Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Terminology of HVAC Terms
Caricato da
Naresh Sewdin0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
41 visualizzazioni2 pagineHVAC refers to heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at that temperature. Dewpoint is the temperature at which water vapor condenses into liquid water droplets. Infiltration is the unintentional introduction of outside air into a building through cracks or doors, and the air exchange rate is the number of air changes per hour inside the building. Sensible heat changes the temperature but not other properties like volume or pressure, while latent heat absorbs or releases energy during a constant-temperature process like condensation or evaporation. A psychrometric chart graphs the thermal properties of moist air, and dehumidification removes moisture
Descrizione originale:
It provides basic information about terms used in HVAC system
Titolo originale
Terminology of HVAC terms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHVAC refers to heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at that temperature. Dewpoint is the temperature at which water vapor condenses into liquid water droplets. Infiltration is the unintentional introduction of outside air into a building through cracks or doors, and the air exchange rate is the number of air changes per hour inside the building. Sensible heat changes the temperature but not other properties like volume or pressure, while latent heat absorbs or releases energy during a constant-temperature process like condensation or evaporation. A psychrometric chart graphs the thermal properties of moist air, and dehumidification removes moisture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
41 visualizzazioni2 pagineTerminology of HVAC Terms
Caricato da
Naresh SewdinHVAC refers to heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at that temperature. Dewpoint is the temperature at which water vapor condenses into liquid water droplets. Infiltration is the unintentional introduction of outside air into a building through cracks or doors, and the air exchange rate is the number of air changes per hour inside the building. Sensible heat changes the temperature but not other properties like volume or pressure, while latent heat absorbs or releases energy during a constant-temperature process like condensation or evaporation. A psychrometric chart graphs the thermal properties of moist air, and dehumidification removes moisture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Terminology
HVAC: Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
Humidity is expressed in absolute terms, i.e. moisture content which is the mass of
water vapour per unit mass of dry air or vapour pressure.
Relative humidity is defined as the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air at a
temperature to the amount of moisture in the saturated air at the same
temperature. It is also defined as the ratio of partial pressure of water vapour in
moist air at a given temperature to the partial pressure of saturated water vapour in
air at the same temperature.
Dewpoint is the temperature below which water vapour condenses to form liquid
water drops when cooled at constant pressure. It is also defined as the temperature
air would have to be cooled for saturation to occur.
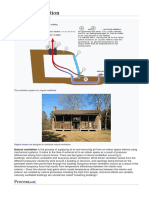
Infiltration is the unintentional or accidental introduction of outside air into a
building, typically through cracks in the building envelope and through use of doors
for passage. Infiltration is sometimes called air leakage. The infiltration rate is the
volumetric flow rate of outside air into a building, typically in cubic feet per minute
(CFM) or liters per second (LPS). The air exchange rate, (I), is the number of interior
volume air changes that occur per hour, and has units of 1/h. The air exchange rate
is also known as air changes per hour (ACHs).
Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system that
changes the temperature, and some macroscopic variables of the body, but leaves
unchanged certain other macroscopic variables, such as volume or pressure.
Latent heat is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic
system, during a constant-temperature process. Latent heat however, does not
affect the temperature of a substance. Latent capacity is the capacity to remove the
moisture from the air.
Sensible heat ratio is the ratio of the sensible heat to the total heat where the
total heat is the sum of the sensible and latent heat.
The cooling load is the amount of heat energy that would need to be removed
from a space (cooling) to maintain the temperature in an acceptable range. It is the
sum of the sensible and latent cooling loads.
Condensation is the most common form of dampness in buildings. This occurs
when liquid water drops out of the air. The temperature at which condensation
begins is the dewpoint temperature (i.e. when the relative humidity reaches 100%).
Surface condensation is condensation which occurs on the visible surfaces of a
construction, rather than between the layers. Internal surface condensation can
promote mould growth, thus reducing indoor air quality, as well as creating
unsightly pattern staining
Interstitial condensation is condensation which occurs between layers of the
construction, i.e. inside the roof, wall or floor elements. Interstitial condensation
can cause deterioration or even failure of the components of the assembly,
potentially shortening their useful lifespan
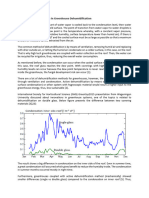
A psychrometric chart is a graph of the thermodynamic parameters of moist air
at a constant pressure, often equated to an elevation relative to sea level. A
psychrometric chart presents physical and thermal properties of moist air in a
graphical form.
Dehumidication is the process in which the moisture or water vapour or the
humidity is removed from the air keeping its dry bulb (DB) temperature constant.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemDa EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface and Interstitial CondensationDocumento3 pagineSurface and Interstitial CondensationAmirulAzahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture1 HumidifictionDocumento20 pagineLecture1 HumidifictionmjunaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionDa EverandWeather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative Humidity (RH) : Fungi (Mould) and BacteriaDocumento3 pagineRelative Humidity (RH) : Fungi (Mould) and BacteriaHARSH VARDHAN SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- CONDensation and Moisture SummaryDocumento1 paginaCONDensation and Moisture SummaryLidetNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Ventilation: ProcessDocumento5 pagineNatural Ventilation: ProcessLupuNicusorNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1 ADocumento24 pagineLec 1 Ashah muhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Conditioning Processes Illustrated On A Psychrometric ChartDocumento2 pagineAir Conditioning Processes Illustrated On A Psychrometric Chartvv260513Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topics To Be Covered This TermDocumento23 pagineTopics To Be Covered This TermZain Ul AbideenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 Hvac IntroDocumento27 pagineLecture 3 Hvac Intromanu guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensation 1Documento8 pagineCondensation 1Fasil ENessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 2 (Precipitation)Documento51 pagineHydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 2 (Precipitation)joelkyeswa97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dry Bulb Temperature - TDocumento3 pagineDry Bulb Temperature - TAlFred NeñuraNessuna valutazione finora
- AIR CON Diti ONI NGDocumento25 pagineAIR CON Diti ONI NGTOBIN THOMAS MENessuna valutazione finora
- VENTILATIONDocumento16 pagineVENTILATIONMwine Isaac NormanNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Evaporative CoolerDocumento12 pagineProject Report On Evaporative Coolersourabh singh tomerNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensation - The Basics PDFDocumento5 pagineCondensation - The Basics PDFvadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Humidity HandoutsDocumento3 pagineHumidity HandoutsAlFred NeñuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaporation and Condensation Geography Notes For UPSCDocumento1 paginaEvaporation and Condensation Geography Notes For UPSCENGINEER SHAHID LODhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Climatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFDocumento13 pagineClimatology PPT 3-Day Lighting and Natural Ventilation PDFMushthaq MahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- 4A - Condensation - (Updated, 08-11-2020)Documento29 pagine4A - Condensation - (Updated, 08-11-2020)Zhori DuberryNessuna valutazione finora
- Humidity: - Humidity (Psychrometric) Charts and Their Use - Terminology - Psychrometric Chart - ApplicationsDocumento30 pagineHumidity: - Humidity (Psychrometric) Charts and Their Use - Terminology - Psychrometric Chart - ApplicationsGlory UsoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyDocumento12 pagineFundamental Questions:: Heat, The Ultimate Form of EnergyMohd HaniffNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By: Aishwarya Deopujari Prerana Das Nishtha Duggal Vasundhra Singh SrideviDocumento110 paginePresented By: Aishwarya Deopujari Prerana Das Nishtha Duggal Vasundhra Singh Sridevikothat82Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: UNIT-5 Dr. Devendra Kumar PatelDocumento20 pagineThe Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: UNIT-5 Dr. Devendra Kumar Patelteja100% (1)
- Unit 5.3 DryingDocumento71 pagineUnit 5.3 DryingMutale InongeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventilation (Architecture) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento8 pagineVentilation (Architecture) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediagnitinNessuna valutazione finora
- HumidityDocumento9 pagineHumidityRay Lorenz OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Evaporative Cooling System: Course ContentsDocumento0 paginePrinciples of Evaporative Cooling System: Course ContentsSalley BukhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Copy 2Documento20 pagineChapter 4 - Copy 2ch4nt333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Condensation On Double Glazing RoofDocumento2 pagineCondensation On Double Glazing RoofDon GivsyitNessuna valutazione finora
- REGIO HVAC-Quiz1Documento3 pagineREGIO HVAC-Quiz1Clim RegioNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychrometrics Short NotesDocumento6 paginePsychrometrics Short NotesMustafa FalihNessuna valutazione finora
- VentilationDocumento9 pagineVentilationSangeet PunNessuna valutazione finora
- Humidity ControlDocumento16 pagineHumidity ControlHanan SFNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Need For Air CoolingDocumento10 pagine1.1 Need For Air CoolingSONUNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative HumidityDocumento6 pagineRelative HumidityresultbhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of HumidityDocumento1 paginaTypes of HumidityIqubal Hussain100% (1)
- Natural Ventilation: by Andy WalkerDocumento9 pagineNatural Ventilation: by Andy WalkerSurya SundarNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Conditioning Principles and ConceptsDocumento64 pagineAir Conditioning Principles and ConceptsILYAS AHMED100% (1)
- Sublimation Is The Process of Transformation Directly From The Solid Phase To The Gas PhaseDocumento3 pagineSublimation Is The Process of Transformation Directly From The Solid Phase To The Gas PhaseChristian SoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento18 pagineModule 3Dheeshna DileepNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural VentilationDocumento3 pagineNatural VentilationGeeryl Tayone100% (1)
- Report On Dehumidification: Haldia Institute of TechnologyDocumento18 pagineReport On Dehumidification: Haldia Institute of Technologyindrajit majumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Conditioning-Principles and ConceptsDocumento64 pagineAir Conditioning-Principles and ConceptsAbhishek Venkitaraman Iyer98% (40)
- Natural Ventilation - Whole Building Design GuideDocumento8 pagineNatural Ventilation - Whole Building Design Guidedhwani.talati5920Nessuna valutazione finora
- Psych Rome TricsDocumento46 paginePsych Rome TricsDenitta D'RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Ventilation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento7 pagineNatural Ventilation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediadasaNessuna valutazione finora
- AIR CHEMISTRY and HVAC TypesDocumento6 pagineAIR CHEMISTRY and HVAC Typeskesavaganesan58Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module Ii. Measurement of HumidityDocumento20 pagineModule Ii. Measurement of HumidityDryx LetranNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effects of Weather Onto Glazing and Their Influence Part IIIDocumento4 pagineThe Effects of Weather Onto Glazing and Their Influence Part IIICAMELIA Neagu-COGALNICEANUNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor of Engineering Technology in A C & I R: FCD 20603 (Heating and Cooling Load) TitleDocumento7 pagineBachelor of Engineering Technology in A C & I R: FCD 20603 (Heating and Cooling Load) TitleYuzzyne ZainolNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric Lapse RateDocumento8 pagineAtmospheric Lapse RateWajid HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychometrics Nonequilibrium Properties of AirDocumento5 paginePsychometrics Nonequilibrium Properties of AirRicardo BecNessuna valutazione finora
- Airconditioning ReviewerDocumento6 pagineAirconditioning ReviewerMikaela Grace OrenseNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGI 273 Lec 5Documento48 pagineENGI 273 Lec 5Haidy T. SakrNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Moon Calendar-Cosmic RevolutionDocumento47 pagine2021 Moon Calendar-Cosmic RevolutionYahira NoeliNessuna valutazione finora
- Deposition and Characterization of Copper Oxide Thin FilmsDocumento5 pagineDeposition and Characterization of Copper Oxide Thin FilmsmirelamanteamirelaNessuna valutazione finora
- WikipediaDocumento1 paginaWikipediaKarthik GundaNessuna valutazione finora
- TimeseriesprojectDocumento33 pagineTimeseriesprojectapi-497291597Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Week 10 Topic 9Documento14 pagineTutorial Week 10 Topic 9patricia93limNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic EquilibriumDocumento22 pagineIonic EquilibriumbeherasubhammikunNessuna valutazione finora
- Voriconazole Film-Coated Tablets: To Split Them or Not?: Zahra Sahraei, Saghar BaratiDocumento2 pagineVoriconazole Film-Coated Tablets: To Split Them or Not?: Zahra Sahraei, Saghar BaratinickeycoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture-1: Course Plan / OutlineDocumento3 pagineLecture-1: Course Plan / OutlineNaiem IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 - Written Report - Personalities, Values, and LifestyleDocumento24 pagineGroup 5 - Written Report - Personalities, Values, and LifestyleLex LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- TLE 7 - 8 - Carpentry - Module 1Documento24 pagineTLE 7 - 8 - Carpentry - Module 1Marycon Nacito92% (13)
- Charles Stanley - Let Go and Let GODDocumento50 pagineCharles Stanley - Let Go and Let GODTheAgapeIncNessuna valutazione finora
- ISC HydroCom ComparisonDocumento22 pagineISC HydroCom Comparisonrahilshah100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sita's RamayanaDocumento2 pagineSita's RamayanaAnonymous dSuPcxyn0% (1)
- Pic 18 F 46 K 40Documento594 paginePic 18 F 46 K 40Nelson FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Blast Injury ManagementDocumento16 pagineBlast Injury Managementheart wisdomNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cognitive Science of Learning - Concepts and Strategies For The Educator and LearnerDocumento14 pagineThe Cognitive Science of Learning - Concepts and Strategies For The Educator and LearnerNicholas BoonNessuna valutazione finora
- English Convents in ExileDocumento6 pagineEnglish Convents in ExilePickering and ChattoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cimt in Children WTH CP: Sample Measures/ FindingsDocumento6 pagineCimt in Children WTH CP: Sample Measures/ Findingsapi-253994356Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz ErrorsDocumento5 pagineQuiz Errorsanon_843459121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 EMADocumento36 pagineLecture 4 EMAYai IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Govt. College of Nusing C.R.P. Line Indore (M.P.) : Subject-Advanced Nursing PracticeDocumento17 pagineGovt. College of Nusing C.R.P. Line Indore (M.P.) : Subject-Advanced Nursing PracticeMamta YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Chart Manual For Rt60 Rough Terrain Crane: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocumento47 pagineLoad Chart Manual For Rt60 Rough Terrain Crane: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineRomario OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- ApplianceDocumento2 pagineApplianceTatanHenckerNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Prepared By: Ms. Shiela Mae B. CombalicerDocumento31 pagineUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Prepared By: Ms. Shiela Mae B. CombalicerAzeLuceroNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of The Book That Made Your World. by Vishal MangalwadiDocumento6 pagineA Review of The Book That Made Your World. by Vishal Mangalwadigaylerob100% (1)
- Linear Motion GraphsDocumento2 pagineLinear Motion GraphsNajwa Huda ShaharilNessuna valutazione finora
- Tantric Poetry of Kobo Daishi Kukai - Translated From Classical Chinese by Ronny GreenDocumento20 pagineTantric Poetry of Kobo Daishi Kukai - Translated From Classical Chinese by Ronny GreenHerko van BergenNessuna valutazione finora
- IvtDocumento32 pagineIvtArlhona Juana RagoNessuna valutazione finora
- ZF 2000 Series: Product DetailsDocumento4 pagineZF 2000 Series: Product DetailsJhonAlexRiveroNessuna valutazione finora
- Return To Sport After Surgical Management of Posterior Shoulder InstabilityDocumento13 pagineReturn To Sport After Surgical Management of Posterior Shoulder InstabilityAziz CupinNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDa EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDa EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingDa EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EDa EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (6)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDa EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- Culture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsDa EverandCulture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil: An Overview of the Petroleum IndustryDa EverandOil: An Overview of the Petroleum IndustryValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesDa EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Benchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementDa EverandBenchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignDa EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Advanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationDa EverandAdvanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideDa EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyDa EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDa EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsDa EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesDa EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsDa EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresDa EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsDa EverandHydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Petroliferous BasinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingDa EverandHybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesDa EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeDa EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (21)