Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Rec Ept or Agonist Potency Order Selected Action of
Caricato da
zuftDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rec Ept or Agonist Potency Order Selected Action of
Caricato da
zuftCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rec
ept
Agonist potency
Selected action
order
of agonist
or
Smooth
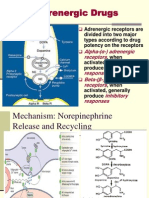
Mechanism
1:
Norepinephrine > epi
A, B
nephrine >> isoprena musclecontraction,mydri
ase C (PLC)
, D
line
asis,vasoconstrictionin
activated,IP3,a
the skin, muscosa and
nd DAG, rise
abdominalviscera &
in calcium
sphincter contraction of
the GI tract andurinary
Gq:phospholip
Agonists
(Alpha-1
agonists)
bladder
Nor
adrenal
ine
Ph
enylep
hrine
Met
hoxami
ne
Cir
azoline
Xyl
ometaz
oline
Mid
odrine
Met
aramin
ol
Antagonis
ts
(Alpha-1
blockers)
Alf
uzosin
Do
xazosi
n
Ph
enoxy
benza
mine
Ph
entola
mine
Pr
azosin
Ta
msulo
sin
Ter
azosin
Tra
Chl
zodon
oroethy
e
lclonidi
ne
(TCA:s)
Am
itriptyli
ne
Clo
mipra
mine
Do
xepin
Tri
mipra
mine
Ty
pical
and
atypic
al
antips
ychotic
s
Antihistam
ines (H1
antagonist
s)
2:
Epinephrine norepi
Smooth musclemixed
Gi: adenylate
A, B
nephrine >> Isopren
effects, norepinephrine
cyclaseinactiv
,C
aline
(noradrenaline)
ated,cAMP do
inhibition,plateletactivati
wn
(Alpha-2
agonists)
Ag
matine
De
xmedet
omidin
e
Me
detomi
dine
on
Ro
mifidin
e
Clo
nidine
Hy
droxyz
ine
(Alpha-2
blockers)
Ph
entola
mine
Yo
himbin
e
Ida
zoxan
Ati
pamez
ole
Tra
zodon
e
Isoprenaline > epine
PositiveChronotropic,Dr
Gs: adenylate
phrine = norepinephr
omotropicand inotropicef
cyclaseactivat
ine
fects,
ed,cAMP up
increasedamylasesecreti
on
Chl
oroethy
lclonidi
ne
Bri
monidi
ne
Det
omidin
e
Lof
exidine
Xyl
azine
Tiz
anidine
Gu
anfacin
e
Ami
traz
Do
butami
ne
Iso
prenali
ne
Nor
adrenal
ine
Ty
pical
and
atypic
al
antips
ychotic
s
(Beta
blockers)
Me
toprolo
l
Ate
nolol
Bis
oprolol
Pr
oprano
lol
Ti
molol
Ne
bivolol
Vor
tioxeti
ne
(Short/long
)
Sal
butamo
l(Albut
erol in
USA)
Bito
lterol
mesyla
te
(Beta
For blockers)
moterol
But
oxami
Iso
ne
prenali
ne
Ti
molol
Lev
Gs: adenylate
Isoprenaline > epine
2
phrine >> norepinep
hrine
Muscle relaxation
(Ex.Bronchodilation)
cyclaseactivat
ed,cAMP up
(alsoGi,
see 2)
albuter
ol
Met
aproter
enol
Sal
meterol
Ter
butalin
e
Rit
odrine
Pr
oprano
lol
L796568
[4]
Isoprenaline = norepi Enhance lipolysis,
Gs: adenylate
nephrine > epinephri
promotes relaxation of
cyclaseactivat
ne
detrusor in the bladder
ed,cAMP up
Ami
begron
Sol
abegro
n
SR
59230
A
[5]
There is no 1C receptor. At one time, there was a subtype known as C, but was found to be identical
to one of the previously discovered subtypes. To avoid confusion, naming was continued with the
letter D.
receptors
receptors have several functions in common, but also individual effects. Common (or still
unspecified) effects include:
Vasoconstriction of veins[6]
Decrease motility of smooth muscle in gastrointestinal tract[7]
1 receptor[edit]
Main article: Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor
1-adrenergic receptors are members of the Gq protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Upon
activation, a heterotrimeric G protein, Gq, activates phospholipase C (PLC). The PLC
cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), which in turn causes an increase in inositol
triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerols (DAG). The former interacts with calcium channels of
endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum, thus changing the calcium content in a cell. This triggers
all other effects.
Specific actions of the 1 receptor mainly involve smooth muscle contraction. It
causes vasoconstriction in many blood vessels, including those of the skin, gastrointestinal
system, kidney (renal artery)[8] and brain.[9] Other areas of smooth muscle contraction are:
ureter
vas deferens
hair (arrector pili muscles)
uterus (when pregnant)
urethral sphincter
urothelium and lamina propria[10]
bronchioles (although minor due to the relaxing effect of 2 receptor on bronchioles)
blood vessels of ciliary body (stimulation causes mydriasis)
Further effects include glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis from adipose tissue[11] and liver, as well
as secretion from sweat glands[11] andNa+ reabsorption from kidney.[11]
Antagonists may be used primarily in hypertension, anxiety disorder, and panic attacks.
2 receptors
Main article: Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor
The 2 receptor couples to the Gi/o protein.[2] It is a presynaptic receptor, causing negative feedback
on, for example, norepinephrine. When NA is released into the synapse, it feeds back on the
2 receptor, causing less NA release from the presynaptic neuron. This decreases the effect of NA.
There are also 2 receptors on the nerve terminal membrane of the post-synaptic adrenergic neuron.
There are 3 highly homologous subtypes of 2 receptors: 2A, 2, and 2C.
Specific actions of the 2 receptor include:
Inhibition of insulin release in the pancreas.[11]
Induction of glucagon release from the pancreas.
contraction of sphincters of the gastrointestinal tract
negative feedback in the neuronal synapses - presynaptic inhibition of noradrenalin (NA)
release in CNS
increased thrombocyte aggregation
receptors[edit]
1 receptor[edit]
Main article: Beta-1 adrenergic receptor
Specific actions of the 1 receptor include:
Increase cardiac output by increasing heart rate (positive chronotropic effect), conduction
velocity (positive dromotropic effect), and stroke volume (by enhancing contractilitypositive
inotropic effect).
Increase renin secretion from juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney.
Increase ghrelin secretion from the stomach.[12]
2 receptor[edit]
Main article: Beta-2 adrenergic receptor
Beta-2 adrenergic receptor (PDB 2rh1), which stimulates cells to increase energy production and utilization.
The membrane is shown schematically with a gray stripe.
Specific actions of the 2 receptor include the following:
Smooth muscle relaxation, e.g. in bronchi,[11] GI tract (decreased motility).
Lipolysis in adipose tissue.[13]
Anabolism in skeletal muscle.[14][15]
Relax non-pregnant uterus
Relax detrusor urinae muscle of bladder wall
Dilate arteries to skeletal muscle
Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Inhibits insulin secretion
Contract sphincters of GI tract
Thickened secretions from salivary glands.[11]
Inhibit histamine-release from mast cells
Increase renin secretion from kidney
Relaxation of Bronchioles (salbutamol, a 2 agonist relieves bronchiole constriction)
Involved in brain - immune communication[16]
3 receptor[edit]
Main article: Beta-3 adrenergic receptor
Specific actions of the 3 receptor include:
Enhancement of lipolysis in adipose tissue. 3 activating drugs could theoretically be used as
weight-loss agents, but are limited by the side effect of tremors.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)Da EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Receptor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento7 pagineAdrenergic Receptor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChandra TappyNessuna valutazione finora
- ADR PharmacologyDocumento30 pagineADR PharmacologySumanth Kumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- 12adrenergic ReceptorDocumento5 pagine12adrenergic ReceptorZiedTrikiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Adrenergic SystemDocumento14 pagine2 Adrenergic SystemAli EllaffiNessuna valutazione finora
- SympathomimeticDocumento71 pagineSympathomimeticahmad tariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic DrugsDocumento58 pagineAdrenergic DrugsMuzammil Nawaz100% (1)
- SympathomimeticsDocumento25 pagineSympathomimeticsMirza Shaharyar BaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticholinergic DrugsDocumento6 pagineAnticholinergic Drugshlouis8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Effects: Alpha Receptor GeneralDocumento4 pagineEffects: Alpha Receptor GeneralNishanthy PirabakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Agonists 1Documento90 pagineAdrenergic Agonists 1OMAR NASSERNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of Action of RAASDocumento15 pagineMechanism of Action of RAASvinita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Beta blockers (β-blockers, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, beta antagonists, beta-adrenergicDocumento2 pagineBeta blockers (β-blockers, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, beta antagonists, beta-adrenergicShielaMarieCabotageNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat SimpatomimetikDocumento42 pagineObat SimpatomimetiknatinlalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sympathomimetic Drugs: Dumrongsak Pekthong M.Sc. (Pharmacology)Documento77 pagineSympathomimetic Drugs: Dumrongsak Pekthong M.Sc. (Pharmacology)lagharijamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiological Review For CV DrugsDocumento21 paginePhysiological Review For CV DrugsatinafansifNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology of Adrenergic AgonistsDocumento9 paginePharmacology of Adrenergic Agonistsfiena92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Autacoids (Par II)Documento22 pagineAutacoids (Par II)Akhila AkhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Agonists Lecture 1 - ClarkDocumento49 pagineAdrenergic Agonists Lecture 1 - ClarkHaileris1Nessuna valutazione finora
- By: Mary Lloyd, MSN, RN, CNE: NervousDocumento42 pagineBy: Mary Lloyd, MSN, RN, CNE: Nervousmystery126Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANS ReceptorsDocumento14 pagineANS ReceptorsAisha AliNessuna valutazione finora
- C C C CDocumento7 pagineC C C CMadel de GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- YogeshDocumento49 pagineYogeshapi-3741769Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHARMACOLOGY (Autocoid-Renal-GI-CV-CNS)Documento33 paginePHARMACOLOGY (Autocoid-Renal-GI-CV-CNS)Famela Anne GOmez MadambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Agonists and AntagonistsDocumento9 pagineAdrenergic Agonists and Antagonistsstephanienwafor18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenolytics Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Umum Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaDocumento33 pagineAdrenolytics Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Umum Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaagungNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Adrenergic ReceptorDocumento13 pagineAssignment On Adrenergic ReceptoryannaingNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Receptors and DrugsDocumento67 pagineAdrenergic Receptors and DrugsNaghman Zuberi100% (2)
- Inotropes and VasopressorsDocumento63 pagineInotropes and VasopressorsCraig DuHaney50% (2)
- AdrenomimimeticsDocumento40 pagineAdrenomimimeticshealer sruthyNessuna valutazione finora
- II-Pharmacology of The Autonomic Autonomic Ne Nervous Rvous Sys System TEMDocumento88 pagineII-Pharmacology of The Autonomic Autonomic Ne Nervous Rvous Sys System TEMks asNessuna valutazione finora
- ANS-Pharmacology Adrenergic DrugsDocumento65 pagineANS-Pharmacology Adrenergic DrugsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.75% (4)
- Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics, Adrenomimetics) : Assoc. Prof. I. LambevDocumento43 pagineAdrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics, Adrenomimetics) : Assoc. Prof. I. LambevYeshaa MiraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Exam 4 - ReviewDocumento18 paginePathophysiology Exam 4 - ReviewWaqas GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocumento37 paginePharmacology FirecrackerEinstein MKNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocumento120 pagineAutonomic Nervous System Agentscoosa liquors100% (1)
- Adrenergic AHSDocumento143 pagineAdrenergic AHSAditya RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic PharmacologyDocumento60 pagineAutonomic Pharmacologyنور الإسلامNessuna valutazione finora
- L18 - Adrenergics IIIDocumento10 pagineL18 - Adrenergics IIIyasaira707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Renin-Angiotensin System: I: (The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus)Documento1 paginaRenin-Angiotensin System: I: (The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus)reioctabianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic DrugsDocumento45 pagineAdrenergic DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNessuna valutazione finora
- CVS - AntihypertensivesDocumento15 pagineCVS - Antihypertensiveshlouis8Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHFDocumento11 pagineCHFGwendolyn Talahiban LusaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Analgesics Non OpioidDocumento6 pagineAnalgesics Non Opioidhlouis8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agonist Mechanism Agonists Antagonists: Adrenore Ceptor Agonist Potency Order Selected Action ofDocumento1 paginaAgonist Mechanism Agonists Antagonists: Adrenore Ceptor Agonist Potency Order Selected Action ofdwNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 19Documento15 pagineCH 19Emmanuel GaliciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic AgentsDocumento45 pagineAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.25 Norepinephrine and SerotoninDocumento7 pagine9.25 Norepinephrine and SerotoninSTelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Receptor: History CategoriesDocumento11 pagineAdrenergic Receptor: History CategoriesUnggul YudhaNessuna valutazione finora
- RAAS & RAAS AntagonistsDocumento7 pagineRAAS & RAAS AntagonistsMahmoud AboudNessuna valutazione finora
- Nsaids Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Maher Khdour Msc. Phd. Clinical PharmacyDocumento65 pagineNsaids Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Maher Khdour Msc. Phd. Clinical PharmacyYousef JafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Saraf OtonomDocumento55 pagineSistem Saraf OtonomElizar JarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analgesic Agents: Maya Ganda Ratna Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy Faculty of Medicine - Lampung UniversityDocumento46 pagineAnalgesic Agents: Maya Ganda Ratna Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy Faculty of Medicine - Lampung UniversityMuhammad GilangNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic DrugsDocumento2 pagineAutonomic DrugsDouglas Greg CookNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 230327072253 9bf1fc09Documento23 pagineChapter 2 230327072253 9bf1fc09parmarkeval1610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vasodilators by Hiren PatelDocumento28 pagineVasodilators by Hiren PatelHiren_Patel_2427Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Documento99 pagineSympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Raheel JavaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Drug ListDocumento20 paginePharm Drug Listsxymd321Nessuna valutazione finora
- UW Notes - 5 - PharmacologyDocumento12 pagineUW Notes - 5 - PharmacologyDarshi BNessuna valutazione finora
- DavenportDocumento2 pagineDavenportzuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology 4Documento53 paginePathophysiology 4Lorenzo FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pumpkin BoogieDocumento2 paginePumpkin Boogiezuft67% (3)
- Included in The Biochemical Profile (SMA-12) : Normal Lab ValuesDocumento5 pagineIncluded in The Biochemical Profile (SMA-12) : Normal Lab ValueszuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations With Defined VariableDocumento2 pagineEquations With Defined VariablezuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Viro Immuno QuestionsDocumento7 pagineViro Immuno QuestionszuftNessuna valutazione finora
- B4PB-B 0410w PDFDocumento184 pagineB4PB-B 0410w PDFzuft100% (1)
- Cell Biology Multiple ChoiceDocumento47 pagineCell Biology Multiple Choicezuft82% (11)
- Behavioral Terms and DefintionsDocumento8 pagineBehavioral Terms and DefintionszuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunoloy Lippincott Qs 1Documento48 pagineImmunoloy Lippincott Qs 1zuft100% (2)
- Bio 1 Sig Trans RDocumento8 pagineBio 1 Sig Trans RzuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Anatomy QuestionsDocumento9 pagineClinical Anatomy QuestionszuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Each of The Following Is True of Both Cadherins and Integrins EXCEPTDocumento5 pagineEach of The Following Is True of Both Cadherins and Integrins EXCEPTzuftNessuna valutazione finora
- Song Book Inner PagesDocumento140 pagineSong Book Inner PagesEliazer PetsonNessuna valutazione finora
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Co File Nghe Nam 2020Documento11 pagineDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Co File Nghe Nam 2020HiềnNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Satisfaction VariableDocumento2 pagineJob Satisfaction VariableAnagha Pawar - 34Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Chemistry of The Colorful FireDocumento9 pagineThe Chemistry of The Colorful FireHazel Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial ExperienceDocumento30 pagineIndustrial ExperienceThe GridLockNessuna valutazione finora
- FHWA Guidance For Load Rating Evaluation of Gusset Plates in Truss BridgesDocumento6 pagineFHWA Guidance For Load Rating Evaluation of Gusset Plates in Truss BridgesPatrick Saint-LouisNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultracold Atoms SlidesDocumento49 pagineUltracold Atoms SlideslaubbaumNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessDocumento208 pagine4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessManbir ArinNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023Documento119 pagineActive Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023jagdeepchkNessuna valutazione finora
- Breastfeeding W Success ManualDocumento40 pagineBreastfeeding W Success ManualNova GaveNessuna valutazione finora
- СV Nestor RodriguezDocumento28 pagineСV Nestor RodriguezKate BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- Lady in The House, Her Responsibilities & Ambitions: Amrita DuhanDocumento7 pagineLady in The House, Her Responsibilities & Ambitions: Amrita DuhanFitness FableNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership and Management in Different Arts FieldsDocumento10 pagineLeadership and Management in Different Arts Fieldsjay jayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra ConductorsDocumento28 pagineUltra ConductorsAnu Kp50% (8)
- 7Documento6 pagine7Joenetha Ann Aparici100% (1)
- Dialectical Relationship Between Translation Theory and PracticeDocumento5 pagineDialectical Relationship Between Translation Theory and PracticeEverything Under the sunNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin ManualDocumento186 pagineOrigin ManualmariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Formulas For IGCSEDocumento2 pagineMaths Formulas For IGCSEHikma100% (1)
- DJ Crypto ResumeDocumento1 paginaDJ Crypto ResumeNitin MahawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Jacob Stewart ResumeDocumento2 pagineJacob Stewart Resumeapi-250063152Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5-8 PrintingDocumento17 pagineUNIT 5-8 PrintingNOODNessuna valutazione finora
- KDE11SSDocumento2 pagineKDE11SSluisgomezpasion1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acting White 2011 SohnDocumento18 pagineActing White 2011 SohnrceglieNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocumento27 pagineCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityDocumento7 pagineThe Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityIJAR JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- The Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishDocumento4 pagineThe Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishAdriana MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatrics: The Journal ofDocumento11 paginePediatrics: The Journal ofRohini TondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kissoft 15,69,0.4Documento10 pagineKissoft 15,69,0.4Daggupati PraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- SP-Chapter 14 PresentationDocumento83 pagineSP-Chapter 14 PresentationLoiDa FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- AIIMS 2015 Solved PaperDocumento436 pagineAIIMS 2015 Solved PaperSurya TejaNessuna valutazione finora