Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sample Test On Work (Physics)
Caricato da
Mariano Valiente Jr.Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sample Test On Work (Physics)
Caricato da
Mariano Valiente Jr.Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 1
University of San Carlos
Name: __________________________________ Yr. & Sec.: _______________Date: ____________ Score:
__________
Topic: WORK: This chapter focuses on the scientific conception of work in contrast with its
Laymans equivalence, and on its importance and relevance in our daily life. The learner shall
demonstrate an understanding of work done by a constant force, work-energy theorem, kinetic
energy, and gravitational potential energy, conservative vs. non-conservative forces,
conservation of mechanical energy, power and work done by a variable force.
Objective/s: Student will be able to: define work, power and energy; describe the relationship
between work and power, work and kinetic energy, work and potential energy, gravitational
potential energy and kinetic energy, work and energy, & power and work; distinguish
conservative and non-conservative forces; distinguish whether work is or is not done in a
particular situation.
I. Multiple Choice: Encircle the letter of the correct answer.
1. What is the capacity or ability to do work?
a. energy
b. force
c. power
d. pressure
2. Which of the following is a situation where work is NOT done?
a. A boy climbing up a tree
b. A vendor pushing a cart of coconuts
c. A girl lifting a basket of fruits from the table
d. A businessman carrying a briefcase to his office
3. Two forces F1 and F2 are acting on a box as shown in the figure, causing this box to move
across the surface. The force vectors are drawn into scale. Which of the following statements
is TRUE?
F1
F2
a. F1 is equal to F2 so F1 does equal work as F2.
b. F1 is equal to F2 but F1 does more work than F2.
c. F1 is bigger than F2 but F1 does equal work as F2.
d. F1 is bigger than F2 so F1 does more work than F2.
4. Which of the following refers to power?
I.
Rate at which work is changing
II.
Rate at which energy is changing
III.
Rate at which momentum is changing
a. I only
b. II only
c. I & II
d. I, II, & III
(For questions 5 & 6): A suitcase is pulled along a horizontal surface by a force F exerted
by the owner at an angle as shown in the figure.
5. In this case, which force does the negative
work?
a. Friction
b. Applied force
c. Normal Force
d. Force of the gravity
6. Which force/force component does the
positive work?
a. Friction
b. Weight of the suitcase
c. Vertical component of the applied force
d. Horizontal component of the applied force
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 2
University of San Carlos
7. When will the gravitational potential energy of an object change?
I.
When its mass is increased or decreased
II.
When it is brought to other planets or heavenly bodies
III.
When it is lowered or lifted from a position relative to the ground
a. I & II
b. II & III
c. I & III
d. I, II, & III
8. The force F is directed at an angle relative to the displacement s. In such a case, which of
the following is/are TRUE?
I.
When is zero, the force does work.
II.
When is not zero, the force component parallel to the displacement does work.
III.
When is not zero, the force component perpendicular to the displacement does work.
a. I only
b. I & II
c. I & III
d. II &
III
9. Car A has a mass of 1000 kg and a velocity of 100 km/hr. Car B has a mass of 500 kg and a
velocity of 50 km/hr. Which of the following statements CORRECTLY describes the kinetic
energy of car A and B?
a. The kinetic energy of car B is 1/6 of that of car A.
b. The kinetic energy of car B is 1/8 of that of car A.
c. The kinetic energy of car B is 6 times as big as that of car A.
d. The kinetic energy of car B is 8 times as big as that of car A.
10.As the time required for a person to do work increases, his power output ___________.
a. increases
b. decreases
c. remains the same
d. increases then decreases
11.After a strenuous activity done by two persons namely Ann and Ben, a conclusion is made
that Ann is more powerful than Ben. Which of the following statements are CORRECT?
I.
Ann can do more work than Ben can for the same time interval.
II.
Ann can do the same amount of work as Ben in a lesser time interval.
III.
Ann can do the same amount of work as Ben but for a longer time interval.
a. I only
b. I & II
c. I & III
d. II & III
12.What happens with the balls potential and kinetic energies as it is falling?
a. Its kinetic energy increases but its potential energy decreases.
b. Its kinetic energy decreases but its potential energy increases.
c. Its kinetic energy increases but its potential energy remains the same.
d. Its potential energy decreases but its kinetic energy remains the same.
13.Two forces F1 & F2 are of equal magnitudes. They both act on an object which is initially at
rest. As a consequence, the speed of the object increases. Which of the following is NOT
possible?
a. The work done by each force is positive.
b. The work done by each force is negative.
c. F1 does positive work and F2 does zero work.
d. F1 does positive work and F2 does negative work.
14.Going up a set of stairs requires exerting a force against gravity to carry oneself to a
particular height. If you climb upstairs then, you will exert _________________________________.
a. no work at all
b. less work when you walk than when you run
c. more work when you walk than when you run
d. equal amounts of work when you walk or when you run
15.A 2-kg ball is dropped freely from rest in a height of 20m from the ground. Air-resistance is
negligible. What are the magnitudes in Joules of the initial gravitational potential energy
(GPEi) and initial kinetic energy (KEi) respectively? (use g=10m/s2 if applicable)
a. GPEi = 400 J; KEi = 400 J
b. GPEi = 400 J; KEi = zero J
c. GPEi = zero J; KEi = 400 J
d. GPEi = zero J; KEi = zero J
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 3
University of San Carlos
16.An apple had a potential energy of 50 Joules. Then, it falls from rest from the tree. The only
force that acts on the apple as it falls is the gravitational force. What is its kinetic energy in
Joules upon reaching the ground or just before the normal force by the ground acts on it?
a. 50 Joules
b. less than 50 Joules
c. more than 50 Joules
d. cannot be determined
17.Two identical vaults are to be loaded simultaneously on the back of a truck by sliding them
up using two ramps. One ramp is steeper than the other ramp. The same amount of force is
applied in both cases. If friction is negligible in both ramps, the work done of the applied
force when the steeper ramp is used is _________ the work done of the applied force when the
other ramp is used.
a. equal to
b. greater than
c. less than
d. every much greater than
18.Two spheres of different masses are dropped simultaneously from a cliff. Air-resistance is
negligible. When they are 10 meters from the ground, they have the same
____________________.
a. acceleration
b. potential energy
c. kinetic energy
d. both b & c
(For questions no. 19 & 20) For a satellite in circular orbit around the earth, the gravitational
force provides the centripetal force.
19. At any point along the satellites orbit, what is the angle in
degree/s between the gravitational force and the displacement of
the satellite?
a. Zero
b. More than zero but less than 90
c. 90
d. More than 90
20. Does the gravitational force do work?
a. No, because the path of the satellite is not straight
b. Yes, because both displacements and gravitational force have magnitudes
c. No, because the direction of gravitational force is parallel to the direction of the
displacement
d. Yes, because the direction of gravitational force is perpendicular to the direction of the
displacement
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 4
University of San Carlos
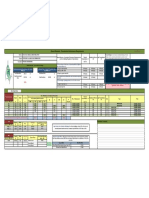
Item Analysis for the Physics Quiz on Work
conducted in Cansojong National High School for their IV-Earth Class last August 14,
2014
(Legend: Green items are retained or revised a little, orange items are revised or improved while red
items are discarded)
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 5
University of San Carlos
Breakdown of Items
Retained: 7 items (1,6,8,9,10,11,18)
Revised:
5 items (3,4,5,13,15)
Discarded: 8 items (2,7,12,14,16,17,19,20)
Mean: Index of Difficulty - 0.27
Index of Discrimination
- 0.26
Index of Effectiveness
- (-0.09)
Total No. of Items: 20
Total No. of Takers: 53
Highest Score: 9
Lowest Score: 2
Assessment and Evaluation in Science/Mathematics Education 6
University of San Carlos
Mariano L. Valiente Jr.
MA ScEd Physics
TEST CONSTRUCTION
ITEM ANALYSIS
RATING
Completeness
Punctuality
09
Quality of the Original Test Item
Total
10
54
35
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- T A X o N o M yDocumento2 pagineT A X o N o M yMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6 BondingDocumento43 pagine1.6 BondingArvinderSingh100% (1)
- The Cell CycleDocumento2 pagineThe Cell CycleMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1 - MacromoleculesDocumento3 pagineQuiz 1 - MacromoleculesMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1 - MacromoleculesDocumento3 pagineQuiz 1 - MacromoleculesMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Covalent Bond TestDocumento2 pagineCovalent Bond TestMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cutnell & Johnson: "Physics," Sixth Edition: Introduction and Mathematical ConceptsDocumento28 pagineCutnell & Johnson: "Physics," Sixth Edition: Introduction and Mathematical ConceptsMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCDocumento27 pagineCCMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test On Metallic and Chemical BondingDocumento2 pagineTest On Metallic and Chemical BondingMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Telescope PlantillaDocumento7 pagineTelescope PlantillaMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paref Springdale School Inc.: Center of Gravity and TorqueDocumento5 pagineParef Springdale School Inc.: Center of Gravity and TorqueMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept TestDocumento3 pagineMole Concept TestMariano Valiente Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Decision Wise Whitepaper 3 Essential Components of Employee EngagemenDocumento8 pagineDecision Wise Whitepaper 3 Essential Components of Employee EngagemenRatna Srinivas Kosuri100% (1)
- Numark Orbit - VirtualDJ 8 Operation GuideDocumento13 pagineNumark Orbit - VirtualDJ 8 Operation GuideCasiLokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Memory Lunguanga Exam No.: 1131520016 Center No: 3012 Class: 12 N5 Topic: Dairy Milk Processing at Finta Teacher: Mr. Musaka Year: 2014Documento12 pagineName: Memory Lunguanga Exam No.: 1131520016 Center No: 3012 Class: 12 N5 Topic: Dairy Milk Processing at Finta Teacher: Mr. Musaka Year: 2014LuzîyêñNessuna valutazione finora
- Final QuestionDocumento5 pagineFinal QuestionrahulNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 Agent Price ListDocumento2.732 pagine2020 Agent Price ListEngr XsadNessuna valutazione finora
- Suppliers of Ese Lightning Conductor Kalre Lightning ArresterDocumento2 pagineSuppliers of Ese Lightning Conductor Kalre Lightning ArresterRemedies EarthingNessuna valutazione finora
- MPF1533 SEM II 2014/2015 Organizational Theory and Educational Administration LecturerDocumento295 pagineMPF1533 SEM II 2014/2015 Organizational Theory and Educational Administration LecturerazuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect Design On Store ImageDocumento13 pagineEffect Design On Store Imagebermand75Nessuna valutazione finora
- ExportDocumento361 pagineExportStefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Chemistry: Analytical MethodsDocumento7 pagineFood Chemistry: Analytical Methodswildan ariefNessuna valutazione finora
- PlacementDocumento3 paginePlacementNishanth GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Phone Brand Selection FactorsDocumento14 pagineMobile Phone Brand Selection FactorsTushar MathurNessuna valutazione finora
- Astrology MathematicsDocumento34 pagineAstrology MathematicsDrFaisal ShawqeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alzheimers and DementiaDocumento4 pagineAlzheimers and DementiaNidhi ManojNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Student Subject AllocationDocumento5 pagineForm 4 Student Subject Allocationapi-484150872Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Electric BikeDocumento47 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Electric BikeHarish Dangeti100% (1)
- The Wheel and The BobsleighDocumento2 pagineThe Wheel and The BobsleighHarisNessuna valutazione finora
- SOLVED NUMERICALS EXAMPLES in Machine LearningDocumento59 pagineSOLVED NUMERICALS EXAMPLES in Machine LearningYash SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ignou Assignment 2018 BA III YearDocumento6 pagineIgnou Assignment 2018 BA III YearTelika RamuNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 DM BLDG Glazed+Schedule V01+Documento1 pagina04 DM BLDG Glazed+Schedule V01+Saahil KhaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Android Caputre CameraDocumento7 pagineAndroid Caputre CameraSagarraj WangdareNessuna valutazione finora
- Persuasive Writing G7Documento18 paginePersuasive Writing G7Shorouk KaramNessuna valutazione finora
- GyratoryDocumento4 pagineGyratoryFrancisco M. RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationDocumento6 pagineCri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationKyle Adrian FedranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Spitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Documento11 pagineSpitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Shafawati ShahneelNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd BeatitudeDocumento18 pagine3rd BeatitudeDonna ANessuna valutazione finora
- APMA 3100 Chapter 1-HandoutDocumento10 pagineAPMA 3100 Chapter 1-HandoutMichael ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Model 9200-2123: 1 RS-422 Input/3 RS-422 Output ModuleDocumento2 pagineModel 9200-2123: 1 RS-422 Input/3 RS-422 Output ModuleNisar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Status of Technical Education in India - Emerging Issues and ChallengesDocumento11 pagineStatus of Technical Education in India - Emerging Issues and ChallengesSreeram MandaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To Acoustics PDFDocumento296 pagineAn Introduction To Acoustics PDFmatteo_1234Nessuna valutazione finora