Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
13-Electrolysis of Brine1
Caricato da
Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
13-Electrolysis of Brine1
Caricato da
Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrolysis of brine
Recap of previous knowledge
-
Define the terms: electrolysis and electrolyte.
State two functions of cryolite (Na3AlF6) in the extraction of aluminium.
Electrolysis of brine
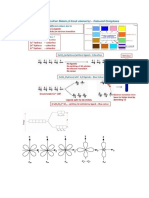
Brine is concentrated solution of sodium chloride (NaCl (aq)). Due slight ionisation of water;
H2O(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq), an aqueous solution of sodium chloride contains four ions as shown on the
table below.
Compound producing ion
Cation
Anion
+
NaCl
Na
ClH2O
H+
OHSources of brine: Brine is obtained
- From sea water
- By dissolving rock salt in water
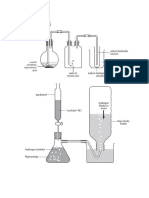
The diaphragm cell below is used to electrolyse brine.
In the set-up above,
- The electrolyte is concentrated NaCl solution
- The anodes are titanium
- The cathodes are steel
- A porous diaphragm separating the anode compartment and the cathode compartment.
Brine therefore contains Na+ and Cl ions from the sodium chloride and H+ and OH ions from
water.
At the cathode: Na+(aq) and H+(aq) present. H+(aq) is discharged, since H is below Na in
reactivity.
2H+(aq) + 2 H2(g)
OR
2H2O(l) + 2 H2(g) + 2OH-(aq).
The discharged H+ ions is replaced by the shift in equilibrium process H2O(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq), to
the right. As the H+ ions are discharged, Na+ ions are left in solution.
At the anode: OH and Cl present. Cl is discharged, since it is in high concentration.
2Cl-(aq) Cl2(g) + 2eAs the Cl- ions are discharged, OH- ions are left in solution. Na+ and OH- ions left in solution form
NaOH solution as H+ and Cl- ions are discharged. Thus electrolysis of brine forms three products:
- Hygrogen gas at the cathode
Chlorine gas at the anode
Aqueous NaOH solution left behind in the diaphragm cell.
The solution is removed and concentrated to form sodium hydroxide.
Precaution taken:
- The brine level in the anode compartment is kept higher than in the cathode. This is to
ensure that brine always flows from the anode compartment to cathode compartment
thereby preventing the flow of NaOH to the anode compartment. In this case, any
undesirable reactions are prevented.
The formation of the three products can be confirmed using tests on the table below:
Product
Hydrogen
Chlorine gas
Sodium hydroxide
Test
Flame brought closer to gas
Damp red litmus lowered into gas
Add a drop of phenolphthalein
observation
Gas burns with a pop sound
Litmus turns red and get bleached
Colourless solution turns pink
Bleach (NaOCl) such as LA CROIX is produced by recting Cl2 with NaOH.
Electrolytic purification of copper
Pure copper in large quantities is only obtained through electrolysis of crude copper. The electrolysis is
carried out using:
- An electrolyte of copper (II) sulphate acidified with sulphuric acid
- An anode of impure copper
- A cathode of pure copper
Anode
sludge
At the anode
At the anode, copper atoms lose electrons and become oxidised to copper ions.
Cu Cu2+ + 2
In solution, the copper ions are attracted to the cathode. Impurities from the anode (impure copper)
are deposited on the bottom of cell anode as sludge.
At the cathode
Copper ions gain electrons and become reduced to copper atoms.
Cu2+ + 2 Cu
The copper atoms are deposited at the cathode.
Observations made during the purification
- Anode reduces in size.
- Cathode increases in size
- Impurities are deposited at the bottom of the electrolytic cell
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Flame Tests, Atomic Spectra & Applications Activity C12!2!02 & 03Documento11 pagineFlame Tests, Atomic Spectra & Applications Activity C12!2!02 & 03Nurul Hana OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Documento2 pagineActivity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic ObjectsDocumento1 paginaMetallic ObjectsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox Equations To Be BalancedDocumento1 paginaRedox Equations To Be BalancedNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- MIXTURESDocumento13 pagineMIXTURESNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 QuestionsDocumento20 pagineTopic 2 QuestionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic ObjectsDocumento1 paginaMetallic ObjectsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDocumento4 pagineSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet-09 (Symbols and Atomic Numbers of The 1st 20 Elements)Documento2 pagineActivity Sheet-09 (Symbols and Atomic Numbers of The 1st 20 Elements)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDocumento6 pagineStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDocumento6 pagineStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDocumento4 pagineSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Documento2 pagineActivity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Nkemzi Elias Nzetengenle100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDocumento6 pagineStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption Spectra of Complex IonsDocumento2 pagineAbsorption Spectra of Complex IonsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- TEST Rate and EnergeticsDocumento1 paginaTEST Rate and EnergeticsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Documento3 pagine2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Rate and Rate ConstantDocumento1 paginaRate and Rate ConstantNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Rate of ReactionsDocumento21 pagineRate of ReactionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDocumento4 pagineSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Form Three ChemitryDocumento1 paginaForm Three ChemitryNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- StereochemistryDocumento6 pagineStereochemistryNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereoalo 07Documento5 pagineStereoalo 07Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereoalo 07Documento5 pagineStereoalo 07Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Practice Questions On PeriodicityDocumento5 pagineHL Practice Questions On PeriodicityNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 2HQDocumento5 pagineChemistry 2HQVongai Christine MlamboNessuna valutazione finora
- T3HQDocumento9 pagineT3HQNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Soap and Detergent Cleaansing ActivityDocumento8 pagine2 Soap and Detergent Cleaansing ActivityhudahilmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic QuestionsDocumento22 pagineAtomic QuestionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry SetupsDocumento5 pagineChemistry SetupsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNessuna valutazione finora