Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1 Electrostatics
Caricato da
pradeep707rediffmailCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1 Electrostatics
Caricato da
pradeep707rediffmailCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electricity and Magnetism
1 Electrostatics
1 lab EM1 E/statics investigations - 2
lessons, during lab cover:
atomic structure; excess electrons -> -ve
charge, etc
charging by induction and by contact
(shared charge) - OHP
testing charge of charged object
why neutral objects attracted to charged
object - both neutral insulators and
neutral conductors - OHP
e/static induction - temporary (charge
distribution) and permanent
conductors and insulators, including
materials that are insulators at low V but
conduct at high V (eg paper, wood)
electroscope - OHP
earthing: charging Earth by contact,
therefore sharing but capactitance Earth
so large that negligible charge remains
on object
show charging e/scope with kV supply > pds created by charging by friction
~1000s volts
using charged e/scope to determine sign
of charge, note neutral object gives same
response (leaf drops) as opposite sign
charge - OHP
Faradays ice pail - OHP
charge distribution over surface of
conductor depends on curvature of
surface - flat, concave, convex
2
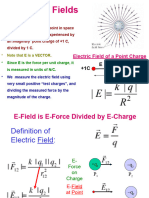
4 electric field
v - quantitative
v F
define E =
q
v k Qq
2
q
for isolated charge E = r = k 2
q
r
compare w. grav field
calc total E for collection point charges
Etot = E1 + E2 + E3 + ...
null pointfor pair unequal charges
E1 = -E2
Qa = -3.0 C
0
Qb = -2.0 C
X
2
x/m
3
find:
Ex due to Qa alone
Ex due to Qa and Qb
location of null point
Wh Ch43 #16, 17, 18
issue E and V worksheet
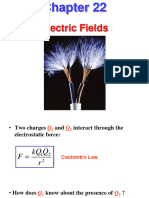
electric force
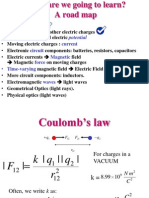
intro Coulombs law
disc units - coulomb, units of k
do simple eg on board, then Wh Ch42
#21
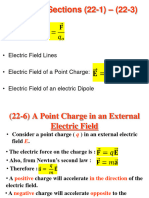
electric field - diagrams
define magnitude and direction - vector
test charge
sketch for: +
+ - (review vector addn)
+ + (null point)
uniform field - straight, parallel,
equidistant
rules: E lines begin on +, end on never cross
never enter conductor
meet surface conductor 90
density of lines measure E
# lines proportional E
h/w: sketch +2 -1 (solution as h/out)
Steve Udy Teaching Notes
page 1 of 2
Printed on 29/6/04
5 electric potential and p.e.
for isolated charge E p = 0 at
Ep = k
r
potential at point is work done per C to
q from infinity to that
mover charge
point
W Ep
Q
V=
=
=k
q
q
r
V is scalar
V +ve around + charges and -ve around charges, therefore V=0 between opposite
charges
demo w.
W
potential difference VAB = VA V B = AB
q
WA B
B
+Q
A
+ work against field? left
- work?
right
0 work?
up or down
-> equipotential lines perpendicular E
lines
equipotential lines on E diagrams
equipotential surfaces
electronvolt - 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J
E vs r and V vs r graphs - OHP
issue e/statics applications h/out
WA B > 0
->
VB >VA
conservative fields
disc 9V battery - move +1C from + to terminal, battery does 9J work (chem to
elect. conversion)
move -1C from + to - terminal, do work
on battery, ie recharging
V at
Wh Ch45 #13,17,18,19,29,30
6 relationship between E and V
4 cm
12V
10V
8V
6V
4V
V
x
2V
=
0.04 m
= 50 V m -1
E=
dir of E? hi V to lo V therefore E =
+Q
V
x
which way to move +Q to do:
Steve Udy Teaching Notes
page 2 of 2
Printed on 29/6/04
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Charge Force Field PotentialDocumento23 pagineCharge Force Field Potentialasifmalik138Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic FieldDocumento53 pagineElectrostatic FieldNilesh NarkhedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec Electric Fields Part 1Documento24 pagineLec Electric Fields Part 1Muhammad MoizNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipotential SurfaceDocumento10 pagineEquipotential SurfaceWilmer R. Jiménez ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21. Electric Charge and Electric Field: © Physics 72 ArciagaDocumento4 pagineChapter 21. Electric Charge and Electric Field: © Physics 72 ArciagaNathan VeracruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Fields and Gauss’ Law ExplainedDocumento31 pagineElectric Fields and Gauss’ Law ExplainedRobert PuckettNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3 - Gauss LawDocumento34 pagineLec 3 - Gauss LawhiransfNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Section 1: The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For Presentation or DisplayDocumento285 pagineChapter 5 Section 1: The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For Presentation or DisplayPriyanka ChauahnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 23 Electric FieldsDocumento35 pagineChapter 23 Electric FieldsTsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 21 Part 2 - May 12Documento21 pagineLecture 1 - Chapter 21 Part 2 - May 12Mircea PanteaNessuna valutazione finora
- A107 L11-13 Lecture Notes Part B (Student)Documento39 pagineA107 L11-13 Lecture Notes Part B (Student)Hui YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Charge and the Electric FieldDocumento36 pagineElectric Charge and the Electric FieldAmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DVS PhysChem 6 2011Documento35 pagineDVS PhysChem 6 2011Jake GaynonNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Physics Notes ch01 Electric Charges and Field PDFDocumento3 pagine12 Physics Notes ch01 Electric Charges and Field PDFVirendra GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.0 Serway PhysicsDocumento71 pagine16.0 Serway PhysicsCalvinNguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed PPT: Electric Potential, Work and Point ChargesDocumento18 pagineCompressed PPT: Electric Potential, Work and Point ChargesJaylanie EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Electric Potential: - The Potential Energy Per Unit Charge, U/q, Is The Electric Potential The Electric PotentialDocumento29 pagineThe Electric Potential: - The Potential Energy Per Unit Charge, U/q, Is The Electric Potential The Electric PotentialMurtaza LokhandwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- EIT ReviewDocumento54 pagineEIT ReviewozzxNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapping Electric Fields Between Charged ConductorsDocumento6 pagineMapping Electric Fields Between Charged ConductorsMágicos OchentasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 NotesDocumento53 pagineChapter 12 NotesCikgu SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric FieldDocumento42 pagineElectric FieldMuhammad Kashif IshaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate Electric Field StrengthDocumento19 pagineCalculate Electric Field Strengthno no no noNessuna valutazione finora
- Demos: Capacitor Separation With Distance - Introduce Dielectrics (Foam, Glass) and See The Voltage Decrease As The Capacitance IncreasesDocumento94 pagineDemos: Capacitor Separation With Distance - Introduce Dielectrics (Foam, Glass) and See The Voltage Decrease As The Capacitance IncreasesZim ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Field Lecture1Documento21 pagineElectric Field Lecture1Vicente ScottNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipotential Lines-1Documento3 pagineEquipotential Lines-1hassantamer2005a1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric FieldDocumento15 pagineElectric FieldNurdian SyahNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Lecture Outline - ppt52Documento64 pagine21 Lecture Outline - ppt52Jumar CadondonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 HW#3: 7 Edition (p591) : 1, 4, 5, 6, 14, 16, 22, 26, 27, 36, 41Documento37 pagineChapter 16 HW#3: 7 Edition (p591) : 1, 4, 5, 6, 14, 16, 22, 26, 27, 36, 41Bellony SandersNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical PotentialDocumento6 pagineElectrical PotentialSalsabila Al-BasheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential and Potential EnergyDocumento7 pagineElectric Potential and Potential EnergyAHMAD AbdelrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- AP-C Objectives (From College Board Learning Objectives For AP Physics)Documento5 pagineAP-C Objectives (From College Board Learning Objectives For AP Physics)testman969Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric ForceDocumento48 pagineElectric ForceHassan AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Field Lecture2Documento19 pagineElectric Field Lecture2Vicente ScottNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Energy and CapacitanceDocumento26 pagineElectrical Energy and CapacitanceshahjafferNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Charge and Electric Field Chapter-21: Topics CoveredDocumento8 pagineElectric Charge and Electric Field Chapter-21: Topics CovereddibyamparidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Field Summary NotesDocumento11 pagineElectric Field Summary NotesVoyce Xavier PehNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocumento19 pagineElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceNancy SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 9Documento35 paginePhy 9OMER ABNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Potential, Potential Difference and ApplicationsDocumento11 pagineElectrical Potential, Potential Difference and ApplicationsatkindsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 Electric FieldsDocumento70 pagine1.2 Electric FieldsSiti Aminah HubadillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemmu Sahu Institutes: Q VR RDocumento30 pagineHemmu Sahu Institutes: Q VR RRamWaghmareNessuna valutazione finora
- Kahatdugan NG PhysicsDocumento9 pagineKahatdugan NG PhysicsGeminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 4 Electricity and MagnetismDocumento52 paginePart 4 Electricity and MagnetismLai Chuen ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Energy and CapacitanceDocumento57 pagineElectric Energy and CapacitanceLuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNessuna valutazione finora
- Couloms Law-Ctu 2020Documento45 pagineCouloms Law-Ctu 2020Zllehb BhelayzNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential PDFDocumento31 pagineElectric Potential PDFEka NurbaizuraNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics II: Electric Charge and FieldsDocumento56 pagineGeneral Physics II: Electric Charge and Fieldsbobby indaeyoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Electric Potential PHY131Documento20 pagine2 Electric Potential PHY131Hisyammudin RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II Marathon 1-FinalDocumento68 pagineUnit II Marathon 1-FinalAntonio JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 123 Module 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocumento22 paginePHYS 123 Module 2 Electric Potential and CapacitanceGabriel BilerNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric PotentialDocumento25 pagineElectric Potentialsalman104alviNessuna valutazione finora
- SP12 212 c21 PDFDocumento6 pagineSP12 212 c21 PDFsiddhartha2862Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Fields Lecture: Field Lines, Charged PlatesDocumento25 pagineElectric Fields Lecture: Field Lines, Charged PlatesJohn McNellNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential: By: Gift ChilesheDocumento16 pagineElectric Potential: By: Gift ChilesheGiftNessuna valutazione finora
- 206 E3 Lab ReportDocumento3 pagine206 E3 Lab ReportJustin KanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter (23: (Electric (FieldsDocumento4 pagineChapter (23: (Electric (FieldsAhmad KhooryNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric FieldsDocumento17 pagineElectric Fieldsමේනුක සූවින්දNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 122 Lecture 4 (Revised)Documento18 paginePHYS 122 Lecture 4 (Revised)BENJAMIN MALUWAZINessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsDa EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Wave Questions EquationsDocumento3 pagineWave Questions Equationspradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Belt Friction Model DerivationDocumento4 pagineBelt Friction Model Derivationpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Belt FrictionDocumento6 pagineBelt Frictionpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary NumbersDocumento1 paginaBinary Numberspradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Sound quest#1C2D5Documento2 pagineReview of Sound quest#1C2D5pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Gates PracDocumento2 pagineLogic Gates Pracpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Resonance PracDocumento2 pagineResonance Pracpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Yr 10 Wave Questions: Speed of Sound 340m/s: /conversion/tmp/scratch/360744911.doc Page 1 of 1Documento1 paginaYr 10 Wave Questions: Speed of Sound 340m/s: /conversion/tmp/scratch/360744911.doc Page 1 of 1pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2b A Brief Guide To IADocumento2 pagine2b A Brief Guide To IApradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Waves Prac 1Documento1 paginaWaves Prac 1pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage Dividers NotesDocumento1 paginaVoltage Dividers Notespradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Subj Report May 01Documento37 pagineSubj Report May 01pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Extended Essays at LPC: A Getting Started On Your Extended EssayDocumento4 paginePhysics Extended Essays at LPC: A Getting Started On Your Extended Essaypradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Timing investigation: mean, deviation, difference analysisDocumento1 paginaTiming investigation: mean, deviation, difference analysispradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Y1 Self TCH UnitDocumento1 paginaY1 Self TCH Unitpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Test For Self-Teaching Unit On Motion: Magan Savant and Steve Udy Page 1 of 1 Printed On 2/7/04Documento1 paginaPre-Test For Self-Teaching Unit On Motion: Magan Savant and Steve Udy Page 1 of 1 Printed On 2/7/04pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2b Designing A Practical InvestigationDocumento2 pagine2b Designing A Practical Investigationpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2b A Brief Guide To IADocumento2 pagine2b A Brief Guide To IApradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics EE Progress Assessment Form: General Assessment Achievement LevelDocumento2 paginePhysics EE Progress Assessment Form: General Assessment Achievement Levelpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- FinalReport Mumbai Nov 2001Documento6 pagineFinalReport Mumbai Nov 2001pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Thermal SchemeDocumento8 pagine2 Thermal Schemepradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Stationary Waves On A StringDocumento2 pagineStationary Waves On A Stringpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Science Group 4 Project Planning SessionsDocumento2 pagineIB Science Group 4 Project Planning Sessionspradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2b A Brief Guide To IADocumento2 pagine2b A Brief Guide To IApradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Read Me FirstDocumento2 pagineRead Me Firstpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Test For Self-Teaching Unit On Motion: Magan Savant and Steve Udy Page 1 of 1 Printed On 2/7/04Documento1 paginaPre-Test For Self-Teaching Unit On Motion: Magan Savant and Steve Udy Page 1 of 1 Printed On 2/7/04pradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- RelativityDocumento1 paginaRelativitypradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Doppler EffectDocumento1 pagina6 Doppler Effectpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Read Me FirstDocumento2 pagineRead Me Firstpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Muon Decay and Failed Michelson-Morley ExperimentDocumento1 paginaMuon Decay and Failed Michelson-Morley Experimentpradeep707rediffmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio P3 2007Documento7 pagineBio P3 2007Noor ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- CertoClav Autoclaves Brochure 2014Documento6 pagineCertoClav Autoclaves Brochure 2014Maruthi KNessuna valutazione finora
- VSBXDocumento33 pagineVSBXDylan HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- STS4001&STS5001Documento24 pagineSTS4001&STS5001Shrishty RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Astrological Sign: Western Zodiac SignsDocumento3 pagineAstrological Sign: Western Zodiac SignsmackNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Methods For Business - 1 NotesDocumento34 pagineQuantitative Methods For Business - 1 NotesSOLOMON GHUNNEYNessuna valutazione finora
- cc1101 p25Documento105 paginecc1101 p25fadfadfNessuna valutazione finora
- CPUID instruction reveals processor detailsDocumento4 pagineCPUID instruction reveals processor detailsGianmarco EspinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Duct Sizing and HVAC CalculationDocumento21 pagineDuct Sizing and HVAC Calculationsardarmkhan80% (5)
- Paper JLP 2019 224 Original V0Documento17 paginePaper JLP 2019 224 Original V0ЮрийNessuna valutazione finora
- PME2M MD2 Lec 04 Belt Drive Tech Aspects 3 FinDocumento17 paginePME2M MD2 Lec 04 Belt Drive Tech Aspects 3 Finjonnel batuigasNessuna valutazione finora
- IP 346-92 Determination of PAC in LubrificantsDocumento6 pagineIP 346-92 Determination of PAC in LubrificantsMark Foster Jr.100% (1)
- EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES Final (1) 1Documento41 pagineEPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES Final (1) 1Tooba Nadeem100% (1)
- CD4051BCDocumento10 pagineCD4051BCBakhtiar TiarNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational ManagementDocumento2 pagineOperational ManagementNur Amalienna SyaheraNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication ofDocumento9 pagineDesign and Fabrication ofKarthi Keyan R KNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Solution: Investment Science: Solution Problem 5.2: The RoadDocumento7 pagineHomework Solution: Investment Science: Solution Problem 5.2: The RoadAbdu AbdoulayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Wyong Road Enviro Factors Appendix PDocumento314 pagineWyong Road Enviro Factors Appendix PAniculaesi MirceaNessuna valutazione finora
- HDL Course Explores Multiplier ArchitecturesDocumento26 pagineHDL Course Explores Multiplier ArchitecturesChien DoMinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Waffle SlabsDocumento5 pagineWaffle Slabseugenia omuhindiNessuna valutazione finora
- Travelling MicroscopeDocumento3 pagineTravelling MicroscopeRohan MohantyNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Analysis of Trestle Leg Conveyor Support Structures Buried in StockpilesDocumento7 pagineLoad Analysis of Trestle Leg Conveyor Support Structures Buried in StockpilesJakesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lin e Hanratty 1986 Prediction PDFDocumento20 pagineLin e Hanratty 1986 Prediction PDFFrancisco OppsNessuna valutazione finora
- tb-02 Product - Spec V 1Documento15 paginetb-02 Product - Spec V 1Marian VerdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec. 6.7 Peak Structural Response From The Response SpectrumDocumento2 pagineSec. 6.7 Peak Structural Response From The Response SpectrumIt'x PathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Postgresql InterviewQuestionDocumento5 paginePostgresql InterviewQuestionmontosh100% (1)
- Group 7 - Hypothesis Testing - 1Documento25 pagineGroup 7 - Hypothesis Testing - 1John Christopher GozunNessuna valutazione finora
- WebAccess - SCADA 8.2 - Final20161019111852Documento3 pagineWebAccess - SCADA 8.2 - Final20161019111852imadz853Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry Concepts ExplainedDocumento404 pagineAnalytic Geometry Concepts ExplainedTshegofatso NtsimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - AntennasDocumento126 pagineChapter 6 - AntennasMag100% (1)