Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Transcription and Translation Exercise VER2 - Solution
Caricato da
Matin Ahmad KhanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Transcription and Translation Exercise VER2 - Solution
Caricato da
Matin Ahmad KhanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Transcription and Translation Exercise
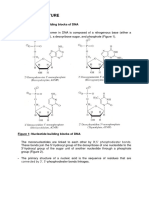
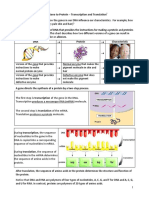
1. A portion of the kernel pigment gene (in corn) is shown below. This portion of the gene
encodes the very first part of the kernel pigment protein. Use the base sequence for
mRNA to complete the columns on the following table. Be sure to include the polarity of
the DNA and tRNA strands.
DNA
mRN
A
G5
G
T
C
T
A
T
G
T
C
A
G
G
C
C
A
C
C
T
G
C
C
G
C
G
G
A
C
T3
C3
C
A
G
A
T
A
C
A
G
T
C
C
G
G
T
G
G
A
C
G
G
C
G
C
C
T
G
A5
Complement
Gene/templat
e
G5
G
U
C
U
A
U
G
U
C
A
G
G
C
C
A
C
C
U
G
C
C
G
C
G
G
A
C
U3
tRNA
C
C
A
G
A
U3
A
C5
A3
G
U5
C3
C
G5
G3
U
G5
G3
A
C5
G3
G
C5
G3
C
C5
U3
G
A5
2. Describe the relationship between
the gene sequence and the mRNA
sequence.
The gene sequence and the mRNA
sequence are complements of each
other.
3. Describe the relationship between
the gene sequence and the tRNA
sequence.
They are the same except RNA
contains Us while DNA contains
Ts.
4. If the coding region of a protein
coding gene contains 300 DNA
nucleotides, how many amino acids
will be used in protein synthesis?
99 amino acids. Every three
nucleotides = 1 amino acid, so
300/3 = 100, but the stop codon
does not code for an amino acid,
therefore 99 amino acids.
5. If a protein has 150 amino acids,
how many DNA nucleotides would
make up the coding region of the
gene?
150 x 3 = 450, plus one codon for stop, 450 + 3 = 453.
6. What is the amino acid sequence for the very first part of the kernel pigment protein in
the exercise above?
Met-Ser-Gly-His-Leu-Pro-Arg-Thr
7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is
designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for
white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the
second nucleotide (base) in the second codon of the open reading frame (or coding
region) is an adenine.
What does the second codon in the r allele code for?
UCA becomes UAA = STOP
8. A protein has the following amino acid sequence. Construct a DNA nucleotide
sequence of this portion of the gene.
Phenylalanine-Glycine-Glycine-Alanine-Proline-Valine-Asparagine-Alanine
There are multiple correct answers for this.
9. If you compared your sequence to one constructed by a classmate, would you expect to
see any variations? What would be the reason for the difference?
This is due to the redundancy or degeneracy of the code. (multiple codons code for
the same amino acid)
10. Complete the following table:
Nucleotide Components and Function
Nucleic Acid Type
DNA
deoxyribose
mRNA
ribose
tRNA
ribose
Name of the sugar present
in nucleotides
Name of bases present in
nucleotides
Function of the type of
nucleic acid
Describe the relative size
and number of stands in
each of the nucleic acids
Where can you find each
of these in a eukaryotic
cell?
Adenine,
Guanine,
Cytosine,
Thymine
Storage of
genetic info
Adenine, Guanine,
Cytosine, Uracil
Adenine, Guanine,
Cytosine, Uracil
Molecular
middleman used in
protein synthesis.
Very, very
large.
Copy an of
individual gene,
used as
instructions to
synthesize a
protein.
Fraction of the
genome size.
nucleus
Cytosol
cytosol
Relatively small.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021Documento11 pagineLab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021thesoccerprince.10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kami Export - Worksheet 14 Central DogmaDocumento2 pagineKami Export - Worksheet 14 Central DogmaLindsey TamlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids and Their MetabolismDocumento58 pagineNucleic Acids and Their Metabolismnareshph28100% (1)
- Isolation of Plant Genomic DnaDocumento3 pagineIsolation of Plant Genomic DnaSudheer Kumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionDocumento3 pagineTranscription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionShanny McshannsNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Volume Molar Dan Termo CmpuranDocumento6 pagineTugas Volume Molar Dan Termo CmpuranHeppy Yessya100% (1)
- Restriction Enzyme DigestionDocumento5 pagineRestriction Enzyme DigestionAqsa ImtiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6 Paper ChromatographyDocumento8 pagineLab 6 Paper Chromatographyapi-384770852Nessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrogravimetryDocumento11 pagineElectrogravimetryElijah AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3Documento67 pagineChap 3mariam_scitech8389Nessuna valutazione finora
- Signed.: BIO 10100 Exam 4 Version 1Documento62 pagineSigned.: BIO 10100 Exam 4 Version 1Claribel SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 12 Protein SynthesisDocumento10 pagineCHAPTER 12 Protein SynthesisNadeem IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 8.1: Task Sheet No. 8 Ñares, Eros Husse VDocumento8 pagineActivity 8.1: Task Sheet No. 8 Ñares, Eros Husse VEros Husse BañaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocumento27 pagineCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- Mod3 PDFDocumento65 pagineMod3 PDFRAKISHO WORLD100% (1)
- TranscriptionDocumento30 pagineTranscriptionAizelle TarataraNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsDocumento21 pagineQuestions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsBindu JayachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication: The Semi-Conservative ProcessDocumento7 pagineDNA Replication: The Semi-Conservative ProcessMuhammad QayumNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic AcidsDocumento3 pagineNucleic AcidsBio Sciences100% (2)
- Department of Chemistry GC Women University, Sialkot: Name: Roll No.Documento2 pagineDepartment of Chemistry GC Women University, Sialkot: Name: Roll No.Esha Rani Waheed100% (1)
- Estimation of DNADocumento1 paginaEstimation of DNATjcbt BiosciencesNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Nucleic AcidsDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To Nucleic AcidsAsif AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna StructureDocumento23 pagineDna StructureAnonymous mHS76aNessuna valutazione finora
- E 01 Mean ActivityDocumento9 pagineE 01 Mean ActivityLân Võ Thành100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Redox Titration Percent Purity AnalysisDocumento5 pagineExperiment 3 Redox Titration Percent Purity AnalysisnanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 3 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocumento50 pagineDay 3 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingAniket ParabNessuna valutazione finora
- tmpD944 TMPDocumento7 paginetmpD944 TMPFrontiersNessuna valutazione finora
- Central DogmaDocumento4 pagineCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasmid DNA Quantification of DNADocumento3 paginePlasmid DNA Quantification of DNAHuishin LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Nucleic AcidDocumento26 pagineChapter 2 Nucleic Acidapi-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tanabe-Sugano Diagram ExplainedDocumento5 pagineTanabe-Sugano Diagram Explainedd4nk4rNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Documento33 pagineProtein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??jodyjodzNessuna valutazione finora
- Recrystallization of Acetanilide Organic ChemistryDocumento6 pagineRecrystallization of Acetanilide Organic ChemistryBangkit Putra SagaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of HPLC Conditions for Aromatic Hydrocarbon SeparationDocumento11 pagineOptimization of HPLC Conditions for Aromatic Hydrocarbon SeparationNolzConxNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Isolation, Restriction, Visualitation, and QuantificationDocumento20 pagineDNA Isolation, Restriction, Visualitation, and QuantificationSonianto kuddi100% (5)
- Restriction Endonuclease Digestion of Plasmid DNADocumento3 pagineRestriction Endonuclease Digestion of Plasmid DNAPaulo R. LatonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes: Properties and KineticsDocumento59 pagineEnzymes: Properties and Kineticsthamizh555100% (2)
- Gel Electrophoresis Lab Questions - Answer KeyDocumento7 pagineGel Electrophoresis Lab Questions - Answer Keyapi-406513659100% (1)
- Semiconductor Physics TutorialDocumento12 pagineSemiconductor Physics TutorialKadis PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Titrasi NetralisasiDocumento45 pagineTitrasi NetralisasiPhantom of Venice33% (3)
- Chapter Quiz General Biology 2Documento7 pagineChapter Quiz General Biology 2Nikki San GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocumento21 pagineMass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsVince DulayNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids HandoutDocumento3 pagineNucleic Acids HandoutAlifah SyarafinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini PreparationDocumento8 pagineMini PreparationrohishaakNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme and Acid - Base CatalysisDocumento64 pagineEnzyme and Acid - Base Catalysisbinseung skzNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA ReplicationDocumento55 pagineDNA ReplicationZainab Jamal Siddiqui100% (1)
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsDocumento6 pagineChemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsSherlock Wesley ConanNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Protein 221 1Documento27 pagineStructure of Protein 221 1Dawlat SalamaNessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento64 pagineTranscriptionmadhura480Nessuna valutazione finora
- Orcinol Reagent Reaction for Detecting Pentoses in RNADocumento2 pagineOrcinol Reagent Reaction for Detecting Pentoses in RNAChristian Rey Hallera BalmoriNessuna valutazione finora
- RNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDDocumento7 pagineRNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDcokcreNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)Documento3 pagineProtein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)sidney berjaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription Translations HandoutDocumento13 pagineTranscription Translations HandoutMedina Zahic100% (1)
- Week 4 Supplementary Activity 4 - Central Dogma of Genetics - ANSWERDocumento3 pagineWeek 4 Supplementary Activity 4 - Central Dogma of Genetics - ANSWERBernadette Vidon-PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- S-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYDocumento5 pagineS-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYcokcreNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription Translation ProtocolDocumento10 pagineTranscription Translation ProtocoladindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Expression AssignmentDocumento5 pagineGene Expression AssignmentLauren EatonNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13 Study Guide KeyDocumento5 pagineCH 13 Study Guide Keyi_wana_readNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis Paper Lab InstructionsDocumento11 pagineProtein Synthesis Paper Lab Instructionsapi-292473508Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Semen: CompositionDocumento2 pagineHuman Semen: CompositionMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminal Fluid Composition and Fertilization ProcessDocumento1 paginaSeminal Fluid Composition and Fertilization ProcessMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein StructureDocumento2 pagineProtein StructureMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- HIV at A GlanceDocumento8 pagineHIV at A GlanceMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- HIV Theraphy PDFDocumento9 pagineHIV Theraphy PDFTitik Tri ArdianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineProtein SynthesisMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid Residues: Proteins (Documento1 paginaAmino Acid Residues: Proteins (Matin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors and Their Inserting Size: Enveloped Virus Poxvirus DNA Genome KBP GenesDocumento5 pagineVectors and Their Inserting Size: Enveloped Virus Poxvirus DNA Genome KBP GenesMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- AIIMS General Knowledge 2Documento13 pagineAIIMS General Knowledge 2Matin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assam doctor claims cure for HIV/AIDS, cured 86 peopleDocumento2 pagineAssam doctor claims cure for HIV/AIDS, cured 86 peopleMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything You Need to Know About HIV/AIDSDocumento1 paginaEverything You Need to Know About HIV/AIDSMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Can I Reduce My Risk of Getting Hiv Through Sexual ContactDocumento4 pagineHow Can I Reduce My Risk of Getting Hiv Through Sexual ContactMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For Third ProfDocumento9 pagineRules For Third ProfMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency Evaluation FormDocumento13 pagineCompetency Evaluation FormMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Bio Phy Chem StatDocumento13 pagineBook Bio Phy Chem StatMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Government Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET ScoreDocumento5 pagineTop 50 Government Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET ScoreMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 BCQ MRCP QuestionsDocumento31 pagine100 BCQ MRCP QuestionsMatin Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- Sample Neurological HDocumento3 pagineSample Neurological HMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- List of surgical prefixes, suffixes and proceduresDocumento6 pagineList of surgical prefixes, suffixes and proceduresMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- NEUROLOGY MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZDocumento11 pagineNEUROLOGY MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZzhai bambalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Med MBBSDocumento8 pagineCommunity Med MBBSMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mnemonics On NutritionDocumento3 pagineMnemonics On NutritionMatin Ahmad Khan100% (2)
- 1st Prof Mbbs ReguDocumento38 pagine1st Prof Mbbs ReguMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- LyricsDocumento2 pagineLyricsMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- PG Medical Question BankDocumento12 paginePG Medical Question BankMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Government Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET ScoreDocumento5 pagineTop 50 Government Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET ScoreMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- AIPMT 2015 Paper Leak Lawyer Vaibhav Choudhary Explains Why MondayDocumento5 pagineAIPMT 2015 Paper Leak Lawyer Vaibhav Choudhary Explains Why MondayMatin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- MMWR June 5 1981 (First Report by DR Michel Gotleib)Documento3 pagineMMWR June 5 1981 (First Report by DR Michel Gotleib)Matin Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs on Biomolecules DNA RNA Proteins CarbsDocumento4 pagineMCQs on Biomolecules DNA RNA Proteins CarbsMatin Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- Condy LatorDocumento11 pagineCondy LatorrekabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To OpmDocumento30 pagineIntroduction To OpmNaeem Ul HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- IELTS Vocabulary ExpectationDocumento3 pagineIELTS Vocabulary ExpectationPham Ba DatNessuna valutazione finora
- Insize Catalogue 2183,2392Documento1 paginaInsize Catalogue 2183,2392calidadcdokepNessuna valutazione finora
- AtmDocumento6 pagineAtmAnkit JandialNessuna valutazione finora
- SiBRAIN For PIC PIC18F57Q43 SchematicDocumento1 paginaSiBRAIN For PIC PIC18F57Q43 Schematicivanfco11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesDocumento15 pagineLesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesRose Angel Manaog100% (1)
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocumento18 pagineME6404 Thermal EngineeringAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNessuna valutazione finora
- Diemberger CV 2015Documento6 pagineDiemberger CV 2015TimNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptDocumento2 pagine14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptsubiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Documento11 pagineSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Rohana YahyaNessuna valutazione finora
- SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSDocumento3 pagineSOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSwaleedNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz-Travel - Beginner (A1)Documento4 pagineQuiz-Travel - Beginner (A1)Carlos Alberto Rodriguez LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Key ssl101 Academic Skills For University Success ssl101cDocumento196 pagineKey ssl101 Academic Skills For University Success ssl101cHùng NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Afu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsDocumento4 pagineAfu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsHashim SaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Honors Biology Unit 2 - Energy Study GuideDocumento2 pagineHonors Biology Unit 2 - Energy Study GuideMark RandolphNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyDocumento4 pagineAssessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyVijay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The DronesDocumento43 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of The DronesVysual ScapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tygon S3 E-3603: The Only Choice For Phthalate-Free Flexible TubingDocumento4 pagineTygon S3 E-3603: The Only Choice For Phthalate-Free Flexible TubingAluizioNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps To Configure Linux For Oracle 9i Installation: 1. Change Kernel ParametersDocumento5 pagineSteps To Configure Linux For Oracle 9i Installation: 1. Change Kernel ParametersruhelanikNessuna valutazione finora
- Driving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorsDocumento10 pagineDriving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorskellendadNessuna valutazione finora
- Um 0ah0a 006 EngDocumento1 paginaUm 0ah0a 006 EngGaudencio LingamenNessuna valutazione finora
- NetsimDocumento18 pagineNetsimArpitha HsNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferenceDocumento16 pagineProgramming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferencekrishnamarajublrNessuna valutazione finora
- Urodynamics Griffiths ICS 2014Documento198 pagineUrodynamics Griffiths ICS 2014nadalNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Theory: Frequency or AmplitudeDocumento11 pagineRadio Theory: Frequency or AmplitudeMoslem GrimaldiNessuna valutazione finora
- Roadmap For Digitalization in The MMO Industry - For SHARINGDocumento77 pagineRoadmap For Digitalization in The MMO Industry - For SHARINGBjarte Haugland100% (1)
- 2007 Bomet District Paper 2Documento16 pagine2007 Bomet District Paper 2Ednah WambuiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Singular Mind of Terry Tao - The New York TimesDocumento13 pagineThe Singular Mind of Terry Tao - The New York TimesX FlaneurNessuna valutazione finora
- IP68 Rating ExplainedDocumento12 pagineIP68 Rating ExplainedAdhi ErlanggaNessuna valutazione finora