Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Diseño en Mediciones Repetidas-Trabajo Social
Caricato da
Luis Miguel Mejia GiraldoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diseño en Mediciones Repetidas-Trabajo Social
Caricato da
Luis Miguel Mejia GiraldoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Universidad de Caldas, Departamento de Matemticas, Profesor Luis Miguel Meja Giraldo
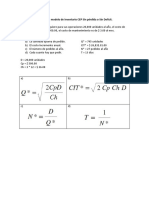
DISEO EN MEDICIONES REPETIDAS
Cuando se lleva a cabo una investigacin para evaluar el comportamiento no solo de los
diferentes tratamientos asociados a una variable; sino tambin detectar la variabilidad al
interior de los individuos, con base en una caracterstica de inters para el investigador, se
evalan con base en un diseo conocido como diseo en mediciones repetidas.
Sin embargo, este diseo se puede fusionar con los anteriores
Posee el siguiente anlisis bsico de varianza:
ANAVA
FV
GL
Tratamiento
k 1
N Individuos 1
Entre
SC
2
i.
N inds
E.2j
N Ttos
GLTotal GLEntre
Dentro
Error Exp.
FC
FC
SCTotal SCEntre
f Calculado
FTabla , 5%,1%
CM Dentro
CM ErrorExp
GLDentro , GlError
SCTratamient o CM Tratamient o GL Tratamient o , Gl Error
GL Tratamient o CM ErrorExp
CM Entre
SC Entre
GLEntre , GlError
CM
GLEntre
ErrorExp
SC Dentro
GLDentro
GLDentro GLTratamient oSC Dentro SCTratamient o SC ErrorExp
GL ErrorExp
n1
Total
Si
CM
fcalc ftabla0.05,0.01
y i2
yi 2
n
: El modelo no es significativo.
Si f calc f : El modelo es significativo y se denota al lado del valor de F calculado
con un asterisco (*), indicando que el modelo se explica con un 95% de confiabilidad.
Si f calc f : El modelo es altamente significativo y se denota al lado del valor de F
calculado con dos asteriscos (**), indicando que el modelo se explica con un 99% de
confiabilidad.
tabla 0.05
tabla 0.01
Es de resaltar que este diseo ha sido de amplia aplicacin en el rea social y de sicologa
debido a la posibilidad de evaluar tratamientos y determinar a su vez como es la respuesta
de las personas objeto de estudio (fuente de variacin Dentro de) y determinar la
variabilidad y viabilidad de los tratamientos bajo estudio.
Universidad de Caldas, Departamento de Matemticas, Profesor Luis Miguel Meja Giraldo
Universidad de Caldas, Departamento de Matemticas, Profesor Luis Miguel Meja Giraldo
Multiple Regression Analysis
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Dependent variable: Col_1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Standard
T
Parameter
Estimate
Error
Statistic
P-Value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------CONSTANT
27.4559
85.7843
0.320058
0.7699
Col_2
-0.619217
2.7852
-0.222324
0.8383
Col_3
-1.08393
5.02946
-0.215515
0.8432
Col_4
-1.46491
1.4876
-0.984744
0.3974
Col_5
0.890397
1.46941
0.605954
0.5873
Col_2*(Col_3*Col_
0.00222319
0.0100034
0.222245
0.8384
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Analysis of Variance
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Source
Sum of Squares
Df Mean Square
F-Ratio
P-Value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Model
0.872149
5
0.17443
0.56
0.7316
Residual
0.927851
3
0.309284
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Total (Corr.)
1.8
8
R-squared = 48.4527 percent
R-squared (adjusted for d.f.) = 0.0 percent
Standard Error of Est. = 0.556133
Mean absolute error = 0.287516
Durbin-Watson statistic = 2.36649
The StatAdvisor
--------------The output shows the results of fitting a multiple linear
regression model to describe the relationship between Col_1 and 5
independent variables. The equation of the fitted model is
Col_1 = 27.4559 - 0.619217*Col_2 - 1.08393*Col_3 - 1.46491*Col_4 +
0.890397*Col_5 + 0.00222319*Col_2*(Col_3*Col_3)
Since the P-value in the ANOVA table is greater or equal to 0.10,
there is not a statistically significant relationship between the
variables at the 90% or higher confidence level.
The R-Squared statistic indicates that the model as fitted
explains 48.4527% of the variability in Col_1. The adjusted R-squared
statistic, which is more suitable for comparing models with different
numbers of independent variables, is 0.0%. The standard error of the
estimate shows the standard deviation of the residuals to be 0.556133.
This value can be used to construct prediction limits for new
observations by selecting the Reports option from the text menu. The
mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.287516 is the average value of the
residuals. The Durbin-Watson (DW) statistic tests the residuals to
determine if there is any significant correlation based on the order
in which they occur in your data file. Since the DW value is greater
than 1.4, there is probably not any serious autocorrelation in the
residuals.
In determining whether the model can be simplified, notice that the
highest P-value on the independent variables is 0.8432, belonging to
Col_3. Since the P-value is greater or equal to 0.10, that term is
not statistically significant at the 90% or higher confidence level.
Consequently, you should consider removing Col_3 from the model.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Actividad 5. Regresión y Correlación MúltipleDocumento5 pagineActividad 5. Regresión y Correlación MúltipleAsociacion mNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad 9 Sandra Zapatero PDFDocumento4 pagineActividad 9 Sandra Zapatero PDFpablo cervantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bloques Aleatorizados 21 AbrilDocumento4 pagineBloques Aleatorizados 21 AbrilLUCERO FALFAN DE LA CRUZ100% (1)
- Evidencia 2Documento12 pagineEvidencia 2Pablo Alexis Ortega AmarillasNessuna valutazione finora
- DISEñOS EXPERIMENTALESDocumento55 pagineDISEñOS EXPERIMENTALESEnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Teoria TP 6 - Puntaje ZDocumento11 pagineTeoria TP 6 - Puntaje ZVictoria GravisacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Metodología de Investigación en Enfermería Del TrabajoDocumento7 pagineMetodología de Investigación en Enfermería Del TrabajoEdgar MauricioNessuna valutazione finora
- Juegos Estáticos Con Información Incompleta (Teoría)Documento54 pagineJuegos Estáticos Con Información Incompleta (Teoría)Bruno MarchettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejemplos y Ejercicios CEPDocumento6 pagineEjemplos y Ejercicios CEPJosé Francisco Carbajal ViolanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicio 2Documento3 pagineEjercicio 2Talia0% (1)
- 7 Analisis de Elasticidad Economia General 2013Documento5 pagine7 Analisis de Elasticidad Economia General 2013Jimmy VMNessuna valutazione finora
- Desarrollo de La Unidad 3 AsturiasDocumento4 pagineDesarrollo de La Unidad 3 AsturiasMabel Liliana LizcanoNessuna valutazione finora
- ProbabilidadDocumento20 pagineProbabilidadDiego Alejandro SuárezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cantidad Económica de Pedido PDFDocumento4 pagineCantidad Económica de Pedido PDFJuan Carlos Lara GallegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo Mode LosDocumento162 pagineTrabajo Mode LosManuel HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Juegos en Forma NormalDocumento12 pagineJuegos en Forma Normalwsq2nnx2gcNessuna valutazione finora
- Arboles de Desiciones NataliaDocumento37 pagineArboles de Desiciones NataliaNatalia PaezNessuna valutazione finora
- IsmaelDocumento11 pagineIsmaelDante Palacios ValdiviezoNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario ANOVA de Un FactorDocumento1 paginaFormulario ANOVA de Un FactorJaque PecuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 1 EconometriaDocumento56 pagineTema 1 EconometriaJesus MoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad 3Documento3 pagineActividad 3paola pintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrega Final Simulación DEFINITIVADocumento6 pagineEntrega Final Simulación DEFINITIVAyesica100% (1)
- Cuestiones Examen TeoricaDocumento44 pagineCuestiones Examen TeoricaBruno Joan BabyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen EFII Diciembre 2014Documento3 pagineExamen EFII Diciembre 2014sofia goicocheaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Prueba de Wilcoxon PDF CompressDocumento9 paginePDF Prueba de Wilcoxon PDF CompressFrank GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Semana 13, Prueba de HipotésisDocumento27 pagineSemana 13, Prueba de HipotésisMartín VigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 09 Modelo de Regresión ExponencialDocumento13 pagineClase 09 Modelo de Regresión ExponencialMaribel Sanhueza SotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucion Ova Semana 14Documento20 pagineSolucion Ova Semana 14FABRICIO ANDRES LEON NAVARRONessuna valutazione finora
- EstadisticaaaaaaaaaDocumento4 pagineEstadisticaaaaaaaaaFabiana Gutiérrez0% (1)