Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Determinants
Caricato da
OmarMustafaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Determinants
Caricato da
OmarMustafaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
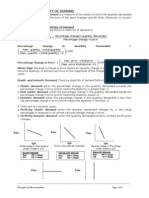
Price elasticity of demand and its determinants
Price elasticity of demand: measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in
price, along a given demand curve.
Mathematically the value is negative, but we treat it as positive.
Price elastic demand (less than infinity).
Figure 2.1 - Price elastic demand
Price inelastic demand (greater than zero)
Figure 2.2 - Price inelastic demand
Unit elastic demand
%change in P = %change in Qd
Total revenue will not change when price changes (same revenue box)
Figure 2.3 - Unit elastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand, demand is zero at all but one price.
Figure 2.4 - Perfectly elastic demand
Perfectly inelastic demand, demand is constant at any price.
Figure 2.5 - Perfectly inelastic demand
Determinants of PED:
1.
Number and closeness of substitutes: more substitutes available & closer higher PED
2.
Degree of necessity (and how widely it is defined): lower the degree of necessity higher
PED; the more vague it is defined, i.e. food higher PED
o
3.
As it is more narrowly defined more subjective
Time period considered: more time to consider higher PED
o
4.
Inelastic in the short term, elastic in the long term
Income spent: the higher the income spent higher PED
Value of PED falls as the measuring points move down a demand curve. PED is not
represented by the slope of the demand curve.
Applications of price elasticity of demand
Applications of PED:
1.
Governments: if inelastic (low) PED less consequence if P impose more indirect tax
2.
Firms: if inelastic (low) PED more revenue if P price of the product rises
ncome elasticity of demand and its determinants
Income elasticity of demand: measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in consumers
income.
Shifts demand curve due to changed income
Determinants:
Normal goods: positive value of YED
Inferior goods: negative value of YED
Necessities: Income inelastic of demand
Luxuries: Income elastic of demand
Applications of income elasticity of demand
Application:
1.
Firms: can predict the effect of a business cycle on sales
Price elasticity of supply
(PES)
Price elasticity of supply and its determinants
Price elasticity of supply: measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price
along a given supply curve.
The value will always be positive
Price elastic supply (less than infinity).
Figure 2.6 - Price elastic supply
Price inelastic supply (greater than zero).
Figure 2.7 - Price inelastic supply
Unit elastic of supply
Mathematically, any straight-line supply curve passing through the origin is unit elastic of
supply.
Figure 2.8 - Unit elastic supply
Perfectly elastic supply, only supplied at a certain price level.
Figure 2.9 - Perectly elastic supply
Perfectly inelastic supply, supply is constant at any price level.
Figure 2.10 - Perfectly inelastic supply
Determinants of PES:
1.
Time period considered: longer the time period considered the more elastic (time to
increase the factors of production, such as capital)
2.
Mobility of factors of production: higher the mobility of factors of production the more
elastic (easier to change to another production with less costs when price rises)
3.
Unused capacity: if more capacity productive resources not being fully used the more
elastic (increase output easily without great costs)
4.
Ability to store stocks: if able to store high level of stocks the more elastic (able to react
to price increases with swift supply increases)
Applications of price elasticity of supply
Commodities: are raw materials in the primary production. (i.e. cotton & coffee)
Inelastic PED, PES, & YED.
Higher degree of necessity, takes time to grow/harvest to increase Qs, few or no
substitutes
Manufactured products & service relatively high (elastic) PED, PES, YED.
ncome elasticity of demand (YED)
income elasticity of demand and its determinants
Income elasticity of demand: measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in
consumers income.
Shifts demand curve due to changed income
Determinants:
Normal goods: positive value of YED
Inferior goods: negative value of YED
Necessities: Income inelastic of demand
Luxuries: Income elastic of demand
Applications of income elasticity of demand
Application:
1. Firms: can predict the effect of a business cycle on sales
Cross price elasticity of demand (XED)
Cross price elasticity of demand and its determinants
Cross price elasticity of demand: measures the responsiveness of a demand for one good to a
change in price of another good.
Movement along the curve for one good causing a shift in demand for
another good
Determinants of XED:
Substitute goods: positive value of XED
Complementary goods: negative value of XED
The absolute value of XED depends on the closeness of the relationship
between the two goods. (Two goods are unrelated if XED =0)
Applications of cross price elasticity of demand
Applications of XED:
1. Firms on substitutes goods: low positive value?the better?increase price of
the product
2. Firms on complementary goods: high negative value?the better?increase
price of the product
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Eco Notes On DemandDocumento25 pagineEco Notes On DemandSenu AustinNessuna valutazione finora
- ELASTICITYDocumento5 pagineELASTICITYRaymark Raymundo MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics For Managers - Notes-2Documento15 pagineEconomics For Managers - Notes-2Phillip Gordon MulesNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategyDocumento20 pagineEconomics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategySwathy SidharthanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandDocumento5 pagineCh. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandVarun SanjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of Elasticty and Its Application (+ Handwritten Notes Too)Documento41 pagineConcept of Elasticty and Its Application (+ Handwritten Notes Too)Aishwarya ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Apuntes de Introducción A La MicroeconomíaDocumento31 pagineApuntes de Introducción A La MicroeconomíaJose Carlo BermudezNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesDocumento5 pagineElasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesNastya CurcubetNessuna valutazione finora
- DIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandDocumento5 pagineDIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandjavedhanifNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of DemandDocumento8 pagineElasticity of Demandgyanendra_paudelNessuna valutazione finora
- DEMAND - ConceptsDocumento30 pagineDEMAND - ConceptsSebin Sara SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Libara GruopDocumento25 pagineLibara GruopRegie FaulveNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1Documento12 pagineAyaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1AzharNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsDocumento15 pagineModule 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsAyman Al HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 The Basics of Supply and DemandDocumento25 pagineChapter 2 The Basics of Supply and DemandRitesh RajNessuna valutazione finora
- COMM 220 Notes PDFDocumento42 pagineCOMM 220 Notes PDFTejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics 1Documento9 pagineManagerial Economics 1vinodrawat74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 8 Report DEMANDDocumento22 pagineGroup 8 Report DEMANDMa'am Roma GualbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of Demand & SupplyDocumento27 pagineElasticity of Demand & Supplysaidkhatib368Nessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Hubbard Chapter 6 ReviewDocumento2 pagineEconomics Hubbard Chapter 6 ReviewgeorgixpieNessuna valutazione finora
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocumento5 paginePrice Elasticity of DemandManoj KNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Basic Supply DemandDocumento28 pagine1 - Basic Supply DemandYohanes AnggoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Santosh Bhandari Assignment1Documento18 pagineSantosh Bhandari Assignment1Santosh BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco 400 Assignment 1Documento5 pagineEco 400 Assignment 1Muhammad Usman AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterDocumento29 pagineCh. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterSpencer AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson-4 EcoDocumento21 pagineLesson-4 EcoKhirtz Angel AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two Introduction To EconomicsDocumento36 pagineChapter Two Introduction To Economicsnigusu deguNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocumento29 pagineElasticity of Demand and SupplyEmily Canlas DalmacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento37 pagineChapter 5Ahmed ElbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome: Submitted By: Vishwaroopayadav Nikitha Sushmitha BinduDocumento28 pagineWelcome: Submitted By: Vishwaroopayadav Nikitha Sushmitha BinduLeni ZymeriNessuna valutazione finora
- SupplyDocumento19 pagineSupplykimcy19Nessuna valutazione finora
- C5 Micro EconomicsDocumento31 pagineC5 Micro Economicshht2107Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Demand SupplyDocumento9 pagineChapter 2 Demand SupplyYus LindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of Elasciticity of DemandDocumento9 pagineMeaning of Elasciticity of DemandDonasco Casinoo ChrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics ECO 502 Sbs - Mba / MSC: Submission Date: 12 March, 2020Documento27 pagineManagerial Economics ECO 502 Sbs - Mba / MSC: Submission Date: 12 March, 2020SZANessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesDocumento5 pagineElasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesJyoti SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Elasticity of Demand and Supply PDFDocumento12 pagineChapter 3 Elasticity of Demand and Supply PDFLiling Cassiopeia67% (3)
- Chap 1: 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Documento9 pagineChap 1: 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Ivy ZouNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics NotesDocumento20 pagineEconomics NotesVikram SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of DemandDocumento38 pagineElasticity of Demandhitesh sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mikroekonomi Untuk Kebijakan - Permintaan Dan PenawaranDocumento28 pagineMikroekonomi Untuk Kebijakan - Permintaan Dan PenawaranCyntia DelfianNessuna valutazione finora
- Blen EconDocumento35 pagineBlen EconheldanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 5: Microeconomics Pgp-IDocumento21 pagineSession 5: Microeconomics Pgp-IAkash DeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Demand, Supply and EquilibriumDocumento29 pagineDemand, Supply and EquilibriumdkNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On PBEDocumento38 pagineReport On PBEJohnson PuñoNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento4 pagineUntitledTraining & Development GWCNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Theme: "The Basic of Supply and Demand Chapter 2" - Presentation TranscriptDocumento2 paginePresentation On Theme: "The Basic of Supply and Demand Chapter 2" - Presentation TranscriptAllena RusianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 23032022173030 C Demand SupplyDocumento5 pagine6 23032022173030 C Demand SupplyRayan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Elasticity of DemandDocumento53 pagineThe Elasticity of DemandShekhar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Demand Analysis-RevisedDocumento54 pagineDemand Analysis-RevisedVishal ManwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics A Contemporary Introduction 10Th Edition Mceachern Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento30 pagineMicroeconomics A Contemporary Introduction 10Th Edition Mceachern Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjason.powell550100% (11)
- Economics Unit 2Documento20 pagineEconomics Unit 2ppriyasonuNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics Unit One 2021tyDocumento201 pagineManagerial Economics Unit One 2021tyApong LkrNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 ElasticityDocumento36 pagine05 ElasticityBhaskar KondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Lecture 3: Micro-Economics of Product MarketsDocumento43 pagineEconomics Lecture 3: Micro-Economics of Product MarketsAnanna AfroseNessuna valutazione finora
- Class - Xi - Microeconomics - Consumer Behaviour and DemandDocumento6 pagineClass - Xi - Microeconomics - Consumer Behaviour and DemandYajata VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two: Theory of Demand and SupplyDocumento40 pagineChapter Two: Theory of Demand and SupplyOromay EliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics NotesDocumento13 pagineEconomics Noteskarankumar67656Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Review of Supply and Demand FunctionsDocumento19 pagineTopic 1 Review of Supply and Demand FunctionsCHOPLAZNessuna valutazione finora
- Achilles Fights HectorDocumento1 paginaAchilles Fights HectorOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alevel BookletDocumento1 paginaAlevel BookletOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- China Edexcel Notes Unit 1Documento10 pagineChina Edexcel Notes Unit 1OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- China PRT 1 1911-1949Documento22 pagineChina PRT 1 1911-1949OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary in Economics (WEC01/01) Unit 1: Markets in ActionDocumento24 pagineMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary in Economics (WEC01/01) Unit 1: Markets in ActionOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- China PRT 1 1911-1949Documento22 pagineChina PRT 1 1911-1949OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Booklet1Documento4 pagineRevision Booklet1OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Latitude WorksheetDocumento1 paginaLatitude WorksheetOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects 10 Million Kuiaks KilledDocumento2 pagineEffects 10 Million Kuiaks KilledOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- P2 Topic 1 NotesDocumento25 pagineP2 Topic 1 NotesOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- History, Tsarist RussiaDocumento2 pagineHistory, Tsarist RussiaOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- My Name Asis OmarDocumento1 paginaMy Name Asis OmarOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- History Essa1Documento2 pagineHistory Essa1OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocumento28 pagineUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- TourismDocumento5 pagineTourismOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse and Gcse TourismDocumento11 pagineIgcse and Gcse TourismOmarMustafa100% (1)
- Revision For GCSE Economics Section 6Documento3 pagineRevision For GCSE Economics Section 6Carmen YongNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Booklet1Documento4 pagineRevision Booklet1OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Colorado RiverDocumento1 paginaColorado RiverOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science - Physics - Lab Report: Hypothesis Part A: PlanningDocumento2 pagineScience - Physics - Lab Report: Hypothesis Part A: PlanningOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- My Name Asis OmarDocumento1 paginaMy Name Asis OmarOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicssasdaDocumento64 pagineEconomicssasdaOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- GeogawgyDocumento18 pagineGeogawgyOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Booklet1Documento4 pagineRevision Booklet1OmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- MigrationDocumento5 pagineMigrationOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics RevisionDocumento43 pagineEconomics Revisionig studentNessuna valutazione finora
- Colorado RiverDocumento1 paginaColorado RiverOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Mice and MenDocumento4 pagineOf Mice and MenOmarMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- TSM PharmaDocumento6 pagineTSM PharmaPrateek Ashatkar0% (1)
- Tutorial Solutions - Week 2Documento6 pagineTutorial Solutions - Week 2ongchamchi960% (1)
- Managing Director: Gokce YanasmayanDocumento1 paginaManaging Director: Gokce YanasmayanDana GnNessuna valutazione finora
- SalesDocumento20 pagineSalesDea Lyn Bacula100% (2)
- ABC Address Fo Sneder: Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash MemoDocumento1 paginaABC Address Fo Sneder: Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memobigboss2276623Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Ice Cream Industry: An OverviewDocumento37 pagineThe Ice Cream Industry: An OverviewSonali JalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Go PRODocumento27 pagineGo PROPaul Ul100% (6)
- ER ExamplesDocumento6 pagineER ExamplesSameen Fatima100% (1)
- SCM QP EFF Based Pricing StrategyDocumento47 pagineSCM QP EFF Based Pricing StrategysreeharireddylNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy Opted by The Apollo Tyres1Documento90 pagineMarketing Strategy Opted by The Apollo Tyres1Shivalya MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Case - Blue Mine GroupDocumento34 pagineBusiness Case - Blue Mine GroupLungisaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Buss2: Practice Exam Paper - Paper TUT-BUSS2-1Documento17 pagineBuss2: Practice Exam Paper - Paper TUT-BUSS2-1api-26301710Nessuna valutazione finora
- RESA Final Preboard P1Documento10 pagineRESA Final Preboard P1rjn191% (11)
- Tutorial 7 SolutionDocumento3 pagineTutorial 7 SolutionSitla Reddy75% (4)
- Plunketts Airline Hotel and Travel Industry Almanac-Plunkett Research (2011)Documento510 paginePlunketts Airline Hotel and Travel Industry Almanac-Plunkett Research (2011)rajat sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advertising and Sales Promotion Techniques Used by Retail Businesses With Special Reference To Big BazaarDocumento4 pagineAdvertising and Sales Promotion Techniques Used by Retail Businesses With Special Reference To Big BazaarDipanjan Das0% (2)
- Psychological SegmentationDocumento29 paginePsychological SegmentationMahesh NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Quotation Structures Poles RGGVY XII DVVNLDocumento2 pagineQuotation Structures Poles RGGVY XII DVVNLSharafat AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Boston Consulting Group MatrixDocumento20 pagineBoston Consulting Group MatrixReema Mamtani100% (1)
- Milk Tea in The FinlandDocumento33 pagineMilk Tea in The FinlandJessicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tax Invoice: Gift From: Gift To: Customer CommentsDocumento1 paginaTax Invoice: Gift From: Gift To: Customer Commentsaman05147% (17)
- Deleiverable - 4: Livestock Management SystemDocumento10 pagineDeleiverable - 4: Livestock Management SystemMuhammad UzairNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Business For CSEC®: 2nd EditionDocumento3 paginePrinciples of Business For CSEC®: 2nd Editionyuvita prasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitsubishi Corporation-Manila Branch, Petitioner, vs. Commissioner of Internal REVENUE, RespondentDocumento5 pagineMitsubishi Corporation-Manila Branch, Petitioner, vs. Commissioner of Internal REVENUE, RespondentevilsageNessuna valutazione finora
- Contract Law CasesDocumento6 pagineContract Law CasesRith Try100% (2)
- Proforma Invoice and Purchase Agreement No.923788-003506Documento2 pagineProforma Invoice and Purchase Agreement No.923788-003506Cesar Barco OliveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ERP: ApplicationsDocumento40 pagineIntroduction To ERP: Applicationsanup20janNessuna valutazione finora
- Remedies of BuyerDocumento40 pagineRemedies of BuyerAdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Relevant Cost NotesDocumento69 pagineRelevant Cost NotesXena NatividadNessuna valutazione finora