Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
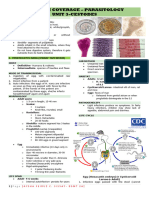
(OS 213) LAB 03 Paragonimus Westermani (A)
Caricato da
Yavuz DanisTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
(OS 213) LAB 03 Paragonimus Westermani (A)
Caricato da
Yavuz DanisCopyright:
Formati disponibili
OS 213: Human Disease and Treatment 3(Circulation
and Respiration)
LAB 03: PARAGONIMUS WESTERMANI
Exam 1 | Parasitology Faculty | August 25, 2013
OUTLINE
I. Life Cycle
II. Ovum
III.Vectors
A. Primary: Antemelania
B. Secondary:
Sundathelphusa
IV. Metacercaria
V. Adult
A. General Features
B. Reproductive
LIFE CYCLE
First
intermediate
host:
the
snails
Antemelania asperata; Antemelania dactylus
Miracidium enters snail sporocyst stage
redial stage cercaria emerges exit snail to infect 2 0
host
Cercaria
o Covered with spines and has an ellipsoidal body
with small tail
o Stylet present at dorsal side of the oral sucker
Figure 04. Sundathelphusa
Figure 01. Life Cycle of Paragonimus westermani
OVUM
Oval, yellowish-brown, thick-shelled
Flat but prominent operculum (larger end)
Abopercular portion is thickened (smaller end)
Unembryonated at deposition
Embryonates in water, moist soil or feces
Develops into a miracidium within 2-7 weeks
Figure 02.Ovum
Secondary: Sundathelphusa
Second intermediate host: mountain crab
Sundathelpusa philippina
o Cercaria penetrates soft parts (gills, body muscles,
viscera and legs) and encysts into a metacercaria
o Crab may be infected by eating infected snails
METACERCARIA
Definitive host (man) acquires infection by
eating raw or insufficiently cooked crabs harboring
metacercaria
Metacercaria is round and measures from 381457 micrometers
After ingestion, metacercaria excysts in
duodenum of host
o Cysteine proteinases secreted by metacercarias
excretory bladder help in excystment and host
immune modulation
Adolescent
worm
then
traverses
through the intestinal wall, into the peritoneal
cavity, where it wanders about and embeds itself in
the abdominal wall for several days
Afterwards, returns to coelom, migrates
through diaphragm to pleural cavity where it
develops into adulthood
Completion of development in the
definitive host: 65-90 days
Can persists in man up to 20 years or
more
Can also infect dogs, cats, rats
VECTORS
Primary: Antemelania
Figure 05. Metacecaria
Figure 03. Antemelania
Ronan | Kim | KevChan
UPCM 2016 B: XVI, Walang
Kapantay!
1of 3
OS 213: Human Disease and Treatment 3(Circulation
and Respiration)
LAB 03: PARAGONIMUS WESTERMANI
Exam 1 | Parasitology Faculty | August 25, 2013
Figure 10. Caudal part with caecum (slightly
tapered end)
Figure 06. Actual Metacercaria Specimen
ADULT
GENERAL FEATURES
An adult may be as large as a coffee bean (712mm long, 4-6mm wide, and are 3.5-5mm thick)
Rounded anteriorly, slightly tapered posteriorly
Vitellaria are branched extensively
Found in pairs; threes in fibrotic capsules or
cysts in hosts lungs
Capsules have openings that allows eggs to
escape; transported by ciliary epithelium along with
lung exudates
REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
Two testes are lobed, midway between
ventral sucker
Ovary located anterior to testes but posterior
to ventral sucker
Uterus is filled with eggs
They are hermaphroditic
Figure 11.Uterus in focus (filled with eggs)
Figure 07.Adult
Figure 08. Paragonimus sp. Adult Lung Fluke.
Figure 12. Male and Female Genitalia
(Key: AC=acetabulum (ventral sucker); OV=ovary;
CE=cecum; TE=testes; OS=oral sucker; UT=uterus;
EB=excretory bladder)
Figure 13.Testes (Key: Paired lobulated pink
structures)
Figure 09. Anterior end of Paragonimus sp.
Ronan | Kim | KevChan
UPCM 2016 B: XVI, Walang
Kapantay!
2of 3
OS 213: Human Disease and Treatment 3(Circulation
and Respiration)
LAB 03: PARAGONIMUS WESTERMANI
Exam 1 | Parasitology Faculty | August 25, 2013
Figure 14. Other Paragonimus structures
(Key: orange arrow=cecum; blue arrow=uterus; violet
arrow=ovary; yellow arrow=testes; surrounding
green=vitellaria)
END OF TRANSCRIPTION
What med students do.
Ronan | Kim | KevChan
UPCM 2016 B: XVI, Walang
Kapantay!
3of 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Phylum NematodaDocumento285 paginePhylum NematodaBrielleNessuna valutazione finora
- New Zealand Moths and Butterflies (Macro-Lepidoptera)Da EverandNew Zealand Moths and Butterflies (Macro-Lepidoptera)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phylum Nematoda PDFDocumento257 paginePhylum Nematoda PDFsummer dj100% (1)
- Platheminthes. CestoideaDocumento11 paginePlatheminthes. CestoideaAdnan SosiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestode SDocumento79 pagineCestode SVincent Manganaan67% (3)
- CESTODESDocumento10 pagineCESTODEScole_danielleNessuna valutazione finora
- Intestinal NematodesDocumento88 pagineIntestinal NematodesVincent Manganaan100% (1)
- ParaDocumento73 pagineParaeasysleezeNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology - Parastrongylus CantonensisDocumento20 pagineParasitology - Parastrongylus CantonensisNicole ManogNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesDocumento16 pagineParasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesEnaWahahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multicellular Parasites: Palao, Anamarie D. Peluta, Charry Shane B. Bsed Science 3Documento38 pagineMulticellular Parasites: Palao, Anamarie D. Peluta, Charry Shane B. Bsed Science 3ANAMARIE DUNGGON. PALAONessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP 2-HES-032-BSN-Lab-Activity-7Documento10 pagineGROUP 2-HES-032-BSN-Lab-Activity-7Divo Skye CrawfordNessuna valutazione finora
- Para-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Documento11 paginePara-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Aysha AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpDocumento7 pagineHymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpSusan GachukiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestodes NotesDocumento27 pagineCestodes NotesShanmathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise No. 13 Identification of Trematodes Objectives:: Schistosoma JaponicumDocumento3 pagineExercise No. 13 Identification of Trematodes Objectives:: Schistosoma JaponicumCherryl SurigaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Hideo Hasegawa OitaUniversityDocumento12 pagineJurnal Hideo Hasegawa OitaUniversitymfft67f2sdNessuna valutazione finora
- Para-Transes Midterm Exam - Unit 3Documento8 paginePara-Transes Midterm Exam - Unit 3Aysha AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 7 - Lab Activity 7 1Documento9 pagineGroup 7 - Lab Activity 7 1Sabrina MascardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes On FasciolidaeDocumento7 pagineLecture Notes On FasciolidaeGaniu MustaphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Medically Significant NematodesDocumento134 pagineClassification of Medically Significant Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- The Intestinal NematodesDocumento107 pagineThe Intestinal Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- Knowledge ReviewDocumento81 pagineKnowledge ReviewAmr EldemardashNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung FlukeDocumento4 pagineParasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung Flukemiguel cuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- Platyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Documento6 paginePlatyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Julianna Rheaven JoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestodes 1Documento86 pagineCestodes 1Kendon D. TajanlangitNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 2Documento8 pagineCS 2Lyka PapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Para-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Documento20 paginePara-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Aysha AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iosob 2008 Observations On The Embryonic Devepolment of Triturus Lissotriton Vulgaris LDocumento12 pagineIosob 2008 Observations On The Embryonic Devepolment of Triturus Lissotriton Vulgaris LGabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahsakam KotaeyDocumento19 pagineBahsakam Kotaeysoran najebNessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department SubjectDocumento20 pagineMinistry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department Subjectsoran najebNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Schistosomiasis and Katayama Syndrome in Returning TravellersDocumento6 pagineLaboratory Diagnosis of Schistosomiasis and Katayama Syndrome in Returning Travellersaminu ibrahim gadakaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Veterinary Protozoology Webinar SeriesDocumento137 pagineGeneral Veterinary Protozoology Webinar SeriesJamaicah PattungNessuna valutazione finora
- Mosquitoes: Amal Almuhanna 2012Documento54 pagineMosquitoes: Amal Almuhanna 2012Stefani A rachmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Nematodes: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-ValenzuelaDocumento29 pagineIntroduction To Nematodes: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-ValenzuelaMichNessuna valutazione finora
- WS B. Invertebrates On Land - AgsaldaDocumento11 pagineWS B. Invertebrates On Land - AgsaldaEj AgsaldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nematodes IntroDocumento2 pagineNematodes IntroayaamrsharfNessuna valutazione finora
- NematodesDocumento9 pagineNematodesMomo ShinNessuna valutazione finora
- Amoeba and FlagellatesDocumento1 paginaAmoeba and FlagellatesJoseph DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Ascariasis: Presenter: Malik Nadeem Moderator: Dr. AngmoDocumento58 pagineAscariasis: Presenter: Malik Nadeem Moderator: Dr. AngmoMalik NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Trichinella SpiralisDocumento2 pagineTrichinella SpiralisJayricDepalobosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestodes Raw Doc AnchetaDocumento53 pagineCestodes Raw Doc Anchetaaya basilioNessuna valutazione finora
- RingwormsDocumento5 pagineRingwormsCitrusNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematodes Fasciola HepaticaDocumento52 pagineTrematodes Fasciola HepaticaAshik MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Lecture 11 - AphasmidsDocumento4 pagineParasitology Lecture 11 - Aphasmidsmiguel cuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- 3) TrematodesDocumento38 pagine3) Trematodesmisgshlove1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zoolab Act 10Documento24 pagineZoolab Act 10莉安Nessuna valutazione finora
- SchistosomiasisDocumento26 pagineSchistosomiasiskgenilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Poraginumus WestermaniDocumento23 paginePoraginumus WestermaniMika AndiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Schistosomes: Diecious TrematodesDocumento6 pagineSchistosomes: Diecious TrematodesShivanshi KNessuna valutazione finora
- Helminthes (Nematodes) : General CharacteristicsDocumento7 pagineHelminthes (Nematodes) : General CharacteristicsAhmed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- TrematodesDocumento10 pagineTrematodesUhjafwnuijhnfa Kmerkgoe100% (1)
- Unit - Three: HelminthsDocumento177 pagineUnit - Three: HelminthsDembalu NuguseNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology - Trematodes - Intestinal & Liver FlukesDocumento76 pagineParasitology - Trematodes - Intestinal & Liver FlukesNicole ManogNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Documento40 pagineParasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Moeen HyderNessuna valutazione finora
- Schistosomiasis & FascioliosisDocumento40 pagineSchistosomiasis & FascioliosisWahyudi YusmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ascarididae & HeterakidaeDocumento11 pagineAscarididae & Heterakidaesany AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- TI Analog HandbookDocumento101 pagineTI Analog HandbookJenory DenemyNessuna valutazione finora
- (Os 213) Lec 05.2 Drugs For RtiDocumento1 pagina(Os 213) Lec 05.2 Drugs For RtiYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- LogmakDocumento2 pagineLogmakYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- A Durable Ultrasound Phantom For Trainees Using Common MaterialsDocumento7 pagineA Durable Ultrasound Phantom For Trainees Using Common MaterialsYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Review of Normal Lung Structure and FunctionDocumento8 pagine(OS 213) LEC 03 Review of Normal Lung Structure and FunctionYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio 25 E1 Lec 10 MSK RadiologyDocumento3 pagineRadio 25 E1 Lec 10 MSK RadiologyYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 May - NCDocumento36 pagine2016 May - NCYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Review of Normal Lung Structure and FunctionDocumento8 pagine(OS 213) LEC 03 Review of Normal Lung Structure and FunctionYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 15 Surgery For Peripheral Vascular Diseases I (B)Documento8 pagine(OS 213) LEC 15 Surgery For Peripheral Vascular Diseases I (B)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (Os 213) Pictotrans Ws 02 - Ecg Skills Enhancement (A)Documento16 pagine(Os 213) Pictotrans Ws 02 - Ecg Skills Enhancement (A)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Medicine OSCE Collection: By: Fatimah Al-IbrahimDocumento69 pagine5 Medicine OSCE Collection: By: Fatimah Al-IbrahimJim JordenNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Procedures in Ophthalmology Full ColourDocumento488 pagineDiagnostic Procedures in Ophthalmology Full ColourAnquito100% (4)
- (OS 213) LEC 13 Paragonimus Westermani (A)Documento4 pagine(OS 213) LEC 13 Paragonimus Westermani (A)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 15 Pneumonia (B) - 1Documento7 pagine(OS 213) LEC 15 Pneumonia (B) - 1Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 02 Cardinal Symptoms of Heart Disease (A)Documento14 pagine(OS 213) LEC 02 Cardinal Symptoms of Heart Disease (A)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) CASE 01 Case PresentationsDocumento3 pagine(OS 213) CASE 01 Case PresentationsYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Documento16 pagine(OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 10 Rheumatic Fever and RHD (B)Documento6 pagine(OS 213) LEC 10 Rheumatic Fever and RHD (B)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (Os 213) Lec 09 TB Dots (A)Documento2 pagine(Os 213) Lec 09 TB Dots (A)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LAB 03 Paragonimus Westermani (B) - 2Documento3 pagine(OS 213) LAB 03 Paragonimus Westermani (B) - 2Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- RADIO 250 (8) LEC 08 Genitourinary Pelvis RadiologyDocumento14 pagineRADIO 250 (8) LEC 08 Genitourinary Pelvis RadiologyYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC36 CVS Course SummaryDocumento12 pagine(OS 213) LEC36 CVS Course SummaryYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio 250 (8) Lec 05 Gi RadiologyDocumento11 pagineRadio 250 (8) Lec 05 Gi RadiologyYavuz Danis100% (1)
- RADIO 250 (8) LEC 11 Introduction To Interventional RadiologyDocumento6 pagineRADIO 250 (8) LEC 11 Introduction To Interventional RadiologyYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 09 Physical Diagnosis of The Respiratory System (B) - 2Documento8 pagine(OS 213) LEC 09 Physical Diagnosis of The Respiratory System (B) - 2Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- RADIO 250 (8) LEC 09 Musculoskeletal RadiologyDocumento4 pagineRADIO 250 (8) LEC 09 Musculoskeletal RadiologyYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio 250 E1 Lec 01 Intro To Radiology and RadioprotectionDocumento6 pagineRadio 250 E1 Lec 01 Intro To Radiology and RadioprotectionYavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 10 Rheumatic Fever and RHD (B)Documento6 pagine(OS 213) LEC 10 Rheumatic Fever and RHD (B)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- (OS 213) LEC 11 Viral and Fungal Diseases of The Lung (A)Documento7 pagine(OS 213) LEC 11 Viral and Fungal Diseases of The Lung (A)Yavuz DanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Table - TrematodesDocumento4 pagineSummary Table - TrematodesNeil Joshua SuyatNessuna valutazione finora
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocumento5 pagineTable For Cestodes and TrematodesDawn WRein Legaspi100% (3)
- TrematodesDocumento16 pagineTrematodesRenz Gerard AmorNessuna valutazione finora
- HarrmicroDocumento16 pagineHarrmicroMariel AbatayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematode SDocumento26 pagineTrematode SothnielNessuna valutazione finora
- Phylum Platyheminthes TrematodesDocumento12 paginePhylum Platyheminthes TrematodesRona SalandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Trematodes PDFDocumento70 pagineIntroduction To Trematodes PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Table ReviewDocumento8 pagineParasitology Table ReviewAliehsEiram18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amphistomate & Distomate FlukeDocumento12 pagineAmphistomate & Distomate FlukeJayricDepalobosNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematodes LECDocumento2 pagineTrematodes LECAki SuzumeNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Parasitology QuestionsDocumento6 pagineMedical Parasitology QuestionsIdrissa ContehNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology Midterm-TransesDocumento11 pagineParasitology Midterm-TransesJISOO KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematodes - PreFinalDocumento13 pagineTrematodes - PreFinalAndriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paragonimus Westermani: Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocumento26 pagineParagonimus Westermani: Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas PPT Parasito PDFDocumento61 pagineTugas PPT Parasito PDFAnna DananjayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paragonimus Family NEWDocumento19 pagineParagonimus Family NEWADARSH ARUNNessuna valutazione finora
- Paragonimus Westermani: Lynn Marie P. Simporios ReporterDocumento9 pagineParagonimus Westermani: Lynn Marie P. Simporios ReporterLynn Marie P. SimporiosNessuna valutazione finora
- TrematodesDocumento30 pagineTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Infection and ChemotherapyDocumento4 pagineJournal of Infection and Chemotherapyanggit julianingsihNessuna valutazione finora
- PARASITOLOGYDocumento35 paginePARASITOLOGYMcarl Matel100% (8)
- TrematodesDocumento20 pagineTrematodesmiguel gaquitNessuna valutazione finora
- Para Midterm ExamDocumento10 paginePara Midterm ExamKlenn Orteza100% (1)
- Paragonimus Westermani: Name: Sava Sherko Savin Pshko Arazw Fazil Lava Akbar Shadman Brzo ASSIST:DR - Latif Omer MuhamadDocumento6 pagineParagonimus Westermani: Name: Sava Sherko Savin Pshko Arazw Fazil Lava Akbar Shadman Brzo ASSIST:DR - Latif Omer MuhamadSava Sherko OthmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniDocumento51 pagineParasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniNicole ManogNessuna valutazione finora
- TrematodesDocumento5 pagineTrematodesdhaineyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Trematodes (Flukes) Presented by Happy SimozuDocumento93 pagineThe Trematodes (Flukes) Presented by Happy SimozuWilliam C ChishaNessuna valutazione finora
- PARAGONIMUSDocumento17 paginePARAGONIMUSMelody PardilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasitology - TrematodesDocumento16 pagineParasitology - TrematodesMarlex SuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasites: QZ Board StudyDocumento133 pagineParasites: QZ Board StudyBrenner CelegansNessuna valutazione finora
- Para Lec Comprehensive Reviewer Chapter 1 2Documento20 paginePara Lec Comprehensive Reviewer Chapter 1 2Alli Vega100% (1)