Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter-6 Iterative Control Instruction
Caricato da
avinashavi93Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter-6 Iterative Control Instruction
Caricato da
avinashavi93Copyright:
Formati disponibili
SCA Pvt. Ltd.
(Sharma Computer Academy)
Author: Saurabh Shukla
Chapter-6
Iterative Control Instruction
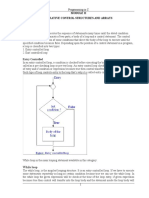
Loop
Iterative control instruction is also known as repetitive control instruction or loop.
Sometimes it is desirable to executed same statement again and again. This can be done
with the help of loops.
There are three ways to implement loops in C language:
l while
l do-while
l for
Syntax of while
main()
{
.
.
while(condition)
{
.
.
}
}
Syntax of while is similar to if. In the case of if, when the condition is TRUE control
moves inside if block and execute statements of if-block. After executing if-block control
moves to the statement written immediately after if-block (outside if-block).
In the case of while, when the condition is TRUE control moves inside while-block and
execute statements of while-block. After executing while-block control does not moves
to the statement written immediately after while-block rather it goes back to the condition
of while block. This condition will be checked again and if it is again TRUE control
moves again inside while-block. This repeats till the condition becomes FALSE.
Example:
main()
{
int i=1;
.
while(i<=5)
{
printf(SCA );
SCA Pvt. Ltd. (Sharma Computer Academy)
Author: Saurabh Shukla
i++;
}
printf(Out of loop);
}
Output:
SCA SCA SCA SCA SCA
In this example, printf is executed 5 times. You have to think about three things to control
loop execution. They are initialization, termination condition and flow. Here, i is used to
control loop. In the very first line of the main function i is initialized by 1. So when the
condition is evaluated first time it is interpreted as 1<=5, thus it is TRUE. Control enters
in while block and execute printf statement. After printf i is incremented by 1. This is
important as we want to execute loop body only five times. Initially i was 1 and in each
iteration it is incremented by 1, this makes i to reach a value where condition i<=5
becomes FALSE.
Syntax of do-while loop
main()
{
.
.
do
{
.
.
} while(condition);
Learn a new keyword do. The code block that has to put in loop is prefixed with keyword
do and post-fixed with keyword while along with termination condition. Remember to
put semicolon after while.
Do-while works similar to while but the only difference is earlier is executed at least
once. Since in while loop condition is evaluated first then goes into loop body, on the
other hand in do while loop first control enters in loop body then condition will be
checked. This makes possible to control enters in loop body even though the condition is
false. Although once the condition is checked FALSE loop is terminated.
Syntax of for
main()
{
SCA Pvt. Ltd. (Sharma Computer Academy)
Author: Saurabh Shukla
.
for( ; ;)
{
}
for loop is programmers choice as it contains initialization, termination and flow at same
place. Notice the two semicolons inside fors round braces, these are part of syntax,
hence should always be mentioned.
Two semicolons create three sections. First section is used for initialization, second
section is used for termination condition and third section is used to mention flow.
Example: Program to calculate factorial of a number
main()
{
int n,i,f=1;
printf(Enter a number );
scanf(%d,&n);
for(i=1 ; i<=n ; i++)
{
f = f * i;
}
printf(Factorial is %d, f);
}
Output
Enter a number 4
Factorial is 24
User enters a number which is stored in n. This loop executes n times as it goes from 1 to
n. Let us suppose value entered by user is 4. So n contains 4. Loop start with initialization
of i from 1. After initialization, termination condition is evaluated, which is TRUE, thus
control moves inside the code block. Initially f is containing 1 and it is multiplied by i
which also contains 1. The product is finally stored in f. Now control moves to the flow
part (i++). Condition is evaluated again but this time i become 2. Condition is again
TRUE. Control again enters in code block and the product of f and i will store in f.
Same process is repeated till the condition i<=n becomes FALSE.
Keyword break
The keyword break is used only in:
l Loop body
l Switch body
SCA Pvt. Ltd. (Sharma Computer Academy)
Author: Saurabh Shukla
break in loop body
The keyword break is used in loop body to terminate loop. When break executes, it
transfers the control out of loop body.
Whenever you are not sure with when the loop should stop, you can use break to
terminate loop.
Example:
main()
{
int x,i=1;
while(i<=5)
{
printf(Enter an even number);
scanf(%d,&x);
if(x%2==0)
{
printf(You Win);
break;
}
i++;
}
if(i==6)
printf(You lost);
}
In this program, break is used to terminate loop when user enters an even number. This
program is a sort of game where user has at most 5 chances to enter correct value. If he is
fail to enter correct value in all five chances he would lost the game. He may win the
game if he enters correct value in any of the five chances. Game must stop as soon as he
enters the correct data.
Let us assume first time user enters 3. Since x contains 3, condition x%2==0 is FALSE
so skipped if block and increments i by 1. On its second iteration, assume user enters 6.
This time condition x%2==0 is TRUE, so enters in if block. User gets a message You
Win. Now break works and it transfers the control out of while block. Where another
condition is evaluated, which is false.
Try executing above program for different inputs.
Keyword continue
The keyword continue is used only in loop body. It is used to move control at termination
condition in the case of while and do-while loop. continue is used in for loop to transfer
control at flow part (increment/decrement).
SCA Pvt. Ltd. (Sharma Computer Academy)
Author: Saurabh Shukla
Example
main()
{
int x;
while(1)
{
printf(Enter an even number);
scanf(%d,&x);
if(x%2==1)
continue;
else
{
printf(This is the correct value);
break;
}
}
}
This time condition of while loop is always TRUE as we wrote 1 which is a non zero
number. (Non zero number is always treated as TRUE). The loop only ends at the
execution of break. If the user enters an odd number condition x%2==1 becomes TRUE,
thus continue works. Continue transfers the control at while loop condition.
As long as user enters odd number, continue works every time, but when user enters an
even number, break terminates loop.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab 4Documento5 pagineLab 4Malik Burair NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- Loop NotesDocumento6 pagineLoop Notesyashas221009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3: Loops: by Alex AllainDocumento4 pagineLesson 3: Loops: by Alex AllainPraveen PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- By P.Vinitha M.SC., M.PhilDocumento38 pagineBy P.Vinitha M.SC., M.PhilVinitha ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming UNIT 3.1 LoopsDocumento32 pagineC Programming UNIT 3.1 LoopsrishikaNessuna valutazione finora
- CPP Lec4-LoopDocumento25 pagineCPP Lec4-LoopHemed hafidhNessuna valutazione finora
- Do While Loop in CDocumento3 pagineDo While Loop in Cayan shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming - Decision Making - LoopingDocumento7 pagineC Programming - Decision Making - Loopingneo_411Nessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 2Documento6 pagineMODULE 2lijin bNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento48 pagineChapter 8dinesh9866119219Nessuna valutazione finora
- Looping Control Structures: C&Dsforimca Unit-2 VvitDocumento10 pagineLooping Control Structures: C&Dsforimca Unit-2 VvitN. Janaki RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial No 6 SolutionDocumento9 pagineTutorial No 6 SolutionPrasad BadheNessuna valutazione finora
- C Looping StatementDocumento5 pagineC Looping StatementPrincess DianneNessuna valutazione finora
- C ProgramingDocumento15 pagineC Programingshreya ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento12 pagineTheorytanya.a.s.0825Nessuna valutazione finora
- Loops: Pretest Loops Post Test LoopsDocumento33 pagineLoops: Pretest Loops Post Test LoopsravitejabavandlaNessuna valutazione finora
- NestedDocumento7 pagineNestedvipularunpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Unit 2 2020Documento16 paginePython Unit 2 2020devNessuna valutazione finora
- Group3 PDFDocumento27 pagineGroup3 PDFChris Dantley ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprog 3 Looping in C#Documento3 pagineComprog 3 Looping in C#erikalast.acadNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory Notes Unit-Ii: LoopsDocumento18 pagineTheory Notes Unit-Ii: LoopsLakshay GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Conditional Branching-LoopsDocumento35 pagineConditional Branching-LoopsSatgur gaming worldNessuna valutazione finora
- Conditional Operator DM 11Documento23 pagineConditional Operator DM 11Dogan RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Statements in Java (Loop's)Documento9 pagineControl Statements in Java (Loop's)HeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 12 - 1 - If For Do WhileDocumento21 pagineTutorial 12 - 1 - If For Do Whilethanhtrungthuc107Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cont. Loop TypesDocumento16 pagineCont. Loop TypesKainat KabeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3.1Documento44 pagineUnit 3.1BhagavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Looping Statements in CDocumento7 pagineLooping Statements in Cgopi9966957145Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control StatementDocumento11 pagineControl StatementworkNessuna valutazione finora
- Labsheet 5Documento15 pagineLabsheet 5saurabharpitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Decision Control StructureDocumento42 pagineThe Decision Control StructureAmir AmirthalingamNessuna valutazione finora
- C' Programming: Topics CoveredDocumento10 pagineC' Programming: Topics CoveredHemangini Sanjaykumar PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Week4-JS-Web ProgrammingDocumento25 pagineWeek4-JS-Web ProgrammingRyan ObligarNessuna valutazione finora
- Loop ConceptsDocumento7 pagineLoop ConceptsMagarsaa Qana'iiNessuna valutazione finora
- Loop 2Documento3 pagineLoop 2ajaykaundalNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento14 pagineUntitledEmmanuel MaritimNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 Question and AnsweresDocumento23 pagineUnit-2 Question and Answeresmallajasmitha7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Loops in CDocumento13 pagineLoops in CjanlixalmendralNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Programming: Control StatementsDocumento14 pagineComputer Programming: Control StatementsSruthy SasiNessuna valutazione finora
- While Loops in JavaDocumento6 pagineWhile Loops in JavaAzira TeamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-5 Control InstructionDocumento7 pagineChapter-5 Control Instructionavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control Structure:: Conditional StatementDocumento14 pagineControl Structure:: Conditional StatementAtit ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming 4Documento26 pagineC Programming 4AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- QA Unit2Documento16 pagineQA Unit2alysonmicheaalaNessuna valutazione finora
- CP Lab08Documento4 pagineCP Lab08Arbab shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- MC0078 Assignment 2Documento19 pagineMC0078 Assignment 2satish chaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3: in Which The Instructions in A Program Must Be ExecutedDocumento20 pagineUnit 3: in Which The Instructions in A Program Must Be ExecutedkrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- COMP1 - Lab Act3. Algorithm - Loop CS - WhileDocumento5 pagineCOMP1 - Lab Act3. Algorithm - Loop CS - Whilepeter vanderNessuna valutazione finora
- LoopsDocumento14 pagineLoopskavyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-6 Repetition LoopingDocumento6 pagineModule-6 Repetition LoopingjunNessuna valutazione finora
- PST - Unit 3Documento6 paginePST - Unit 3cs235114414Nessuna valutazione finora
- C Notes LoopsDocumento8 pagineC Notes LoopsSandyNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE1002 LO VL2020210504934 Reference Material I 15-Feb-2021 3 C FLOW CONTROLDocumento31 pagineWINSEM2020-21 CSE1002 LO VL2020210504934 Reference Material I 15-Feb-2021 3 C FLOW CONTROLVickyNessuna valutazione finora
- JavaDocumento27 pagineJavashoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5: Repetition / Iteration StructureDocumento24 pagineLesson 5: Repetition / Iteration StructureLim CNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2.1 Control StatementsDocumento58 pagineUnit-2.1 Control Statementsanurag232003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 AnswerDocumento12 pagineUnit 2 Answerbolt sparkNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1.2Documento19 pagineModule 1.2shreyu8pro2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 3 - Repetition Control StructureDocumento10 pagineTutorial 3 - Repetition Control Structurewiliam hongNessuna valutazione finora
- BE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertDa EverandBE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertNessuna valutazione finora
- #Character Guy DarshiDocumento25 pagine#Character Guy Darshiavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Astral Script 231218 PDFDocumento19 pagineAstral Script 231218 PDFavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware InfoDocumento1 paginaHardware InfoAnoop Jacob KunnappuzhaNessuna valutazione finora
- ShootDocumento1 paginaShootavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Start of Byte Win SHP Pla For Qin TNL Venue End of Byte Total Number of BytesDocumento4 pagineStart of Byte Win SHP Pla For Qin TNL Venue End of Byte Total Number of Bytesavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFDocumento1 paginaA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- DemonoidDocumento1 paginaDemonoidavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative Theory NotesDocumento7 pagineNarrative Theory Notesavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard TemplateDocumento3 pagineA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Templateavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic ResultsDocumento1 paginaDiagnostic Resultsavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard TemplateDocumento22 pagineA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Templateavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- KeysDocumento1 paginaKeyspmalgiNessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFDocumento1 paginaA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- General GuidelinesDocumento12 pagineGeneral GuidelinesvajidqcNessuna valutazione finora
- New Rich Text DocumentDocumento1 paginaNew Rich Text Documentavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9Documento3 pagineChapter 9avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Development and Under Development ............................................... 27Documento16 pagineEconomic Development and Under Development ............................................... 27avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medha Spoken English Material PDF FreeDocumento2 pagineMedha Spoken English Material PDF Freeavinashavi9370% (20)
- FB SceneDocumento2 pagineFB Sceneavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nod32 9 & 8 Serial License Keys Username and Password Eset Antivirus Ess Activation - SSECDocumento2 pagineNod32 9 & 8 Serial License Keys Username and Password Eset Antivirus Ess Activation - SSECavinashavi9322% (9)
- New Rich Text DocumentDocumento1 paginaNew Rich Text Documentavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- C LanguageDocumento91 pagineC LanguageRan JeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento3 pagineChapter 1avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChapterDocumento4 pagineChapteravinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChapterDocumento4 pagineChapteravinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chaer 8Documento13 pagineChaer 8avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- EE GATE 2009 SolutionDocumento11 pagineEE GATE 2009 SolutionUTKAL.4575% (4)
- Chapter-5 Control InstructionDocumento7 pagineChapter-5 Control Instructionavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChapterDocumento7 pagineChapteravinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gate EceDocumento25 pagineGate Ecegreatbuddy2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Java MCQ Ch2 SssDocumento72 pagineAdvance Java MCQ Ch2 SssRupesh BavgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Abap OopsDocumento117 pagineAbap OopsRajiv KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 JavaScript Coding QuestionsDocumento13 pagine25 JavaScript Coding Questionspgkalex455Nessuna valutazione finora
- InheritanceDocumento26 pagineInheritanceRoshan ShawNessuna valutazione finora
- All C++ TutorialsDocumento30 pagineAll C++ TutorialsNazmi AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric FormulaeDocumento3 pagineTrigonometric FormulaeAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Codes Arduino SketchDocumento1 paginaKey Codes Arduino SketchDado GaudiNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ JavaDocumento9 pagineMCQ JavaJanmejay PantNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemverilog Quick Reference Guide: Author: Shanthi V ADocumento44 pagineSystemverilog Quick Reference Guide: Author: Shanthi V ARAJ NARNOLINessuna valutazione finora
- Python - Objective 01 Learn How To Write Structured Programs WorkbookDocumento19 paginePython - Objective 01 Learn How To Write Structured Programs WorkbookNirros SarvamohanNessuna valutazione finora
- JavaDocumento60 pagineJavaPapithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Screen TestDocumento9 paginePython Screen TestABHINAY SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento23 pagineModule 2Jayashree NNessuna valutazione finora
- Navisworks Manage%2Documento3 pagineNavisworks Manage%2cuongtdbsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved JavaDocumento28 pagineSolved JavaAbhishek JohariNessuna valutazione finora
- CPBO423 - Lesson 3 - Instruction Sets-Characteristics and FunctionsDocumento49 pagineCPBO423 - Lesson 3 - Instruction Sets-Characteristics and FunctionsMichaelangelo AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- AvSol Coding Guidelines For CSharp 3.0 and 4.0 Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineAvSol Coding Guidelines For CSharp 3.0 and 4.0 Cheat Sheetkpcc9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Exercise 5-1Documento11 pagineLab Exercise 5-1Allysa CasisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Juelg - Templates With Strings and Auto in C++17Documento23 pagineJuelg - Templates With Strings and Auto in C++17Radu CostacheNessuna valutazione finora
- (XC350 Final Exam Fall 2020 S2020052008Documento14 pagine(XC350 Final Exam Fall 2020 S2020052008Syed Muhammad Musa Zaighum NaqviNessuna valutazione finora
- OOPS Module I & IIDocumento94 pagineOOPS Module I & IIBibinNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Code For AIDocumento219 paginePython Code For AIabc55n100% (3)
- Static and Dynamic Subroutine CALLsDocumento4 pagineStatic and Dynamic Subroutine CALLsBharath KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 ArraysDocumento19 pagine05 ArraysCiprian MocanuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Little C PrimerDocumento36 pagineA Little C PrimerAditya BhuyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Selection Structure Week 4Documento17 pagineSelection Structure Week 4Ahmad ShahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Int 105 FunctionDocumento13 pagineInt 105 Functionkunal jadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- HCT216: Programming 2: Assignment 2: Methods, Encapsulation, Inheritance & Polymorphism, ExceptionsDocumento5 pagineHCT216: Programming 2: Assignment 2: Methods, Encapsulation, Inheritance & Polymorphism, Exceptionsmunashe chibayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing Delegate' To Cover Event.: - Declare Delegate - Bind Method(s) To The Delegate - InvokeDocumento13 pagineIntroducing Delegate' To Cover Event.: - Declare Delegate - Bind Method(s) To The Delegate - InvokeANKIT KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Abap Oo BasicsDocumento20 pagineAbap Oo Basicssrihariram20Nessuna valutazione finora