Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
ME 530 Assignment 1 PDF
Caricato da
Anonymous or50iwsDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ME 530 Assignment 1 PDF
Caricato da
Anonymous or50iwsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assignment-1
ME530 Advance Mechanics of Solids 26.08.2015
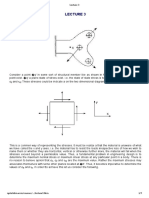
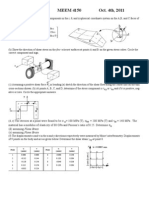
1. A uniform pressure of 500 psi is developed on faces
EGHF and ABCD of the solid block shown in the
figure. Also, a uniform tensile force distribution
(suction) is maintained on the faces GHCB and
EFDA having the value of 100 psi. What are the
normal stress and shear stresses on the interface
shown on the diagonal surface GHDA of the block?
2. Analysis of a particular body indicates that stresses for orthogonal interfaces associated with
reference xyz at a given point are, in kPa.
xx = 3000kPa, xy = -1000kPa , xz = 0kPa, yx = -1000kPa, yy = 2000kPa,yz = 2000kPa, zx = 0 kPa
zy = 2000 kPa, zz = 0 kPa. Determine the normal stress nn on the infinitesimal interface at this
point whose unite is n = 0.60j+0.80k
500 0 100
0 0 0 kPa
100 0 800
3. The stress tensor at a point in a body is given as follows: ij =
for a given
reference xyz. A reference x ' y ' z ' is formed by rotating the references about the z axis an angle
. What are the components of stresses for the primed reference?
4. In the figure, we have a case of uniform stress wherein the stress tensor is given as
3000
0
0
3000 4000 0 kPa
0
0
5000
(a) What is the shear stress on face ABC along the edge AC?
(b) What is the shear stress on face DAEC, also along edge AC?
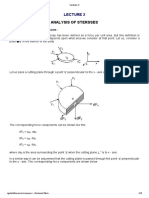
5. It was assumed that across any infinitesimal surface element in a solid,
the action of the exterior material upon the interior is equipollent (i.e.
equal in strength or effect) to only a force. It is also possible to assume
that in addition to a force, there is also a couple, i.e. at any point across
n
any plane n, there is a stress vector T and a couple stress vector M as
shown in the figure. Show that a set of equations similar to Cauchys
equations can be derived, i.e. if we know the couple-stress vectors on
three mutually perpendicular planes passing through the point P, then we
can determine the couple-stress vector on any plane n passing through
n
the point. The equations are
n
M x = M xx nx + M yx n y + M zx nz ,
n
M y = M xy nx + M yy n y + M zy nz ,
n
M z = M xz nx + M yz n y + M zz nz . M x , M y , M z are the x, y and z components of the vector M
acting on plane n.
T11 2 1
0 2 .
1 2 0
6. The state of stress at a point is characterized by the matrix ( ) = 2
ij
Determine T11 such
that there is at least one plane passing through the point in such a way that the resultant stress
on that plane is zero. Determine the direction cosines of the normal to that plane.
a 0 d
7. If the rectangular components of stress at a point are as in the matrix ( ij ) = 0 b e ,
d e c
determine the unit normal of a plane parallel to the z axis, i.e. nz = 0, on which the resultant
stress vector is tangential to the plane.
8. Determine the principal stresses and their axes for the states of stress characterized by the
3
following stress matrix (unites are 1000 kPa). ( ij ) = 10
10
0
30
30
27
9. The state of stress at a point is characterized by the components x = 12.31 , y = 8.96 ,
z = 4.34 , xy = 4.20 , xy = 5.27 , z = 0.84 . Determine the principal shears and the associated
normal stresses.
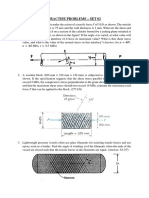
10. A solid shaft of diameter d = 10 cm (in the figure)
is subjected to a tensile force p = 10,000 N and a
torque T = 5000 N-cm. At point A on the surface,
Determine the Principal stresses, the octahedral
shearing stress and the maximum shearing stress.
11. A cylindrical rod (in the figure) is subjected to a torque
T. at any point P of the cross-section LN, the following
stresses occur.
x = y = z = xy = yz = 0, xz = zx = G y, yz = zy = G x,
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDocumento2 pagineA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar on Micro-Local Analysis. (AM-93), Volume 93Da EverandSeminar on Micro-Local Analysis. (AM-93), Volume 93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Problems (Ed 5)Documento167 pagineChapter Problems (Ed 5)ابو النمرNessuna valutazione finora
- Constructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisDa EverandConstructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises On Stress StateDocumento4 pagineExercises On Stress StatecusanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Documento4 pagineIntroduction of Solid Mechanics (ME 621) : Problem 1Ritunjay JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- StressDocumento3 pagineStressdamastergen326Nessuna valutazione finora
- SEISMOLOGY, Lecture 2Documento38 pagineSEISMOLOGY, Lecture 2Singgih Satrio WibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsDa EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- CM LC1Documento28 pagineCM LC1Eng W EaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1Documento2 pagineTutorial 1SijuKalladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Stresses:: X y XyDocumento7 pagineAnalysis of Stresses:: X y Xypmm05479Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practise Problems Set02Documento5 paginePractise Problems Set02rohit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanic of Materials (Normal Stress)Documento44 pagineMechanic of Materials (Normal Stress)moj33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetDocumento3 pagineAdvanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetAshish ZachariahNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 D LectureDocumento36 pagine3 D LectureAisha AbuzgaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1. Stress-Strain AnalysisDocumento36 pagineChap 1. Stress-Strain Analysisteknikpembakaran2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture4 3-d Stress Tensor and Equilibrium EquationsDocumento18 pagineLecture4 3-d Stress Tensor and Equilibrium Equationssamurai7_77Nessuna valutazione finora
- IMoM 6BDocumento42 pagineIMoM 6BDaniel Laurence Salazar ItableNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Stress in Beams NotesDocumento4 pagineShear Stress in Beams NotesMubark Al-haidariNessuna valutazione finora
- Transverse ShearDocumento4 pagineTransverse ShearrajdrklNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Materials by S K Mondal 2 PDFDocumento31 pagineStrength of Materials by S K Mondal 2 PDFajaykrishna_99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Mech Assignment 2Documento4 pagineSolid Mech Assignment 2sayan mukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Stersses: General State of Stress at A PointDocumento8 pagineAnalysis of Stersses: General State of Stress at A Pointpmm05479Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANALYSIS OF STRESSES (Assignment#1)Documento4 pagineANALYSIS OF STRESSES (Assignment#1)jowasa92050% (2)
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Documento2 pagineAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Rahul PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Documento2 pagineAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Documento2 pagineAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Documento3 pagineTutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Kiat HauNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Questions ElasticityDocumento3 pagineModel Questions Elasticityrameshbabu_1979Nessuna valutazione finora
- in This Module Text in "Italic" Indicates Advanced Concepts. 2., Are Used For Shear' in Books and LiteratureDocumento35 paginein This Module Text in "Italic" Indicates Advanced Concepts. 2., Are Used For Shear' in Books and LiteratureKanti SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress PresentationDocumento26 pagineStress PresentationDhakshina KNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 7 PDFDocumento1 paginaExercise 7 PDFchetanNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress and StrainDocumento17 pagineStress and StrainakshatbhargavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Material Interview Question and AnswersDocumento27 pagineStrength of Material Interview Question and AnswersArjun M Betageri66% (29)
- 3D Stress Tensors, Eigenvalues and RotationsDocumento12 pagine3D Stress Tensors, Eigenvalues and RotationsVimalendu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Load and Stress AnalysisDocumento27 pagine1 - Load and Stress AnalysisAyesha KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.8 A State of Hydrostatic Stress Is Given By: N N N NDocumento1 pagina2.8 A State of Hydrostatic Stress Is Given By: N N N Nkelvito09Nessuna valutazione finora
- 17.lecture 27 Finite Element Derivation PDFDocumento17 pagine17.lecture 27 Finite Element Derivation PDFKarina NaudéNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZDocumento2 pagineAnswer Any Five Questions.: U Kxy, V Kxy and W 2k (X +y) ZNitesh AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- AMM Assignment 2Documento2 pagineAMM Assignment 2Rino NelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2D Cartesian ElasticityDocumento13 pagine2D Cartesian ElasticityMartin KoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample 1st Midterm 4Documento2 pagineSample 1st Midterm 4Dr. Madhukar VableNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Any Five Questions.: B, B and BDocumento2 pagineAnswer Any Five Questions.: B, B and BNitesh AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Tensor Lec.2Documento24 pagineStress Tensor Lec.2Malak ShatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment#1Documento1 paginaAssignment#1Ayush53Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Mechanics Assignment HelpDocumento29 pagineStructural Mechanics Assignment HelpMechanical Engineering Assignment HelpNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mechanics Ii: M N A P Area Orload ForceDocumento57 pagineApplied Mechanics Ii: M N A P Area Orload ForceMutiu Toheeb OpeyemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Som Unit 5Documento30 pagineSom Unit 5Robinson PrabuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Equilibrium EquationsDocumento6 pagineThe Equilibrium EquationsJoão DiasNessuna valutazione finora
- MP206 Ex1Documento6 pagineMP206 Ex1anush_swaminathanNessuna valutazione finora
- 307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFDocumento9 pagine307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFNusret MeydanlikNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Documento2 pagineExam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Rayleight SilversNessuna valutazione finora
- StressDocumento7 pagineStressapi-296773500Nessuna valutazione finora
- ASHRAE Final Operating Room 508 PDFDocumento13 pagineASHRAE Final Operating Room 508 PDFSilisteanu AndreiNessuna valutazione finora
- EQUIP9-Operations-Use Case ChallengeDocumento6 pagineEQUIP9-Operations-Use Case ChallengeTushar ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Promotion of Coconut in The Production of YoghurtDocumento4 paginePromotion of Coconut in The Production of YoghurtԱբրենիկա ՖերլինNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Ref 70 483 Programming in C by Wouter de Kort PDFDocumento2 pagineExam Ref 70 483 Programming in C by Wouter de Kort PDFPhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Uxc01387a PDFDocumento16 pagineUxc01387a PDFmahesh123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Invenio Flyer enDocumento2 pagineInvenio Flyer enErcx Hijo de AlgoNessuna valutazione finora
- GSP AllDocumento8 pagineGSP AllAleksandar DjordjevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Random Variables: 4.1 Definition, Mean and VarianceDocumento15 pagineDiscrete Random Variables: 4.1 Definition, Mean and VariancejordyswannNessuna valutazione finora
- Language EducationDocumento33 pagineLanguage EducationLaarni Airalyn CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- LCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Documento80 pagineLCP-027 VectraLCPDesignGuideTG AM 0613Evert100% (1)
- Green ProtectDocumento182 pagineGreen ProtectLuka KosticNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Flow Meter TypesDocumento2 pagineWater Flow Meter TypesMohamad AsrulNessuna valutazione finora
- Glory in The Cross - Holy Thursday - Schutte PDFDocumento1 paginaGlory in The Cross - Holy Thursday - Schutte PDFsharon0murphyNessuna valutazione finora
- C7.5 Lecture 18: The Schwarzschild Solution 5: Black Holes, White Holes, WormholesDocumento13 pagineC7.5 Lecture 18: The Schwarzschild Solution 5: Black Holes, White Holes, WormholesBhat SaqibNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1-2 Module 1 Chapter 1 Action RseearchDocumento18 pagineWeek 1-2 Module 1 Chapter 1 Action RseearchJustine Kyle BasilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Clearing 2019Documento11 pagineRules of Bursa Malaysia Securities Clearing 2019Evelyn SeethaNessuna valutazione finora
- SeaTrust HullScan UserGuide Consolidated Rev01Documento203 pagineSeaTrust HullScan UserGuide Consolidated Rev01bong2rmNessuna valutazione finora
- Annotated Bibliography 2Documento3 pagineAnnotated Bibliography 2api-458997989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Promoting The Conservation and Use of Under Utilized and Neglected Crops. 12 - TefDocumento52 paginePromoting The Conservation and Use of Under Utilized and Neglected Crops. 12 - TefEduardo Antonio Molinari NovoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaDocumento8 pagineStudy of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaPratikDedhia99Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22Documento6 pagineCBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22Aryan BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- English 6, Quarter 1, Week 7, Day 1Documento32 pagineEnglish 6, Quarter 1, Week 7, Day 1Rodel AgcaoiliNessuna valutazione finora
- HSG 2023 KeyDocumento36 pagineHSG 2023 Keyle827010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Ijrerd-C153Documento9 pagine20 Ijrerd-C153Akmaruddin Bin JofriNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper A and CDocumento9 pagineTerm Paper A and CKishaloy NathNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-CHAPTER-1 - Edited v1Documento32 pagine3-CHAPTER-1 - Edited v1Michael Jaye RiblezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection - Reading and Writing 3Documento3 pagineReflection - Reading and Writing 3Quỳnh HồNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech SharmitDocumento16 pagineTech SharmitRishu SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- MultiZone Limitations and HintsDocumento2 pagineMultiZone Limitations and HintsRubén Darío Becerra GalindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Solitax SCDocumento8 pagineSolitax SCprannoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresDa EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (2)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignDa EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (138)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsDa EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignDa EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Flow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesDa EverandFlow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesTomomichi NakamuraValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDa EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (12)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignDa EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (19)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDa EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsDa EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Predicting Lifetime for Concrete StructureDa EverandPredicting Lifetime for Concrete StructureNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDa EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDa EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDa EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityDa EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesDa EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbDa EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (15)
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersDa EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersNessuna valutazione finora