Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chorioamnionitis Drug Study
Caricato da
junard2580100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
317 visualizzazioni9 paginethis is my original care study--based on our school format UC-B..hope this will help you..
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentothis is my original care study--based on our school format UC-B..hope this will help you..
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
317 visualizzazioni9 pagineChorioamnionitis Drug Study
Caricato da
junard2580this is my original care study--based on our school format UC-B..hope this will help you..
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 9
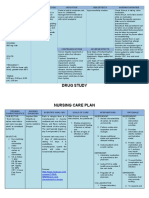
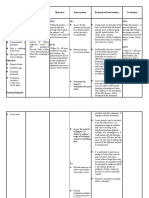
APPENDIX A:
Drug Study
Patient: M.R.C. Age: 16 Hospital No.: 11256-2010 Room No.: Ward 1-Bed 11
Impression/ Diagnosis: PUFT cephalic female live birth secondary to CPD Attending Physician: Dr. Maglasang
Allergy to: NONE
Generic Name & Dose, Strength, Indication/ Adverse/ Side Effects Nursing Rationale Client
Brand Name &Formulation Mechanism of Drug Interaction Responsibilities Teaching
Action
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessment:
Cefuroxime Give Cefuroxime
Sodium 750 mg IVTT Perioperative CNS: dizziness, Asses patient’s To establish Instruct the
every 8 hrs. prevention. headache, malaise, infection before good baseline patient to take
ANST Uncomplicated paresthesia. therapy and data regarding the drug
skin and skin GI: abdominal regularly patient’s exactly as
Brand: Timing: structure cramps, diarrhea thereafter. condition. prescribed,
Zinacef Every 8 hrs. infection. HEMATOLOGIC: Before giving To confirm even of he feels
Uncomplicated eosinophilia, first dose, obtain accurately if better.
Duration: UTI. haemolytic anemia, specimen for patient is not Advise patient
18-24 hrs. Uncomplicated transient culture and allergic to the to take oral
gonorrhoea. neutropenia sensitivity tests. medication. suspension
Otitis media. RESPIRATORY: Begin therapy with food to
Other forms: dyspnea pending test enhance
Infusion: Mechanisms of SKIN: results. absorption.
750 mg, 1.5 g Action: erythematous Assess patient’s For the family Explain that
premixed, rashes, urticuria and family’s to acquire tablets may be
frozen solution Chemical Effect: OTHERS: knowledge of knowledge of crushed, but
- Inhibits hypersensitivity drug therapy. the appropriate drug has bitter
Injection: cell-wall reactions, pain actions and tastes.
750 mg, 1.5 g synthesis, interventions. Tell the patient
promoting to report any
osmotic adverse
instability , reactions.
usually Nursing
bacteriocidal Interactions: Diagnosis:
Drug – Drug: Ineffective
Therapeutic - Diuretics: protection R/T
Effect: may increase bacteria
- Hinders or risk of susceptible to
kills adverse renal drug.
susceptible reactions. Risk for
bacteria Monitor renal deficient fluid
including function volume R/T
many gram- closely. drug adverse
positive Drug- Food: GI reactions.
organisms May increase Deficient
and enteric drug absorption knowledge R/T
gram- and drug therapy.
negative bioavailability
bacilli. of suspension.
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessment:
Celecoxib Give celecoxib Relief of signs CNS: dizziness, Assess patient To be able to Instruct patient
200 mg 1 tab. and symptoms of headache, for have a good to immediately
osteoarthritis. insomnia. appropriateness baseline data. report any
Brand: Timing: Acute pain and CV: hypertension of therapy. signs of GI
Celebrex BID primary EENT: pharyngitis, Monitor patient To be able to bleeding.
dysmenorrhea. rhinitis, sinusitis. for evidence of conduct Advise patient
Other forms: Relief of signs G I: abdominal occult bleeding. appropriate to report
Capsules: and symptoms of pain, diarrhea, measures. immediately
50 mg, 100 rheumatoid dyspensia. Monitor patient To be able to rash,
mg, 200 mg, arthritis. METABOLIC: for signs and assess the level unexplained
400 mg hyperchloremia, symptoms of of toxicity the weight gain or
hypophosphatemia. hepatomegaly. drug have to the edema.
patient. Instruct to take
drug with
food.
Mechanisms of MUSCULOSKEL Nursing
Action: ETAL: Diagnosis:
back pain
Chemical effect: RESPIRATORY: Acute pain R/T
- May upper respiratory underlying
selectively tract infection. infection.
inhibit SKIN: Risk for injury
COX2, Erythema, rash. R/T drug-
decreasing OTHERS: induced adverse
prostaglandi accidental injury. reactions.
ne synthesis. Deficient
Therapeutic knowledge R/T
effect: Interactions: therapy.
- Relieves Drug- Drug:
pain and - Aspirin:
inflammatio May increase
n in joints risk of ulcers.
and smooth - Fluconazole:
muscle May increase
tissue. celecoxib level.
Drug- Lifestyle:
- Chronic
alcoholic use
smoking; may
increase risk
for GI
irritation or
bleeding.
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessment:
Gentamicin Give Gentamicin Meningitis CNS: headache, Assesse To be able to Instruct patient
Sulfate 80 mg IVTT patient’s provide a good to notify
lethargy, numbmess
every 8 hrs. infection and baseline data. prescribier
ANST hearing before about adverse
therapy. reactions.
Brand: Timing: Endocarditis EENT: ototoxicity Obtain specimen To be able to Emphasizes
AgentAmp-amp Every 8 hrs. ANST prophylaxis for GI GU: nephrotoxicity For culture abd confirm if importance of
Bellagen-vial or GU procedure HEMATOLOGY: sensitivity tests patient have drinking at
Elin Gentamicin- Duration: or surgery. agranulocytosis, before giving the other problems least 2L of
amp 7-12 days Posthemodialysis leukopenia, first dose. that may result. fluids daily, it
Garemycin to maintain thrombocytopenia. Be alert for To be able to not
Cream Other forms: therapeutic level. OTHER: adverse provide contraindicated
Gentrolex-vial Injection: hypersensitivity reactions and appropriate .
RiteMed 40 Mechanism of reactions. drug measures.
Gentamicin-vial mg/mL(adult) Action: interactions.
10mg/mL(pedia) Chemical effect: Interactions: Assess patient’s For the patient
IV infusion - Inhibits Drug-Drug and family’s and the family
premixed: protein - Atrocurium: knowledge of to acquire
40mg, 60 mg, synthesis by may increase therapy. knowledge.
70mg, 80 mg, binding to neutomuscula
90mg, 100 mg, ribosomes. r blockade. Nursing
120mg, 160 mg, Therapeutic - Cephalothin: Diagnosis:
180mg Effect: may increase Risk for
- Kills nephrotoxicit infection R/T
susceptible y. presence of
bacteria. - Diuretics: susceptible
Drug only may increase bacteria.
may act ototoxicity. Impaired
against urinary
some elimination R/T
aminoglycos nephrotoxicity.
ide-resistant Deficient
bacteria. knowledge R/T
drug therapy.
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessment:
Metronidazole Give Amebic hepatic CNS: ataxia, To monitor Tell patient to
Assess patient
hydrochloride metronidazole 80 abscess. confusion,depressio drug’s effect. avoid alcohol
infection before
mg IVTT every n. therapy. or drugs.
8hrs. ANST.
Brand: Timing: Intestinal CV: edema, Watch To monitor Instruct
Flagel IV RTU Every 8 hrs. amebiasis. flattened T wave, carefully for sodium patient to take
Metro IV Pelvic flushing edema. retention. oral form with
Novonidazol Duration; inflammatory EENT: eye tearing. Be alert for To establish meal to
1-2 hrs. disease. GI: abdominal adverse proper minimize
Bacterial cramping, reactions. precautionary reactions.
Other forms; vaginosis. anorexia, measures for Instruct
Capsule: 375 mg constipation. possible patient in
Injection: Mechanism of GU: cystitis, Nursing adverse effects. proper
5mg/mL Actions: darkened urine, dry Diagnosis; hygiene.
Tablets: 250 mg , Chemical Effects: vagina. Teach patient
500mg - Direct HEMATOLOGIC: Risk for to cleanse
Tablets(extended acting neutropenia, infection R/T affected areas
release): 750 mg trichomacid thrombocytopenia, presence of twice daily
e and transient leukymia. susceptible before
amebicide SKIN: burning and organisms. applying
that works stinging, contact Risk for MetroLotion.
at both dermatitis, dry deficient fluid
intestinal skin. volume R/T
and OTHERS: drug- induced
extraintestin decreased libido, adverse GI
al sites. glossitis, reactions.
Therapeutic gynecomastia. Deficient
Effects: knowledge
- Hinders Interactions: R/T drug
growth of Drug-Drug therapy.
selected - Disulfiram:
organisms. may cause
acute
psychosis and
confusion.
- Lithium: may
increase
lithium level
resulting in
toxicity.
Drug- Lifestyle;
- Alcohol
use: may
cause
disulfira
m like
reactions.
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessment:
Paracetamol Give Paracetamol Mild fever or HEMATOLOGIC Assess To be able to Tell the
1 amp every 4 hrs pain. : patient’s pain establish a patient not to
PRN for fever. Osteoarthritis hemolytic or temperature good baseline use drug for
Brand: anemia, before giving data of the fever higher
Abenol Timing: leukopenia, the therapy. patient. than 39.5ºC.
FeverAll infant Every 4 hrs PRN Mechanism of neutropenia Be alert for To establish Warn patient
Mapap Actions: HEPATIC: liver adverse the most that high
Tylenol Duration: damage, jaundice reactions and appropriate doses of
Aceta Elixir 4-6 hrs. Chemical METABOLIC: drug measures. unsupervised
Tempra Effects; hypoglycaemia interactions long-term use
Biogesic Other forms: - Blocks SKIN: urticaria . can cause liver
Capsules: pain’s Provide TSB To lessen the damage.
500mg impulses, patient’s Tell patient
Gelcaps: 500mg probably by Interactions; Nursing temperature. not to exceed
Liquid: inhibiting Drug-Drug: Diagnosis: total
160mg/5ml, prostaglandi - Lamotrig recommended
500mg/15ml n or pain ine: Acute pain dose of
Solution: 80mg/ receptor serum R/T patient’s acetaminophe
1.66ml, sensitizers. lamotrigi underlying n per day
100mg/ml ne condition. because of
concentra risk of
tion may hepatotoxicit.
be Tell a breast-
reduced feeding
and mother about
the drug.
Tablets: 160 Therapeutic may decrease Risk for
mg, 325mg, Effects: therapeutic injury R/T
500mg, 650 - Relieves effect. drug induced
mg pain and - Warfarin: may liver damage
reduces increase with toxic
fever. hypoprothrom doses.
binemic effect Deficient
with long knowledge
lasting use of R/T therapy.
acetaminophe
n.
Generic: Ordered: Indications: Adverse Reactions: Assessement:
Retinol (Vitamin Give Vit. A 4 cups RDA CNS: fatigue, Assess To monitor Warn patient
A) 5000u OD Sever Vitamin A headache, patient’s drug’s in taking
Deficiency irritability vitamin A effectiveness. mega doses
Brand: Timing: Maintenance EENT: intake. To be able to of vitamin A
Aquasol A, OD dosage to exopthalmos, If dose are have the without
Palmitate-A prevent papilledema high watch appropriate specific
5000 Duration: recurrence of GI: anorexia, for adverse measures to do. indications.
3-5 hrs vitamin A epigastric pain, reactions. To be able to Explain
deficiency. polydipsia. conclude if importance
Other forms: GU: Assess significant of avoiding
Capsules: 10000 Mechanism of hypomenorrhea, patient’s and others and the prolonged
IU, 15000IU, Action: polyuria. family’s patient was use of
25000IU, Chemical HEPATIC: knowledge of able to gain mineral oil
50000IU effects: cirrhosis, therapy. knowledge. while taking
hepatomegaly the drug.
Injection: 2- - Stimulates MUSCULOSKELET Instruct
mL vials retinal AL: cortical patient to
thickening over the Nursing sort vitamin
function, radius and tibia, Diagnosis: A in tight
Tablets: 5000 bone growth, decalcification of container.
IU reproduction. bone. Imbalanced
Therapeutic Effects: SKIN: alopecia, dry, nutrition: less
- Raises cracked, skin, than body
vitamin A inflamed tongue. requirement
level in body. R/T
OTHER: inadequate
anaphylactic shock intake.
Ineffective
Interactions: health
Drug- Drug; maintenance
- Cholestyrami R/T vitamin A
ne resin: may toxicity caused
decrease GI by excessive
absorption of intake.
fat-soluble Deficient
vitamins. knowledge
- Hormonal R/T drug
contraceptive therapy.
s: may
increase
vitamin A
level.
- Neomycin:
may decrease
vitamin A
level.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocumento3 pagineDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyDocumento8 paginePedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- CDU Care Plan. UTIDocumento7 pagineCDU Care Plan. UTImutiso mutieNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineCefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDeva HiyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study CP3Documento18 pagineDrug Study CP3Camille T. SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCefuroxime Drug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineNeonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyAlvincent D. BinwagNessuna valutazione finora
- DS - Format - MedDocumento3 pagineDS - Format - MedChristian MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineNeonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyAlvincent D. BinwagNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Biographic DataDocumento12 pagineI. Biographic DataYsrael AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- HI Drug Study - v.3Documento13 pagineHI Drug Study - v.3Mary Claire AbenidoNessuna valutazione finora
- CefuroximeDocumento6 pagineCefuroximeJoyce Joyx Joycee SalonoiNessuna valutazione finora
- DS (Ibuprofen)Documento6 pagineDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Tab Ms (SBGH)Documento4 pagineDrug Tab Ms (SBGH)tinaydelossantos2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- JM Drug Study CaseDocumento4 pagineJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Uep - Edu.ph: Generic NameDocumento13 pagineUep - Edu.ph: Generic NameKenneth JazminNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 1Documento6 pagineActivity 1Jastinne Andrei ATIENZANessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineDrug StudyDummy AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Ward DrugsDocumento5 pagineWard DrugsMary Grace AgataNessuna valutazione finora
- Mefenamic CefalexinDocumento4 pagineMefenamic CefalexinDani DaniNessuna valutazione finora
- DrugsDocumento6 pagineDrugsEllenare RacionNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocumento8 pagineDrug Study - Paracetamoldamtere71% (7)
- Drug Study IbuprofenDocumento3 pagineDrug Study IbuprofenblaireNessuna valutazione finora
- PiperacillinDocumento3 paginePiperacillinNicholas TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study G1P0Documento4 pagineDrug Study G1P0Hazel Mae ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento5 pagineDocumentPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Indicat ION Action Side/Ad Verse Effect S Nursing Considera Tion Patient TeachingsDocumento8 pagineDrugs Indicat ION Action Side/Ad Verse Effect S Nursing Considera Tion Patient Teachingsjaninenicole0% (1)
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineCefuroxime Drug StudyJC LumayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyTrexie ScattNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocumento5 pagineCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxomine Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineCefuroxomine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyMenard VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocumento4 pagineDrug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityjenny_lopez_48Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 DrugsuDocumento8 pagine4 Drugsuahmad ryanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP DS Patient 2020Documento13 pagineNCP DS Patient 2020Silvestre SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineDrug StudyDONITA DALUMPINESNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Documento1 paginaDRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Echanique, James F.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiDocumento5 pagineDrug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiKANT JAMES D. MAHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug CiproDocumento1 paginaDrug CiproSrkocherNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento12 pagineDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification: Indication: CNS: Ototoxicity-: Name: L.Y.C Age/Sex: 59 Y.o/ FDocumento8 pagineClassification: Indication: CNS: Ototoxicity-: Name: L.Y.C Age/Sex: 59 Y.o/ FEden Marie FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Case PresDocumento9 pagineDrug Study Case PresDaisy Jane TabonNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyNathalia CabalseNessuna valutazione finora
- CeftazidimeDocumento3 pagineCeftazidimemgbabyloveNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineDrug StudyAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study EntecavirDocumento4 pagineDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocumento2 pagineDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocumento2 pagineCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Polypectomy CSDocumento30 paginePolypectomy CSMASIINessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study CHNDocumento3 pagineDrug Study CHNelijahdale.guillergan-05Nessuna valutazione finora
- PiperacillinDocumento3 paginePiperacillinmyer pasandalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Duty RequirementsDocumento4 pagineDuty RequirementsDOLL RESHELLE MASABENessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacological SheetDocumento4 paginePharmacological SheetFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study FinalDocumento10 pagineDrug Study FinalJashine DajayNessuna valutazione finora
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!Da EverandIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hope in Cancer Therapy: A holistic approach to cancer with curcumin, b17, insulin, methadone & co.Da EverandHope in Cancer Therapy: A holistic approach to cancer with curcumin, b17, insulin, methadone & co.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphylactic Reactions in Anesthesia and Intensive CareDa EverandAnaphylactic Reactions in Anesthesia and Intensive CareNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Myasthenia Gravis (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Myasthenia Gravis (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Randy - Michaux Missing Link in Epstein-Barr VirusDocumento15 pagineRandy - Michaux Missing Link in Epstein-Barr Virusiomast100% (1)
- English For Nursing 2 TBDocumento80 pagineEnglish For Nursing 2 TBstorming2580% (10)
- Dr. Reeves ProlotherapyDocumento172 pagineDr. Reeves Prolotherapyesma bekiroglu100% (1)
- 97 Questions For CouplesDocumento24 pagine97 Questions For Couplesadbombs100% (1)
- Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Risk ... 2010Documento9 pagineChemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Risk ... 2010gemita aldeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sonia Sheth SOCDocumento18 pagineSonia Sheth SOCChris PorteousNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Care Plan 1Documento3 paginePatient Care Plan 1api-311242332Nessuna valutazione finora
- Local AnesthesiaDocumento40 pagineLocal AnesthesiaKY HoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blocked Writer's Book of The DeadDocumento130 pagineThe Blocked Writer's Book of The DeadDavid A Rasch, PhD100% (1)
- Clinical Reasoning in Manual TherapyDocumento12 pagineClinical Reasoning in Manual TherapyLizzie PhilbinNessuna valutazione finora
- Local AnestheticsDocumento35 pagineLocal AnestheticsLuluul MaghfirohNessuna valutazione finora
- Short-Term Effects of Mobilization-With-Movement (MWM) and Auto-Mwm Application in Recreational Runners With Iliotibial Band SyndromeDocumento8 pagineShort-Term Effects of Mobilization-With-Movement (MWM) and Auto-Mwm Application in Recreational Runners With Iliotibial Band SyndromeRia PuputNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Back Pain in Car Drivers: A Review of Studies Published 1975 To 2005Documento15 pagineLow Back Pain in Car Drivers: A Review of Studies Published 1975 To 2005ViolintsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Peter Singer - Animal LiberationDocumento3 paginePeter Singer - Animal LiberationHuyen Nguyen50% (2)
- 1330 Fernando Cervero - Mechanisms of Visceral Pain and HyperalgesiaDocumento38 pagine1330 Fernando Cervero - Mechanisms of Visceral Pain and HyperalgesiaCaesar Bornie AgustioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ante NatalDocumento8 pagineAnte Natalrevathidadam55555Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hamstring Injury: A Clinician'S GuideDocumento6 pagineHamstring Injury: A Clinician'S GuidejavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Picot Presntation 2Documento18 paginePicot Presntation 2api-650274498Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mentally Strong People Hold The PowerDocumento8 pagineMentally Strong People Hold The PowerReaz ReazNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermoneuromodulation Treatment Manual: Self-Published June 2007 by Diane Jacobs, PTDocumento57 pagineDermoneuromodulation Treatment Manual: Self-Published June 2007 by Diane Jacobs, PTXavier De Haro MiretNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Guidelines LowerbackDocumento38 pagineClinical Guidelines LowerbackDavid Mor-YosefNessuna valutazione finora
- Safran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 4finals (8th Rotation)Documento5 pagineSafran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 4finals (8th Rotation)Jayrelle D. SafranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 10 - Lewis MSN Philippine 8eDocumento26 pagineChap 10 - Lewis MSN Philippine 8eCHABELITA DAVIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Sensation, Myers Psychology 8eDocumento28 pagineChapter 5 Sensation, Myers Psychology 8emrchubs93% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Fractures"Documento21 pagineNursing Care Plan For "Fractures"jhonroks97% (34)
- Biopsicosocial Approach To Chronic PainDocumento44 pagineBiopsicosocial Approach To Chronic PainBessy SpNessuna valutazione finora
- Opioid Free Anesthesia A Different Regard To.98965 PDFDocumento6 pagineOpioid Free Anesthesia A Different Regard To.98965 PDFgabriel herreraNessuna valutazione finora
- After Lumbar Spine Surgery: What Can I Expect After The Surgery Is Finished?Documento8 pagineAfter Lumbar Spine Surgery: What Can I Expect After The Surgery Is Finished?Dian RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain - Marcos NCPDocumento4 pagineAcute Pain - Marcos NCPArian May MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Metamorphosis of YouDocumento112 pagineThe Metamorphosis of YouRichel CacanogNessuna valutazione finora