Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Reference and Calibration Standards
Caricato da
Mahade Hasan Dipu0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
73 visualizzazioni2 pagineUltrasonic testing equipment must be standardized and calibrated so that data taken by different operators are comparable and can be matched against inspection norms. Reference standards, such as those designed to ASTM, ASME or AWS specifications, are used to standardize equipment responses. A Reference Standard varying acoustically from the test object by more than 6 decibels are usually considered unacceptable for use.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Reference and Calibration Standards.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoUltrasonic testing equipment must be standardized and calibrated so that data taken by different operators are comparable and can be matched against inspection norms. Reference standards, such as those designed to ASTM, ASME or AWS specifications, are used to standardize equipment responses. A Reference Standard varying acoustically from the test object by more than 6 decibels are usually considered unacceptable for use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
73 visualizzazioni2 pagineReference and Calibration Standards
Caricato da
Mahade Hasan DipuUltrasonic testing equipment must be standardized and calibrated so that data taken by different operators are comparable and can be matched against inspection norms. Reference standards, such as those designed to ASTM, ASME or AWS specifications, are used to standardize equipment responses. A Reference Standard varying acoustically from the test object by more than 6 decibels are usually considered unacceptable for use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
TNT FYI:
Reference and Calibration Standards
To ensure accurate and repeatable inspection, ultrasonic testing equipment must
be standardized and calibrated so that data taken by different operators are
comparable and can be matched against inspection norms. This is accomplished
through the use of reference and calibration standards or test blocks.
Selecting a Reference Standard. Selection of a reference standard is
determined by testing technique, type of material to be inspected and form, type
of discontinuity to be detected, and specification requirements. Reference
standards, such as those designed to ASTM, ASME or AWS specifications, are
used to standardize equipment responses. Blocks with flat bottom holes (Fig. 1)
are often used to standardize amplitude of the detected signal with respect to the
effective area or distance of known reflectors. Area (amplitude or distance)
amplitude curves are usually constructed using such blocks. In some cases,
blocks with side drilled holes are also used for such standardizations. Reference
standards varying acoustically from the test object by more than 6 decibels are
usually considered unacceptable for use.
Preparing a Reference Standard. Sometimes, it is preferable or required to
prepare a reference standard from a piece of the same material as that to be
tested, by introducing notches or holes into a sample or into the actual test
object. The advantage of such a reference standard is that the test object and the
standard will have the same composition, manufacturing history, surface
condition and geometry. the disadvantages are that usually there will be fewer
artificial reflectors and it may not be possible to manufacture the reflectors as
accurately as might be done with a separate standard.
Other types of standard test blocks (and some of the above reference blocks) are
used to calibrate the ultrasonic testing equipment with respect to essential
variables such as sweep length, pulse energy and amplification, search unit
characteristics, sensitivity, resolution and linearity. Typical calibration blocks
include IIW type blocks, DC, SC, DSC and MAB blocks. Two uses of the IIW type
blocks are shown in Fig. 2a and b.
Conclusion. In all cases, reference standards must be prepared and used in
strict accordance with well designed specifications that cover the material, the
fabrication and the application of the blocks.
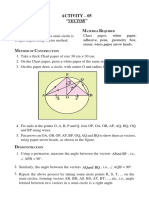
Figure 1. Reference block diagrams (a) and (b)
illustrate flat bottom hole for are and distance
amplitude blocks, (c) side drilled, (d) known
dimension notch and (e) flat bottom hole in
blocked manufactured from actual part.
Figure 2. Two uses of the IIW type block
include (a) IIW verification of angle beam search
unit beam index point and (b) IIW determination
of straight beam dept resolution
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Masdars - Arabic PatternsDocumento11 pagineMasdars - Arabic Patternsspeed2kxNessuna valutazione finora
- TMCP Material TestingDocumento3 pagineTMCP Material TestingMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- International Workshop On SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES NDT in Canada 2013conference & NDT For The Energy IndustryDocumento10 pagineInternational Workshop On SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES NDT in Canada 2013conference & NDT For The Energy IndustryMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 GinzelDocumento12 pagine7 GinzelMahade Hasan Dipu100% (1)
- Volumetric X-Ray Testing: Back To BasicsDocumento4 pagineVolumetric X-Ray Testing: Back To BasicsMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Radiography in The ElectricDocumento4 pagineDigital Radiography in The ElectricMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Ultrasonic Beam FrequencyDocumento6 pagineEffect of Ultrasonic Beam FrequencyMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pixel Stretch Effect Photoshop Tutorial: Column Marquee Tool (Documento1 paginaPixel Stretch Effect Photoshop Tutorial: Column Marquee Tool (Mahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- NDT of Precipitation Hardened SteelsDocumento12 pagineNDT of Precipitation Hardened SteelsMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Blocks For Ultrasonic TestingDocumento3 pagineBlocks For Ultrasonic TestingMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Wave Testing of Water Loaded StructuresDocumento5 pagineGuided Wave Testing of Water Loaded StructuresMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Infrared CamerasDocumento18 pagineInfrared CamerasMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Testing Methodology of MaterialsDocumento11 pagineUltrasonic Testing Methodology of MaterialsMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Asnt Certification Scheme Radiography Method Level - Ii Home Work - Interpretation, Standards & Codes Name: DateDocumento3 pagineAsnt Certification Scheme Radiography Method Level - Ii Home Work - Interpretation, Standards & Codes Name: DateMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Preventing Magnetic Particle TankDocumento5 paginePreventing Magnetic Particle TankMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Using Flat Reference Blocks for Ultrasonic Testing of Cylindrical MaterialsDocumento8 pagineProblems Using Flat Reference Blocks for Ultrasonic Testing of Cylindrical MaterialsMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Level II QuestionsDocumento28 pagineUT Level II QuestionsMahade Hasan Dipu100% (6)
- NDT Necessary Evil or BenefitDocumento14 pagineNDT Necessary Evil or BenefitMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- B4.52 IIBI Global Fin Crisis Can If HelpDocumento9 pagineB4.52 IIBI Global Fin Crisis Can If HelpMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Within The Islamic Framework 2Documento30 pagineMicroeconomics Within The Islamic Framework 2Amine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Within The Islamic Framework 2Documento30 pagineMicroeconomics Within The Islamic Framework 2Amine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Materials Science Chapter 1Documento24 pagineIntroduction to Materials Science Chapter 1Maya RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Level I Questions ExplainedDocumento23 pagineUT Level I Questions ExplainedMahade Hasan Dipu100% (1)
- Developing Microeconomics From An Islamic PerspectiveDocumento39 pagineDeveloping Microeconomics From An Islamic PerspectiveAmine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- International Financial Crisis and Islamic FinanceDocumento11 pagineInternational Financial Crisis and Islamic FinanceAmine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Wealth Creation and Wealth Management in An Islamic EconomyDocumento16 pagineWealth Creation and Wealth Management in An Islamic EconomyAmine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Treasury Management in An Islamic Financial Institution JeddahDocumento10 pagineTreasury Management in An Islamic Financial Institution JeddahAmine ElghaziNessuna valutazione finora
- PT Level II QuestionsDocumento10 paginePT Level II QuestionsMahade Hasan Dipu100% (1)
- MT Level I QuestionsDocumento11 pagineMT Level I QuestionsMahade Hasan Dipu100% (2)
- Mass Spec Level I QuestionsDocumento9 pagineMass Spec Level I QuestionsMahade Hasan DipuNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Solidcam 5 Axis Tutorial: Volume 1 - BeginnerDocumento45 pagineSolidcam 5 Axis Tutorial: Volume 1 - BeginnerReza VahdatparastNessuna valutazione finora
- Orchard Hideout PortfolioDocumento8 pagineOrchard Hideout Portfolioapi-494110834Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure (GWRET) QUANTITY Chainage Length Left RightDocumento50 pagineStructure (GWRET) QUANTITY Chainage Length Left RightLokendra KhatriNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion and Force GlossaryDocumento3 pagineMotion and Force GlossaryLi OliviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drawing Flow and Dimension LinesDocumento9 pagineDrawing Flow and Dimension LinesAdeyemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Four Types of Horizontal Curves ExplainedDocumento22 pagineFour Types of Horizontal Curves ExplainedWaseem AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineIGCSE Physics Lesson Plangdsuta92% (12)
- Turkish Ney Measurements and AnalysisDocumento8 pagineTurkish Ney Measurements and Analysispablojorgeandres100% (1)
- Envision 6 02 05 APDocumento2 pagineEnvision 6 02 05 APhot stuffNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Fault-Tolerant Metric Dimension of Convex PolytopesDocumento14 pagineOn The Fault-Tolerant Metric Dimension of Convex PolytopesUsman KheraNessuna valutazione finora
- Taxi CirclesDocumento3 pagineTaxi Circlesapi-255059274Nessuna valutazione finora
- GRHW 1Documento2 pagineGRHW 1Kastalia Delaporta0% (1)
- WZRDocumento76 pagineWZRhorned_god80% (5)
- 2.1 Describing MotionDocumento25 pagine2.1 Describing MotionncvpsCR100% (2)
- Simbrain Tutorial for v0.02Documento5 pagineSimbrain Tutorial for v0.02Waldo Caceres NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Clustering TechniquesDocumento38 pagineClustering TechniqueskmkatariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH 4 Q3 W6 Visualizes, Measures and Finds The Perimeter of Any Given Plane FigureDocumento18 pagineMATH 4 Q3 W6 Visualizes, Measures and Finds The Perimeter of Any Given Plane FigureJuvi EspejonNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Bridge Detailing-ODocumento15 pagineFinal Bridge Detailing-O11520035Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocumento6 pagineWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade - 9,10 - Math - Project - Term 1 - 2023-2024Documento3 pagineGrade - 9,10 - Math - Project - Term 1 - 2023-2024rukhsanayasmin26Nessuna valutazione finora
- MDP408a Lecture14Documento35 pagineMDP408a Lecture14Hisham Ahmed FouadNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity - 05: "Vector"Documento11 pagineActivity - 05: "Vector"Prannaav Ashwath VelavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Distance-Based ML MethodsDocumento8 pagineDistance-Based ML Methodsshreya sarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 7 - Module 1 - Version 3Documento16 pagineScience 7 - Module 1 - Version 3Abegail PanangNessuna valutazione finora
- Gis Modeling FrameworkDocumento23 pagineGis Modeling FrameworkLuis Carlos PaniaguaNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepInsta Handbook For Quantitative AbilityDocumento151 paginePrepInsta Handbook For Quantitative AbilityShobhit RahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffer tool creates polygons around featuresDocumento4 pagineBuffer tool creates polygons around featuresBOVIC OLIVIERNessuna valutazione finora
- The Elements of Non-Euclidean GeometryDocumento322 pagineThe Elements of Non-Euclidean Geometrybladieboe67% (3)
- GSC101 HandoutsDocumento316 pagineGSC101 HandoutsYaman Askary100% (1)
- Different Models For Facility Location/Assignment: Min CXDocumento5 pagineDifferent Models For Facility Location/Assignment: Min CXRakesh VNessuna valutazione finora