Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Faculty of Engineering
Caricato da
avinashavi93Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Faculty of Engineering
Caricato da
avinashavi93Copyright:
Formati disponibili
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Code No. 2216
B.E. 4/4 (EEE) I-Semester (Suppl) Examination, May 2013
Subject : Power System Operation and Control
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 75
Note: Answer all questions of Part - A and answer any five questions from Part-B.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
PART A (25 Marks)
List out the assumptions made in FDLF method.
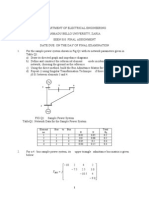
For the system show in figure 1 find Y-Bus?
(2)
(3)
The incremental fuel costs in Rs/MWh of two generating plants are given as (3)
dF1
dF2
0.008 P1 8;
0.012 P2 9
dP1
dP2
The system is operating on economic dispatch with P1=P2 =500 MW and
PL
0.2 .Find the penally factor of plant 2.
P2
Define the following terms :
(2)
(i) Incremental fuel rate (ii) Incremental efficiency
What is flat-frequency control? How is different from flat-tie line frequency
control?
(3)
How PV buses are handled in G-s method?
(2)
Define :
(2)
(i) Steady state stability
(ii) Transient stability
A 50 Hz, four pole turbo generator rated 100 MVA, 11KV has an inertia
constant of 10 MJ/MVA. Find the stored energy in the rotor at synchronous
speed.
(2)
Explain the AVR with neat diagram.
(3)
Draw and explain the operation of STATCOM.
(3)
PART B (5x10=50 Marks)
11.(a) List the various data required for the formulation of a load flow problem and
hence formulated voltage equations for a general 'n' bus power system. (3)
(b) For the system shown in figure 2 use Gauss-Seidel method and obtain
voltages buses (2) and (3) at the end of the first iteration?
(7)
The line impedances marked in the figure are in p.u.
Bus No
1
2
3
Voltage
Reactive power limit Remarks
|V|
P
Q
Qmin
Qmax
1.0
slack
1.1
0
5.32
PV
3.64 0.53
PQ
Generation Load
P
5.32
-
Q
-
..2
Code No. 2216
..2..
12.(a) Derive the necessary condition for economic operation of n-plants considering
transmission losses.
(5)
(b) The incremental fuel costs of two units are
dC1
0.1P1 22 ; 20 P1 100 Mw
dP1
dC2
0.12 P2 16 ; 20 P2 100 Mw
dP2
Determine the economic load allocation between the units when the total
load on the system is
160 Mw. C is in Rs/hr and P is in MW.
(5)
13.(a) What is single area system? Deduce dynamic models for a single area
system. Show the full block diagram.
(6)
(b) Two generators rated 200 MW and 400 MW are operated in parallel.
The drop characteristics of their generators are 4% and 5 % respectively
from no load to full load. Determine the load shared by each unit for a load
of 500 MW.
(4)
14.(a) Using equal area criterion, derive an expression for critical clearing angle
for a system having a generator feeding a large system through double
circuit line.
(4)
(b) For the system show in figure 3, the generator has a rating of 50 MVA
and H=2.7 MJ/MVA at rated speed.
E=1.05, V=1, X1d=0.2, X1=X2=0.4 pu. The generator is supplying 50 MW
to the infinite bus when a 3-phase fault occurs at the middle of the line 2.
Plot the swing curve for a sustained fault upto a time of 0.5 sec t = 0.05 sec.
Figure 3
15.(a) Explain the reactive power generation by synchronous generators.
(b) What are the basic FACTS controllers and with neat diagram explain the
working of UPFC?
(6)
(5)
(5)
16.(a) Distinguish between rotor angle stability and voltage stability.
(4)
(b) A 3-phase over head transmission line in which voltages at both ends are
kept fixed at 66 kV has a negligible resistance and an inductive reactance
of 20 ohms / conductor. What is the maximum power that could be transmitted
over this line. If this line when working at 60% of the above steady state limit
suffers a short circuit which is cleared soon after and circuit restored.
What are the limits of angular oscillations for transient stability ?
(6)
17.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Tie line bias control
(b) Advantages and disadvantages of series compensation
(c) Dynamic response of single area system
*****
(3)
(3)
(4)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ee2404 Set1Documento121 pagineEe2404 Set1Sachin Samy0% (1)
- 209 Power System - 3Documento4 pagine209 Power System - 3sukirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Operation ControlDocumento4 paginePower System Operation Controlvidya_vihar666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab WorkDocumento22 pagineLab WorkTamil SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Merged DocumentDocumento25 pagineMerged DocumentAshokAbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocumento7 pagineComputer Methods in Power SystemssuhrudkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of EngineeringDocumento2 pagineFaculty of EngineeringAvĩńăśĥBůņņÿNessuna valutazione finora
- Eeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Documento5 pagineEeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Kabir MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- R5410204-Power System Operation and ControlDocumento4 pagineR5410204-Power System Operation and ControlShakthi BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- X10407EE8702 WatermarkDocumento4 pagineX10407EE8702 WatermarkP.Barani Tharan -EEENessuna valutazione finora
- PSOC Model II - Set1Documento2 paginePSOC Model II - Set1Mario BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDocumento2 pagineInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksAmit PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008Documento8 pagine2008Medha AravindNessuna valutazione finora
- PSOC Model II - Set3Documento2 paginePSOC Model II - Set3Vidhya Priya SenthilNessuna valutazione finora
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDa EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNessuna valutazione finora
- QP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocDocumento8 pagineQP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocMohammed AlhakeemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoc 2015 NewDocumento20 paginePsoc 2015 Newvenki249Nessuna valutazione finora
- PSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFDocumento10 paginePSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFsagar R Rao0% (1)
- Psa Solved May 2019Documento18 paginePsa Solved May 2019Bestowal Infotechs 2018Nessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC4612 - Power System Analysis Tutorial 2 Power FlowDocumento2 pagineELEC4612 - Power System Analysis Tutorial 2 Power FlowDeepak BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee4173 - Power System Operation & ControlDocumento7 pagineBee4173 - Power System Operation & Controlsemuty92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical MeachinesDocumento4 pagineElectrical MeachinesMohamed RiyaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter Connected Power System - CombinedDocumento11 pagineInter Connected Power System - CombinedPalak AriwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1792Documento7 pagine1792Mohd AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 1401 - PsocDocumento7 pagineEe 1401 - PsocRameez FaroukNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoc Grand Test-1 QPDocumento2 paginePsoc Grand Test-1 QPsatish reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- PSOC Model II - Set2Documento2 paginePSOC Model II - Set2Vidhya Priya SenthilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlDocumento8 pagineNr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- PSOC Assignment2015-2016 StudentsDocumento2 paginePSOC Assignment2015-2016 StudentsVijaya Aditya TadepalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System AnalysisDocumento5 paginePower System AnalysisVidyavihar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electrical Past PaperDocumento5 paginePower Electrical Past PaperNadeesha BandaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolDocumento8 pagine07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolSamiullah MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- C F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksDocumento3 pagineC F1055 Pages: 3: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksPranav R KrishNessuna valutazione finora
- PsocqpDocumento3 paginePsocqpNadeem KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CIA Test 2 Psoc 2013Documento2 pagineCIA Test 2 Psoc 2013Anbalagan GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Power SystemsDocumento92 paginePower SystemsJhon CenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester I Examinations - 2011/2012Documento7 pagineSemester I Examinations - 2011/2012Ismail HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- 07-01-2022 - EEE3100S 2022 November EXAM - 2Documento6 pagine07-01-2022 - EEE3100S 2022 November EXAM - 2Stalin KosterNessuna valutazione finora
- 171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFDocumento3 pagine171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFPalak AriwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Control of AC / DC Power Networks: System of Systems Approach Based on Spatio-temporal ScalesDa EverandAdvanced Control of AC / DC Power Networks: System of Systems Approach Based on Spatio-temporal ScalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Operation and ControlDocumento9 paginePower System Operation and ControlNogdalla ShareefNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankDocumento3 pagine2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankJeril joseNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee Iii Year 2017-2018Documento48 pagineEee Iii Year 2017-2018J JulietNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Documento14 pagineUnit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Ragul RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Documento11 pagineEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- Power System Analysis ImportantDocumento8 paginePower System Analysis Importantsparkle courageNessuna valutazione finora
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDocumento4 paginePSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemestermahesNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsDocumento5 pagineFaculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsLibraryNessuna valutazione finora
- PSADocumento25 paginePSAramyadspNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System AnalysisDocumento23 paginePower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Final3423 Sem1sesi0708Documento4 pagineFinal3423 Sem1sesi0708Khairunnas FirdousNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee306 ADocumento3 pagineEe306 AAparna JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- CapsaDocumento4 pagineCapsasumikannuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignments PSOCDocumento4 pagineAssignments PSOCRajat Rai100% (2)
- Btech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Documento2 pagineBtech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Raj KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- 117 GQ 052018Documento3 pagine117 GQ 052018Bala Raju ReddyboyaNessuna valutazione finora
- European Journal of Electrical Engineering: Received: 10 March 2020 Accepted: 6 May 2020Documento9 pagineEuropean Journal of Electrical Engineering: Received: 10 March 2020 Accepted: 6 May 2020farid kerroucheNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocumento4 pagine9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersDa EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorDa EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNessuna valutazione finora
- Start of Byte Win SHP Pla For Qin TNL Venue End of Byte Total Number of BytesDocumento4 pagineStart of Byte Win SHP Pla For Qin TNL Venue End of Byte Total Number of Bytesavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- #Character Guy DarshiDocumento25 pagine#Character Guy Darshiavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Astral Script 231218 PDFDocumento19 pagineAstral Script 231218 PDFavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard TemplateDocumento22 pagineA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Templateavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative Theory NotesDocumento7 pagineNarrative Theory Notesavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFDocumento1 paginaA4 Landscape 6 Storyboard Template PDFavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Development and Under Development ............................................... 27Documento16 pagineEconomic Development and Under Development ............................................... 27avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-5 Control InstructionDocumento7 pagineChapter-5 Control Instructionavinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nod32 9 & 8 Serial License Keys Username and Password Eset Antivirus Ess Activation - SSECDocumento2 pagineNod32 9 & 8 Serial License Keys Username and Password Eset Antivirus Ess Activation - SSECavinashavi9322% (9)
- Medha Spoken English Material PDF FreeDocumento2 pagineMedha Spoken English Material PDF Freeavinashavi9370% (20)
- Chapter-13 Dynamic Memory Allocation (DMA)Documento5 pagineChapter-13 Dynamic Memory Allocation (DMA)avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11Documento7 pagine11avinashavi93Nessuna valutazione finora
- E Installation of BatteryDocumento16 pagineE Installation of BatteryPrashant KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook (P)Documento224 pagineHandbook (P)Joe80% (5)
- Tas 5731Documento60 pagineTas 5731charly36Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Experiment 3 Test For CarbohydratesDocumento9 pagineLaboratory Experiment 3 Test For CarbohydratesRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNessuna valutazione finora
- Barium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsDocumento3 pagineBarium Chloride 2h2o LRG MsdsAnas GiselNessuna valutazione finora
- Ground PlaneDocumento1 paginaGround Planeaeronautical rajasNessuna valutazione finora
- Neoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaDocumento26 pagineNeoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaErwin SuryanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Syllabus Class 7 1Documento3 pagineAnnual Syllabus Class 7 1Ni shNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDFDocumento6 pagineEe115hw+sol03 06 N PDFthinkberry22100% (1)
- NCP DehydrationDocumento4 pagineNCP DehydrationYnah Sayoc100% (2)
- Cad, CamDocumento16 pagineCad, CamRakhi Mol BVNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4: Palm Oil and Oleochemical Industries.: Presented By: Lovelyna Eva Nur Aniqah Siti MaryamDocumento15 pagineChapter 4: Palm Oil and Oleochemical Industries.: Presented By: Lovelyna Eva Nur Aniqah Siti MaryamdaabgchiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.PsychoCrash Social Psy-1Documento62 pagine2.PsychoCrash Social Psy-1Gopika Sureshnv0% (1)
- Mold Maintenance StepDocumento0 pagineMold Maintenance StepMonica JoynerNessuna valutazione finora
- RocketsDocumento2 pagineRocketsAlin VoicuNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental and Sustainability Issues - 1Documento21 pagineEnvironmental and Sustainability Issues - 121. PLT PAGALILAUAN, EDITHA MNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohd Mopti Bin Yassin V Lembaga Kemajuan Perusahaan Pertanian Negeri Pahang (LKPP) Corp SDN BHD & AnorDocumento12 pagineMohd Mopti Bin Yassin V Lembaga Kemajuan Perusahaan Pertanian Negeri Pahang (LKPP) Corp SDN BHD & AnorA random humanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Redesigning of Junction: Tatya Tope Square BhopalDocumento15 pagineThe Redesigning of Junction: Tatya Tope Square BhopalAr Raj YamgarNessuna valutazione finora
- EV Connect What Is EVSE White PaperDocumento13 pagineEV Connect What Is EVSE White PaperEV ConnectNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruger MKIIDocumento1 paginaRuger MKIIMike Pape100% (1)
- CA InsideDocumento1 paginaCA InsideariasnomercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Danh M C AHTN 2017 - HS Code 2017 PDFDocumento564 pagineDanh M C AHTN 2017 - HS Code 2017 PDFBao Ngoc Nguyen100% (1)
- 9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaDocumento2 pagine9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaAfrina FaziraNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of The IEEE Color BooksDocumento6 pagineAn Overview of The IEEE Color BooksOhm666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asutphin Client Assessment Matrix Fitt Pros Unit 8Documento4 pagineAsutphin Client Assessment Matrix Fitt Pros Unit 8api-307235123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Truong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CDocumento6 pagineTruong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CTrương Quang TườngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunfix Blue SPRDocumento7 pagineSunfix Blue SPRDyeing 2 Wintex100% (2)
- Emerging Therapeutic Options in The Management of Diabetes Recent Trends, Challenges and Future DirectionsDocumento21 pagineEmerging Therapeutic Options in The Management of Diabetes Recent Trends, Challenges and Future DirectionsGabriela PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoDocumento7 pagine6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoBaldev SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffers Notes1Documento3 pagineBuffers Notes1Lara MonevaNessuna valutazione finora