Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Comparison Between Two Private Sector Banks
Caricato da
Parag MoreTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Comparison Between Two Private Sector Banks
Caricato da
Parag MoreCopyright:
Formati disponibili
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
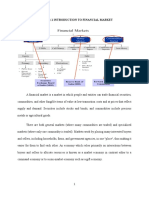
The world of banking has assumed a new dimension at dawn of the 21st century
with the advent of tech banking, thereby lending the industry a stamp of
universality. In general, banking may be classified as retail and corporate
banking. Retail banking, which is designed to meet the requirement of
individual customers and encourage their savings, includes payment of utility
bills, consumer loans, credit cards, checking account and the like. Corporate
banking, on the other hand, caters to the need of corporate customers like bills
discounting, opening letters of credit, managing cash, etc. Metamorphic changes
took place in the Indian financial system during the eighties and nineties
consequent upon deregulation and liberalization of economic policies of the
government. India began shaping up its economy and earmarked ambitious plan
for economic growth. Consequently, a sea change in money and capital markets
took place. Application of marketing concept in the banking sector was
introduced to enhance the customer satisfaction he policy of privatization of
banking services aims at encouraging the competition in banking sector and
introduction of financial services. Consequently, services such as Demat,
Internet banking, Portfolio Management, Venture capital, etc, came into
existence to cater to the needs of public. An important agenda for every banker
today is greater operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. The mew
watchword for the bank is pretty ambitious: customer delight. The introduction
to the marketing concept to banking sectors can be traced back to American
Banking Association Conference of 1958. Banks marketing can be defined as
the part of management activity, which seems to direct the flow of banking
services profitability to the customers. The marketing concept basically requires
that there should be thorough understanding of customer need and to learn about
1
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
market it operates in. Further the market is segmented so as to understand the
requirement of the customer at a profit to the banks.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 2
DEFINITION OF BANK
The Oxford dictionary defines the Bank as,
An establishment for the custody of money, which it pays out, on a customers
order.
According to Whitehead
A Bank is defined as an institution which collects surplus funds from the
public, safeguards the, and makes them available to the true owner when
required and also lends sums be their true owners to those who are in need of
funds and can provide security.
Banking Company in India has been defined in the Banking Companies
act1949,One which transacts the business of banking which means the
accepting, for the purpose of lending or investment of the deposits of money
from the public, repayable on demand, or otherwise and withdraw able be
cheque draft, order or otherwise.The banking system is an integral subsystem
of the financial system. It represents an important channel of collecting small
savings form the households and lending it to the corporate sector. The Indian
banking system has Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as the apex body for all
matters relating to the banking system. It is the central Bank of India. It is also
known as the Banker to All Other Banks.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 3
PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
All those banks where greater parts of stake or equity are held by the private
shareholders and not by government are called "private-sector banks". These are
the major players in the banking sector as well as in expansion of the business
activities India. The present private-sector banks equipped with all kinds of
contemporary innovations, monetary tools and techniques to handle the
complexities are a result of the evolutionary process over two centuries. They
have a highly developed organizational structure and are professionally
managed. Thus they have grown faster and stronger since past few years
The part of the economy that is not state controlled, and is run by individuals
and companies for profit. The private sector encompasses all for-profit
businesses that are not owned or operated by the government. Companies and
corporations that are government run are part of what is known as the public
sector, while charities and other nonprofit organizations are part of the voluntary
sector.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 4
PRIVATIZATION OF INDIAN BANKING
For the public sector banks, the era of bumper profit is over. For much of the
last decade the process of collaborated financial liberalization had cleared up
the Banks balance sheet enabling them to with stand increased competition,
global financing, turmoil and even unprotected industrial slow down. But the
cycle of liberalization has run its full course. Now it is the time for the big
structural leap, rationalization, mergers, and privatization. Unless the banks
undertake these fundamental changes, their profit will stay under pressure.
There are two areas of competitions which banking industry is facing
internationally and nationally. In the pre-liberalization era, Indian banks could
grow in a closed economy but the banking sector opened up for private
competition. It is possible that private banks could become dominant players
even within India. It has been recorded a rapid rise of the new private sector
banks and it has tracked the transformation of the public sector banks as they
grapple with the changes of financial deregulation.
Use of ATM cards, Internet Banking, Phone Banking, Mobile Banking are the
new innovative channels of banking which are being widely used as they result
in saving both time and money which are two essential things that every one is
short of and is running to catch hold of them. Moreover private sector banks
are aligning its infrastructures, marketing quality and technology to build
deep commitment in building consumer and retail banking. The main focus of
these banks is on innovative range of services or products.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 5
HISTORY & EVALUATION OF PRIVATE SECTOR
BANKS
Private-sector banks have been functioning in India since the very beginning of
the banking system. Initially, during 1921, the private banks like bank of
Bengal, bank of Bombay and bank of Madras were in service, which all
together formed Imperial Bank of India.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) came in picture in 1935 and became the centre of
every other bank taking away all the responsibilities and functions of Imperial
bank. Between 1969 and 1980 there was rapid increase in the number of
branches of the private banks. In April 1980, they accounted for nearly 17.5
percent of bank branches in India. In 1980, after 6 more banks were
nationalized, about 10 percent of the bank branches were those of private-sector
banks. The share of the private bank branches stayed nearly same between 1980
and 2000.
Then from the early 1990s, RBI's liberalization policy came in picture and with
this the government gave licenses to a few private banks, which came to be
known as new private-sector banks.
There are two categories of the private-sector banks: "old" and "new".
The old private-sector banks have been operating since a long time and may be
referred to those banks, which are in operation from before 1991 and all those
banks that have commenced their business after 1991 are called as new privatesector banks.[
6
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited was the first private bank
in India to receive license from RBI as a part of the RBI's liberalization policy
of the banking sector, to set up a bank in the private-sector banks in India.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
LIST OF PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Old private sector banks
New private banks
Catholic Syrian Bank Ltd.
Axis Bank Ltd.
City Union Bank Ltd.
Development Credit Bank Ltd.
Dhanalakshmi bank Ltd.
HDFC Bank Ltd.
Federal Bank Ltd.
ICICI Bank Ltd.
ING Vysya Bank Ltd.
Induslnd Bank Ltd.
Jammu & Kashmir Bank Ltd.
Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd.
Karnataka Bank Ltd.
Yes Bank Ltd.
Karur Vysya Bank Ltd.
Lakshmi Vilas Bank Ltd.
Nainital Bank Ltd.
Ratnakar Bank Ltd.
South Indian Bank Ltd.
Tamilnad Mercantile Bank Ltd.
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 6
7 PS OF THE PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
PRODUCT
(A) DEPOSITS: Savings, Current, Fixed etc.
(B) ADVANCES: a) Term Loan, b) Clean Loan, c) Bills Discounting, d)
Advances, e) Pre-shipment Finance, f) Post-shipment finance, g) Secured and
Unsecured lines of credit.
(2) Non-fund oriented: a) Guarantees, and b) Letter of Credit.
(C) INTERNATIONAL BANKING: a) Letter of Credit, and b) Foreign
Currency.
(D) CONSULTANCY: a) Investment Counseling, b) Project Counseling, c)
Merchant Banking, and d) Tax Consultancy.
(E) MISCELLANEOUS: a) Traveler Cheques, b) Credit card, c) Remittances,
d) Collections, e) Sale of Drafts, f) Standing instructions, and g) Trusteeship.
As seen in the goods-service continuum, your product can have both tangible
and intangible aspects, and is the thing you offer to satisfy your customers
wants and needs. Within this element, you need to consider such things as your
product range; its quality and design; its features and the benefits it offers;
sizing and packaging; and any add-on guarantees and customer service
offerings.
PRICE
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
The price mix in the banking sector is nothing but the interest rates charged by
the different banks.
Let's understand this with an example. A particular buyer approaches for a car
loan say for a period of 3 years. He is charged Rs. 20,000 as interest. however if
a sales representative of another bank comes to know of this deal he will try to
attract the customer by giving him a better deal that is a loan at a lower rate on
interest. In this way due to the high level of competition the customer benefits.
PROMOTION
Promotion is nothing but making the customer more and more aware of the
services and benefits provided by the bank.
The banks today can use a lot of new technology to communicate to their
customers. Two of the fastest growing modern tools of communicating with the
customers are:
1. Internet Banking
2. Mobile Banking
PLACE
Place mix is the location analysis for banks branches. There are number a
factors affecting the determination of the location of the branch of bank. Like
population characteristics, commercial, proximity of other commercial outlets.
Your choice of such channels is important, as is the variety of channels you use.
For example, a common issue for businesses beginning to trade on-line is how
that will affect their off-line business, for example selling directly through the
10
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
web could alienate retail outlets that have been the mainstay of your business in
the past.
PEOPLE
The impact that your people can have on your marketing cannot be
underestimated. At its most obvious, this element covers your front line sales
and customer service staff who will have a direct impact on how your product is
perceived. You need to consider the knowledge and skills of your staff; their
motivation and investment in supporting your brand. Any element of the
marketing mix will also have its impact on other elements of your business, but
the people element is one where the importance of regarding marketing as an
integral part of the way you do business is crystal clear.
PROCESS
The process mix constitutes the overall procedure involved in using the services
offered by the bank.
Let's take for example the process for application for a car loan.
Now this mainly involves 3 things.
1. Producing of proper documents
2. Filling up of application form
3. Paying for the initial down payment
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE
Physical evidence is the overall layout of the place. How the entire bank has
been designed. Physical evidence refers to all those factors that helps make the
11
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
process much easier and smoother. For example in case of a bank the physical
evidence would be the placement of the customer service executive's desk, or
the location of the place for depositing Cheques.
CHAPTER 7
COMPANY PROFILE
INDUSTRIAL CREDIT & INVESTMENT
CORPORATION OF INDIA
INTRODUCTION TO ICICI BANK
ICICI Bank is Indias second-largest bank with total assets of Rs. 3,663.74
billion (US$ 76 billion) at September 30, 2009 and profit after tax Rs. 19.18
billion (US$ 398.8 million) for the half year ended September 30, 2009. The
Bank has a network of 1,588 branches and about 4,883 ATMs in India and
presence in 18 countries. ICICI Bank offers a wide range of banking products
12
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
and financial services to corporate and retail customers through a variety of
delivery channels and through its specialised subsidiaries and affiliates in the
areas of investment banking, life and non-life insurance, venture capital and
asset management. The Bank currently has subsidiaries in the United
Kingdom, Russia and Canada, branches in United States, Singapore, Bahrain,
Hong Kong, Sri Lanka, Qatar and Dubai International Finance Centre and
representative offices in United Arab Emirates, China, South Africa,
Bangladesh, Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Our UK subsidiary has
established branches in Belgium and Germany.
ICICI Banks equity shares are listed in India on Bombay Stock Exchange and
the National Stock Exchange of India Limited and its American Depositary
Receipts (ADRs) are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
HISTORY OF ICICI BANK
ICICI Bank was originally promoted in 1994 by ICICI Limited, an Indian
financial institution, and was its wholly-owned subsidiary. ICICIs
shareholding in ICICI Bank was reduced to 46% through a public offering of
shares in India in fiscal 1998, an equity offering in the form of ADRs listed on
the NYSE in fiscal 2000, ICICI Banks acquisition of Bank of Madura Limited
in an all-stock amalgamation in fiscal 2001, and secondary market sales by
ICICI to institutional investors in fiscal 2001 and fiscal 2002. ICICI was
formed in 1955 at the initiative of the World Bank, the Government of India
and representatives of Indian industry. The principal objective was to create a
development financial institution for providing medium-term and long-term
project financing to Indian businesses. In the 1990s, ICICI transformed its
business from a development financial institution offering only project finance
to a diversified financial services group offering a wide variety of products and
13
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
services, both directly and through a number of subsidiaries and affiliates like
ICICI Bank. In 1999, ICICI become the first Indian company and the first
bank or financial institution from non-Japan Asia to be listed on the NYSE.
After consideration of various corporate structuring alternatives in the context
of the emerging competitive scenario in the Indian banking industry, and the
move towards universal banking, the managements of ICICI and ICICI Bank
formed the view that the merger of ICICI with ICICI Bank would be the
optimal strategic alternative for both entities, and would create the optimal
legal structure for the ICICI groups universal banking strategy. The merger
would enhance value for ICICI shareholders through the merged entitys
access to low-cost deposits, greater opportunities for earning fee-based income
and the ability to participate in the payments system and provide transactionbanking services. The merger would enhance value for ICICI Bank
shareholders through a large capital base and scale of operations, seamless
access to ICICIs strong corporate relationships built up over five decades,
entry into new business segments, higher market share in various business
segments, particularly fee-based services, and access to the vast talent pool of
ICICI and its subsidiaries. In October 2001, the Boards of Directors of ICICI
and ICICI Bank approved the merger of ICICI and two of its wholly-owned
retail finance subsidiaries, ICICI Personal Financial Services Limited and
ICICI Capital Services Limited, with ICICI Bank.
14
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
THE 7 Ps OF ICICI BANK
PRODUCT MIX:
1. DEPOSITS:
ICICI Bank offers wide variety of Deposit Products to suit our requirements.
Coupled with convenience of networked branches/ over 1800 ATMs and
facility of E-channels like Internet and Mobile Banking, ICICI Bank brings
banking at your doorstep.
Savings Account: ICICI Bank offers a power packed Savings Account with a
host of convenient features and banking channels to transact through. So now
you can bank at your convenience, without the stress of waiting in queues.
15
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Senior Citizen Services: The Senior Citizen Services from ICICI Bank has
several advantages that are tailored to bring more convenience and enjoyment
in your life.
Young Stars: Its really important to help children learn the value of finances
and money management at an early age. Banking is a serious business, but we
make banking a pleasure and at the same time children learn how to manage
their personal finances.
Fixed Deposits: Safety, Flexibility, Liquidity and Returns!!!! A combination
of unbeatable features of the Fixed Deposit from ICICI Bank.
Recurring Deposits: Through ICICI Bank Recurring Deposit you can invest
small amounts of money every month that ends up with a large saving on
maturity. So you enjoy twin advantages- affordability and higher earnings.
Roaming Current Account: Only Roaming Current Account from ICICI
Bank travels the distance with your business. You can access your accounts at
over 500 networked branches across the country.
Bank @ Campus: Thanks to bank@campus, child can now surf the Net and
access all the details of his / her account at the click of a mouse! No need to
visit the bank branch at all.
ICICI Bank Salary Account: is a benefit-rich payroll account for Employers
and Employees. As an organization, you can opt for our Salary Accounts to
enable easy disbursements of salaries and enjoy numerous other benefits too.
2. INVESTMENTS
16
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Along with Deposit products and Loan offerings, ICICI Bank assists you to
manage your finances by providing various investment options such as:
ICICI Bank Tax Saving Bonds
Government of India Bonds
Investment in Mutual Funds
Initial Public Offers by Corporate
Investment in Pure Gold
Foreign Exchange Services
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme, 2004
3. ANYWHERE BANKING
ICICI Bank is the second largest bank in the country. It services a customer
base of more than 5 million customer accounts through a multi-channel access
network. This includes more than 500 branches and extension counters, over
1800 ATMs, Call Centre and Internet Banking.
Thus, one can access the various services ICICI Bank has to offer at anytime,
anywhere and from anyplace.
4. LOAN
a) Home Loans
b) Personal Loans
c) Car Loans
d) Two Wheeler Loans
e) Commercial Vehicle Loans
f) Loans against Securities
g) Farm Equipment Loans
h) Construction Equipment Loans
i) Office Equipment Loans
17
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
j) Medical Equipment Loans
5. CARDS
a) Credit Card: ICICI Bank Credit Cards give you the facility of cash,
convenience and a range of benefits, anywhere in the world. These benefits
range from life time free cards, Insurance benefits, global emergency
assistance service, discounts, utility payments, travel discounts and much
more.
b) Debit ATM Card: The ICICI Bank Debit Card is a revolutionary form of
cash that allows customers to access their bank account around the clock,
around the world. The ICICI Bank Debit Card can be used for shopping at
more than 100,000 merchants in India and 13 million merchants worldwide.
c) Travel Card: Presenting ICICI Bank Travel Card. The Hassle Free way to
Travel the world. Traveling with US Dollar, Euro, Pound Sterling or Swiss
Francs; Looking for security and convenience; take ICICI Bank Travel Card.
Issued in duplicate. Offers the Pin based security. Has the convenience of
usage of Credit or Debit card.
6. DEMAT SERVICES
ICICI Bank Demat Services boasts of an ever-growing customer base of over 7
lacs account holders. In their continuous endeavor to offer best of the class
services to our customers we offer the following features:
Digitally signed transaction statement by e-mail.
Corporate benefit tracking.
18
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
e-Instruction facility facility to transfer securities 24 hours a day, 7 days
a week through Internet Interactive Voice Response (IVR) at a lower cost.
Dedicated specially trained customer care executives at their call centre,
to handle all queries.
7. MOBILE BANKING
With ICICI Bank, banking is no longer what it used to be. ICICI Bank offers
Mobile Banking facility to all its Bank, Credit Card and Demat customers.
ICICI Bank Mobile Banking enables you to bank while being on the move.
8. NRI SERVICES
ONLINE MONEY TRANSFER facility available to NRIs worldwide
through www.money2India.com at the click of a button
Benefits:
FREE Money transfers into accounts with over 30 banks in India
Demand Drafts issued and payable at over 1250 locations in India
ONLINE Tracking of the status of your funds
SUPERIOR Exchange rates
OFFLINE MONEY TRANSFER facility is also available across
geographies through
Local branches and in association with partner banks/ exchange houses.
19
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
PRICING MIX:
The pricing decisions or the decisions related to interest and fee or commission
charged by banks are found instrumental in motivating or influencing the
target market.
The RBI and IBA are concerned with regulations. The rate of interest is
regulated by the RBI and other charges are controlled by IBA.
The pricing policy of a bank is considered important for raising the number of
customers the accretion of deposits. Also the quality of service provided has
direct relationship with the fees charged. Thus while deciding the price mix
customer services rank the top position.
20
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
The banking organizations are required to frame two- fold strategies. First, the
strategy is concerned with interest and fee charged and the second strategy is
related to the interest paid. Since both the strategies throw a vice- versa
impact, it is important that banks attempt to establish a correlation between
two. It is essential that both the buyers as well as the sellers have feeling of
winning.
PROMOTION MIX:
Advertising: Television, radio, movies, theatres
Print media: hoardings, newspaper, magazines
Publicity: road shows, campus visits, sandwich man, Sponsorship
Sales promotion: gifts, discount and commission, incentives,etc.
Personal selling: Cross-sale (selling at competitors place),personalized
service.
Telemarketing: ICICI one source Call center (mind space)
IMPORTANT 4 P`S OF ICICI BANK
PLACE:
This component of marketing mix is related to the offering of services. The
services are sold through the branches.
The 2 important decision making areas are: making available the promised
services to the ultimate users and selecting a suitable place for bank branches.
The number of branches OF ICICI: 1900 in India and 33 in Mumbai.
21
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
PEOPLE:
All people directly or indirectly involved in the consumption of banking
services are an important part of the extended marketing mix. Knowledge
Workers, Employees, Management and other Consumers often add significant
value to the total product or service offering. It is the employees of a bank
which represent the organisation to its customers.
In a bank organization, employees are essentially the contact personnel with
customer. Therefore, an employee plays an important role in the marketing
operations of a service organisation.
To realize its potential in bank marketing, ICICI become conscious in its
potential in internal marketing the attraction, development, motivation and
retention of qualified employee-customers through need meeting job-products.
Internal marketing paves way for external marketing of services. In internal
marketing a variety of activities are used internally in an active, marketing like
manner and in a coordinated way.
The starting point in internal marketing is that the employees are the first
internal market for the organization.
The basic objective of internal marketing is to develop motivated and customer
conscious employees.
A service company can be only as good as its people. A service is a
performance and it is usually difficult to separate the performance from the
people.
If the people meet customers expectations, then neither does the service.
Therefore, investing in people quality in service business means investing in
product quality.
22
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
PROCESS:
Flow of activities: All the major activities of ICICI banks follow RBI
guidelines. There has to be adherence to certain rules and principles in the
banking operations. The activities have been segregated into various
departments accordingly.
Standardization: ICICI bank has got standardized procedures got typical
transactions. In fact not only all the branches of a single-bank, but all the
banks have some standardization in them. This is because of the rules they are
subject to. Besides this, each of the banks has its standard forms,
documentations etc. Standardization saves a lot of time behind individual
transaction.
Customization: There are specialty counters at each branch to deal with
customers of a particular scheme. Besides this the customers can select their
deposit period among the available alternatives.
Number of steps: Numbers of steps are usually specified and a specific
pattern is followed to minimize time taken.
Simplicity: In ICICI banks various functions are segregated.
Separate
counters exist with clear indication. Thus a customer wanting to deposit
money goes to deposits counter and does not mingle elsewhere. This makes
procedures not only simple but consume less time. Besides instruction boards
in national boards in national and regional language help the customers further
.
23
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Customer involvement: ATM does not involve any bank employees. Besides,
during usual bank transactions, there is definite customer involvement at some
or the other place because of the money matters and signature requires.
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE:
Physical evidence is the material part of a service. Strictly speaking there are
no physical attributes to a service, so a consumer tends to rely on material
cues. There are many examples of physical evidence, including some of the
following:
Internet/web pages
Paperwork
Brochures
Furnishings
Business cards
The building itself (such as prestigious offices or scenic headquarters)
The physical evidences also include signage, reports, punch lines, other
tangibles, employees dress code etc.
Signage: Each and every bank has its logo by which a person can identify the
company. Thus such sign ages are significant for creating visualization and
corporate identity.
Financial reports: The Company financial reports are issued to the customers
to emphasis or credibility.
24
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Tangibles: Bank gives pens, writing pads to the internal customers. Even the
passbooks, cheque books, etc reduce the inherent intangibility of services.
Punch lines: Punch lines or the corporate statement depict the philosophy and
attitude of the bank. Banks have influential punch lines to attract the
customers.
Employees dress code: ICICI bank follows a dress code for their internal
customers. This helps the customers to feel the ease and comfort.
ICICI STRATEGY FOR PROMOTION OF FINANCIAL INCLUSION
ICICI Bank has taken up specific initiatives to ramp up financial literacy as well
as intermediation to the underserved and under banked segments in both rural
and urban areas.
ICICI Banks financial intermediation models, both through the microfinance
institutions and business correspondents have been designed to build a
repository of information with regard to financial behaviour of the customers.
ICICI Banks Financial Intermediation Models:
25
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
With focus on low-income segments, ICICI Bank has come up with innovative
delivery channels:
Microfinance
ICICI Bank works closely with MFIs and NGOs to adapt its products to suit
consumer needs.
Two innovative models have helped achieve scale in serving the low-income
household:
a) Partnership Model being implemented with NGOs and MFIs: Under this
model ICICI Bank forges an alliance with existing MFIs wherein the MFI
undertakes the promotional role of identifying, training and promoting the
micro-finance clients and the ICICI Bank finances the clients directly on the
recommendation of the MFI, so the customer and portfolio resides in the Banks
book.
b) Securitisation of Portfolios of MFIs: Under this model ICICI Bank buys out
portfolios from MFIs. The MFI continues to service the clients and acts as the
collection agent. Here again, the MFI shares the credit risk with the Bank. A
variant of the securitisation model is on-tap securitisation, wherein the MFI
receives an advance purchase consideration to create a portfolio of loans that
could then be periodically sold to ICICI Bank.
Technology
26
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
The Bank has been actively looking at technology solutions to scale up the
micro finance portfolio. Further, the Bank has been considering adopting a 'Core
Banking System' (CBS) for managing the loan portfolio generated under the
partnership model. In this regard, the Bank has found an able partner in FINO to
provide technology solutions to the micro finance sector. The technology
solution comprises of core banking and smart card systems. In light of the
technology solutions available through FINO, the Bank has designed a new
process for delivering loans under the partnership model.
Some of the key aspects where a strong technology platform will add value to
the micro finance operations include reduction in transaction cost; better data
management and reporting capacities and capability to interface with multiple
peripherals, etc. This will also enable enhanced disclosure and transparency in
the operations of MFIs, setting a platform for robust securitisation / buyout
opportunities to meet the priority sector lending objectives of the regulator.
Business Correspondent
In line with the RBI guidelines ICICI Bank employs Business Correspondent
(BC) model to extend financial services, especially the much-needed savings
services to rural customers.
In the pilot stage, the transactions by BC are being done with the help of an 'ePassbook' and an Authentication Device (AD). The e-Passbook can display and
store the customer KYC information, customer account details and the
transactions in each account. It also has a unique feature of biometric
authentication by the way of fingerprints, thereby mitigating the risk related to
PIN (Personal Identification Number) in the rural scenario.
27
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
ADs provide Customer interface with user-friendly menu options, enabling
transactions. An authorized operator is enrolled by capturing the fingerprints of
all the 10 fingers to mitigate fraud risk, can operate each AD. The transaction is
recorded on the AD, which at specific intervals would be uploaded and updated
in the Bank's system through a normal telephone line, which is a widely
available infrastructure even in remote rural areas. Further connectivity through
GSM and CDA would also be made possible to ensure that the transaction
details are updated in the Banks system at higher frequency.
Multiple products
ICICI Bank offers a complete suite of products and services to meet the
individual
financial requirements of customer segments. Savings, investments and
insurance
products are made available to its rural and agri customer base. The Bank also
offers microfinance services to low-income households and crop loans, farm
equipment loans, commodity based loans to farmers.
Hybrid channels
ICICI Bank employs delivery channels backed by technological innovations to
achieve scale and outreach in a sustainable manner. The Banks channel
28
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
architecture includes branch and non-branch channels. Branches act as a
business
hub providing banking services on the one hand, while facilitating the fulfilment
of
products that have been sourced by the business facilitators and business
correspondents.
Non-branch channels are of two types, business facilitators and business
correspondents.
CHAPTER 8
COMPANY PROFILE
HOUSING DEVELOPMENT FINANCE
CORPORATION
HDFC BANK
HDFC Bank is India's second-largest bank with total assets of Rs.
3,849.70 billion (US$ 82 billion) at September 30, 2008 and profit after tax Rs.
17.42 billion for the half year ended September 30, 2008. The Bank has a
network of about 1,400 branches and 4,530 ATMs in India and presence in 18
countries. HDFC Bank offers a wide range of banking products and financial
services to corporate and retail customers through a variety of delivery channels
and through its specialized subsidiaries and affiliates in the areas of investment
29
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
banking, life and non-life insurance, venture capital and asset management. The
Bank currently has subsidiaries in the United Kingdom, Russia and Canada,
branches in United States, Singapore, Bahrain, Hong Kong, Sri Lanka, Qatar
and Dubai International Finance Centre and representative offices in United
Arab Emirates, China, South Africa, Bangladesh, Thailand, Malaysia and
Indonesia. Our UK subsidiary has established branches in Belgium and
Germany.
HDFC Bank's equity shares are listed in India on Bombay Stock Exchange and
the National Stock Exchange of India Limited and its American Depositary
Receipts (ADRs) are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
HISTORY OF HDFC BANKS
HDFC Bank was originally promoted in 1994 by HDFC Limited, an Indian
financial institution, and was its wholly-owned subsidiary. HDFC's shareholding
in HDFC Bank was reduced to 46% through a public offering of shares in India
in fiscal 1998, an equity offering in the form of ADRs listed on the NYSE in
fiscal 2000, HDFC Bank's acquisition of Bank of Madura Limited in an allstock amalgamation in fiscal 2001, and secondary market sales by HDFC to
institutional investors in fiscal 2001 and fiscal 2002. HDFC was formed in 1955
at the initiative of the World Bank, the Government of India and representatives
of Indian industry.
The principal objective was to create a development financial institution for
providing medium-term and long-term project financing to Indian businesses. In
the 1990s, HDFC transformed its business from a development financial
30
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
institution offering only project finance to a diversified financial services group
offering a wide variety of products and services, both directly and through a
number of subsidiaries and affiliates like HDFC Bank. In 1999, HDFC become
the first Indian company and the first bank or financial institution from nonJapan Asia to be listed on the NYSE.
OBJECTIVES OF HDFC BANK
HDFC Bank has taken several initiatives as part of its corporate social
responsibility. It has collaborated with several NGOs to assist in its activities.
Initiative
Objective
Activities
Facts/Figures
Sustainable
Provide
Training for Occupation
Reached 20 lakh
Livelihood
livelihood
Skills
households across
finance to
Credit Counseling
24 states
empower rural
Financial Literacy
people,
Market Linkages
especially
women at the
31
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
bottom of the
pyramid
Provide
600 government
affordable
schools across
access to basic
banking
Literacy programs in
Financial
products and
schools
Literacy
services to
Power of Banking
excluded and
workshops
underprivileged
education by
Education
providing
quality
education to
children
Training
literacy programs
3365 students
across 6 locations
workshops
society
importance of
& Odisha in
covered in
sections of the
Spread the
Andhra Pradesh
Galli School Project
Grow with Books
Library programs
Engineering scholarships
Child development
program
Family based care
A large number of
students reached
through various
programs across
the country
programs
Enhance
Skill-based courses
More than 1500
employability
Technical & vocational
youth benefitted
of youth and
training
through various
women in the
Basic computer
programs across
weaker sections programming
32
the country
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
of the society
by providing
training and
capacity
Educational support for
children
development
Enable
Community
economic
Rain water harvesting
growth and
programs
sustainable
Setting up blood storage
development
facilities
through
Construction of sanitation
community
facilities in schools
building
Child Aid Foundation
programs
Go Green
150 tribal girls
benefitted through
sanitation project
350 poor and
needy children
supported
1600+ children
rescued
Take
Promoting paperless
As of Mar 2013,
responsibility
banking
82% of customer-
for the effects
Multi-channel delivery
initiated retail
of the
(Internet, Mobile, Phone,
transactions direct
operations of
ATM)
banking channels,
the Bank on the Energy efficiency
reducing the need
environment
to commute
Green infrastructure
and the society.
66 lakh retail
customers
subscribed for estatement
20 ATMs
33
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
operating on clean
energy
PRODUCTS PROVIDED BY HDFC BANK
NRI banking
Under NRI Banking, HDFC offers:
Accounts & Deposits
Money Transfer
Investments & Insurance
Research Reports
34
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Payment Services
Wholesale banking
HDFC offers Wholesale Banking for Corporates and Financial Institutions &
Trusts. The Bank also provides services such as Investment Banking and other
services in the Government sector.
SERVICES PROVIDED BY HDFC BANK
35
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Wholesale banking services
HDFC Bank provides a range of commercial and transactional banking services,
including working capital finance, trade services, transactional services, cash
management, etc. to large, small and mid-sized corporates and agriculture-based
businesses in India. The bank is also a leading provider of these services to its
corporate customers, mutual funds, stock exchange members and banks.[14]
Retail banking services
HDFC Bank was the first bank in India to launch an International Debit Card in
association with VISA (Visa Electron). The bank also issues the
MasterCard Maestro debit card. The Bank launched its credit card business in
late 2001. By the end of June 2013, it had a credit card base of 5.94 million. By
March 2012, the bank had a total card base (debit and credit cards) of over 19.7
million. The Bank is also one of the leading players in the "merchant acquiring"
business with over 240,000 point-of-sale (POS) terminals for debit / credit cards
acceptance at merchant establishments. The Bank is positioned in various net
based B2C opportunities including a wide range of Internet banking services for
Fixed Deposits, Loans, Bill Payments, etc.
Treasury
The bank has three main product areas - Foreign Exchange and Derivatives,
Local Currency Money Market & Debt Securities, and Equities. These services
are provided through the bank's Treasury team. To comply with statutory
reserve requirements, the bank is required to hold 25% of its deposits in
government securities. The Treasury business is responsible for managing the
returns and market risk on this investment portfolio.
EMPLOYMENT PROVIDED BY HDFC BANK
36
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
As of 31 March 2013, the company has 69,065 employees, out of which 12,295
are women (17.80%). In June 2013, the company reported an annual attrition
rate of approx. 20%. During the financial year 2012-13, the company incurred
INR 42 billion on employee benefit expenses.
OPERATIONAL AREA OF HDFC BANK
As of 30 September 2013, HDFC Bank has 3,251 branches and 11,177 ATMs,
in 2,022 cities in India, and all branches of the bank are linked on an online realtime basis. The Bank has overseas branch operations in Bahrain and Hong
Kong.
HDFC Bank has two subsidiaries:
HDB Financial Services Limited (HDBFS): HDBFS is engaged in retail asset
financing. It is a non-deposit taking non-bank finance company (NBFC). Apart
from lending to individuals, the company grants loans to micro, small and
medium business enterprises. It also runs call centers for collection services to
the HDFC Banks retail loan products. HDFC Bank holds 97.4% shares in
HDBFS. As of March 31, 2013, HDBFS has 230 branches in 184 cities. During
the FY 2012-13, HDBFS had turnover of INR 9.6 billion and profit after tax of
INR 1 billion. It has 6,404 employees as of 31 March 2013.
HDFC Securities Limited (HSL): HSL is engaged in stock broking. As of
March 31, 2013, HDBFS has 194 branches across 150 cities. HDFC Bank has
62.1% shareholding in HSL. During the FY 2012-13, HSL had turnover of INR
37
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
2.3 billion and profit after tax of INR 668 million. During the year, the
Company received the Best e-Brokerage Award - 2012 in the Outlook Money
Awards in the runner up category.
38
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
CHAPTER 9
SWOT ANALYSIS
ICICI:STRENGTHS:
Branch network, brand name, very fast service, No. one private sector bank of
India,
WEAKNESS:
High average balance maintenance, maintenances charges are high.
OPPORTUNITIES:
Untapped rural market of India
THREATS:
Emerging private banks like Citibank and HDFC bank
HDFC:STRENGTH:
Maintains the highest level of ethical standards, professional integrity, corporate
governance and regulatory compliance, Operational Excellence, Customer
Focus, Product Leadership and People.
WEAKNESS:
39
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Limited number of branches
OPPRTUNITIES:
Untapped rural markets of India.
THREATS:
Competition among the private players.
CHAPTER 10
COMPARISON OF FINANCIAL RATIOS OF TWO
BANKS
TOTAL ASSETS
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
491599.50
594641.60
590503
649129.29
120.11
109.16
TOTAL SHARE CAPITAL
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
479.81
1155.04
501.30
1159.66
100.70
100.39
NET WORTH
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
43478.63
62009.42
142.62
40
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
ICICI
73213.32
80429.36
109.85
DEPOSITS
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
367337.48
331913.66
450795.64
361562.73
122.71
108.93
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
303000.27
338702.65
365495.03
387552.07
120.62
114.42
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
120951.07
177021.82
166459.95
186580.03
137.62
105.39
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
39438.99
154759.05
45213.56
172417.35
114.64
111.41
ADVANCES
INVESTMENTS
BORROWINGS
TOTAL DEBT
41
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
406776.47
486672.71
496009.20
533980.08
121.93
109.72
TOTAL LIABILITIES
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
491599.50
594641.58
590503.08
649129.30
120.11
109.16
CASH & BALANCES WITH RBI
BANKS IN RS.
2014
2015
% change
(CRORES)
HDFC
ICICI
25345.63
21821.83
27510.45
25652.91
108.54
117.55
CHAPTER 11
CONCLUSION
42
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
Almost all the Banks offer similar features and facilities with their Savings
accounts. There are certain reasons for existing customers of Saving Account
of any Bank to shift to another Bank.
The level of service in terms of delivering whatever is promised, fast
response in case of problems, is the most important benefit that the
customers seek, from the Bank they have a Saving Account with.
1. Network reach and visibility of a Bank is a very important criterion for
the customer while opening a Saving Account. We can also conclude
from our analysis that network reach in terms of Branches and ATMs is
directly proportional to the market share in case of Private Players.
2. In case of a new customer, if a bank approaches it first for opening a
Saving Account with them, then there is a good chance for the bank of
getting many future businesses and cross sales from the deal.
3. Aggressive Marketing is the key to increasing the market share in this
area, since the market has a lot of potential both in terms of untapped
market.
AS COMPARED TO OTHER PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN INDIA,
NOW-A-DAYS HDFC BANK IS GROWING RAPIDLY IN IT`S ALL THE
DEPARTMENTS
LIKE
TOTAL
ASSETS,
SHARE
CAPITAL,
NETWORTH & IT`S INVESTMENTS.
WHEN WE COMPARED HDFC BANK AMONG ICICI BANK MOST
OF CUSTOMERS GO WITH THE HDFC BANK BECAUSE OF ITS
INNOVATIVE PRODUCTS & BETTER SERVICE QUALITY.
CHAPTER 12
WEBILOGRAPHY
43
COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS
http://www.icicibank.com/
http://www.hdfcbank.com/
www.moneycontrol.com/
44
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Introduction and Functions of Nationalized BankDocumento10 pagineIntroduction and Functions of Nationalized BankPrashant MunnolliNessuna valutazione finora
- SBIDocumento62 pagineSBISuru SurelaNessuna valutazione finora
- SBI (State Bank of India)Documento2 pagineSBI (State Bank of India)dashgreevlankeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Services of ICICI and HDFC BankDocumento64 pagineCustomer Services of ICICI and HDFC BankShahzad Saif100% (1)
- Icici BankDocumento108 pagineIcici Bankmultanigazal_4254062100% (3)
- Axis Bank Research PaperDocumento53 pagineAxis Bank Research PaperRuchika Rai0% (1)
- Introduction To IciciDocumento3 pagineIntroduction To Iciciayushitanwar94Nessuna valutazione finora
- CP of Sbi BankDocumento4 pagineCP of Sbi Bankharman singh0% (1)
- Black Book ProjectDocumento4 pagineBlack Book ProjectSwapnil HengadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Axis Bank (Black Book) (1) TejuDocumento55 pagineAxis Bank (Black Book) (1) TejuTEJASHVINI PATEL0% (2)
- Case Study of SbiDocumento6 pagineCase Study of Sbiसंजय साहNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Axis BankDocumento32 pagineReport Axis Bankyakthung panyamboNessuna valutazione finora
- Finanial Analysis of HDFC BankDocumento15 pagineFinanial Analysis of HDFC BankShweta SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Internship Project HDFC Bank PDFDocumento109 pagineSummer Internship Project HDFC Bank PDFarunima100% (1)
- Comparative Analysis of The Products and Servies of Axis BankDocumento29 pagineComparative Analysis of The Products and Servies of Axis Bankpavan100% (1)
- SOUTH INDIAN BANK PresentationDocumento13 pagineSOUTH INDIAN BANK PresentationSourabh KondkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank of MaharashtraDocumento12 pagineBank of MaharashtraPravin Shivale67% (3)
- AXIS BANK Project Word FileDocumento28 pagineAXIS BANK Project Word Fileअक्षय गोयलNessuna valutazione finora
- Ramya Canara Bank Project Final ReportDocumento106 pagineRamya Canara Bank Project Final ReportShiva Kumar Mahadevappa79% (14)
- Evolution of SbiDocumento6 pagineEvolution of Sbiarchana_anuragiNessuna valutazione finora
- TJSBDocumento59 pagineTJSBMonik Maru Fakra He63% (8)
- Brief History of State Bank of IndiaDocumento3 pagineBrief History of State Bank of IndiaNikhil Sonawane67% (6)
- Comparative Analysis of HDFC Bank and SBIDocumento37 pagineComparative Analysis of HDFC Bank and SBIsiddhantkamdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Canara BankDocumento2 pagineCanara Bankkarthic kariappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms Archana. Wali MBA II Semester Exam No. MBA0702009Documento78 pagineMs Archana. Wali MBA II Semester Exam No. MBA0702009vijayakooliNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Banking SystemDocumento57 pagineIndian Banking Systemsamadhandamdhar6109100% (1)
- HDFC BankDocumento46 pagineHDFC BankAakash Atri100% (1)
- HOME LOAN HDFC AND SBiDocumento48 pagineHOME LOAN HDFC AND SBiLucky XeroxNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project SBI ProductDocumento56 pagineFinal Project SBI Productkunal hajareNessuna valutazione finora
- ICICI Bank StructureDocumento13 pagineICICI Bank StructureSonaldeep100% (1)
- Introduction of Banking IndustryDocumento15 pagineIntroduction of Banking IndustryArchana Mishra100% (1)
- Retail Banking Front Office Management Activity For HDFC Bank by Nisha Wadekar This Project Is Very Useful To StudentDocumento51 pagineRetail Banking Front Office Management Activity For HDFC Bank by Nisha Wadekar This Project Is Very Useful To Studentganeshkhale7052Nessuna valutazione finora
- Retail Banking Project BOIDocumento107 pagineRetail Banking Project BOIPooja Mathur100% (1)
- Bhavin kkkkkkkkk38Documento87 pagineBhavin kkkkkkkkk38Sandip ChovatiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento57 pagineProject Reportadi6187100% (1)
- Idbi Bank Project ReportDocumento49 pagineIdbi Bank Project ReportVinay Chawla0% (1)
- Comprative Analysis of Services Provided by HDFC and Axis BankDocumento58 pagineComprative Analysis of Services Provided by HDFC and Axis BankNitinAgnihotriNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On IDBI BankDocumento9 pagineReport On IDBI BankParth patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Icici Bank FileDocumento7 pagineIcici Bank Fileharman singhNessuna valutazione finora
- HDFC ProjectDocumento93 pagineHDFC ProjectDevdutt Raina100% (1)
- Organisational Setup and Management of The State Bank of IndiaDocumento6 pagineOrganisational Setup and Management of The State Bank of IndiapandisivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kotak Mahindra BanksDocumento73 pagineKotak Mahindra Banksanshu185100% (1)
- Union Bank of IndiaDocumento7 pagineUnion Bank of IndiamerlinjenniferNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report PNBDocumento60 pagineProject Report PNBa_blackeyed86% (21)
- Bank of Baroda HomeloanDocumento63 pagineBank of Baroda HomeloansantoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 1Documento14 pagineUntitled 1Tushar BhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Two BanksDocumento49 pagineComparison of Two BanksAarti50% (2)
- Comparative Study On Seavices of Public Sector and Private Sector Banks OptDocumento49 pagineComparative Study On Seavices of Public Sector and Private Sector Banks OptWashik Malik100% (1)
- Introduction:-: MeaningDocumento6 pagineIntroduction:-: MeaningDeepak YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonfund Banking BusinessDocumento95 pagineNonfund Banking BusinessAnkita GargNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 P's of Private Sector BankDocumento21 pagine7 P's of Private Sector BankMinal DalviNessuna valutazione finora
- Black BookDocumento104 pagineBlack BookSoni PalNessuna valutazione finora
- MBA Project Report On ICICI BankDocumento71 pagineMBA Project Report On ICICI BankCyberfun50% (2)
- Comparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksDocumento36 pagineComparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksjudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Executive Summary: SECTOR BANKS AND PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS" Aims To Analyze Various ServicesDocumento42 pagineExecutive Summary: SECTOR BANKS AND PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS" Aims To Analyze Various ServicesSidharth GeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Comparative Analysis of Private Sector Bank On Basis of Current Account, Saving Account & Fixed DepositDocumento14 pagineProject Report On Comparative Analysis of Private Sector Bank On Basis of Current Account, Saving Account & Fixed DepositJamar WebbNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Project Report On Commercial BankDocumento8 pagineA Study On Project Report On Commercial BankGAME SPOT TAMIZHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Services Offered by BankDocumento52 pagineFinancial Services Offered by BankIshan Vyas100% (2)
- Project On NPADocumento37 pagineProject On NPABasappaSarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Travel InsuranceDocumento81 pagineTravel InsuranceParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Mutual FundsDocumento75 pagineProject On Mutual FundsParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Rural InsuranceDocumento45 pagineRural InsuranceAmeySalaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Metlife InsuranceDocumento73 pagineMetlife InsuranceParag More100% (1)
- Recruitment Project On Life Insurance Co.Documento87 pagineRecruitment Project On Life Insurance Co.Devpratapsinh Bilkha100% (1)
- HRM in Banking (100 Marks Project)Documento62 pagineHRM in Banking (100 Marks Project)Shekhar Nm85% (13)
- Chapter 1: Corporate GovernanceDocumento60 pagineChapter 1: Corporate Governancesteffibiswas2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Swot Analysis in Bancassurance.Documento50 pagineSwot Analysis in Bancassurance.Parag More100% (2)
- Lucky 08bs0001551 Insurance Law ThesisDocumento29 pagineLucky 08bs0001551 Insurance Law Thesisluckyproject100% (2)
- CSR Project On InsuranceDocumento69 pagineCSR Project On Insurancedhwani0% (1)
- Micro Insurance ProjectDocumento56 pagineMicro Insurance ProjectParag More50% (4)
- Final Project On Health InsuranceDocumento61 pagineFinal Project On Health InsuranceYatriShah50% (14)
- Project On LICDocumento54 pagineProject On LICHament Singh71% (38)
- Aviavtion InsuranceDocumento75 pagineAviavtion InsuranceParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Merger Acquisition in BankingDocumento113 pagineRole of Merger Acquisition in BankingParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Blackbook Project On Consumer Perception About Life Insurance PoliciesDocumento80 pagineBlackbook Project On Consumer Perception About Life Insurance PoliciesMohit Kumar89% (28)
- Project On Claims Management in Life InsuranceDocumento60 pagineProject On Claims Management in Life Insurancepriya_1234563236986% (7)
- Cargo Insurance ProjectDocumento63 pagineCargo Insurance ProjectParag More100% (2)
- Impact of Fiscal Policy On Indian EconomyDocumento24 pagineImpact of Fiscal Policy On Indian EconomyAzhar Shokin75% (8)
- Comparative Study of Life InsuranceDocumento61 pagineComparative Study of Life InsuranceParinShah83% (6)
- Social Media in Banking - ProjectDocumento29 pagineSocial Media in Banking - ProjectHiraj KotianNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Banking Sector in IndiaDocumento75 pagineRole of Banking Sector in IndiaOna JacintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Moenetary and Fiscal Policies in Economic DevelopmentDocumento16 pagineRole of Moenetary and Fiscal Policies in Economic Developmentprof_akvchary85% (13)
- Role of Advertising in BankingDocumento49 pagineRole of Advertising in BankingParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate BankingDocumento100 pagineCorporate BankingParag MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Trends in BankingDocumento8 pagineRecent Trends in BankingAdalberto MacdonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Debt InstrumentsDocumento43 pagineDebt InstrumentsSiddhi Kadakia88% (16)
- Project On Indian Financial MarketDocumento44 pagineProject On Indian Financial MarketParag More85% (13)
- Corporate BankingDocumento122 pagineCorporate Bankingrohan2788Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Merchant BankingDocumento71 pagineProject On Merchant Bankingmandar_1381% (32)
- Teaching The Art of Market Making With A Game SimulationDocumento4 pagineTeaching The Art of Market Making With A Game SimulationRamkrishna LanjewarNessuna valutazione finora
- Shriram Life InsuranceDocumento78 pagineShriram Life InsuranceManoj N Jainani67% (12)
- Express Trust (Contract For Bailment)Documento2 pagineExpress Trust (Contract For Bailment)Michael Kovach100% (18)
- Class 12 Cbse Economics Sample Paper 2012-13Documento23 pagineClass 12 Cbse Economics Sample Paper 2012-13Sunaina RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Working Capital and Cash Flow ManagementDocumento13 pagineChapter 4 - Working Capital and Cash Flow ManagementAnna Mae SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Relevant CostingDocumento40 pagineRelevant CostingUtsav ChoudhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Assignment Tax RPGTDocumento19 pagineFull Assignment Tax RPGTVasant SriudomNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank - Economic Value AddDocumento3 pagineChaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank - Economic Value AddPhaniee Kumar VicharapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Legal Aspects of Business 3E PDFDocumento112 pagineLegal Aspects of Business 3E PDFsasikumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Branches of AccountingDocumento54 pagineBranches of AccountingAbby Rosales - Perez100% (1)
- Direct Tax AssignmentDocumento3 pagineDirect Tax AssignmentCHAITANYA ANNE100% (1)
- Aggregate Demand Aggregate SupplyDocumento32 pagineAggregate Demand Aggregate SupplySandesh Lokhande100% (1)
- Minor Project Report On Bajaj Automobiles IndiaDocumento55 pagineMinor Project Report On Bajaj Automobiles IndiaAmit Jain71% (7)
- QuestionsDocumento2 pagineQuestionsTeh Chu LeongNessuna valutazione finora
- ISJ005Documento99 pagineISJ0052imediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pet Kingdom IncDocumento20 paginePet Kingdom Incjessica67% (3)
- THFJ Europe 50 2011Documento15 pagineTHFJ Europe 50 2011nickmontNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Private Equity - Mrs Rupa Vora, IDFCDocumento17 paginePresentation On Private Equity - Mrs Rupa Vora, IDFCAnkit KesriNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Structures SummaryDocumento5 pagineBusiness Structures SummaryMrudula V.100% (2)
- Advacc 1001-1014Documento15 pagineAdvacc 1001-1014Camille SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Real Estate Development ProcessDocumento7 pagineThe Real Estate Development Processahmed100% (1)
- Audit ProgrammesDocumento11 pagineAudit ProgrammesSajjad CheemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wyoming Entrepreneur-Business Plan TemplateDocumento13 pagineWyoming Entrepreneur-Business Plan TemplateBrooke TillmanNessuna valutazione finora
- John Gokongwei Success StoryDocumento11 pagineJohn Gokongwei Success StoryGershNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Level StrategiesDocumento26 pagineCorporate Level StrategiesIrin I.gNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is GAAP?: Accounting PrinciplesDocumento3 pagineWhat Is GAAP?: Accounting PrinciplesShoaib YousufNessuna valutazione finora
- ATW108 Chapter 24 TutorialDocumento1 paginaATW108 Chapter 24 TutorialShuhada ShamsuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- TBNC 60th Anniversary Celebration JournalDocumento29 pagineTBNC 60th Anniversary Celebration JournaleetbncNessuna valutazione finora
- LLC Subscription AgreementDocumento3 pagineLLC Subscription Agreementnworkman100% (1)
- SAP ConsolidationDocumento110 pagineSAP Consolidationnanduri.aparna161Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingDa EverandThe Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (17)
- 2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNDa Everand2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursDa EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaDa EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisDa EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Da EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (32)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelDa Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionDa EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successDa EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (93)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialDa EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (32)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceDa EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (18)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursDa EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (34)
- The Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetDa EverandThe Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- The 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamwork Workbook: Embrace Them and Empower Your TeamDa EverandThe 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamwork Workbook: Embrace Them and Empower Your TeamNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessDa EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerDa EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistDa EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (73)
- Private Equity and Venture Capital in Europe: Markets, Techniques, and DealsDa EverandPrivate Equity and Venture Capital in Europe: Markets, Techniques, and DealsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanDa EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (79)
- Venture Deals: Be Smarter Than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistDa EverandVenture Deals: Be Smarter Than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (32)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceDa EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialDa EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityDa EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Da EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- The Synergy Solution: How Companies Win the Mergers and Acquisitions GameDa EverandThe Synergy Solution: How Companies Win the Mergers and Acquisitions GameNessuna valutazione finora