Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and Polymers
Caricato da
Adnan ChowdhuryCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and Polymers
Caricato da
Adnan ChowdhuryCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY
TOPIC 4.8
AMINO ACIDS
TOPIC 4.9
POLYMERS
BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
1.
(a)
Write an equation for the formation of ethyl ethanoate from ethanoyl chloride and ethanol.
Name and outline the mechanism for the reaction taking place.
Equation .....................................................................................................................
Name of mechanism ...................................................................................................
Mechanism
(6)
(b)
Explain why dilute sodium hydroxide will cause holes to appear in clothing made from
polymers such as Terylene but a poly(phenylethene) container can be used to store sodium
hydroxide.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
2.
(a)
Classify the following reaction.
C3H7Br + KOH C3H6 + KBr + H2O
...............................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
How do the physical properties of the alkene homologous series change as the chain length
increases?
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c)
For the reaction shown in the equation:
nC 2 H 4
(i)
H n
give the name of this process:
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
Most ethanol used in the chemical industry is manufactured by reacting together water and
ethene.
(i)
Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
Outline the reaction conditions for this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(iii)
Classify this reaction, indicating the type of initial attack on the ethene.
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
3.
Consider the reaction sequence shown below.
OH
Step 1
CH 3 CH 2 CHO
CH 3 CH 2
HCN
CN
propanal
(a)
OH
Step 2
CH 3 CH 2
COOH
Q
Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction in Step 1.
Name of mechanism ..................................................................................................
Mechanism
(5)
(b)
(i)
Name compound Q formed in Step 2.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Two stereoisomers are formed by the dehydration of Q. Give the structures of these
two isomers and name the type of stereoisomerism shown.
Structures of isomers
Type of stereoisomerism ..............................................................................................
(4)
(c)
An isomer of Q which has the structure shown below is polymerised to form the
biodegradeable polymer known as PHB.
CH 3
HO
CH 2 COOH
(i)
Draw the repeating unit of the polymer PHB.
(ii)
Suggest a reason why the polymer is biodegradeable.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
The amino acid R is shown below.
NH 2
CH 3 CH 2
COOH
R
(i)
Draw the structure of the zwitterion formed by R.
(ii)
Draw the structure of the major organic product formed when an excess of R is
reacted with bromomethane.
(iii)
Name the mechanism of the reaction which results in the formation of the product
given in part (ii).
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 14 marks)
5
4.
The amino acid alanine is shown below.
(a)
A sample of alanine is dissolved in water.
(i)
Draw the structure of the main alanine species present in this aqueous solution
and give the name of this type of species.
Structure
Type of species .................................................................................
(ii)
Draw the structure of the alanine species formed when an excess of hydrochloric
acid is added to the solution.
(3)
(b)
Alanine molecules may be reacted together to form a polypeptide. Give the repeating unit
of this polypeptide and name the type of polymerisation involved in its formation.
Repeating unit
Type of polymerisation .......................................................................
(2)
(c)
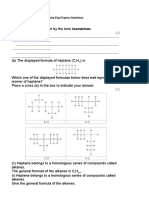
The repeating unit of a polyalkene is shown below.
H
CH 3
CH3 CH 2 CH 3
Give the name of the alkene which is used to form this polymer.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
5.
(a)
The compound H2C=CHCN is used in the formation of acrylic polymers.
(i)
Draw the repeating unit of the polymer formed from this compound.
(ii)
Name the type of polymerisation involved in the formation of this polymer.
............
(2)
(b)
When the dipeptide shown below is heated under acidic conditions, a single amino acid is
produced.
CH 2 CH 3
H2 N
(i)
CH 2 CH 3
COOH
Name this amino acid.
............
(ii)
Draw the structure of the amino acid species present in the acidic solution.
(2)
(c)
The repeating unit of a polyester is shown below.
CH 2CH 2
C
O
(i)
CH2CH 2
Deduce the empirical formula of the repeating unit of this polyester.
............
(ii)
Draw the structure of the acid which could be used in the preparation of this
polyester and give the name of this acid.
Structure ...
Name .
(iii)
Give one reason why the polyester is biodegradable.
............
............
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
6.
(a)
The hydrocarbon M has the structure shown below.
CH3 CH2
CH2
CH 3
(i)
Name hydrocarbon M.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Draw the repeating unit of the polymer which can be formed from M. State the type
of polymerisation occurring in this reaction.
Repeating unit
Type of polymerisation .....................................................................................
(iii)
The reaction between M and benzene in the presence of HCl and AlCl3 is similar to
the reaction between ethene and benzene under the same conditions. Name the type
of mechanism involved and draw the structure of the major product formed in the
reaction between M and benzene.
Name of mechanism ..........................................................................................
Major product
(iv)
Draw a structural isomer of M which shows geometrical isomerism.
(6)
(b)
Draw the repeating unit of the polymer formed by the reaction between butanedioic acid
and hexane-1,6-diamine. State the type of polymerisation occurring in this reaction and
give a name for the linkage between the monomer units in this polymer.
Repeating unit
Type of polymerisation ...............................................................................................
Name of linkage ..........................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 10 marks)
9
7.
(a)
Terylene is a condensation polymer that can be formed from benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic
acid and ethane-1,2-diol. Draw graphical formulae to represent:
(i)
benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid;
(1)
(ii)
ethane-1,2-diol;
(1)
(iii)
the polymer Terylene.
(2)
(b)
Give the name of the type of condensation polymer of which Terylene is an example.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
Outline the difference between the formation of an addition polymer and a condensation
polymer.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
Give the name of one addition polymer.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
10
8.
Ethylbenzene is made by the reaction shown below.
CH 2 CH 3
+
(a)
H2 C
CH 2
Identify two other substances required as catalysts in this preparation.
Substance 1 ............................................................................................................
Substance 2 ............................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
Write an equation for the reaction of these two substances with ethene to form the reactive
intermediate involved in the formation of ethylbenzene.
................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction between this reactive intermediate and
benzene.
Name of mechanism ................................................................................................
Mechanism
(4)
(d)
Draw the structure of the product formed in a similar reaction between benzene and
cyclohexene.
(1)
(e)
Ethylbenzene is used to make phenylethene which can be polymerised to form
poly(phenylethene). Name this type of polymerisation and draw the structure of the
repeating unit in the polymer.
Type of polymerisation ...........................................................................................
Repeating unit ........................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
11
9.
(a)
Synthetic polyamides are produced by the reaction of dicarboxylic acids with compounds
such as H2N(CH2)6NH2
(i)
Name the compound H2N(CH2)6NH2
.....................................................................................................................
(ii)
Give the repeating unit in the polyamide nylon 6,6.
.....................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
Synthetic polyamides have structures similar to those found in proteins.
(i)
Draw the structure of 2-aminopropanoic acid.
(ii)
Draw the organic product formed by the condensation of two molecules of
2-aminopropanoic acid.
(2)
12
(c)
Compounds like H2N(CH2)6NH2 are also used to make ionic compounds such as X, shown
below.
CH3
CH3
H3C
(CH 2 )6 N +
CH3
CH 3
2Br
CH3
Compound X
(i)
X belongs to the same type of compound as (CH3)4N+Br
Name this type of compound.
.....................................................................................................................
(ii)
State a reagent which could produce X from H2N(CH2)6NH2 and give a necessary
condition to ensure that X is the major product.
Reagent ........................................................................................................
Condition .....................................................................................................
(iii)
Name the mechanism involved in this reaction to form X.
.....................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
10.
The polymer poly(chloroethene), commonly known as poly(vinyl chloride) or PVC, can be
produced as follows:
H2C
CH 2
Cl 2
Step 1
Cl
heat
C 2 H 4 Cl 2
C 2 H 3 Cl
Step 2
Step 3
PVC
(a)
Using your knowledge of the reaction between bromine and ethene, name and outline a
mechanism for Step 1.
Name of mechanism ..................................................................................................
Mechanism
(5)
13
(b)
Write an equation for Step 2 showing clearly the structure of the organic product.
..............................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
Plasticisers are often incorporated into polymers such as PVC. Name a type of compound
used as a plasticiser.
..............................................................................................................................
(1)
(d)
(i)
Draw the structure of the organic product of the reaction of C2H4C12 with an excess
of warm aqueous sodium hydroxide.
(ii)
Suggest why C2H3Cl, the organic product of Step 2, does not react with warm
aqueous sodium hydroxide.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
11.
This question concerns the chemistry of ethene and compounds derived from it. Consider the
following statements and then answer the questions below.
Ethene may be polymerised to form poly(ethene).
Treatment of ethene with bromine gives a compound C.
Compound C may be converted in the laboratory into a compound D, which has a
percentage composition by mass of: C 38.71%; H 9.68%; O 51.61%. The relative
molecular mass, Mr, of D is 62.
(a)
(i)
Explain what is meant by the term polymerisation.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii)
Write an equation to represent the polymerisation of ethene.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
14
(b)
Give the name of compound C.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
Give the name of the mechanism of the reaction between ethene and bromine. Draw the
mechanism for this reaction.
Name of the mechanism.
.....................................................................................................................................
Mechanism
(4)
(d)
(i)
Use the analytical data provided at the start of the question to deduce the molecular
formula of compound D.
(3)
(ii)
Give the reagent(s) and condition(s) for the conversion of C into D.
Reagent(s) .........................................................................................................
Condition(s) ......................................................................................................
(2)
(iii)
Write an equation for the conversion of C into D.
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 15 marks)
15
12.
A possible synthesis of 1,4-diaminobenzene is shown below.
NHCOCH 3
NH2
Step 1
NHCOCH 3
Step 2
NO 2
Step 3
NH 2
NH 2
Step 4
NH 2
(a)
NO 2
Identify a suitable reagent or combination of reagents for Step 1. Name and outline a
mechanism for the reaction.
(6)
(b)
Identify a suitable reagent or combination of reagents for Step 2. Name and outline a
mechanism for the reaction.
(6)
(c)
Identify a suitable reagent or combination of reagents for Step 4. Draw the repeating unit of
the polymer formed by reaction of 1,4-diaminobenzene with pentanedioic acid.
(3)
(Total 15 marks)
16
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2.8 Assessed HWDocumento5 pagine2.8 Assessed HWlilaNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Paper 2 pp2Documento16 pagineA-Level Paper 2 pp2Charlie MarstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation and Ethanol ProductionDocumento184 pagineFermentation and Ethanol Productionan7li721Nessuna valutazione finora
- Isomerism 1 QPDocumento10 pagineIsomerism 1 QPClemency OuroussoffNessuna valutazione finora
- AS LEVEL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC TOPIC TESTDocumento14 pagineAS LEVEL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC TOPIC TESTBee Jay JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Mechanisms 3 QPDocumento7 pagineReaction Mechanisms 3 QPSiti NuraqidahNessuna valutazione finora
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocumento11 pagineAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksAlia ShabbirNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Level Chemistry Topic 7 Organic Chemistry HomeworkDocumento14 pagineAS Level Chemistry Topic 7 Organic Chemistry HomeworkShirmara Pile-fordeNessuna valutazione finora
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocumento10 pagineAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksChryssa EconomouNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Mechanisms 4 QPDocumento9 pagineReaction Mechanisms 4 QPklaksmanan1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 7 TestDocumento11 pagineTopic 7 Testab9652378Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acids & Esters 3 QPDocumento10 pagineCarboxylic Acids & Esters 3 QPjasonNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsDocumento9 pagine4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsHyder OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkenes 1 QPDocumento11 pagineAlkenes 1 QPasddf asdafNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.8, 4.9 TestDocumento12 pagine4.8, 4.9 TestVinh HoangNessuna valutazione finora
- WS 4 (18.07.22)Documento4 pagineWS 4 (18.07.22)Micheelle JeannethNessuna valutazione finora
- Al KanesDocumento12 pagineAl KanessamanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 2 Practice Paper 2Documento16 pagineA-Level Chemistry: Paper 2 Practice Paper 2Alia ShabbirNessuna valutazione finora
- Isomerism 2 QPDocumento9 pagineIsomerism 2 QPPragna AnanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixed 3Documento15 pagineMixed 3Yaakkw100% (1)
- 2.10 HWDocumento5 pagine2.10 HWChong BengNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Questions Organic ChemistryDocumento4 pagineExam Questions Organic Chemistrymalikimran28Nessuna valutazione finora
- AS Level Topic 6A TestDocumento14 pagineAS Level Topic 6A TestMorvan BarnesNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4, 4.5 TestDocumento9 pagine4.4, 4.5 TestezajihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of 2-methylbut-2-ene formationDocumento88 pagineMechanism of 2-methylbut-2-ene formation22S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANessuna valutazione finora
- Compounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsDocumento69 pagineCompounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsmarvellousadenugaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4 4.5 TestDocumento10 pagine4.4 4.5 TestesfwefweNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam QuestionsDocumento17 pagine4.4, 4.5 Exam Questionsmegaman31080% (1)
- Nomenclature 3 QPDocumento11 pagineNomenclature 3 QPklaksmanan1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Anaylsis: Aqa As ChemistryDocumento17 pagineOrganic Anaylsis: Aqa As ChemistryHamza AbulailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beaconhouse School System, Mandi Bahauddin Work Sheet of Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry - Alcohols Class: XI-Cambridge Name: - Date: - Q1Documento4 pagineBeaconhouse School System, Mandi Bahauddin Work Sheet of Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry - Alcohols Class: XI-Cambridge Name: - Date: - Q1Qurrat Ul AinNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry 2 QDocumento7 pagineOrganic Chemistry 2 Qindianjacob72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol and Carboxylic Acid 1Documento5 pagineAlcohol and Carboxylic Acid 1Geraldine LatupeirissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDocumento149 pagineAlkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsFaria TahsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters 22-26 Past Papers QuestionsDocumento10 pagineChapters 22-26 Past Papers QuestionsHehe Haah100% (1)
- A2 Ch.11 QuestionsDocumento18 pagineA2 Ch.11 QuestionsDigola WillsNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids 1 QPDocumento12 pagineAlcohols & Carboxylic Acids 1 QPChess MemezNessuna valutazione finora
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 80 MarksDocumento14 pagineAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 80 MarksChryssa EconomouNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Cover Work 7th FebruaryDocumento6 pagineOrganic Cover Work 7th FebruaryjcdiekcNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Documento12 paginePractice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Маша ЖуковскаяNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1. (A) Gas Oil (Diesel), Kerosine (Paraffin), Mineral Oil (Lubricating Oil) and PetrolDocumento96 pagineQ1. (A) Gas Oil (Diesel), Kerosine (Paraffin), Mineral Oil (Lubricating Oil) and Petrolwerkape1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 13.6 Assessed HomeworkDocumento8 pagine13.6 Assessed Homeworkarch0wnzNessuna valutazione finora
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocumento10 pagineAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksNav MehrganNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogenoalkanes Structural IsomersDocumento5 pagineHalogenoalkanes Structural IsomersDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogenoalkanes - Test Yourself. QDocumento8 pagineHalogenoalkanes - Test Yourself. QAhsn17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Techniques 1 QPDocumento6 pagineExperimental Techniques 1 QPImran MushtaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Questions For 2.8 Haloalkanes 1Documento18 pagineExtra Questions For 2.8 Haloalkanes 1Younes AlahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 0902Documento4 pagineTest 0902Nav MehrganNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic ChemistryDocumento12 pagineOrganic ChemistryBushra HanifNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogenoalkane reactions and mechanismsDocumento8 pagineHalogenoalkane reactions and mechanismsBarminga KamurenNessuna valutazione finora
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 8Documento9 paginet2 Chem Revision Ex 8Nicholas OwNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkenes QDocumento10 pagineAlkenes Qlucylovesbooks6770Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento19 pagineChemmelissaaverinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.3 Synthetic & Naturally Occurring Polymers 3 QPDocumento13 pagine7.3 Synthetic & Naturally Occurring Polymers 3 QPke poNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkenes 2 QPDocumento10 pagineAlkenes 2 QPIyad AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Paper 2 pp1Documento20 pagineA-Level Paper 2 pp1Amaan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal Catalysed Carbon-Carbon Bond-Forming ReactionsDa EverandMetal Catalysed Carbon-Carbon Bond-Forming ReactionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chirality in Transition Metal Chemistry: Molecules, Supramolecular Assemblies and MaterialsDa EverandChirality in Transition Metal Chemistry: Molecules, Supramolecular Assemblies and MaterialsNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Da EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- GFP Self Registration-Ticket 2Documento1 paginaGFP Self Registration-Ticket 2Adnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- 87793Documento2 pagine87793Adnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Rates and Equilibria AnswersDocumento25 pagineApplications of Rates and Equilibria AnswersAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- RedOx Reactions 1552Documento19 pagineRedOx Reactions 1552Adnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae: Name: Adnan ChowdhuryDocumento3 pagineCurriculum Vitae: Name: Adnan ChowdhuryAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Balancing Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocumento28 pagineBalancing Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Photo Description Price: QTY Requir EdDocumento9 paginePhoto Description Price: QTY Requir EdAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheikh Shakib Ahsan Operations Experience ResumeDocumento3 pagineSheikh Shakib Ahsan Operations Experience ResumeAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Confidential Teacher QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineConfidential Teacher QuestionnaireAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 5.4 TRANSITION METALS PART 1 COMPLEX IONSDocumento12 pagineAQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 5.4 TRANSITION METALS PART 1 COMPLEX IONSAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ItemsDocumento44 pagineLab ItemsAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Moles ExplainedDocumento53 pagineMoles ExplainedAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqa Chem5 QP Jun13 PDFDocumento20 pagineAqa Chem5 QP Jun13 PDFSumaira AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Minerals SingleDocumento5 pagineMinerals SingleAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Projectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento6 pagineProjectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Adnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersDocumento16 pagine4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 QuestionsDocumento24 pagine5.1 QuestionsHalil ZeybekogullariNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2013 QP - Unit 4 AQA ChemistryDocumento20 pagineJune 2013 QP - Unit 4 AQA ChemistryAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqa Chem5 QP Jan12Documento20 pagineAqa Chem5 QP Jan12mpatel13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry QuestionsDocumento40 pagineChemistry Questionskaotao1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersDocumento16 pagine4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqa Chem4 QP Jun12Documento24 pagineAqa Chem4 QP Jun12Adnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSDocumento30 pagine4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding GuideDocumento59 pagineIonic and Covalent Bonding GuideAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- CUP IBChemistry c04 It Periodic TableDocumento37 pagineCUP IBChemistry c04 It Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- CUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsDocumento33 pagineCUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry EnergeticsDocumento62 pagineChemistry EnergeticsWeb Books100% (1)
- Moles ExplainedDocumento53 pagineMoles ExplainedAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- CUP IBChemistry c02 It Atomic StructureDocumento30 pagineCUP IBChemistry c02 It Atomic StructureAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Annex To The European Commission Guideline On Excipients in The Labelling and Package Leaflet of Medicinal Products For Human Use' (2019)Documento21 pagineAnnex To The European Commission Guideline On Excipients in The Labelling and Package Leaflet of Medicinal Products For Human Use' (2019)janoscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 10Documento9 pagineExp 10ChantalDanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Dosage Form ExcipientsDocumento48 pagineLiquid Dosage Form ExcipientsNurfitriyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Benefits of Volatile Silicones in Personal Care PDFDocumento6 pagineThe Benefits of Volatile Silicones in Personal Care PDFRinaldhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Determining Ethanol Content in Domestic AlcoholDocumento15 pagineDetermining Ethanol Content in Domestic Alcoholေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNessuna valutazione finora
- Afe All PDFDocumento10 pagineAfe All PDFjigar patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Disease Diagnosis Practical Laboratory Manual: October 2016Documento40 paginePlant Disease Diagnosis Practical Laboratory Manual: October 2016Narendra bahadur chandNessuna valutazione finora
- The Alcohol Alphabet A Glossary of Terms Used in The Ethanol-Producing IndustriesDocumento40 pagineThe Alcohol Alphabet A Glossary of Terms Used in The Ethanol-Producing IndustriesJesus LucesNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual For Chiralpak Ia Columns: Please Read This Instruction Sheet Completely Before Using This ColumnDocumento4 pagineInstruction Manual For Chiralpak Ia Columns: Please Read This Instruction Sheet Completely Before Using This ColumnArtur RamonNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Report Exp 3Documento11 pagineFinal Report Exp 3Daryl T. CaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Kunkle Models 910, 911, 916, 917, 920, 921 and 927Documento24 pagineKunkle Models 910, 911, 916, 917, 920, 921 and 927Alexsandro TorezinNessuna valutazione finora
- Diccionario Técnico de Mineros y Petroleros - Inglés Español - Español InglésDocumento416 pagineDiccionario Técnico de Mineros y Petroleros - Inglés Español - Español Inglésmrmister0010% (1)
- CHE CALCULATIONS FOR ACID TOWERS AND REACTION PRODUCTSDocumento4 pagineCHE CALCULATIONS FOR ACID TOWERS AND REACTION PRODUCTSPatricia Reign BagaoisanNessuna valutazione finora
- LAS ApChem Q4 MELC 1 EditedDocumento15 pagineLAS ApChem Q4 MELC 1 EditedElla de la Cruz GulanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainability 13 02541 v2Documento21 pagineSustainability 13 02541 v2Henrique BelazNessuna valutazione finora
- ML T ML T ML T ML T ML T R L T MT: Separation Columns (Distillation, Absorption and Extraction)Documento4 pagineML T ML T ML T ML T ML T R L T MT: Separation Columns (Distillation, Absorption and Extraction)Sami WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Budget RenukdDocumento57 pagineBudget Renukdsatabache100% (2)
- Organic Syntheses Collective Volume 4Documento1.072 pagineOrganic Syntheses Collective Volume 4caltexas83% (6)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Alcohol 70%Documento7 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Alcohol 70%Nadia CristineNessuna valutazione finora
- Seppic Hand HygieneDocumento37 pagineSeppic Hand HygieneVinay Bahadur KulshreshthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate Gas Heating Value From Gas CompositionDocumento4 pagineCalculate Gas Heating Value From Gas CompositionAsad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/21Documento16 pagineCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/21SasukeNessuna valutazione finora
- Production Optimization and CharacterizaDocumento3 pagineProduction Optimization and CharacterizaMinichil AshebirNessuna valutazione finora
- Paint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Materials: Methods of Inspection, Sampling and TestingDocumento61 paginePaint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Materials: Methods of Inspection, Sampling and TestingBrandonrjo100% (1)
- Differentiation of Organic From InorganicDocumento4 pagineDifferentiation of Organic From InorganicSHARENDRA INJALNessuna valutazione finora
- Etanol 70% (p.17-19) 46-48Documento3 pagineEtanol 70% (p.17-19) 46-48Marsha Fendria PrastikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol Compounds ExplainedDocumento8 pagineAlcohol Compounds ExplainedShyam TannaNessuna valutazione finora
- PPAG Alcohol Content in Peds Meds Poster-4!10!18Documento2 paginePPAG Alcohol Content in Peds Meds Poster-4!10!18herlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanol Production by Yeast PDFDocumento2 pagineEthanol Production by Yeast PDFCharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Extending Carbon Chain Length of 1-Butanol Pathway For 1-Hexanol Synthesis From Glucose by Engineered Escherichia ColiDocumento3 pagineExtending Carbon Chain Length of 1-Butanol Pathway For 1-Hexanol Synthesis From Glucose by Engineered Escherichia ColiAnonymous 9oH7eQ2TNessuna valutazione finora