Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Inverse Square Law Calculation
Caricato da
Jayaneela PrawinCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Inverse Square Law Calculation
Caricato da
Jayaneela PrawinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1/8/2016
Inverse Square Law Calculation
Home
About NDT
Resources
Careers
Teaching
Site Navigation
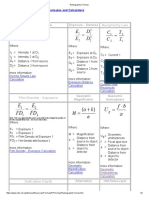
Home - General Resources - Formulas and Calculators - Radiography
Radiographic Inspection - Formula Based on
Newton's Inverse Square Law
In radiographic inspection, the radiation spreads out as it travels
away from the gamma or X-ray source. Therefore, the intensity of the
radiation follows Newton's Inverse Square Law. As shown in the
image to the right, this law accounts for the fact that the intensity of
radiation becomes weaker as it spreads out from the source since
the same about of radiation becomes spread over a larger area. The
intensity is inversely proportional to the distance from the source.
In industrial radiography, the intensity at one distance is typically
known and it is necessary to calculate the intensity at a second
distance. Therefore, the equation takes on the form of:
Where:
I1 = Intensity 1 at D1
I2 = Intensity 2 at D2
D1 = Distance 1 from source
D2 = Distance 2 from source
Note: This is the commonly found form of the equation. However, for some it is easier to remember that
the intensity time the distance squared at one location is equal to the intensity time the distance squared
at another location. The equation in this form is:
I1 x d12 = I2 x d22
Example 1) Use Newton's Inverse Square Law to calculate the intensity of a radioactive source at a
different distance than the distance it was originally measured. If the intensity of a Iridium 192 source was
found to be 62 milliroentgen/hour 100 feet, what is the exposure at a distance of 1 foot.
https://www.nde-ed.org/GeneralResources/Formula/RTFormula/InverseSquare/InverseSquareLaw.htm
1/3
1/8/2016
Inverse Square Law Calculation
Where:
I1
I2
= Intensity at D 1
= Intensity at D 2
D1
D2
= Distance 1
= Distance 2
Reworking the equation to solve for I2
Substitute in the known values and solve for I2
Example 2) A source is producing an intensity of 456 R/h at one foot from the source. What would be the
distance in feet to the 100, 5, and 2 mR/h boundaries.
Convert Rem per hour to mRem per hour
456R/h x 1000 = 456,000 mR/h
Rework the equation to solve for D2
Plug in the known values and solve
https://www.nde-ed.org/GeneralResources/Formula/RTFormula/InverseSquare/InverseSquareLaw.htm
2/3
1/8/2016
Inverse Square Law Calculation
D2= 67.5 feet
Using this equation the 100mR/h boundary would be 68 feet, the 5mR/h boundary would be 301.99 feet,
and the 2mR/h boundary would be 477.5 feet.
Provide Feedback Sponsors & Contributors
Terms & Conditions About the Site
Partial support for this work was provided by the NSF-ATE (Advanced Technological Education)
program through grant #DUE 0101709. Opinions expressed are those of the authors and not
necessarily those of the National Science Foundation.
https://www.nde-ed.org/GeneralResources/Formula/RTFormula/InverseSquare/InverseSquareLaw.htm
3/3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- RT Formulas For CalculationsDocumento4 pagineRT Formulas For CalculationsdanemsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasound Quiz 1: First Name Last NameDocumento7 pagineUltrasound Quiz 1: First Name Last NameahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Asnt Ut L2Documento18 pagineAsnt Ut L2QAMAR ALI KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- A: Self Rectified Circuit: B: Full Wave Rectification CircuitDocumento27 pagineA: Self Rectified Circuit: B: Full Wave Rectification CircuitMarcus Antonius100% (1)
- UT MathDocumento86 pagineUT MathDibyendu Bera100% (1)
- Standard Guide For Radiographic Testing: SE-94 SE-94Documento15 pagineStandard Guide For Radiographic Testing: SE-94 SE-94Jhon HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Lesson 1 - Review Questions - Introduction To Radiographic TestingDocumento1 paginaRT Lesson 1 - Review Questions - Introduction To Radiographic Testingابو المعالي الهمامNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Time Radiography Course BookletDocumento48 pagineReal Time Radiography Course Bookletmusaismail8863Nessuna valutazione finora
- First Name Last Name : LPF Stands ForDocumento35 pagineFirst Name Last Name : LPF Stands ForVicky SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Phased Array Technique For Austenitic Weld Inspection PDFDocumento4 pagineUltrasonic Phased Array Technique For Austenitic Weld Inspection PDFRAFAEL ANDRADENessuna valutazione finora
- CBIP UTL2 General Sample Examination Paper 2Documento3 pagineCBIP UTL2 General Sample Examination Paper 2Kewell Lim0% (1)
- P 14 Cover Sheets 10 07Documento4 pagineP 14 Cover Sheets 10 07carlos100% (1)
- RT FGFDocumento30 pagineRT FGFRaoFarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography Testing Level I and IIDocumento7 pagineRadiography Testing Level I and IIJoshnewfoundNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography Testing Level I and IIDocumento16 pagineRadiography Testing Level I and IIJoshnewfoundNessuna valutazione finora
- RT-2 Radiation Shielding - Laxmi PDFDocumento8 pagineRT-2 Radiation Shielding - Laxmi PDFChandan BeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Level - Ii Examination: General (Set A) : Ultrasonic TestingDocumento5 pagineLevel - Ii Examination: General (Set A) : Ultrasonic Testingshivang naikNessuna valutazione finora
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing of Welds - 141-160Documento20 paginePhased Array Ultrasonic Testing of Welds - 141-160Kevin HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento10 pagineChapter 1kingstonNessuna valutazione finora
- RT NotesDocumento48 pagineRT NotesDevendran Marappan100% (2)
- Ultrasonics Examination Part 3Documento3 pagineUltrasonics Examination Part 3JlkKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography l2 NotesDocumento63 pagineRadiography l2 NotesaasattiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1 UT Lecture-Defect Sizing and EvaluationDocumento24 pagine8.1 UT Lecture-Defect Sizing and EvaluationNikhil KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Penetrant Testing Module 3Documento5 pagineLiquid Penetrant Testing Module 3mujjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual UT 1Documento129 pagineManual UT 1Mahmoud Gaber100% (1)
- Asnt Recer RT QB Level IDocumento9 pagineAsnt Recer RT QB Level IkingstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Phased Array For Corrosion Resistant Alloy (CRA) WeldsDocumento6 pagineApplication of Phased Array For Corrosion Resistant Alloy (CRA) WeldsKevin HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio GraphicDocumento58 pagineRadio GraphicApex AesNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Gen Theroy QuestionsDocumento1 paginaRT Gen Theroy QuestionsMohammed Al-leswas100% (1)
- Level 1 UT Test Part 2Documento12 pagineLevel 1 UT Test Part 2JoshnewfoundNessuna valutazione finora
- UT QuizDocumento6 pagineUT QuizGoutam Kumar Deb100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFDocumento26 pagineUltrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFKarthicWaitingNessuna valutazione finora
- 005.how Phased Arrays Work - FCBDocumento34 pagine005.how Phased Arrays Work - FCBShravanKumar JingarNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocumento14 pagineInterpretation of Weld RadiographsJuliogNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Level III QuestionsDocumento3 pagineRT Level III QuestionsMourad AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Neutron Radiography: Reading IV-Level1,2&3 - ExerciseDocumento251 pagineUnderstanding Neutron Radiography: Reading IV-Level1,2&3 - ExerciseRanendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Level I Radiography TestDocumento33 pagineLevel I Radiography Testndi101100% (1)
- RT FGFDocumento30 pagineRT FGFIke Duaka100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing 8Documento5 pagineUltrasonic Testing 8Duy Le AnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Ut Study GuideDocumento11 pagineUt Study GuideVOLNEY HUMBERTONessuna valutazione finora
- Radiograph FormulaDocumento2 pagineRadiograph Formulaहेमंत कुमार मीणाNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Testing 2Documento19 pagineUltrasonic Testing 2Vijayakumar ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Documento4 pagineRadiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Hussain ShariffNessuna valutazione finora
- Utq Bank 6Documento27 pagineUtq Bank 6kingstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dose Measurement EquationsDocumento7 pagineDose Measurement EquationsAan SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandIndustrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideDa EverandRadiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculating Intensity With The Inverse Square Law (1) TTTTTTTTTTTTDocumento6 pagineCalculating Intensity With The Inverse Square Law (1) TTTTTTTTTTTTAndiappan Pillai100% (1)
- Analysis: I I R R R I I I R K R E E I EDocumento7 pagineAnalysis: I I R R R I I I R K R E E I EJasmin DionisioNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse Square LawDocumento9 pagineInverse Square LawNeil BrionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Doppler Effect and Its Applications PDFDocumento17 pagineDoppler Effect and Its Applications PDFBhumika KansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Great Formulas Explained Physics Mathematics EconomicsDocumento135 pagineGreat Formulas Explained Physics Mathematics EconomicsBrody ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Surveying Mod5 Modern Surveying InstrumentsDocumento81 pagineSurveying Mod5 Modern Surveying InstrumentsAkshay KayapakNessuna valutazione finora
- LN - 10 - 50 - Radar MeteorologyDocumento47 pagineLN - 10 - 50 - Radar MeteorologyPantulu MurtyNessuna valutazione finora
- Doppler-Effect: MTI - Moving Target IndicationDocumento6 pagineDoppler-Effect: MTI - Moving Target IndicationBilal ShahidNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Formulas For CalculationsDocumento15 pagineRT Formulas For CalculationsAwais Jamil70% (10)
- Unit Step 3 Teoria Electromagnetica y OndasDocumento21 pagineUnit Step 3 Teoria Electromagnetica y Ondasdavid1082100% (1)
- FOL Unit 4 PDFDocumento7 pagineFOL Unit 4 PDFShaik RoshanNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB 3 Radiation Heat TrasferDocumento16 pagineLAB 3 Radiation Heat TrasferMastura Ahmad Termizi89% (19)
- Esl Industrial Support Services TRICHY-09: Instrument ListDocumento2 pagineEsl Industrial Support Services TRICHY-09: Instrument ListJayaneela Prawin100% (1)
- 001Documento3.622 pagine001Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Partners ASNT (Contacts)Documento10 pagineCorporate Partners ASNT (Contacts)Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- ProcessFlowChart 1Documento1 paginaProcessFlowChart 1Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- 320 1 Aircraft-TechnicianDocumento4 pagine320 1 Aircraft-TechnicianJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Activities by EslDocumento1 paginaTraining Activities by EslJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Esl Industrial Support Services,: No:6, Neelan Complex, Dheeran Nagar Main Road, Trichy-620009Documento2 pagineEsl Industrial Support Services,: No:6, Neelan Complex, Dheeran Nagar Main Road, Trichy-620009Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Get Fit at Home PreviewDocumento14 pagineGet Fit at Home PreviewclarrissakimNessuna valutazione finora
- TCRADVprofileDocumento91 pagineTCRADVprofileJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Diet For Six Pack Abs - A Complete Diet PlanDocumento42 pagineIndian Diet For Six Pack Abs - A Complete Diet PlanJayaneela Prawin50% (4)
- AccountsDocumento8 pagineAccountsSantosh Kumar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 105 - Muniyakka IIDocumento5 pagine105 - Muniyakka IIJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC CGL Examination 2016 - UNESCO World Heritage Sites in IndiaDocumento4 pagineSSC CGL Examination 2016 - UNESCO World Heritage Sites in IndiaJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- 26384Documento3 pagine26384Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary of Dry Fruits in English and Hindi, Indian Dry Fruits GlossaryDocumento12 pagineGlossary of Dry Fruits in English and Hindi, Indian Dry Fruits GlossaryJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Schedule TemplateDocumento1 paginaDaily Schedule TemplateJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO IEC 17020 Inspection Standard Application DocumentDocumento33 pagineISO IEC 17020 Inspection Standard Application Documentjamilvora100% (1)
- NDT AtoDocumento24 pagineNDT AtoJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Rad ConclusionDocumento1 paginaRad ConclusionJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- EpithalamionDocumento59 pagineEpithalamionJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- 391 Table 1Documento4 pagine391 Table 1Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography in Modern IndustryDocumento212 pagineRadiography in Modern IndustryMohammed Abdul Sayeed50% (2)
- IntroductionDocumento13 pagineIntroductionJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- NDT Question and Answer - UT Level 1 Sample Question Set 1 PDFDocumento7 pagineNDT Question and Answer - UT Level 1 Sample Question Set 1 PDFJayaneela Prawin100% (6)
- NDT Question and Answer - UT Level 1 Sample Question Set 1 PDFDocumento7 pagineNDT Question and Answer - UT Level 1 Sample Question Set 1 PDFJayaneela Prawin100% (6)
- Himachal Pradesh Current Affairs 2016 (Jan - Apr) by AffairsCloudDocumento4 pagineHimachal Pradesh Current Affairs 2016 (Jan - Apr) by AffairsCloudJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Study: Banking Current Affairs "February 2016"Documento15 pagineBank Study: Banking Current Affairs "February 2016"Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Clearsky Hideout Walkthrough - EngDocumento3 pagineClearsky Hideout Walkthrough - EngJayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Communication 2Documento54 pagineHuman Communication 2Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 GB Graphics) Notebook Y567503HIN9 Black Onl...Documento7 pagine4 GB Graphics) Notebook Y567503HIN9 Black Onl...Jayaneela PrawinNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductor Loss Calcs VishayDocumento12 pagineInductor Loss Calcs VishayealbinNessuna valutazione finora
- Planck 'S ConstantDocumento4 paginePlanck 'S ConstantgeetishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bringi V.N., Chandrasekar V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar PDFDocumento664 pagineBringi V.N., Chandrasekar V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar PDFKaren NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Tephigrams For DummiesDocumento28 pagineTephigrams For DummiesmoipedrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics and One Dimensional MotionDocumento24 pagineKinematics and One Dimensional MotionRaven Evangelista CanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Petersen Coils - Principle and ApplicationDocumento2 paginePetersen Coils - Principle and ApplicationadauNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutron Stars, Pulsars, Black HolesDocumento30 pagineNeutron Stars, Pulsars, Black Holesncl12142100% (1)
- Soil CompositionDocumento36 pagineSoil CompositionElla Clent moralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastic PropertiesDocumento15 pagineElastic PropertiesAnang SuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Loss From A Buried Oil PipeDocumento20 pagineHeat Loss From A Buried Oil PipeJuan Pablo ApazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling The Effects of Tool-Edge Radius On Residual Stresses When Orthogonal Cutting AISI 316LDocumento11 pagineModelling The Effects of Tool-Edge Radius On Residual Stresses When Orthogonal Cutting AISI 316LعلىالمهندسNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year Notes 2nd Year Notes Bhattiacademy Com PDFDocumento10 pagine1st Year Notes 2nd Year Notes Bhattiacademy Com PDFAmama zaheerNessuna valutazione finora
- 1e PDFDocumento8 pagine1e PDFEmir RubliovNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Analysis of Stress and Design of Piston Head Using CATIA & ANSYSDocumento10 pagineTheoretical Analysis of Stress and Design of Piston Head Using CATIA & ANSYSinventionjournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- GGPS Syllabus 11Documento42 pagineGGPS Syllabus 11tajbgpNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods and Practice in Cantilever Retaining Wall DesignDocumento14 pagineMethods and Practice in Cantilever Retaining Wall DesignArdalan100% (2)
- Magnetism SC L1-3Documento24 pagineMagnetism SC L1-3Abhishek tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- COM CollisionsDocumento11 pagineCOM CollisionsPranav JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems and Solutions Section 1.1 (1.1 Through 1.26)Documento17 pagineProblems and Solutions Section 1.1 (1.1 Through 1.26)choiNessuna valutazione finora
- Perhitungan Beban Lantai: Review Water Tank Tower Perumahan Bumi Palir Sejahtera-Kota SemarangDocumento13 paginePerhitungan Beban Lantai: Review Water Tank Tower Perumahan Bumi Palir Sejahtera-Kota SemarangOktaSaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Travel PresentationDocumento37 pagineTime Travel PresentationAniruddha Halder75% (4)
- CHEMISTRY#11Documento15 pagineCHEMISTRY#11SUNYNessuna valutazione finora
- Lenses and Imaging (Part I) : MIT 2.71/2.710 09/15/04 wk2-b-1Documento48 pagineLenses and Imaging (Part I) : MIT 2.71/2.710 09/15/04 wk2-b-1wenceslaoflorezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Segment: Subsea Piping: Connections Inlet StreamDocumento16 paginePipe Segment: Subsea Piping: Connections Inlet StreamRaseuki MahadinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Thermoacoustic Refrigerator PDFDocumento3 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Thermoacoustic Refrigerator PDFKishan KitawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuned Track and Locomotion For Midterm 1 - Not Due: BME 473 Applied BiomechanicsDocumento3 pagineTuned Track and Locomotion For Midterm 1 - Not Due: BME 473 Applied BiomechanicskinleyNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY2 Chapter 23 Gauss LawDocumento29 paginePHY2 Chapter 23 Gauss LawChiến PhạmNessuna valutazione finora
- Rank Booster Test Series: 12 and 13 Students (PHYSICS (1) ) Target Iit - Jee - 2016Documento9 pagineRank Booster Test Series: 12 and 13 Students (PHYSICS (1) ) Target Iit - Jee - 2016ashu mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Orifice 1Documento39 pagineOrifice 1Mark MwangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lateral Earth PressureDocumento55 pagineLateral Earth PressureRakesh SheteNessuna valutazione finora