Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
30.trafic in Interfacing-Moc
Caricato da
deepak19m0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
40 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
30.Trafic in Interfacing-moc
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
40 visualizzazioni2 pagine30.trafic in Interfacing-Moc
Caricato da
deepak19mCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
TRAFIC IN INTERFACING
From the subscriber’s point of view, there are two different call setup procedures
requiring a different approach:
Mobile Originated Call (MOC) & Mobile Terminated Call (MTC)
These can be explained as:
Mobile Originated Call (MOC)
If the mobile subscriber initiates the call, we talk about a mobile originated call
(MOC).Then, the mobile subscriber is the calling party.
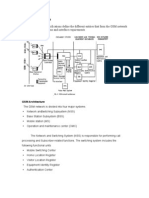
Basically, the necessary functions are carried out by the servicing Mobile-services
Switching center/Visitor Location Register (MSC/VLR). They are:
security control
subscription checking
Call routing towards the destination.
Basic Principles of the MOC
The MSC/VLR procedures for MOC initiation and completion contain all functions to
complete the setting up of call attempts from mobile stations.
MOC initiation:The MOC initiation procedure is triggered by a service request which is
sent from the mobile station to the MSC/VLR via the base station system (BSS).
Depending on the contents of this service request, the MOC initiation procedure handles:
Speech and data calls
Emergency calls
Subscriber controlled inputs
Short messages (mobile originated).
Upon receiving the service request, the MOC initiation procedure will start the
confidentiality (security) functions. This means that the MSC/VLR will carry out
authentication, equipment control, ciphering/deciphering and/or TMSI reallocation
should that be required.
Authentication
The authentication function determines a mobile subscriber’s authorization to access the
PLMN and protects the latter from unauthorized use. For this purpose, triples generated
by the AuC and containing a random number (RAND), a signed response (SRES) and a
cipher key (Kc) are used.
Equipment control
The equipment control function checks the equipment status as to whether the mobile
equipment is allowed, is to be observed or is not allowed within the PLMN. The
equipment control is carried out using the international mobile equipment identity (IMEI)
which is hard-coded at the mobile equipment.
Ciphering/deciphering
Ciphering/deciphering secures the information exchange via the radio interface.
Therefore, both the mobile station and the BSS are loaded with the same cipher key (Kc).
TMSI reallocation
The TMSI (temporary mobile subscriber identity) reallocation function periodically
assigns a new TMSI to a mobile subscriber. The purpose of this function is to prevent an
intruder from identifying a mobile subscriber by listening to the signaling on the radio
path. To increase confidentiality, the TMSI is reallocated at particular moments in time.
For certain projects, however, emergency call setup must be possible without the
subscriber identity module (SIM) being inserted. Then, the IMEI is used for identification
purposes instead of the usual TMSI or IMSI (international mobile subscriber
identity).This also means that authentication, ciphering/deciphering and TMSI
reallocation are
not carried out.
MOC completion
Having received the setup message from the mobile station, the MSC/VLR starts the
MOC completion procedure. The MSC/VLR performs subscription and service
compatibility checks. When these checks are positive, meaning that the mobile
subscriber’s connection request is accepted, the latter is informed. Afterwards, the
MSC/VLR allocates a traffic channel, seizes a terrestrial circuit and continues the
analysis of the dialed digits. The result enables the MSC/VLR to select a free trunk line
towards the destination.
Connection establishment continues and if the called party answers the call, the
MSC/VLR receives an indication from the remote exchange. The MSC/VLR now
completes the call, i.e. connects the mobile subscriber and starts the data collection for
charging purposes.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Information: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTCDocumento17 pagineInformation: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTCAbhishek ShambuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fixed/Mobile Convergence and Beyond: Unbounded Mobile CommunicationsDa EverandFixed/Mobile Convergence and Beyond: Unbounded Mobile CommunicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Switching Subsystem Functions and ComponentsDocumento5 pagineNetwork Switching Subsystem Functions and ComponentsMehboob AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Target Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandAutomatic Target Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Call procedures for mobile subscribersDocumento4 pagineCall procedures for mobile subscribersSarwar Pasha MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Self Management: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandComputer Science Self Management: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- 9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingDocumento35 pagine9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingHồ ThôngNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Call FlowDocumento125 pagineGSM Call Flowkazitamjidali@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandAutomatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Call FlowDocumento125 pagineGSM Call FlowHộp Thư Điện TửNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkDa EverandSummary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- DT DocumentsDocumento10 pagineDT DocumentsSobaan ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- GSMDocumento59 pagineGSMArun Kumar0% (1)
- Mobile: C2 - Safaricom InternalDocumento1 paginaMobile: C2 - Safaricom InternalJane MuliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Typical Signaling Sequences Shows The Following FeaturesDocumento5 pagineThe Typical Signaling Sequences Shows The Following FeaturesishitaNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Call SetupDocumento6 pagineGSM Call SetupArockiaruby RubyNessuna valutazione finora
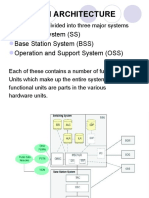
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Documento19 pagineGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Call FlowsDocumento14 pagineCall FlowsSandeep Reddy VajralaNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Services: Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Documento6 pagineGSM Services: Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Sarbjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal TracingDocumento17 pagineSignal TracingmadhunathNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM call flow for routing mobile callsDocumento2 pagineGSM call flow for routing mobile callsnagendra_badamNessuna valutazione finora
- How Cell Phone Calls Are Made Between DevicesDocumento3 pagineHow Cell Phone Calls Are Made Between DevicesZeeshan AmanNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Call Flow GuideDocumento59 pagineGSM Call Flow GuideJalal AldamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Switching SubsystemDocumento7 pagineNetwork Switching SubsystemraufthegreatNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Rady AbdelwahedDocumento168 paginePrepared By: Rady AbdelwahedAmr Sunhawy50% (2)
- GSM Overview 08Documento8 pagineGSM Overview 08Remon Adel AsaadNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Communication Flow GuideDocumento118 pagineGSM Communication Flow GuideVishnu Namboodiri P50% (2)
- GSM SystraDocumento67 pagineGSM SystraHi_Lev100% (1)
- Localization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberDocumento3 pagineLocalization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberHarish SarkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Localization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberDocumento3 pagineLocalization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberHarish SarkiNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Communication Flow GuideDocumento118 pagineGSM Communication Flow Guidevarinz100% (1)
- CS and PS KPI 2414Documento21 pagineCS and PS KPI 2414curtiskamoto0% (1)
- An Approach Towards Locating A Subscriber in The Network: Shelly Gahlawat, Shreya ShivaniDocumento3 pagineAn Approach Towards Locating A Subscriber in The Network: Shelly Gahlawat, Shreya ShivaniinventionjournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocumento66 pagineGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- CAMEL An IntroductionDocumento11 pagineCAMEL An IntroductionManas Ranjan SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityDocumento49 pagineMobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityIslam BarakatNessuna valutazione finora
- Traffic CasesDocumento30 pagineTraffic CasesNitin JainNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 GSM Traffic ManagementDocumento58 pagine3 GSM Traffic ManagementEldineNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report ON GSM Technology &: Infrastructure at Cell SitesDocumento26 pagineProject Report ON GSM Technology &: Infrastructure at Cell SitesAbhishek ChughNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM 1Documento28 pagineGSM 1joydeep12Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Example of SS7 - Global Cellular Network InteroperabilityDocumento3 pagineAn Example of SS7 - Global Cellular Network InteroperabilityKrishanu ModakNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Signaling and Protocols ArchitectureDocumento180 pagineGSM Signaling and Protocols ArchitectureMohammed Sa'dNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM ArchitectureDocumento8 pagineGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Call Flow GSM - CopieDocumento8 pagineCall Flow GSM - CopieStéphanie Océane NadjiNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Mobile Terminated Call Setup ProcessDocumento2 pagineGSM Mobile Terminated Call Setup ProcessE-Trần CmNessuna valutazione finora
- Call Processing in GSMDocumento9 pagineCall Processing in GSMjb1929835Nessuna valutazione finora
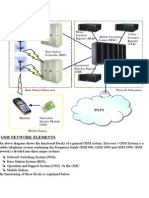
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocumento72 pagineGSM Network ArchitectureAkash Kumar100% (1)
- Mobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure in GSM: Routing Number)Documento1 paginaMobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure in GSM: Routing Number)nilanshumanasNessuna valutazione finora
- TN - SP021 - E1 - 0 Call Flow and Supplementary Service Flow in CS Domain-65Documento62 pagineTN - SP021 - E1 - 0 Call Flow and Supplementary Service Flow in CS Domain-65Tanzyy.2018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To GSM 2Documento12 pagineIntroduction To GSM 2mba_1604Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Maintenance CenterDocumento3 pagineOperation and Maintenance CenterRabia RindNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Reg Auth HoDocumento39 pagineWireless Reg Auth Hossiddiqi6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Call Flow To Simplest)Documento2 pagineCall Flow To Simplest)gagan_555Nessuna valutazione finora
- Call FlowsDocumento12 pagineCall FlowsRiyas MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Call ProcessingDocumento8 pagineCellular Call ProcessingSaibal RayNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network Operations and Traffic ScenariosDocumento18 pagineGSM Network Operations and Traffic Scenarioskamal100% (1)
- GSM MO Call FlowDocumento16 pagineGSM MO Call FlowVenkanna Annam100% (1)
- HandoffDocumento1 paginaHandoffdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 20.cellular SystemDocumento2 pagine20.cellular Systemdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- AcknowledgementDocumento1 paginaAcknowledgementdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 33.benefits From TrainingDocumento1 pagina33.benefits From Trainingdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 18.functions of EirDocumento1 pagina18.functions of Eirdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 24.air Interface ChannelsDocumento2 pagine24.air Interface Channelsdeepak19m100% (1)
- 28.traffic ChannelsDocumento1 pagina28.traffic Channelsdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 31.mobile Terminated CallDocumento1 pagina31.mobile Terminated Calldeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 29.Gsm IdentitiesDocumento2 pagine29.Gsm Identitiesdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 23.bursts and FramesDocumento1 pagina23.bursts and Framesdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Mon Control ChannelsDocumento1 paginaMon Control Channelsdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 17.authentication CenterDocumento2 pagine17.authentication Centerdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 27.dedicated Control ChannelsDocumento1 pagina27.dedicated Control Channelsdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Oadcast ChannelsDocumento2 pagineOadcast Channelsdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 22.transmission Rate& Channel ConceptDocumento1 pagina22.transmission Rate& Channel Conceptdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 21.radio ChannelDocumento2 pagine21.radio Channeldeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.the Base Station ControllerDocumento1 pagina13.the Base Station Controllerdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.functioning of HLRDocumento2 pagine16.functioning of HLRdeepak19m100% (1)
- 14.functioning of MSCDocumento2 pagine14.functioning of MSCdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.the SIMDocumento1 pagina12.the SIMdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- DatabaseDocumento1 paginaDatabasedeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 15.functioning of VLRDocumento1 pagina15.functioning of VLRdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.mobile StationDocumento1 pagina11.mobile Stationdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Work ElementsDocumento1 paginaWork Elementsdeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.introduction To GSM TechnologyDocumento2 pagine9.introduction To GSM Technologydeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.tech. Dept.& Org - StructureDocumento2 pagine8.tech. Dept.& Org - Structuredeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Bharti Airtel Inks USD 1 BillionDocumento1 paginaBharti Airtel Inks USD 1 Billiondeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Company ProfileDocumento2 pagineCompany Profiledeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- Factsheet Name: Bharti Airtel LimitedDocumento1 paginaFactsheet Name: Bharti Airtel Limiteddeepak19mNessuna valutazione finora
- 9590-4002 v5 Wired Control Installation Owners-2Documento32 pagine9590-4002 v5 Wired Control Installation Owners-2Phương LanNessuna valutazione finora
- Norma ISA 5.1Documento1 paginaNorma ISA 5.1Sebastian DragoNessuna valutazione finora
- IPSec VPN LABDocumento7 pagineIPSec VPN LABAparna Garg100% (2)
- Paytm Prepaid Electricity Recharge SolutionDocumento11 paginePaytm Prepaid Electricity Recharge SolutionNM GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Cable-Stayed Bridges Using Fuzzy Finite Element ModelingDocumento227 pagineAnalysis of Cable-Stayed Bridges Using Fuzzy Finite Element ModelingcxwNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Optimization of Random Forest Through The Use of MVO, GWO and MFO in Evaluating The Stability of Underground Entry-Type ExcavationsDocumento22 pagine2022 Optimization of Random Forest Through The Use of MVO, GWO and MFO in Evaluating The Stability of Underground Entry-Type Excavations周牮Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maco - Control2009HA136715 - Iss7 (1) Temper PDFDocumento44 pagineMaco - Control2009HA136715 - Iss7 (1) Temper PDFCesar PomposoNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact Session 2Documento35 pagineContact Session 2api-3724082Nessuna valutazione finora
- OpenTable Case StudyDocumento5 pagineOpenTable Case StudyLi LoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Banner M18T Temperature SensorsDocumento3 pagineBanner M18T Temperature SensorsAnderson FerrazNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)Documento76 pagineAudio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)KennyChoeNessuna valutazione finora
- India's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future TrendsDocumento5 pagineIndia's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future Trendspriyaa2688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philippines Weekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Documento1 paginaPhilippines Weekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Jaeda BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahesh Kumar GS - Technical Project Manager - Technical Lead - Senior Developer - DeveloperDocumento9 pagineMahesh Kumar GS - Technical Project Manager - Technical Lead - Senior Developer - Developernagaraj.hNessuna valutazione finora
- Hands-On With GEL Scripting, Xog and The Rest ApiDocumento166 pagineHands-On With GEL Scripting, Xog and The Rest ApiVicente RJNessuna valutazione finora
- Remote Access ExceptionDocumento2 pagineRemote Access ExceptionRaziye AslanNessuna valutazione finora
- JFLAP Manual PDFDocumento23 pagineJFLAP Manual PDFdolivasdNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII CS-083 Important Points For Term-1 Sweeti KakhaniDocumento4 pagineClass XII CS-083 Important Points For Term-1 Sweeti KakhaniKartik RawalNessuna valutazione finora
- FLEXIBOWL V2.0 - Electrical Panel (EN)Documento7 pagineFLEXIBOWL V2.0 - Electrical Panel (EN)Adolfo ReverteNessuna valutazione finora
- XRC BasicDocumento136 pagineXRC BasicJunior FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bbab 13 Ekontek PDFDocumento16 pagineBbab 13 Ekontek PDFeva apriliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Prediction Techniques in Modern Video Coding Standards PDFDocumento90 pagineBasic Prediction Techniques in Modern Video Coding Standards PDFAndrijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ip ProjectDocumento41 pagineIp ProjectLIGHT YAGAMINessuna valutazione finora
- Statistic TestDocumento4 pagineStatistic Testfarrahnajihah100% (1)
- Data Transmission Via Ethernet - Ip - Sd01293cen - 05.20Documento94 pagineData Transmission Via Ethernet - Ip - Sd01293cen - 05.20Alex AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Risc VDocumento102 pagineRisc VShraddha GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Humalyzer Primus: Semi-Automatic Microprocessor Controlled PhotometerDocumento2 pagineHumalyzer Primus: Semi-Automatic Microprocessor Controlled PhotometerHussein N. Farhat100% (1)
- Research Paper Two-ColumnDocumento22 pagineResearch Paper Two-ColumnJoseph TsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Loss PDFDocumento4 paginePacket Loss PDFRamiz RzaogluNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 QC Tools PresentationDocumento115 pagine7 QC Tools Presentationsumeetsaini88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityDa EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationDa EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Da EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- CEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionDa EverandCEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDa EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (67)
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Da EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDa EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireDa EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDa EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersDa EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Da EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamDa EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Da EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticeDa EverandAdvanced Antenna Systems for 5G Network Deployments: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and PracticeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- ITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachDa EverandIntroduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDa EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsDa EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNessuna valutazione finora
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationDa EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)