Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bio Review
Caricato da
krusnik93Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bio Review
Caricato da
krusnik93Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Properties of life
Order
o Ordered organization
Regulation
o Organism can adjust its internal environment
Growth and Development
o Info carried by genes controls the pattern of growth and
development
Energy utilization
o Organisms take in energy used to perform all of lifes activities
Response to the environment
o Ex. Venus flytrap responds to touch on surface
Reproduction
o Organisms reproduce their own kind
Evolution
o Reproduction underlies to capacity of population changes over time
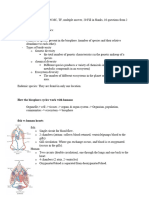
Levels of life
-
Biosphere
o All environments that support life
Ecosystems
o Consists of all organisms living in a particular area(Living and nonliving)
Example: A tide pond in the Galapagos
Communities
o All the organisms within the tide pool ^^^ see example
Populations
o Groups of interacting individuals of one species
Organisms
o An individual living thing
Organ systems and organs
o Systems within the body such as circulatory, muscular, etc.
Tissues
o Each organ is made up of different tissues
Cells
o The smallest unit that can display all characteristics of life
Organelles
o Functional components of cells such as the nucleus
Molecules and atoms
o Molecules are clusters of atoms. Each cell consists of a large
number of chemicals that function together to give the cell the
properties we recognize as life.
Ecosystems
Consumers
o Animals, humans, mammals
Dependent on producers
Producers
o Plants, trees, photosynthetic organisms
Convert light energy to chemical energy(food)
Decomposers
o Fungi, algae, in soil
Decompose waste products and the remains of deceased
organisms
2 Major cell types
-
Prokaryotes
o Simple structure
o Smaller
o Nucleus is not enclosed in a membrane
o Lacks most organelles
Eukaryotes
o Larger
o Most complex structure
o Nucleus enclosed in a membrane
o Contains many types of organelles
Domains
-
Eukarya
o Kingdoms
Plantae, Animalia, Fungi
Plants produce their own sugars and other foods by
photosynthesis
Fungi are decomposers which digest dead organisms
Animals ingest and digest other animals
Bacteria
o Prokaryotic cells
Archea
o Prokaryotic cell type
o Similar to eukaryotes genetically
o Extremophile
Darwin
-
Evolution
Natural selection
o Those with the best traits survive
Artificial selection
Selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals
Experimental process
-
Scientific Method
o Observation
o Question
o Hypothesis
Deduction(if then logic)
o Prediction
o Experiment
Theory
o Much broader in scope
o Needs extensive and varied evidence
Atomic Structure
-
Nucleus
o The atoms central core which consists of protons and neutrons
Electrons
o Negatively charged subatomic particle
Protons(Positive charge) Neutrons(Negative charge)
Chemical bonds
-
Ionic
o The attraction between oppositely charged ions
Covalent
o 2 atoms share one or more pairs of outer shell electrons(molecules)
Hydrogen
o A type of covalent bond that is shared unequally. Because it is
equally shared it is a polar molecule
Water
-
Cohesion is how water molecules stick together
High surface tension
Resistance to temperature change
Can moderate temperature
PH scale
o 1-6 is an acid(stomach acids, lemons)
o 7 is neutral(water)
o 8 and up is a base(bleach, oven cleaner)
o Blood is between 7 and 8
Buffers
o Substances that resist PH change
Accepts H+ ions when in excess
Donates H+ ions in depletion
Hydrophillic
o Love of water
Hydrophobic
o Aversion to water
Carbon
-
Carbon is a versatile atom.
o It has four electrons in an outer shell that holds eight.
o Carbon can share its electrons with other atoms to form up to four
covalent bonds.
Carbon can use its bonds to
o Attach to other carbons
o Form an endless diversity of carbon skeletons
Hydrocarbons
o organic molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Life Science IntroDocumento30 pagineLife Science IntroJc AwarayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology NotesDocumento32 pagineBiology NotesTaylor BonnetNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1 - 1st Quarter ReviewerDocumento5 pagineBiology 1 - 1st Quarter ReviewerPat RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- BioDocumento5 pagineBioashyfairyprincessNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1 - Intro BiosciDocumento57 pagineLec 1 - Intro BiosciKristine VailNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 1 - Living Organisms and The EnvironmentDocumento11 pagineSection 1 - Living Organisms and The EnvironmentOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocumento16 pagineCharacteristics of Living OrganismsSayeef MahdiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 What Is Life? Characteristics of Living SystemsDocumento6 pagine1.1 What Is Life? Characteristics of Living Systemsspencer_jordan_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Is 2 Reviewer For LT1Documento10 pagineIs 2 Reviewer For LT1Lslall SjdbbhssNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Concepts For Organization of Living ThingsDocumento4 pagineKey Concepts For Organization of Living ThingsAnonymous phZt0NNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology 1 (1st Quarter) ReviewerDocumento6 pagineGeneral Biology 1 (1st Quarter) ReviewerAthena Marielle Lorenzo100% (4)
- Living Organisms and The Environment PDFDocumento29 pagineLiving Organisms and The Environment PDFOsmany MadrigalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology, Chapter 1 ReviewerDocumento1 paginaBiology, Chapter 1 ReviewerDrew Dioso0% (1)
- Bio Cheat Sheet MasterDocumento7 pagineBio Cheat Sheet MasterChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Local Media2210703659562817356Documento41 pagineLocal Media2210703659562817356Regie MorialNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocumento2 pagineIntroduction To Life ScienceLiezelMagbooNessuna valutazione finora
- BiologyDocumento8 pagineBiologyAyaz ChampNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolving Concept of LifeDocumento34 pagineEvolving Concept of Lifephilipjayms12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction On LifeDocumento33 pagineIntroduction On LifeKeren Joy WiganNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 BIO101Documento9 pagineLecture 1 BIO101Ahamadul Islam OnonnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Bio2Documento46 pagineIntro To Bio2JuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDocumento8 pagineThe Characteristics of Living ThingsMiy El NinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final SheetDocumento20 pagineFinal SheetSara AlkhaldiNessuna valutazione finora
- VCE Biology Chapter 2 NotesDocumento9 pagineVCE Biology Chapter 2 NotesParis JoannidesNessuna valutazione finora
- Module Q.2 Els 2Documento3 pagineModule Q.2 Els 2altheaveniceholanda02Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2006 Biology NotesDocumento5 pagine2006 Biology NotesroseNessuna valutazione finora
- Living World: Nature and Scope of Biology: Biology Branches of BiologyDocumento11 pagineLiving World: Nature and Scope of Biology: Biology Branches of BiologySIDHARTH SBNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento22 pagineBiochemistryJeremy ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Bisc 102 NotesDocumento49 pagineBisc 102 NotesEvonda HollisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pyramid) : Could Cause Malfunctions To The Brain Although All The "Parts" Are There.Documento5 paginePyramid) : Could Cause Malfunctions To The Brain Although All The "Parts" Are There.Shivana SeeramNessuna valutazione finora
- LifeDocumento35 pagineLifeJannette Jane DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of The Biological Organization Subatomic ParticlesDocumento4 pagineStages of The Biological Organization Subatomic ParticlesBéla JózsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Lecture 1Documento16 pagineBiochemistry Lecture 1azraawsNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Science 7 NotesDocumento22 pagineFull Science 7 Notesnoelcaimoy45Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Preliminary Study NotesDocumento23 pagineBiology Preliminary Study NotesNabiha SyedaNessuna valutazione finora
- SOL Biology Review GuideDocumento26 pagineSOL Biology Review GuidehtyhongNessuna valutazione finora
- Define BiologyDocumento11 pagineDefine BiologyPatricia PaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Living ThingsDocumento14 pagineLiving Thingscourse heroNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Gen BioDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Gen BioPearl Madeleine FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Origin of LifeDocumento30 pagineThe Origin of LifeYvonne Basco100% (1)
- Bio 101 Study Guide Test 1Documento8 pagineBio 101 Study Guide Test 1mattyg35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guideline Note - Chap 2Documento34 pagineGuideline Note - Chap 2Clevendon ChristopherNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 102 - Chapter 1Documento6 pagineBiology 102 - Chapter 1Lucy KillackyNessuna valutazione finora
- BiologyDocumento86 pagineBiologyhoxojew752Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 103 Lecture 1Documento25 pagineBIO 103 Lecture 1Samiul Hasan Pranto100% (1)
- The Evolving Concept of LifeDocumento7 pagineThe Evolving Concept of LifeStopnaplsNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Documento8 pagineModule 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Nathaniel Victor BalerNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Plants and Animals NotesDocumento11 pagineClassification of Plants and Animals Notesmahammalik20142023Nessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento4 pagineUntitledRona Liee PelaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialDocumento9 pagineBiology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialRachel FrankenfieldNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Introduction To Biology-ESADocumento45 pagine1-Introduction To Biology-ESA230102912Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Human Biology, Science and SocietyDocumento51 pagineChapter 1 Human Biology, Science and SocietynanoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocumento12 pagineUnifying Themes in The Study of LifeReyes KathleenNessuna valutazione finora
- L6S1. Introduction To Life ScienceDocumento22 pagineL6S1. Introduction To Life ScienceSichayra GamotiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes in Biology Zoology LectureDocumento18 pagineNotes in Biology Zoology LectureSebastian NarcisoNessuna valutazione finora
- General BiologyDocumento173 pagineGeneral BiologyAshley GaerlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Resumen Biología 1. What Is Earth Like?Documento3 pagineResumen Biología 1. What Is Earth Like?Jesus Hernandez SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Biology NotesDocumento43 pagine2009 Biology NotesRyan NostalgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells and Organization: What Is Life?: The Seven Characteristics of LifeDocumento9 pagineCells and Organization: What Is Life?: The Seven Characteristics of LifeClarisse MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- FR-A800 Plus For Roll To RollDocumento40 pagineFR-A800 Plus For Roll To RollCORTOCIRCUITANTENessuna valutazione finora
- ABC of Effective WritingDocumento4 pagineABC of Effective Writingprada85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asymetry Analysis of Breast Thermograma Using Automated SegmentationDocumento8 pagineAsymetry Analysis of Breast Thermograma Using Automated Segmentationazazel17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento16 pagineChapter 1MulugetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary Watchdogs Domesticated: Conduct of Punjabi Print Media in Punjab During The Assembly Elections of 2007Documento20 pagineContemporary Watchdogs Domesticated: Conduct of Punjabi Print Media in Punjab During The Assembly Elections of 2007Sarban MalhansNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlue AdDocumento153 pagineVlue AdsindhushankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chris Baeza: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineChris Baeza: Objectiveapi-283893712Nessuna valutazione finora
- Of Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFDocumento215 pagineOf Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFCNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading8 PilkingtonDocumento8 pagineReading8 Pilkingtonab_amyNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject: Animal Breeding and Genetics - II Course Code: ABG-301Documento2 pagineSubject: Animal Breeding and Genetics - II Course Code: ABG-301Hamid Ali AfridiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON2100 CO Abdool W21Documento5 pagineECON2100 CO Abdool W21Imran AbdoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingles Nivel 2Documento119 pagineIngles Nivel 2Perla Cortes100% (1)
- F07 hw07Documento2 pagineF07 hw07rahulNessuna valutazione finora
- A Neural Network Based System For Intrusion Detection and Classification of AttacksDocumento6 pagineA Neural Network Based System For Intrusion Detection and Classification of AttacksbharadwajrohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Examination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFDocumento2 pagineExamination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFAntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Jain Gayatri MantraDocumento3 pagineJain Gayatri MantraShil9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad MedinaceliDocumento3 pagineLolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad Medinacelichatmche-06Nessuna valutazione finora
- K 46 Compact Spinning Machine Brochure 2530-V3 75220 Original English 75220Documento28 pagineK 46 Compact Spinning Machine Brochure 2530-V3 75220 Original English 75220Pradeep JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Handbook MCCDocumento32 pagineStudent Handbook MCCeyusuf74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teruhisa Morishige: Mazda Engineering StandardDocumento9 pagineTeruhisa Morishige: Mazda Engineering Standardmohammad yazdanpanahNessuna valutazione finora
- A Research Presented To Alexander T. Adalia Asian College-Dumaguete CampusDocumento58 pagineA Research Presented To Alexander T. Adalia Asian College-Dumaguete CampusAnn Michelle PateñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Henry FayolDocumento4 pagineHenry FayolFaryal MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineCheat SheetFrancis TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Potato Lab ReportDocumento10 paginePotato Lab ReportsimplylailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anglicanism QuestionsDocumento36 pagineAnglicanism QuestionsspringsdanielconceptNessuna valutazione finora
- Reseller Handbook 2019 v1Documento16 pagineReseller Handbook 2019 v1Jennyfer SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Pplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of IndiaDocumento16 paginePplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of Indiagharib mahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Mil CompiledDocumento62 pagineMil CompiledDan VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- SKZ TrackDocumento6 pagineSKZ TrackOliviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Denmark Bayan enDocumento3 pagineDenmark Bayan enTyba314Nessuna valutazione finora