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 3 - El Bautismo - LibritoDocumento8 pagineDiscipulado 3 - El Bautismo - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 2 - La Seguridad Eterna - LibritoDocumento8 pagineDiscipulado 2 - La Seguridad Eterna - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 4 - El Espiritu Santo - LibritoDocumento8 pagineDiscipulado 4 - El Espiritu Santo - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Discipulado 5 - La Comunion Con Dios - LibritoDocumento10 pagineDiscipulado 5 - La Comunion Con Dios - LibritoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo Individual de PlanificacionDocumento4 pagineTrabajo Individual de PlanificacionAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- TI89 Voyage200Guidebook Part1 ESDocumento344 pagineTI89 Voyage200Guidebook Part1 ESOscar GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Cria de Gallinas PonedorasDocumento0 pagineManual Cria de Gallinas Ponedorasyessicampc100% (1)
- La Vigilancia TecnologicaDocumento5 pagineLa Vigilancia TecnologicaAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelo de Facturas de BombasDocumento1 paginaModelo de Facturas de BombasAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- TI89 Voyage200Guidebook Part1 ESDocumento344 pagineTI89 Voyage200Guidebook Part1 ESOscar GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Montaje de Una Granja Avicola - DesbloqueadoDocumento112 pagineMontaje de Una Granja Avicola - DesbloqueadoAnonymous yQo37BGgzlNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 2. Fisica..FinalizadoooDocumento26 pagineTarea 2. Fisica..FinalizadoooYefferson BermudezNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuito de AlimentacionDocumento30 pagineCircuito de AlimentacionAntonio Gomez NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensayo de Flexión (Madera)Documento3 pagineEnsayo de Flexión (Madera)Andy AnthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia para El Analisis y Diseño Sismico de Las Estructuras de Concreto Reforzado para Contener LiquidosDocumento165 pagineGuia para El Analisis y Diseño Sismico de Las Estructuras de Concreto Reforzado para Contener Liquidosrobinson R100% (1)
- Manual Rollgliss R550 DBI SalasDocumento16 pagineManual Rollgliss R550 DBI SalasJesús BárcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Lineas de TransmisionDocumento9 pagine10 Lineas de TransmisionJhon DLNessuna valutazione finora
- Lise MeitnerDocumento13 pagineLise MeitnerLuisa BocanegraNessuna valutazione finora
- Deposito Por Baño Quimico y Su Uso en Una DisoluciónDocumento5 pagineDeposito Por Baño Quimico y Su Uso en Una DisoluciónJulioCesarSanchezRodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluido No NewtonianoDocumento2 pagineFluido No NewtonianoJulia PampaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecto Ondas MecanicasDocumento16 pagineProyecto Ondas Mecanicasipn_esimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidado Analizadore MuestreadoresDocumento8 pagineConsolidado Analizadore MuestreadoresJhonny CorillocllaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculo de Pavimento Rigido AASHTO 93 v11Documento38 pagineCalculo de Pavimento Rigido AASHTO 93 v11JesusJ.JacomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprensión Lectora Descubrimiento de Un Sistema Solar Con Siete Planetas Como La TierraDocumento2 pagineComprensión Lectora Descubrimiento de Un Sistema Solar Con Siete Planetas Como La TierraNicolásNessuna valutazione finora
- Ley de Hooke-MASDocumento5 pagineLey de Hooke-MASRaúl AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Titulo de Ojo Hum, AnoDocumento57 pagineTitulo de Ojo Hum, AnofranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Caidas HidraulicaDocumento9 pagineCaidas HidraulicaYasutaro Castre Ynoue100% (1)
- Los Ventiladores Industriales Son Utilizados en Los Procesos Industriales para Transportar Aire y GasesDocumento5 pagineLos Ventiladores Industriales Son Utilizados en Los Procesos Industriales para Transportar Aire y GasesCarlomagno Bautista OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Metodo 8 TraduccionDocumento10 pagineMetodo 8 TraduccionHeather GatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Informe 2Documento13 pagineInforme 2jfkwhNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 04 Circuito Hidraulico C3 2014 2 PDFDocumento10 pagineLab 04 Circuito Hidraulico C3 2014 2 PDFPiero Rivas FaustinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Partícula en Una Caja Tridimensional 3Documento32 paginePartícula en Una Caja Tridimensional 3andrexfelo1Nessuna valutazione finora
- E Im 4 Cicuitos de Corriente Alterna PDFDocumento23 pagineE Im 4 Cicuitos de Corriente Alterna PDFJoel EncaladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 2 (VECTORES) PDFDocumento2 pagineTaller 2 (VECTORES) PDFasdNessuna valutazione finora
- Destilacion EcuadorDocumento204 pagineDestilacion EcuadorHenry ArenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporte Metodos de AforoDocumento11 pagineReporte Metodos de AforoCarlosAguilarNessuna valutazione finora