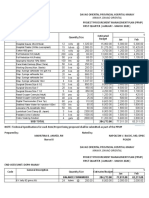
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Band Heterotopia in Zellweger Syndrome (Cerebro-Hepato Renal Syndrome)
Caricato da
ZazzZaffaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Band Heterotopia in Zellweger Syndrome (Cerebro-Hepato Renal Syndrome)
Caricato da
ZazzZaffaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Neuroimage
Band heterotopia in Zellweger syndrome (cerebro-hepato
renal syndrome)
Sandra Young, Yacov Rabi, Abhay K. Lodha
Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology, Foothills Medical Centre, Alberta Children Hospital, Institute of Maternal Child
Health, University of Calgary/Calgary Health Region, Calgary, Alberta T2N2T9, Canada
m
o
fr
Zellweger syndrome (cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome)
d ns
a
is associated with generalized hypotonia, high forehead
lo tio
with flattened facies, hepatomegaly and talipes
n
equinovarus. This pattern of malformations was first
w lica
recognized in 1964 by Bowen and Smith. Zellweger
o
syndrome is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that
d ub
is associated with multiple biochemical markers of
e P ).
e
peroxisomal dysfunction.
r
A full term, intrauterine growth restricted, male neonate f
r ow om
was born to a 32-year-old, gravida 3, para 1 mothero
via
f kn .c
spontaneous vaginal delivery. Polyhydramnios was noted
e
in the pregnancy. Fetal ultrasonography demonstrated
l talipesed ow
b
bilaterally enlarged ventricles in the brain and
n
lascores were
M
equinovarus at 29 weeks of gestation. Apgar
k
i
a presented
y ed
6 and 8 at 1 and 5min respectively. This patient
v
b
with seizures at the time of birth and had
findings
a classical
m brain showed an abnormal band that was isointense with
suggestive of Zellweger syndromesincludingd
generalized
.
e
i
t flat occiput,
matter in the subcortical region of the superior aspect
w gray
hypotonia, large anterior fontanelle (6 x 6 cm),
s
of
both
hemispheres. Dysgenesis of the corpus
w
high forehead with shallowF
supraorbital
ridges,
mild
osinglewtransverse callosumcerebral
was also noted [Figures 1 and 2].
micrognathia, weak suck,D
weak cry,
h
(
P contractures
palmar crease (simian crease),
at elbows and
e
it
is hepatomegaly,
References
knees, short humeri,
patent ductus
s
h
arteriosus and ventricular septal defect and
T a
cryptorchidism.
[1]
[2]
Figures 1 and 2: MRI of brain showing an abnormal band, isointense
with gray matter in the subcortical region of the superior aspect of
both cerebral hemispheres (Arrows). Note the dysgenesis of the
corpus callosum
1.
Zellweger syndrome is one of a number of peroxisome
biogenesis disorders that can manifest as an absence or
reduction in the number of peroxisomes in tissues as
well as multiple enzymes abnormalities. Survivors have
severe mental retardation and epileptic disorders.[2]
Zellweger syndrome is associated with abnormal cortical
gyral patterns, impaired myelination and cerebral
periventricular pseudocysts.[3] In this infant, MRI of the
2.
3.
Bowen P, Lee CS, Zellweger H, Lindenberg R. A familial syndrome
of multiple congenital defects. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp
1964;114:402-14.
Jones KL. Zellweger syndrome (cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome).
In: Jones KL, editor. Recognizable patterns of human malformations.
6th ed. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia; 2006. p. 238-9.
Mochel F, Grebille AG, Benachi A, Martinovic J, Razavi F, Rabier
D, et al. Contribution of fetal MR imaging in the prenatal diagnosis
of Zellweger syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:333-6.
Accepted on 27-08-2006
Abhay Lodha
Foothills Medical Centre, Rm C211, 1403-29 th St NW, Calgary, AB, Canada, T2N 2T9. E-mail: abhay.lodha@calgaryhealthregion.ca
Neurology India | January-March 2007 | Vol 55 | Issue 1
93
CMYK93
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Leukodystrophies and MucopolysacridosisDocumento78 pagineLeukodystrophies and MucopolysacridosisMobin Ur Rehman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter To The Editor: On Cognitive Variability in Velocardiofacial Syndrome: Profound Mental Retardation and AutismDocumento2 pagineLetter To The Editor: On Cognitive Variability in Velocardiofacial Syndrome: Profound Mental Retardation and AutismHarshit AmbeshNessuna valutazione finora
- A Rare Cause of Pancreatic Insufficiency Johanson Blizzard SyndromeDocumento3 pagineA Rare Cause of Pancreatic Insufficiency Johanson Blizzard Syndromeد نبيل عبيدNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Interhemisferic Variant HoloprosencaphalyDocumento4 pagineMiddle Interhemisferic Variant HoloprosencaphalyAhmet Kürşad PoyrazNessuna valutazione finora
- Cri Du ChatDocumento16 pagineCri Du ChatJet LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anancephaly 2Documento3 pagineAnancephaly 2Metta SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Peroksisomal DisordersDocumento27 paginePeroksisomal DisordersLuckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Floppy InfantDocumento7 pagineApproach To Floppy InfantLee Chiang ShengNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento25 pagineCerebral PalsyDr.P.NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cla Eys 1997Documento6 pagineCla Eys 1997jahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Approach To The Dysmorphic Child-R-1Documento108 pagineClinical Approach To The Dysmorphic Child-R-1Drbhupeshwari Gour100% (1)
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento31 pagineCerebral PalsyravannofanizzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cherubism Combined With EpilepsyDocumento7 pagineCherubism Combined With EpilepsywwhhjNessuna valutazione finora
- S D A o (Iii) : S G D, N T D, D D oDocumento10 pagineS D A o (Iii) : S G D, N T D, D D oathayafebNessuna valutazione finora
- UMS Paediatric Short Cases Records 1st EditionDocumento17 pagineUMS Paediatric Short Cases Records 1st EditionHengkai NeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Apparently New Syndrome of Congenital Cataracts, Sensorineural Deafness, Down Syndrome-Like Facial Appearance, Short Stature, and Mental RetardationDocumento5 pagineApparently New Syndrome of Congenital Cataracts, Sensorineural Deafness, Down Syndrome-Like Facial Appearance, Short Stature, and Mental Retardationjahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNessuna valutazione finora
- American Journal of Medical Genetics V PDFDocumento2 pagineAmerican Journal of Medical Genetics V PDFBinod KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Oc Cerebral PalsyDocumento30 pagineOc Cerebral PalsygopikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kulkarni 2004Documento3 pagineKulkarni 2004AlfirahmatikaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9d7f PDFDocumento4 pagine9d7f PDFMubarak HazaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith 1999Documento8 pagineSmith 1999smithl25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDDocumento67 pagineCerebral Palsy: Reported By: Felvee M. Basibas, PTRP MDBobby ReynerNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Epilepsy in A PatientDocumento4 pagine4 Epilepsy in A Patientarturschander3614Nessuna valutazione finora
- Confirmation of The Catania Brachydactylous Type of Acrofacial DysostosisDocumento4 pagineConfirmation of The Catania Brachydactylous Type of Acrofacial DysostosisSergioFernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Delayed Speech DevelopmentDocumento5 pagineDelayed Speech DevelopmentShakirullah KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 10 20 691 PDFDocumento2 pagine3 10 20 691 PDFVaisnaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Down Syndrome, Mental Retardation, Learning DisabilitiesDocumento21 pagineDown Syndrome, Mental Retardation, Learning DisabilitiesMie CorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Shapiro 1997Documento6 pagineShapiro 1997JohnnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento31 pagineCerebral PalsyYunita Amilia0% (1)
- Al Ghamdi1997Documento5 pagineAl Ghamdi1997JohnnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento31 pagineCerebral Palsyfeby1992100% (1)
- Brief Clinical Report: Zimmerman-Laband: Syndrome and Profound Mental RetardationDocumento5 pagineBrief Clinical Report: Zimmerman-Laband: Syndrome and Profound Mental RetardationNorberto Singh Rios (Norbit)Nessuna valutazione finora
- 52 Tripathy EtalDocumento5 pagine52 Tripathy EtaleditorijmrhsNessuna valutazione finora
- 439 2007 Article 362Documento6 pagine439 2007 Article 362Zinik EşanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Gracile Bone Dysplasia (American Journal of Medical Genetics, Vol. 75, Issue 1) (1998)Documento6 pagineGracile Bone Dysplasia (American Journal of Medical Genetics, Vol. 75, Issue 1) (1998)mgNessuna valutazione finora
- RADIOLOGI - NEURORADIOLOGI 2 - Dr. Farah - Kelas ADocumento106 pagineRADIOLOGI - NEURORADIOLOGI 2 - Dr. Farah - Kelas ASeno TanubrataNessuna valutazione finora
- The Developing Human Brain: Growth and AdversitiesDa EverandThe Developing Human Brain: Growth and AdversitiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Retardation, Epilepsy, Short Stature, and Skeletal DysplasiaDocumento3 pagineMental Retardation, Epilepsy, Short Stature, and Skeletal Dysplasiajahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNessuna valutazione finora
- Plomp 1998Documento7 paginePlomp 1998dad dzd adaNessuna valutazione finora
- MRCPCH Guide New QuestionsDocumento11 pagineMRCPCH Guide New QuestionsRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Brain 2014 Yu Brain Awu239Documento5 pagineBrain 2014 Yu Brain Awu239Angeles RbNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento25 pagineCerebral PalsyTINTU JOSEPHNessuna valutazione finora
- January - Hirschsprung's Disease in Africa 21 CenturyDocumento27 pagineJanuary - Hirschsprung's Disease in Africa 21 CenturyVita MadmoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microphthalmia, Marked Short Stature, Hearing Loss, and Developmental Delay: Extension of TheDocumento6 pagineMicrophthalmia, Marked Short Stature, Hearing Loss, and Developmental Delay: Extension of Thejahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNessuna valutazione finora
- Alpers' DiseaseDocumento5 pagineAlpers' DiseaseDANY PAUL BABYNessuna valutazione finora
- Aicardi Goutieres SyndromeDocumento7 pagineAicardi Goutieres Syndromezloncar3Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenDa EverandThe Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenValutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (8)
- HSCI-2 U7P1 Genetics&CongenitalDisordersDocumento7 pagineHSCI-2 U7P1 Genetics&CongenitalDisordersNaima ShireNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroradiological Findings of Trisomy 13 in A Rare Long-Term SurvivorDocumento3 pagineNeuroradiological Findings of Trisomy 13 in A Rare Long-Term Survivorchristian roblesNessuna valutazione finora
- Greenberg1996 PDFDocumento8 pagineGreenberg1996 PDFAraNessuna valutazione finora
- (Sici) 1096 8628 (19981228) 80:5 454::aid Ajmg4 3.0.co 2 o PDFDocumento5 pagine(Sici) 1096 8628 (19981228) 80:5 454::aid Ajmg4 3.0.co 2 o PDFJaymel MaigueNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Genetic DiseasesDocumento77 pagineMetabolic Genetic DiseasesZNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirsch SprungDocumento84 pagineHirsch SprungobligatraftelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sirenomelia: A Case Report of A Rare Congenital Anamaly and Review of LiteratureDocumento3 pagineSirenomelia: A Case Report of A Rare Congenital Anamaly and Review of LiteratureInt Journal of Recent Surgical and Medical SciNessuna valutazione finora
- A Preterm Infant With Semilobar Holoprosencephaly and Hydrocephalus: A CaseDocumento4 pagineA Preterm Infant With Semilobar Holoprosencephaly and Hydrocephalus: A CaseMuhd Idris Aizat AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Sibs With Anencephaly, Anophthalmia, Clefts, Omphalocele, and Polydactyly: Hydrolethalus orDocumento4 pagineSibs With Anencephaly, Anophthalmia, Clefts, Omphalocele, and Polydactyly: Hydrolethalus orSarly FebrianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sammito1988Documento7 pagineSammito1988Aling AyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IDa EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- Case PPT HoloprosensefaliDocumento27 pagineCase PPT HoloprosensefaliMelfi RiqqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Down SyndromeDocumento12 pagineDown SyndromeaksinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocumento13 paginePulmonary Function TestsZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perinatal AsphyxiaDocumento24 paginePerinatal AsphyxiaZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Lactic AcidosisDocumento21 pagineApproach To Lactic AcidosisZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Opportunistic Infections: Dr. Baldev S. PrajapatiDocumento69 pagineOpportunistic Infections: Dr. Baldev S. PrajapatiZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Sedation: Michael R. J. Sury FRCADocumento5 paginePaediatric Sedation: Michael R. J. Sury FRCAZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Marfan Syndrome: General CardiologyDocumento8 pagineManagement of Marfan Syndrome: General CardiologyZazzZaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Electrophysiology, From Cell To Bedside, 6th EditionDocumento1.319 pagineCardiac Electrophysiology, From Cell To Bedside, 6th EditionGabriel CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Revista ImplantologieDocumento52 pagineRevista ImplantologieSebyana100% (1)
- Twin BlockDocumento83 pagineTwin BlockBimalKrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Basic IV Therapy TrainingDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Basic IV Therapy TrainingJay Depakakibo GallardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trust, Compassion and Loyalty Seeing ClearlyDocumento5 pagineTrust, Compassion and Loyalty Seeing Clearlysvetlana_sdNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Room Skills ChecklistDocumento2 pagineOperating Room Skills ChecklistCelso Belala100% (3)
- For Safe & Quality Care of Birthing Mothers & Their NewbornsDocumento24 pagineFor Safe & Quality Care of Birthing Mothers & Their NewbornsCharmaine Rose Inandan Triviño100% (5)
- Cardiology An Illustrated Textbook (Jaypee) PDFDocumento2.136 pagineCardiology An Illustrated Textbook (Jaypee) PDFSarital Boron100% (3)
- Bringing Medicines To JapanDocumento11 pagineBringing Medicines To Japanapi-308447912Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Risk Assessment and Nursing Assessment Charts Presentation Dec 2015 NSW Health TemplateDocumento25 paginePaediatric Risk Assessment and Nursing Assessment Charts Presentation Dec 2015 NSW Health TemplateirinaelenamartiniucNessuna valutazione finora
- FcpsDocumento9 pagineFcpsZoha NaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- PPMP Medical Supplies 2020Documento16 paginePPMP Medical Supplies 2020Jan Oneille Y. VallesNessuna valutazione finora
- Otago MedicineDocumento2 pagineOtago Medicinegus_lionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Endotip Booklet 6Documento2 pagineEndotip Booklet 6Zubna AmbulantaNessuna valutazione finora
- SSM Application SummaryDocumento61 pagineSSM Application SummarySeptaPratamaAptNessuna valutazione finora
- Apexogenesis of A Symptomatic MolarDocumento5 pagineApexogenesis of A Symptomatic MolarFoysal SirazeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetrics by 10 Teachers (18th Ed.)Documento354 pagineObstetrics by 10 Teachers (18th Ed.)keshanraj90% (10)
- Case Studies in FinanceDocumento13 pagineCase Studies in Financechoo QiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tongue Diagnosis of Traditional Chinese Medicine For Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento19 pagineTongue Diagnosis of Traditional Chinese Medicine For Rheumatoid Arthritisluyawin100% (1)
- Cronologia de La Erupcion Dentaria Permanente en Pacientes Con Sindrome de DownDocumento7 pagineCronologia de La Erupcion Dentaria Permanente en Pacientes Con Sindrome de DownArturoGrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine Volume 11 Issue 4 2010 (Doi 10.1016/j.mpaic.2009.12.013) Ben Shelley Nick Sutcliffe - Total Intravenous AnaesthesiaDocumento3 pagineAnaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine Volume 11 Issue 4 2010 (Doi 10.1016/j.mpaic.2009.12.013) Ben Shelley Nick Sutcliffe - Total Intravenous AnaesthesiamikhatiarNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevated Risk of Blood Clots in Women Taking Birth Control Containing Drospirenone, Study ShowsDocumento3 pagineElevated Risk of Blood Clots in Women Taking Birth Control Containing Drospirenone, Study ShowsJomerlyn AbaricoNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital HypothyroidismDocumento44 pagineCongenital Hypothyroidismnayabrizvi1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Assessment of Diverse Frenum Morphology in Permanent DentitionDocumento7 pagineClinical Assessment of Diverse Frenum Morphology in Permanent DentitionBayu Aji KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief CV Shruti ModiDocumento3 pagineBrief CV Shruti ModiMansi JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Trainer Manual For Nusring Care Saves LivesDocumento15 pagineTrainer Manual For Nusring Care Saves LivesEko AwaluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Causes of Myopic ShiftDocumento2 pagine6 Causes of Myopic ShiftNinin Erdininsih Ar0% (1)
- Application Form Clinical Laboratory PDFDocumento6 pagineApplication Form Clinical Laboratory PDFRhodora Benipayo100% (1)
- Introduction To Hospital Pharmacy: OutlineDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To Hospital Pharmacy: OutlinePrincess TiongsonNessuna valutazione finora
- METI Human Patient SimulatorDocumento6 pagineMETI Human Patient Simulatorrafab6970Nessuna valutazione finora