Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Genetics Study Guide
Caricato da
gmanb5Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Genetics Study Guide
Caricato da
gmanb5Copyright:
Formati disponibili
8th Grade Living Environment
Ardito/Sweeney
Study Guide -- Genetics
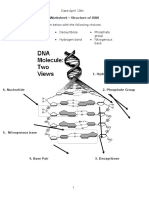
Structure of DNA
DNA has 3 parts:
Phosphate
Sugar - Deoxyribose
Nitrogenous bases
We picture it like this:
phosphate
sugar nitrogenous
base
This group of the parts of DNA is called a nucleotide.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA.
There are four nitrogenous bases
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
One molecule of DNA contains about 3 billion of these bases.
These nitrogenous bases follow certain rules about how to pair up
Adenine always pairs up with Thymine
Guanine always pairs up with Cytosine
Genes are segments of a chromosome that contain the recipe for a specific trait. Genes
are found on all 46 human chromosomes. These recipes are for the proteins that cause
that specific trait.
Genetics Study Guide, Page 1 of 4
DNA Replication
Right before cell division, the chromosomes in the cell make copies of themselves. This
is called DNA Replication.
This process follows the following steps:
The goal of this project is to make a perfect copy of the cellʼs DNA.
DNA Versus RNA
DNA RNA
3 basic parts: 3 basic parts:
Sugar - Deoxyribose Sugar - Ribose
Phosphate Phosphate
Nitrogenous Bases Nitrogenous Bases
4 nitrogenous bases: 4 nitrogenous bases:
adenine adenine
thymine uracil
guanine guanine
cytosine cytosine
Double Stranded Single Stranded
One type Two types:
mRNA - carries the DNA message to the ribosome
tRNA -
3 Billion bases long mRNA - Many bases long
tRNA - 3 bases long
Genetics Study Guide, Page 2 of 4
Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis is the process where the genetic code is translated in order to make
the proteins necessary for a specific trait or function.
The process follows the following steps:
Genetics Study Guide, Page 3 of 4
Mutations
Mutations are any change to the genetic code.
The change in the genetic code will lead to a different protein being made.
There are three types of mutations we have learned about:
Insertions - a base gets added to the genetic code
Deletions - a base gets removed from the genetic code
Substitutions - one base gets swapped for another base
Mutations can be helpful or harmful.
Mutations can be caused by a few things. These are called mutagenic agents.
The most common one is radiation.
Radiation changes the structure of the DNA. And this change in structure changes the
genetic code.
Mutations can also happen spontaneously.
Genetic Engineering
Genetic Engineering is the process by which the genetic code can be intentionally
changed.
It is accomplished by taking the section of desired DNA and adding it to the DNA of a
bacterium. Then, the modified bacteria are let loose in the person, which would result in
the new DNA being incorporated into the old DNA.
Genetics Study Guide, Page 4 of 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 2 Mendelian InheritDocumento12 pagineChapter 2 Mendelian InheritDiego Garcia67% (3)
- Chemmatters Oct2013 TGDocumento153 pagineChemmatters Oct2013 TGAwkward Jaden (The Paranoid Hammer Bro)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mendelian Genetics Assignment InstructionsDocumento13 pagineMendelian Genetics Assignment InstructionspavNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Ch. 11 Use This OneDocumento66 pagineBiology Ch. 11 Use This Oneمعروف عاجلNessuna valutazione finora
- Phylogenetic Trees Click Learn WorksheetDocumento4 paginePhylogenetic Trees Click Learn Worksheetfcm31450% (1)
- Punnett Square Test ADocumento3 paginePunnett Square Test Ao969059Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextDa EverandThe Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextNessuna valutazione finora
- Module: Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento30 pagineModule: Cell Structure and FunctionJohn Daniel Paulino GumbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Purines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides and the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsDa EverandPurines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides and the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SDocumento6 pagine18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SkriishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemmatters Oct2013 TGDocumento154 pagineChemmatters Oct2013 TGWesker HazardNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromosome Number Worksheet Meiosis MitosisDocumento3 pagineChromosome Number Worksheet Meiosis MitosisDaisy GamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDocumento16 pagineCell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDJ ISAACSNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Staar Eoc Review Study GuideDocumento67 pagineBiology Staar Eoc Review Study Guideapi-233187566100% (1)
- Genetics SyllabusDocumento7 pagineGenetics SyllabusAnonymous q6VpovV6pTNessuna valutazione finora
- Preclass Quiz 8 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFDocumento3 paginePreclass Quiz 8 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFElizabeth DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocumento5 pagineDNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheeteula faith miracle andam100% (1)
- Biology Genetics Study GuideDocumento5 pagineBiology Genetics Study GuideAlexa PearsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics - Evolution Web QuestDocumento7 pagineGenetics - Evolution Web Questapi-262283249Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Mendilan and Genetics Study GuideDocumento16 pagineChapter 10 Mendilan and Genetics Study GuideKing AllanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemmatters April2010 Bioplastics PDFDocumento3 pagineChemmatters April2010 Bioplastics PDFMarilyn Mishell GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Digestive SystemDocumento38 pagineThe Digestive SystemrabiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDocumento14 pagineCharacteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDr-Qussai ZuriegatNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells: Unit 2: Subject Standards/Content and OST AlignmentDocumento31 pagineCells: Unit 2: Subject Standards/Content and OST AlignmentTheUniverseIsATotinoPizzaRollNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter05. Ionic BondDocumento5 pagineChapter05. Ionic BondKelso ZwariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.7 Cell TransportDocumento6 pagine5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS MODULE OVERVIEW 2012Documento29 pagineDNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS MODULE OVERVIEW 2012Desiree CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemmatters Dec2013 Pepper PDFDocumento3 pagineChemmatters Dec2013 Pepper PDFAkhirul Kahfi SyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Documento16 pagineGenetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Examview - 8th Grade Science Benchmark YearlyDocumento9 pagineExamview - 8th Grade Science Benchmark Yearlyapi-232424041Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mrs. O'Hare's Motion WebquestDocumento2 pagineMrs. O'Hare's Motion WebquestMrs. Marsha O'Hare20% (5)
- Genetics Unit OutlineDocumento44 pagineGenetics Unit Outlineapi-28375664050% (2)
- CH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021Documento4 pagineCH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021EmileMcBrokeNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics) SyllabusDocumento33 pagineGenetics) Syllabusb.duttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19 Practice Multiple ChoiceDocumento8 pagineChapter 19 Practice Multiple Choicekiden300% (1)
- Nova Evolution Lab WorksheetsDocumento27 pagineNova Evolution Lab Worksheetsapi-29620399520% (5)
- Kaufman’s Atlas of Mouse Development Supplement: With Coronal SectionsDa EverandKaufman’s Atlas of Mouse Development Supplement: With Coronal SectionsRichard BaldockNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Stop-Motion Animation DirectionsDocumento4 pagineMitosis Stop-Motion Animation DirectionsnateNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Eoc Review PacketDocumento29 pagineBio Eoc Review Packetapi-267855902Nessuna valutazione finora
- Monoclonal Antibodies Against Bacteria: Volume IIIDa EverandMonoclonal Antibodies Against Bacteria: Volume IIIAlberto J. L. MacarioNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and FunctionDocumento2 pagineDNA Structure and FunctionAliza SaddalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsDa EverandCellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsCharles G. CochraneNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology I Eoc Review BookDocumento22 pagineBiology I Eoc Review Bookapi-199871042Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Teacher V.Documento3 pagineDNA Teacher V.Angela Joan YedersbergerNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioisotope and Radiation Physics: An IntroductionDa EverandRadioisotope and Radiation Physics: An IntroductionNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Lab-04Documento20 pagineAP Biology Lab-04ldlewis0% (3)
- Anterior Posterior Axis Patterning in DrosophilaDocumento4 pagineAnterior Posterior Axis Patterning in DrosophilaSuresh Babu TNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFDocumento9 pagine2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFMelisa Anne CanilangNessuna valutazione finora
- Phylogenetic Tree Creation Morphological and Molecular Methods For 07-JohnsonDocumento35 paginePhylogenetic Tree Creation Morphological and Molecular Methods For 07-JohnsonCHRISTEROP100% (2)
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocumento21 pagineBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Crest Cells: Evolution, Development and DiseaseDa EverandNeural Crest Cells: Evolution, Development and DiseasePaul TrainorNessuna valutazione finora
- Science behind Non-specific Science: (For Molecular Biologist & Biotechnologist)Da EverandScience behind Non-specific Science: (For Molecular Biologist & Biotechnologist)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flight 143Documento5 pagineFlight 143blackwellbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide HomeostasisDocumento5 pagineStudy Guide Homeostasisgmanb5100% (1)
- Biochemistry Notes-Study GuideDocumento3 pagineBiochemistry Notes-Study Guidegmanb5100% (2)
- Change in PopulationDocumento5 pagineChange in Populationgmanb5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution Study GuideDocumento7 pagineEvolution Study Guidegmanb5100% (3)
- Biology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFDocumento156 pagineBiology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFAnonymous tdtTl8KypNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Material - Dna and RnaDocumento32 pagineGenetic Material - Dna and Rnaapi-217439283Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dna - CotDocumento39 pagineDna - CotJcob BangcayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Garcia - Organic Chemistry and BiochemistryDocumento18 pagineGarcia - Organic Chemistry and BiochemistryPrince SanjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Assignment 2Documento12 pagineDna Assignment 2api-253560385100% (1)
- Human Biology 16th Mader Test Bank PDFDocumento28 pagineHuman Biology 16th Mader Test Bank PDFkuldeep sainiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Quarter 1 Module 6-STRUCTURE-OF-DNADocumento21 pagine6 Quarter 1 Module 6-STRUCTURE-OF-DNAMah Jane Divina100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Module FINALSDocumento12 pagineGeneral Biology 1 Module FINALSChristine Joyce Toledo VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento7 pagineLab ReportJade PategaNessuna valutazione finora
- EK Biology 1 - MoleculesDocumento196 pagineEK Biology 1 - MoleculesNabeel Shahzad90% (29)
- Model Question Paper of Science Xii of Bihar State BoardDocumento168 pagineModel Question Paper of Science Xii of Bihar State BoardAkshay PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Model Parts For Your PresentationDocumento15 pagineDna Model Parts For Your Presentationwa laNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1Documento2 pagineBiology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1api-338578874100% (1)
- Student Exploration Building DNADocumento5 pagineStudent Exploration Building DNASidemen For Life32% (38)
- Biochemistry Book 2Documento119 pagineBiochemistry Book 2Jugnu JugnuNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineDNA Lesson PlanCess Nazarita0% (3)
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocumento4 pagineModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanNessuna valutazione finora
- A LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Documento5 pagineA LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Lexi MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA StructueDocumento74 pagineDNA StructueNeha VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules NotesDocumento11 pagineBiomolecules NotesAyush jaatNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Science Dna Keychains LPDocumento31 pagineLife Science Dna Keychains LPapi-291740178Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration Building DNADocumento5 pagineStudent Exploration Building DNASidemen For Life0% (1)
- 04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocumento51 pagine04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic Acidsrahul singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation and Characterization of Onion's DNADocumento5 pagineIsolation and Characterization of Onion's DNAGab Fondevilla100% (9)
- Lesson Plan FinalDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan Finalapi-242797673Nessuna valutazione finora
- Toxicología Ambiental - Evaluación de Riesgos y Restauración AmbientalDocumento204 pagineToxicología Ambiental - Evaluación de Riesgos y Restauración Ambientalvictor manuel villegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Research in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Documento27 pagineResearch in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Kim GoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat Practice Test 1 AnswersDocumento45 pagineSat Practice Test 1 Answersichikkala100% (1)
- Building DnaDocumento3 pagineBuilding DnaCam0% (1)
- 12 2 PWPT PDFDocumento24 pagine12 2 PWPT PDFapi-262378640Nessuna valutazione finora