Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - PDF-DT
Caricato da
tomardivyaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - PDF-DT
Caricato da
tomardivyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
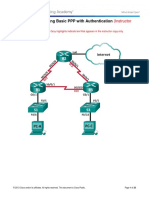
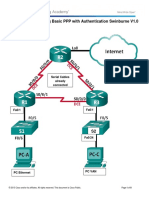
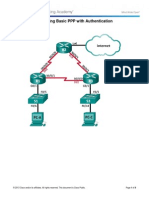
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
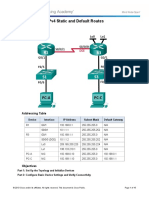
Topology
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
Addressing Table
Device
R1
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/1
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0 (DCE)
192.168.12.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.13.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
Lo0
209.165.200.225
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.12.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1 (DCE)
192.168.23.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/1
192.168.3.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0 (DCE)
192.168.13.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.23.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
PC-A
NIC
192.168.1.3
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
PC-C
NIC
192.168.3.3
255.255.255.0
192.168.3.1
R2
R3
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
Part 2: Troubleshoot the Data Link Layer
Part 3: Troubleshoot the Network Layer
Background / Scenario
The routers at your company were configured by an inexperienced network engineer. Several errors in the
configuration have resulted in connectivity issues. Your manager has asked you to troubleshoot and correct
the configuration errors and document your work. Using your knowledge of PPP and standard testing
methods, find and correct the errors. Ensure that all of the serial links use PPP CHAP authentication, and that
all of the networks are reachable.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with
Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco
IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used.
Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary
from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the
correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you
are unsure, contact your instructor.
Required Resources
3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
2 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology, configure basic settings on the PC hosts, and load
configurations on the routers.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Step 2: Configure the PC hosts.
Step 3: Load router configurations.
Load the following configurations into the appropriate router. All routers have the same passwords. The
privileged EXEC mode password is class. The password for console and vty access is cisco. All serial
interfaces should be configured with PPP encapsulation and authenticated with CHAP using the password of
chap123.
Router R1 Configuration:
hostname R1
enable secret class
no ip domain lookup
banner motd #Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!#
username R2 password chap123
username R3 password chap123
interface g0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
interface s0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
clock rate 128000
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
interface s0/0/1
ip address 192.168.31.1 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication pap
exit
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
passive-interface g0/1
exit
line con 0
password cisco
logging synchronous
login
line vty 0 4
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
password cisco
login
Router R2 Configuration:
hostname R2
enable secret class
no ip domain lookup
banner motd #Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!#
username R1 password chap123
username r3 password chap123
interface lo0
ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252
interface s0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
no shutdown
interface s0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252
clock rate 128000
no shutdown
exit
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
default-information originate
exit
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 loopback0
line con 0
password cisco
logging synchronous
login
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
Router R3 Configuration:
hostname R3
enable secret class
no ip domain lookup
banner motd #Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!#
username R2 password chap123
username R3 password chap123
interface g0/1
ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
no shutdown
interface s0/0/0
ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252
clock rate 128000
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
no shutdown
interface s0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
no shutdown
exit
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
passive-interface g0/1
line con 0
password cisco
logging synchronous
login
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
Step 4: Save your running configuration.
Part 2: Troubleshoot the Data Link Layer
In Part 2, you will use show commands to troubleshoot data link layer issues. Be sure to verify settings, such
as clock rate, encapsulation, CHAP, and usernames/passwords.
Step 1: Examine the R1 configuration.
a. Use the show interfaces command to determine whether PPP has been established on both serial links.
From the show interfaces results for S0/0/0 and S0/0/1, what are possible issues with the PPP links?
b. Use the debug ppp authentication command to view real-time PPP authentication output during
troubleshooting.
R1# debug ppp authentication
PPP authentication debugging is on
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 5 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
c.
Use the show run interface s0/0/0 command to examine the settings on S0/0/0.
Resolve all problems found for S0/0/0. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
After correcting the issue, what information does the debug output provide?
d. Use the show run interface s0/0/1 command to examine the settings on S0/0/1.
Resolve all problems found for S0/0/1. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
After correcting the issue, what information does the debug output provide?
e. Use the no debug ppp authentication or undebug all command to turn off the debug PPP output.
f.
Use the show running-config | include username command to verify the correct username and
password configurations.
Resolve all problems found. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
Step 2: Examine the R2 configuration.
a. Use the show interfaces command to determine if PPP has been established on both serial links.
Have all links been established?
If the answer is no, which links need to be examined? What are the possible issues?
b. Use the show run interface command to examine links that have not been established.
Resolve all problems found for the interfaces. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
c.
Use the show running-config | include username command to verify the correct username and
password configurations.
Resolve all problems found. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 6 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
d. Use the show ppp interface serial command for the serial interface that you are troubleshooting.
Has the link been established?
Step 3: Examine the R3 configuration.
a. Use the show interfaces command to determine whether PPP has been established on both serial links.
Have all links been established?
If the answer is no, which links need to be examined? What are the possible issues?
b. Using the show run interface command to examine on any serial link that has not been established.
Resolve all problems found on the interfaces. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
c.
Use the show running-config | include username command to verify the correct username and
password configurations.
Resolve all problems found. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
d. Use the show interface command to verify that serial links have been established.
e. Have all PPP links been established?
f.
Can PC-A ping Lo0?
g. Can PC-A ping PC-C?
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall for pings between the PCs to succeed.
Part 3: Troubleshoot the Network Layer
In Part 3, you will verify that Layer 3 connectivity is established on all interfaces by examining IPv4 and OSPF
configurations.
Step 1: Verify that the interfaces listed in the Addressing Table are active and configured with
the correct IP address information.
Issue the show ip interface brief command on all routers to verify that the interfaces are in an up/up state.
Resolve all problems found. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
Step 2: Verify OSPF Routing
Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are advertised.
Resolve all problems found. Record the commands used to correct the configuration.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 7 of 8
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication
Can PC-A ping PC-C?
If connectivity does not exist between all hosts, then continue troubleshooting to resolve any remaining
issues.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall for pings between the PCs to succeed.
Router Interface Summary Table
Router Interface Summary
Router Model
Ethernet Interface #1
Ethernet Interface #2
Serial Interface #1
Serial Interface #2
1800
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
1900
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0
(G0/0)
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1
(G0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
2801
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0)
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1)
2811
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
2900
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0
(G0/0)
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1
(G0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many
interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router
class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device.
The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An
example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be
used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 8 of 8
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Da EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Da EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ritual 2 Turning Attraction Into LoveDocumento2 pagineRitual 2 Turning Attraction Into Lovekrlup0% (1)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDa EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDocumento8 pagine6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkParthPatel100% (8)
- Chapter 6 Coming of SpainDocumento4 pagineChapter 6 Coming of SpainJayvee MacapagalNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationDa EverandAdvanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDocumento23 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDaniel Ergicho0% (1)
- Concept of Leadership (Session-1) MARSDocumento14 pagineConcept of Leadership (Session-1) MARShudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar For UtiDocumento2 pagineFdar For UtiCARL ANGEL JAOCHICONessuna valutazione finora
- 1 1 4 6 Lab ConfiguringBasicRouterSettings PDFDocumento17 pagine1 1 4 6 Lab ConfiguringBasicRouterSettings PDFbi hekNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.5 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDocumento11 pagine6.4.3.5 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkfutjulyNessuna valutazione finora
- 17.7.6 Lab - Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues - ILMDocumento9 pagine17.7.6 Lab - Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues - ILMMariano PereyraNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Ob14 PPT 11Documento27 pagineRobbins Ob14 PPT 11daneshnedaieNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocumento15 pagine2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routesbalvinder singh50% (6)
- 4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDocumento10 pagine4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIAhmadHijaziNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMDocumento23 pagine3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMvincent67% (3)
- Lab - Configuring A Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and CCPDocumento30 pagineLab - Configuring A Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and CCPVasan Suryaßoyzz100% (1)
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDocumento13 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsADEL ANessuna valutazione finora
- Conspicuous Consumption-A Literature ReviewDocumento15 pagineConspicuous Consumption-A Literature Reviewlieu_hyacinthNessuna valutazione finora
- CN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualDocumento118 pagineCN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualLongo LaurisNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDocumento8 pagine9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocumento17 pagine3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí0% (2)
- 5.4.1.1 Lab - Configure An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) PDFDocumento21 pagine5.4.1.1 Lab - Configure An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) PDFIvan ZuritaNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNASv1 1 Chp08 Lab B RMT Acc VPN Instructor PDFDocumento33 pagineCCNASv1 1 Chp08 Lab B RMT Acc VPN Instructor PDFAhmadHijaziNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs - ILMDocumento18 pagine9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs - ILMJohann Neethling71% (17)
- 2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocumento8 pagine2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationVianey LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocumento8 pagine3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí17% (6)
- Configuring Zone Based Policy FirewallsDocumento13 pagineConfiguring Zone Based Policy FirewallsNorman Pal-og Madongit17% (6)
- 2675 Test12Documento11 pagine2675 Test12kinabapaul49Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3.12 Lab - Configure ZPFsDocumento12 pagine10.3.12 Lab - Configure ZPFsJesús EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT 504 - Lab - 3 Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI 11Documento11 pagineMIT 504 - Lab - 3 Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI 11umang patnaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-1-4-6-Lab-Configuring-Basic-Router-Settings-With-Ios-Cli - PDF EditedDocumento10 pagine1-1-4-6-Lab-Configuring-Basic-Router-Settings-With-Ios-Cli - PDF EditedYeab SraNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 - Skills ActivityDocumento11 pagineWeek 5 - Skills ActivitykonoweNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDocumento15 pagine1.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIJuan S. MorejónNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Com TestDocumento11 pagineData Com Testkinabapaul49Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDocumento6 pagine6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkMirela ȘorecăuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1.4.6 CiscoDocumento11 pagine1.1.4.6 CiscoZeratul322100% (2)
- Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended Acls: TopologyDocumento9 pagineLab - Configuring and Verifying Extended Acls: TopologyKlodine NogarNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.3.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsDocumento8 pagine9.3.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsSupinder SekhonNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMDocumento9 pagine4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMGuri DhillonNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 9 Lab - Configuring and Modifying Standard IPv4 ACLs - ILMDocumento10 pagineWeek 9 Lab - Configuring and Modifying Standard IPv4 ACLs - ILMAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy Firewalls-ALDO PUGLIESEDocumento21 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy Firewalls-ALDO PUGLIESEsheckie jarabaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocumento7 pagine6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesultracsokiNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-1 RSE-4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDocumento9 pagine10-1 RSE-4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIBala SubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- Configure ZPFsDocumento32 pagineConfigure ZPFsestebanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 05 - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDocumento18 pagineLab 05 - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsFernando MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDocumento13 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy Firewallscesar javierNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDocumento9 pagine9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDaniel Sandoval CaizatoaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3.1.6 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic Frame RelayDocumento6 pagine4.3.1.6 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic Frame Relayzadeli6381Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.1 - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDocumento9 pagineLab 3.1 - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsRas Abel BekeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: Taller 2Documento28 pagineLab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: Taller 2murcielago189Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3 WorksheetDocumento11 pagineLab 3 Worksheetpzydf6wjxvNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallsDocumento15 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy FirewallselizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4Documento8 pagineLab 4pzydf6wjxvNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 - Raziq - w1 - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDocumento9 pagine05 - Raziq - w1 - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIrazqkimi2022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocumento7 pagineWeek 6 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI: TopologyDocumento4 pagineLab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI: TopologyFaritz AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.3 - ZachDocumento5 pagine6.4.3.3 - ZachZack ShoreNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication Swinburne V1.0Documento8 pagine3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication Swinburne V1.0Ishu GaneshaMuralidharanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMDocumento16 pagine4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMCte eduNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratorio 3@Documento9 pagineLaboratorio 3@carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDa EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To BinaryDocumento4 pagine8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To BinarytomardivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ InstructionsDocumento3 pagine2.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ Instructionstomardivya0% (1)
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - PDF-DTDocumento8 pagine3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - PDF-DTtomardivya0% (2)
- 1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTDocumento1 pagina1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTtomardivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTDocumento1 pagina1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTtomardivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTDocumento1 pagina1.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructions - docx-DTtomardivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Walmart Assignment1Documento13 pagineWalmart Assignment1kingkammyNessuna valutazione finora
- If He Asked YouDocumento10 pagineIf He Asked YouLourdes MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Hermeneutical Phenomenology and Human Enviroment SystemDocumento12 pagineHermeneutical Phenomenology and Human Enviroment SystemAllen Rose Buenaflor BuenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 4 Basic ConsolidationDocumento3 paginePart 4 Basic Consolidationtαtmαn dє grєαtNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingles Semana 11. P6. 2Q. 4egb. A y BDocumento2 pagineIngles Semana 11. P6. 2Q. 4egb. A y BWendisilla BelenchisNessuna valutazione finora
- Test - To Kill A Mockingbird - Chapter 17 - Quizlet PDFDocumento2 pagineTest - To Kill A Mockingbird - Chapter 17 - Quizlet PDFchadlia hadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansys Flu - BatDocumento30 pagineAnsys Flu - BatNikola BoskovicNessuna valutazione finora
- House of Wisdom - Bayt Al Hikma (For Recording) - ArDocumento83 pagineHouse of Wisdom - Bayt Al Hikma (For Recording) - ArMaeda KNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Statistics For Business AnalyticsDocumento15 pagineBasic Statistics For Business AnalyticsNeil Churchill AniñonNessuna valutazione finora
- NKU Athletic Director Ken Bothof DepositionDocumento76 pagineNKU Athletic Director Ken Bothof DepositionJames PilcherNessuna valutazione finora
- City Living: Centro de Lenguas ExtranjerasDocumento2 pagineCity Living: Centro de Lenguas Extranjerascolombia RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Rosa Chavez Rhetorical AnalysisDocumento7 pagineRosa Chavez Rhetorical Analysisapi-264005728Nessuna valutazione finora
- I. Title: "REPAINTING: Streetlight Caution Signs"Documento5 pagineI. Title: "REPAINTING: Streetlight Caution Signs"Ziegfred AlmonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Basilio, Paul Adrian Ventura R-123 NOVEMBER 23, 2011Documento1 paginaBasilio, Paul Adrian Ventura R-123 NOVEMBER 23, 2011Sealtiel1020Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Palace in TimeDocumento6 pagineA Palace in TimeSonkheNessuna valutazione finora
- Incremental Analysis 2Documento12 pagineIncremental Analysis 2enter_sas100% (1)
- How To Access Proquest: Off-CampusDocumento9 pagineHow To Access Proquest: Off-CampusZav D. NiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 12 - Gerund and Infinitive (Task)Documento1 paginaUnit 12 - Gerund and Infinitive (Task)AguNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between C, C++ and JavaDocumento3 pagineDifference Between C, C++ and Javasknandish587Nessuna valutazione finora
- NefelometriaDocumento25 pagineNefelometriaJuan Marcos Martinez ZevallosNessuna valutazione finora
- S.I.M. InnovaDocumento51 pagineS.I.M. InnovaPauline Karen ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Transistor Miniature FM TransmitterDocumento2 pagine4 Transistor Miniature FM Transmitterrik206Nessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Report-2020Documento77 pagineInternship Report-2020Hossen ImamNessuna valutazione finora
- Cayman Islands National Youth Policy September 2000Documento111 pagineCayman Islands National Youth Policy September 2000Kyler GreenwayNessuna valutazione finora