Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Congruence and Similarity
Caricato da
Sandra NgCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Congruence and Similarity
Caricato da
Sandra NgCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text Contents
STRAND I: Geometry and
Trigonometry
Unit 33 Congruence and Similarity
Student Text
Contents
Section
33.1
Congruence
33.2
Similarity
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
33 Congruence and Similarity
33.1 Congruence
3 cm
Two shapes are said to be congruent if they are the
same shape and size: that is, the corresponding sides
of both shapes are the same length and corresponding
angles are the same.
The two triangles shown here are congruent.
7 cm
5 cm
7 cm
3 cm
5 cm
Shapes which are of different sizes but which have the same shape are said to be similar.
The triangle below is similar to the triangles above but because it is a different size it is
not congruent to the triangles above.
3.5 cm
1.5 cm
2.5 cm
There are four tests for congruence which are outlined below.
TEST 1 (Side, Side, Side)
If all three sides of one triangle
are the same as the lengths of the
sides of the second triangle, then
the two triangles are congruent.
This test is referred to as SSS.
TEST 2 (Side, Angle, Side)
If two sides of one triangle are
the same length as two sides of
the other triangle and the angle
between these two sides is the
same in both triangles, then the
triangles are congruent.
This test is referred to as SAS.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
33.1
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
TEST 3 (Angle, Angle, Side)
If two angles and the length of
one corresponding side are the
same in both triangles, then
they are congruent.
This test is referred to as AAS.
TEST 4 (Right angle, Hypotenuse, Side)
If both triangles contain a right angle,
have hypotenuses of the same length
and one other side of the same length,
then they are congruent.
This test is referred to as RHS.
Worked Example 1
Which of the triangles below are congruent to the triangle ABC, and why?
F
C
45.5
5 cm
4 cm
3.6 cm
5 cm
E
52.4
4 cm
3.6 cm
52.4
5 cm
4 cm
45.5
I
52.4
G
3.6 cm
Solution
Consider first the triangle DEF:
AB = DF
BC = EF
AC = DE
As the sides lengths are the same in both triangles the triangles are congruent. (SSS)
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
33.1
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
Consider the triangle GHI:
BC = HI
= GHI
ABC
= G IH
ACB
As the triangles have one side and two angles the same, they are congruent. (AAS)
Consider the triangle JKL: Two sides are known but the angle between them is unknown,
so there is insufficient information to show that the triangles are congruent.
A
Worked Example 2
ABDF is a square and BC = EF .
Find the pairs of congruent triangles in the diagram.
G
Solution
F
Consider the triangles ABC and AFE:
AB = AF
BC = FE
= AFE
= 90
ABC
(ABDF is a square.)
(This is given in the question.)
(They are corners of a square.)
The triangles ABC and AFE have two sides of the same length and also have the
same angle between them, so these triangles are congruent. (SAS)
Consider the triangles ACG and AEG:
AG = AG
= CGA
EGA
= 90
ABC and
AC = AE
AFE are congruent.)
(They are the same line.)
(This is given in the question.)
Both triangles contain right angles, have the same length hypotenuse and one other
side of the same length. So the triangles are congruent. (RHS)
Investigation
1.
How many straight lines can you draw to divide a square into two congruent
parts?
2.
How many lines can you draw to divide a rectangle into two congruent parts?
3.
Can you draw two straight lines through a square to divide it into four congruent
quadrilaterals which are not parallelograms?
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
33.1
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
Exercises
1.
Identify the triangles below which are congruent and give the reasons why.
A
5 cm
5 cm
4 cm
8 cm
4 cm
8 cm
E
B
69
K
6 cm
4.61 cm
66
6.08 cm
4.61 cm
45
6.08 cm
O
L
M 85
10 cm
R
75
20
10 cm
T
20
P
4.61 cm
45
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
6 cm
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.1
2.
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
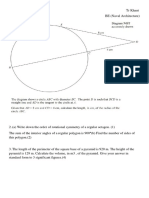
If O is the centre of the circle,
prove that the triangles OAB
and OCB are congruent.
O
3.
D
A
If O is the centre of both circles,
prove that the triangles OAB
and ODC are congruent.
4.
If O is the centre of the circle,
prove that the triangles OAB
and OCD are congruent.
5.
B
E
When BC = EF , this rhombus
contains two congruent triangles.
F
Identify the triangles and prove that
they are congruent.
A
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.1
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
6.
If O is the centre of the circle
and AD = BC , show that ABD
and CDB are congruent triangles.
7.
Two triangles have sides of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm, and contain an angle of 30 .
Show that it is possible to draw 4 different triangles, none of which are congruent,
using this information.
A
8.
The diagram shows the parallelogram
ABCD with diagonals which
intersect at X.
Prove that the parallelogram contains
2 pairs of congruent triangles.
C
D
9.
The diagram shows a cuboid.
The mid-point of the side DC is X.
(a)
Show that triangles AHG
and FAD are congruent.
(b)
Show that triangles ADX
and BCG are congruent.
2
A
Investigation
1.
In how many ways can you cut a square-based cake into two congruent parts?
2.
How can you use eight straight lines of equal length to make a square and four
congruent equilateral triangles?
Challenge!
Study the diagram opposite and then find the ratio of the
area of the large triangle to that of the small triangle.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
33.2 Similarity
Similar shapes have the same shape but may be different sizes. The two rectangles shown
below are similar they have the same shape but one is smaller than the other.
2 cm
6 cm
3 cm
9 cm
They are similar because they are both rectangles and the sides of the larger rectangle are
three times longer than the sides of the smaller rectangle.
It is interesting to compare the area of the two rectangles. The area of the smaller
rectangle is 6 cm 2 and the area of the larger rectangle is 54 cm 2 , which is nine times
(3 ) greater.
2
Note
In general, if the lengths of the sides of a shape are increased by a factor k, then the area is
increased by a factor k 2 .
These two triangles are not similar.
The sides lengths of the triangles
are not in the same ratio and so
the triangles are not similar.
For two triangles to be similar, they must have the same internal angles, as shown in the
similar shapes below.
100
7.84
7.71
30
12
50
50
6
3.92
100
15.42
30
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
33.2
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
The diagrams below show 3 similar cubes.
3 cm
2 cm
1 cm
1 cm
1 cm
2 cm
3 cm
2 cm
3 cm
Length
of side
Area of
one face
Surface
area
Volume
1 cm
1 cm2
6 cm2
1 cm3
2 cm
4 cm2
24 cm2
8 cm3
3 cm
9 cm2
54 cm2
27 cm3
The table gives the lengths of sides, area of one face, total surface area and volume.
Comparing the larger cube with the 1 cm cube we can note that:
For the 2 cm cube
The lengths are
The areas are
The volume is
times greater.
2
times greater.
times greater.
4=2
8=2
For the 3 cm cube
The lengths are
The areas are
The volume is
times greater.
2
times greater.
times greater.
9=3
27 = 3
Note
If the lengths of a solid are increased by a factor, k, its surface area will increase by a
factor k 2 and its volume will increase by a factor k 3 .
Worked Example 1
(a)
Which of the triangles, A, B, C, D, shown below are similar?
A
B
70
6.13 cm
8 cm
70
12.26 cm
16 cm
60
50
60
9.04 cm
50
18.08 cm
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.2
C
D
50
3.5 cm
4 cm
6 cm
60
4.52 cm
70
(b)
How do the areas of the triangles which are similar compare?
Solution
(a)
First compare triangles A and B.
Here all the lengths of the sides are twice the length of the sides of triangle A, so
the two triangles are similar.
Then compare triangles A and C.
Here all the angles are the same in both triangles, so the triangles must be similar.
Finally, compare triangles A and D.
1
1
1
Note that 4 =
8 and 4.52 =
9.04 , but 3.5
6.13 .
2
2
2
So these triangles are not similar.
(b)
The lengths of the sides of triangle B are 2 times greater than the lengths of the
sides of triangle A, so the area will be 2 2 = 4 times greater.
The side lengths of triangle C are
3
of the side lengths of triangle A.
4
3
9
of the area of triangle A.
So the area will be =
4
16
The ratio of the areas of triangles C : A : B can be written as:
9
:1: 4
16
or
9 : 16 : 64
A
Worked Example 2
(a)
Explain why triangles ABE and ACD are similar.
(b)
Find the lengths of x and y.
(c)
Find the ratio of the area of ABE to BCDE.
4
As the lines BE and CD are parallel,
= ACD
ABE
and
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
= ADC
AEB
9
Solution
(a)
B
6
y
C
33.2
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
As the vertex A, is common to both triangles,
= EAB
DAC
So the three angles are the same in both triangles and therefore they are similar.
(b)
Comparing the sides BE and CD, the lengths in the larger triangle are 1.5 times
the lengths in the smaller triangle. Alternatively, it can be stated that the ratio of
the lengths is 2 : 3.
So the length AC will be 1.5 times the length AB.
AC = 1.5 6
= 9
y = 3
So
AD = 1.5 AE ,
In the same way,
so
4 + x = 1.5 x
4 = 0.5 x
x
(c)
= 8
As the lengths are increased by a factor of 1.5 or
3
for the larger triangle, the
2
2
3
areas will be increased by a factor of 1.52 or . We can say that the ratio of
2
the areas of the triangles is 1 : 2.25 or 1 :
9
or 4 : 9.
4
If the area of triangle ABE is 4k, then the area of triangle ACD is 9k and hence the
area of the quadrilateral BCDE is 5k.
So the ratio of the area of ABE to BCDE is 4 : 5.
Worked Example 3
The diagrams show two similar triangles.
D
A
5 cm
3 cm
4 cm
B
F
If the area of triangle DEF is 26.46 cm2, find the lengths of its sides.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
10
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.2
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
Solution
If the lengths of the sides of triangle DEF are a factor k greater than the lengths of the sides
of triangle ABC, then its area will be a factor k 2 greater than the area of ABC.
1
43
2
Area of ABC =
= 6 cm 2 .
So
6 k 2 = 26.46
k 2 = 4.41
k =
4.41
= 2.1
So the lengths of the sides of triangle DEF will be 2.1 times greater than the lengths of the
sides of triangle ABC.
DE = 2.1 5
= 10.5 cm
DF = 2.1 3
= 6.3 cm
EF = 2.1 4
= 8.2 cm
Worked Example 4
A can has a height of 10 cm and has a volume of 200 cm 3 . A can with a similar shape
has a height of 12 cm.
(a)
Find the volume of the larger can.
(b)
Find the height of a similar can with a volume of 675 cm 3 .
Solution
(a)
The lengths are increased by a factor of 1.2, so the volume will be increased by a
factor of 1.2 3 .
Volume = 200 1.2 3
= 345.6 cm 3
(b)
If the lengths are increased by a factor of k, then the volume will be increased by k 3 .
675 = 200 k 3
k 3 = 3.375
k =
3.375
= 1.5
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
11
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.2
So the height must be increased by a factor of 1.5, to give
height = 1.5 10
= 15 cm
Exercises
1.
Which of the triangles below are similar? Diagrams are not drawn to scale.
A
B
5 cm
78.5
60
6 cm
57.1
8 cm
4 cm
30
7 cm
6.92 cm
44.4
D
60
12 cm
20 cm
11 cm
30
14 cm
F
56 cm
44.4
1 cm
48 cm
44 cm
78.5
2.
57.1
The diagram shows 2 similar triangles.
12.99
4.33
5
60
C
F
(a)
Copy the triangles and label all the angles and the lengths of all the sides.
(b)
How do the areas of the two triangles compare?
(Express your answer as a ratio.)
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
12
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
33.2
3.
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
The diagram shows two similar rectangles, ABCD and EFGH.
E
A
B
2 cm
6 cm
C
6 cm
Find the lengths of AB and EH if the ratio of the area of ABCD to the area of
EFGH is:
(a)
4.
1:4
(b)
4 : 9.
A
The diagram shows two regular hexagons and AB = BC .
(a)
(b)
What is the ratio of the area of the smaller
hexagon to the area of the larger hexagon?
I
K
What is the ratio of the area of the smaller
hexagon to that of the shaded area?
F
5.
(a)
Explain why the triangles
ABE and ACD are similar.
(b)
Find the lengths of:
(i)
AD
(ii)
DE
(iii)
BC
6 cm
7 cm
112
2 cm
(c)
Find the ratio of
the areas of:
(i)
ABE to ACD
(ii)
ABE to BCDE.
112
6.
5 cm
(a)
Explain why ABE and ACD are similar triangles.
(b)
What can be deduced about the lines BE and CD?
(c)
Find the lengths x and y.
49.5
3 cm
7.5 cm
B
22.3
(d)
Find the ratio of the area of the triangle ABE
to the area of the quadrilateral BCDE.
6 cm
4 cm
108.2
x
y
D
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
13
33.2
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
7.
A bottle has a height of 8 cm and a volume of 30 cm 3 . Find the volume of
similar bottles of heights:
(a)
8.
9.
12 cm
(b)
10 cm
(c)
20 cm.
A box has a volume of 50 cm 3 and a width of 6 cm. A similar box has a width of
12 cm.
(a)
Find the volume of the larger box.
(b)
How many times bigger is the surface area of the larger box?
A packet has the dimensions shown in the diagram.
All the dimensions are increased by 20%.
(a)
Find the percentage increase in:
(i)
surface area
(ii)
volume.
30 cm
(b)
Find the percentage increase needed in the
dimensions of the packet to increase the
volume by 50%.
CRISPY
BITES
for
CATS
8 cm
20 cm
10.
11.
Two similar cans have volumes of 400 cm 3 and 1350 cm 3 .
(a)
Find the ratio of the heights of the cans.
(b)
Find the ratio of the surface areas of the cans.
One box has a surface area of 96 cm 2 and a height of 4 cm. A second similar box
has a volume of 1728 cm 3 and a surface area of 864 cm 2 .
Find:
(a)
the height of the larger box
(b)
the volume of the smaller box.
X
12.
Diagram not
accurately drawn
18.9 cm
A
4.5 cm
O
15 cm
(a)
Calculate the length of OY.
(b)
Calculate the size of angle XOY.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
14
33.2
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
13.
Triangles ABC, PQR and HIJ are all similar.
Not to
Not to scale
12.5 cm
30
10 cm
5 cm
5 cm
P
(a)
Calculate the length of AB.
(c)
Calculate the length of HJ.
(b)
What is the size of angle B?
14.
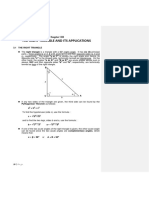
I stood 420 m away from the tallest building in Singapore. I held a piece of
wood 40 cm long at arms length, 60 cm away from my eye. The piece of wood,
held vertically, just blocked the building from my view.
Use similar triangles to calculate the height, h metres, of the building.
15.
AD = 4 cm , BC = 6 cm , angle BCD = 35 .
BD is perpendicular to AC.
N
6 cm
Not to scale
(a)
Calculate BD.
(b)
Calculate angle BAC.
(c)
Triangle A B C is similar to triangle ABC.
The area of triangle A B C is nine times the area of triangle ABC.
35
A
(i)
What is the size of angle A B C ?
(ii)
Work out the length of B C .
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
15
4 cm
33.2
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
16.
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
A roof has a symmetrical frame, with dimensions as shown.
AB = BC
PR = AP
= 90
ATB
Not to scale
5m
R
5m
(a)
(b)
17.
T
18 m
(i)
Write down a triangle which is similar to triangle ABC.
(ii)
Calculate the length PR.
Calculate the value of angle BAT.
Two wine bottles have similar shapes. The standard bottle has a height of 30 cm.
The small bottle has a height of 23.5 cm.
Not to scale
30 cm
23.5 cm
Standard
bottle
Small
bottle
(a)
Calculate the ratio of the areas of the bases of the two bottles.
Give your answer in the form n : 1.
(b)
What is the ratio of the volumes of the two bottles?
Give your answer in the form n : 1.
(c)
Is it a fair description to call the small bottle a 'half bottle'?
Give a reason for your answer.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
16
33.2
MEP Jamaica: STRAND I
18.
UNIT 33 Congruence and Similarity: Student Text
The normal size and selling price of small and medium toothpaste is shown.
SMALL SIZE
60 ml
MEDIUM SIZE
135 ml
50 cents
$1
A supermarket sells the toothpaste on special offer.
19.
(a)
The special offer small size has 20% more toothpaste for the same price.
How much more toothpaste does it contain?
(b)
The special offer medium size costs 90 cents for 135 ml. What is the
special offer price as a fraction of the normal price?
(c)
Calculate the number of ml per cent for each of these special offers.
Which of these special offers gives better value for money?
You must show your working.
(d)
(i)
The 60 ml content of the small size has been given to the nearest
10 ml. What is the smallest number of ml it can contain?
(ii)
The 135 ml content of the medium size has been given to the nearest
5 ml. What is the smallest number of ml it can contain?
(a)
Two bottles of perfume are similar to each other. The heights of the bottles
are 4 cm and 6 cm. The smaller bottle has a volume of 24 cm 3 .
Calculate the volume of the larger bottle.
(b)
Two bottles of aftershave are similar to each other. The areas of the bases
of these bottles are 4.8 cm 2 and 10.8 cm 2 . The height of the smaller
bottle is 3 cm. Calculate the height of the larger bottle.
CIMT and e-Learning Jamaica
17
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/18: D A F EDocumento1 paginaUSA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/18: D A F Eสฮาบูดีน สาและNessuna valutazione finora
- Birds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsDa EverandBirds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution of TriangleDocumento32 pagineSolution of TriangleJr Spark100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 0580 s20 QP 22 PDFDocumento12 pagine0580 s20 QP 22 PDFRaj MalkanNessuna valutazione finora
- π sq.cm - π sq .cm. π sq.cm. π sq.cmDocumento19 pagineπ sq.cm - π sq .cm. π sq.cm. π sq.cmWayne CasanovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 20 Further TrigonometryDocumento22 pagineTopic 20 Further TrigonometryAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress HardieNessuna valutazione finora
- Distance Between Two Points and A Point and A Line Worksheet AnswersDocumento3 pagineDistance Between Two Points and A Point and A Line Worksheet AnswersErwin Joaquin CabigaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Seamo Paper C 2016Documento7 pagineSeamo Paper C 2016Sherlly HastriNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 12 - Shape: Answer All QuestionsDocumento9 pagineUnit 12 - Shape: Answer All QuestionsAnonymous wgrNJjANessuna valutazione finora
- FB GeometryPolygonProblemsDocumento16 pagineFB GeometryPolygonProblemscatranker100% (1)
- 3na Pythagoras Theorem 1Documento5 pagine3na Pythagoras Theorem 1John GohNessuna valutazione finora
- FPS U2 SS PDFDocumento52 pagineFPS U2 SS PDFAnonymous 4VcUAodJ5Nessuna valutazione finora
- IMO Geometry Questions: Level: Intermediate Ref No: M01 Puzz Points: 10Documento26 pagineIMO Geometry Questions: Level: Intermediate Ref No: M01 Puzz Points: 10Jane ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Word Problems GoldDocumento2 pagineFractions, Decimals and Percentages Word Problems GoldMs BNessuna valutazione finora
- 75 Compound MeasuresDocumento8 pagine75 Compound MeasuresJoel GrayNessuna valutazione finora
- AMC Practice ProblemsDocumento6 pagineAMC Practice ProblemsPaul ChaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 WMTC Advanced Level Competition ProblemsDocumento15 pagine2019 WMTC Advanced Level Competition ProblemsAdrian Richard SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Circle ProblemsDocumento26 pagineGeometry Circle ProblemsMohit KalalNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lDocumento3 pagine8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lMahad AsimNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratio Word Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaRatio Word Problems PDFCarmenEnidOrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Area, Perimeter, Circumference Review-1Documento3 pagineArea, Perimeter, Circumference Review-1Ivăn Ôspiino100% (1)
- Chap 8 Review of Congruence and Similarity PDFDocumento32 pagineChap 8 Review of Congruence and Similarity PDFArahNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics WorksheetDocumento4 pagineKinematics WorksheetRobertYue100% (2)
- Grade 9 Cirlce Geometry Unit Test For MeganDocumento5 pagineGrade 9 Cirlce Geometry Unit Test For Meganapi-2731665380% (3)
- S1 Revision / Past Paper Questions / CH 1 - 4Documento8 pagineS1 Revision / Past Paper Questions / CH 1 - 4Kothakonda Praveen Kumar100% (2)
- Area of Shaded RegionDocumento8 pagineArea of Shaded Regionwakarnasirkhan100% (1)
- Similarity Worksheet, Geometry Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocumento2 pagineSimilarity Worksheet, Geometry Revision From GCSE Maths Tutorgcsemathstutor100% (1)
- Absolute Value Equations InequalitiesDocumento2 pagineAbsolute Value Equations InequalitiesE. Ryan PlankNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1 Summative TestDocumento1 paginaQ1 Summative TestArt BrandNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary 1 (GRADE 7) SAMPLE PAPERDocumento3 pagineSecondary 1 (GRADE 7) SAMPLE PAPERJoanna Marie CalibaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Straight Line Graphs WorksheetDocumento5 pagineStraight Line Graphs WorksheetDienta Alias100% (1)
- Congruence of TriangleDocumento15 pagineCongruence of TriangleShlok BaruaoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Whole NumbersDocumento38 pagineChapter 3 - Whole NumbersLy ShanNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoremDocumento8 pagineTheoremJoseph FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment in PhysicsDocumento7 pagineAssignment in PhysicsNorman Vryne CaduaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Maths Book RATIOSDocumento23 pagineGrade 10 Maths Book RATIOSMartin HillNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Expressions and Algebraic FractionsDocumento60 pagineChapter 8 Quadratic Expressions and Algebraic FractionsA Multicultural dinosaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Review For Quads TestDocumento9 pagineReview For Quads TestDwi Ika YuliantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Winter HW 2015 Math HL G12Documento9 pagineWinter HW 2015 Math HL G12MishaZetov100% (1)
- ProportionAndRates WEBDocumento36 pagineProportionAndRates WEByonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadratic Equation Word Problems WorksheetDocumento20 pagineQuadratic Equation Word Problems WorksheetQamar JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Indices LogDocumento25 pagineIndices Logadeskitoku100% (1)
- FOUNDATION - MATHS - STD7 - 8 - M92 - FLOW - PLANNER - SAMPLE - PAPERS of RAJESH SIR 2022-23Documento23 pagineFOUNDATION - MATHS - STD7 - 8 - M92 - FLOW - PLANNER - SAMPLE - PAPERS of RAJESH SIR 2022-23Ramkumar SundaramNessuna valutazione finora
- SMO 2011 Junior QuestionDocumento8 pagineSMO 2011 Junior Questionwmdsg0% (1)
- Imso Essay AnswerDocumento81 pagineImso Essay AnswerYessi Hasri67% (3)
- 2012 State Competition SolutionsDocumento15 pagine2012 State Competition SolutionsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- 3d Trigonometry PDFDocumento16 pagine3d Trigonometry PDFZoon AANessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Pui ChingDocumento48 pagine2nd Pui ChingKeith AndulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Linear Relations Practice TestDocumento9 pagineUnit 4 Linear Relations Practice Testwizard guyNessuna valutazione finora
- ITMO 2015 IndividualDocumento6 pagineITMO 2015 IndividualKanchit SaehoNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerpoints CongruenceDocumento104 paginePowerpoints CongruenceGlen GayagayNessuna valutazione finora
- Self Assessment - Digits and Place Value - Simplifying Expressions - Find Missing Angles in A Triangle - Designing Data Collection SheetsDocumento23 pagineSelf Assessment - Digits and Place Value - Simplifying Expressions - Find Missing Angles in A Triangle - Designing Data Collection SheetsAlex GoldsmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Similarity and CongruenceDocumento13 pagineSimilarity and Congruenceapi-456575733Nessuna valutazione finora
- STATISTICS - Mean Mode MedianDocumento4 pagineSTATISTICS - Mean Mode MedianHizami Li100% (1)
- Equation of A LineDocumento8 pagineEquation of A LinePichakornNessuna valutazione finora
- MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 2: 2013-DSE Math CPDocumento17 pagineMATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 2: 2013-DSE Math CPSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Depression and Cognitive Behavioural TherapyDocumento20 pagineDepression and Cognitive Behavioural TherapySandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 1 Question-Answer Book: 2013-DSE Math CP Paper 1Documento26 pagineMATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 1 Question-Answer Book: 2013-DSE Math CP Paper 1Sandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer: Section A (1) 1. 2. 3. (A) (B) 4. 5. 6 (A) (B) 7. 8. (A) (B) 17. (A) (B)Documento2 pagineAnswer: Section A (1) 1. 2. 3. (A) (B) 4. 5. 6 (A) (B) 7. 8. (A) (B) 17. (A) (B)Sandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- 都明白 chat too long, tell her it's a homework) (write down the name in notebook too)Documento1 pagina都明白 chat too long, tell her it's a homework) (write down the name in notebook too)Sandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra - Fun With Calendars: November 07 SMTWTHF SDocumento7 pagineAlgebra - Fun With Calendars: November 07 SMTWTHF SSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento1 paginaLesson PlanSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- NHS England Drugs List v15 2020 2021 PDFDocumento12 pagineNHS England Drugs List v15 2020 2021 PDFSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Havens2020 Article LinearFractionalTransformation PDFDocumento17 pagineHavens2020 Article LinearFractionalTransformation PDFSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- MathematicsDocumento28 pagineMathematicsSandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Surveying Fundamentals ASSIGNMENT 4Documento4 pagineConstruction Surveying Fundamentals ASSIGNMENT 4CRAIG JOSEPH100% (1)
- Previous Year Boards Questions: Chapter 6 - TrianglesDocumento4 paginePrevious Year Boards Questions: Chapter 6 - TrianglesshamNessuna valutazione finora
- HKMO1992heatans PDFDocumento11 pagineHKMO1992heatans PDFChai Usajai UsajaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Problem SetDocumento26 pagineMath Problem SetGlydle BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 - Q3 - Performance Task 3 SteDocumento1 paginaGrade 7 - Q3 - Performance Task 3 SteAnnaliza Paloma SangcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal MID Inggris Kls VDocumento2 pagineSoal MID Inggris Kls VRahma FadhillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Geometry 1Documento8 pagineCircle Geometry 1Rosemary ReynoldsNessuna valutazione finora
- G6 Math G3 Diagnostic Test DLMADocumento3 pagineG6 Math G3 Diagnostic Test DLMATeacher AppleNessuna valutazione finora
- Math ClearanceDocumento30 pagineMath ClearanceAngel Joy ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- LM Math 9 Module 7Documento87 pagineLM Math 9 Module 7Russel AraniegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento10 pagineTrigonometric FunctionsEdi MuhammNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016-2018 Geo NewDocumento18 pagine2016-2018 Geo NewElenca KyweNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 9 Trigonometry 4Documento3 pagineYear 9 Trigonometry 4api-445198464Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Class ViiiDocumento29 pagineMCQ Class Viiish867783% (6)
- Mathematics: Complete Question BankDocumento15 pagineMathematics: Complete Question Banksumit Tiwari 103Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 16Documento3 pagineMaths Class Ix Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 16DebanshNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 SAILINGSDocumento33 pagineCH 3 SAILINGSJeet Singh100% (1)
- Chapter III The Right Triangle 1Documento23 pagineChapter III The Right Triangle 1RonjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 NotesDocumento34 pagineChapter 6 NotesGabs GaryNessuna valutazione finora
- MATHS Puducherry Sahodaya SET BDocumento12 pagineMATHS Puducherry Sahodaya SET BAura100% (1)
- I. Multiple Choice Direction: Read and Understand Carefully The Following Questions and Encircle The Correct AnswerDocumento4 pagineI. Multiple Choice Direction: Read and Understand Carefully The Following Questions and Encircle The Correct AnswerTomoe NanamiNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2Documento3 pagineCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2Monika SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8B Test Review: Find The Measure of The Arc or Angle IndicatedDocumento6 pagineUnit 8B Test Review: Find The Measure of The Arc or Angle IndicatedVincent GiuntaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trig Formulae: Addition Formulae: Double AngleDocumento1 paginaTrig Formulae: Addition Formulae: Double AngleMaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 Module 8Documento24 pagineMathematics: Quarter 3 Module 8master hamsterNessuna valutazione finora
- Dish EndDocumento5 pagineDish EndalexnomitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap29 - 472-486Documento15 pagineChap29 - 472-486ommathNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry: Lines and AnglesDocumento45 pagineGeometry: Lines and AnglesajayNessuna valutazione finora
- All Math FormulasDocumento27 pagineAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)