Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Classroom Management Mind Map
Caricato da
Khairunnisa SharomCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Classroom Management Mind Map
Caricato da
Khairunnisa SharomCopyright:
Formati disponibili
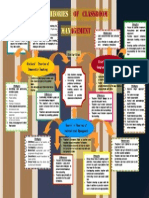
Classroom Management Theories
Strategies
1. Mistaken goal
- Provide lessons with social
interest in mind
- Communicate with one
another
- Mutual respect
- Look for positive attributes in
students
2. Democratic style
- Discussions and teacher
learns how to accept pupils
opinion
- Students involve in making
decisions in the classroom
3. Encouragement
- Give positive reinforcement
- Appreciate students effort of
learning
- Display students work
- Dont require perfection
4. Consequences
-Apply logical consequences
-Give relatable punishments to
students
Strengths
Weaknesses
Differences
Description
A theory which allows pupils
to take part in the teaching
and learning activities along
with the teacher.
Identify and address mistaken goals of misbehaviour.
Act as democratic rather
than autocratic or permissive.
Understand the difference
between praise and
encouragement.
Gives opportunity for the students to participate in the
teaching and learning process.
Logical consequences produce better results than
punishment.
Promotes respect and communication among teacher
and students.
Similarities
Strategies
By Khairunnisa Sharom (5 PISMP TESL 3)
Theories of Democratic
Teaching
by Rudolf Dreikurs
Use logical consequences
rather than punishment.
Theories of Assertive
Tactics by
Lee Canter & Marlene Canter
With-it-ness - constantly scan the
classroom for potential disruptions
and see a disruption almost before it
starts
Momentum - maintain the flow of the
lesson and do not engage in
behaviours that slow down the pace
of the lesson
Smoothness - maintain a smooth
flow of activities
Theories of Instructional
Management
by Jacob Kounin
Focused on a teachers
ability to affect students
behavior through instructional management
Incorporated both the
instructional and disciplinary aspects of the classroom together.
Might be difficult for teachers to identify and understand pupils reasons for misbehaving.
Teachers may not be able to respond properly and to
provide logical consequences for all misbehaviour.
Strengths
Weaknesses
Teachers who use effective instructional management keep their pupils
focused on learning tasks
and minimize behaviour
problems.
Behavior problems are reduced to a minimum.
Smooth teaching and learning processes .
Create a positive classroom environment.
Applicable for a variety of classroom scenario.
Time consuming.
It does not develop personal responsibility in pupils.
Preventing rather than correcting.
Recognizing and removing
roadblocks such as negative
expectations.
Description
Practicing assertive responses :
- Non-assertive (passive). Used by
teachers who fail to establish clear
standards of behaviour.
- Hostile. Use threats and sarcasm.
Has potentials for emotional harm
and possible abuse
- Assertive. Explains what
behaviour is unacceptable and
acceptable. The consequences of
various behaviors are made clear to
the students.
Assertive discipline is a
systematic and objective
way of ensuring a teacher
-controlled classroom.
It is also called the "takecontrol" approach to
teaching, as the teacher
controls their classroom in
a firm but positive manner.
Setting limits
Following through on limits
Implementing a system of positive
assertion such as ; special awards
and positive notes.
The teacher creates a set
of behaviour rules for the
class and a set of negative consequences that
result if the rules are not
followed.
Description
Group alerting - use a range of cues
and signals to keep the group alert
and focussed
Accountability - questioning to keep
the group accountable to the goals
of the lesson
Strategies
Strengths
Weaknesses
Develop good class control.
Student expectations are clearly stated.
No interruptions from students during
teaching and learning session.
Simple and well-structured plan.
Teaching style may not fit the need of all
students.
Teacher can become over controlling.
Minimal students interactions.
Students are not allowed to give ideas.
Democratic Teaching
Instructional Management
Assertive Tactics
Designed to control pupils behaviour in the classroom.
Designed to control pupils behaviour in the classroom.
Designed to control pupils behaviour in the classroom.
Good rapport between teacher and pupils.
Good rapport between teacher and pupils.
Good rapport between teacher and pupils.
Teacher address the pupils mistakes.
Teacher address the pupils mistakes.
Teacher address the pupils mistakes.
Student centered.
Teacher-centered.
Teacher centered.
Use logical consequences.
No punishment.
Has punishment.
Teacher sets rules.
No explicit rules.
Teacher sets rules.
Develop personal responsibility in pupils.
Does not develop personal responsibility in pupils.
Does not develop personal responsibility in pupils.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mind Map Classroom Management TheoriesDocumento1 paginaMind Map Classroom Management Theoriesleahblack100% (1)
- Concept of Eastern EducationDocumento6 pagineConcept of Eastern EducationRaito LurusNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Teaching SkillsDocumento39 pagineMicro Teaching SkillsnitinNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom ManagementDocumento24 pagineClassroom ManagementmightymarcNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management Models of Discipline 2016Documento44 pagineClassroom Management Models of Discipline 2016Durga DeVadassNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengths and Weaknesses of The Theory of DemocraticDocumento12 pagineStrengths and Weaknesses of The Theory of DemocraticQin KaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Borang Skema TLO EDUP3043 EngDocumento12 pagineBorang Skema TLO EDUP3043 EngArthas Rhee HermanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Models Dreikurs, Canter, SkinnerDocumento12 pagineThe Models Dreikurs, Canter, Skinnernoorrfadzreen100% (1)
- Covert & Overt ApproachesDocumento8 pagineCovert & Overt ApproachesMohd TarmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher ProfessionalismDocumento66 pagineTeacher Professionalismgengkapak100% (4)
- Jacob KouninDocumento4 pagineJacob KouninMuhammad Mukhlis WanlahNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Writing Skills in The Primary ESL ClassroomDocumento19 pagineTeaching Writing Skills in The Primary ESL ClassroomClaire B.L.100% (1)
- SAWFCC Micro Teaching PDFDocumento34 pagineSAWFCC Micro Teaching PDFdipjsamNessuna valutazione finora
- Issues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianDocumento22 pagineIssues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianHarrish ZainurinNessuna valutazione finora
- Sten HouseDocumento20 pagineSten HouseFatin AqilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Artifact6 Compare and Contrast CM TheoriesDocumento4 pagineArtifact6 Compare and Contrast CM Theoriesapi-251761140100% (1)
- CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT by Jacob KouninDocumento3 pagineCLASSROOM MANAGEMENT by Jacob KouninShaina jane Uy100% (2)
- Student Teacher RelationshipDocumento10 pagineStudent Teacher RelationshipNur Azimah LamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication in MathematicsDocumento3 pagineCommunication in MathematicsKogilavani MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- TSLB 3063 Tutorial Week 4Documento16 pagineTSLB 3063 Tutorial Week 4siti munirah binti sahrirNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Practice Handbook PDFDocumento42 pagineTeaching Practice Handbook PDFNolwazi NkomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intended VsDocumento14 pagineIntended VsRyan Morales67% (3)
- Yearly Scheme of Work English Year 3 KSSRDocumento19 pagineYearly Scheme of Work English Year 3 KSSRKhirol Azuddin100% (10)
- Self Regulated LearningDocumento28 pagineSelf Regulated LearningMohammed Mohammed Shoukry NaiemNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher Education in MalaysiaDocumento13 pagineTeacher Education in MalaysiaSaufi bin Abdullah100% (3)
- Graphic OrganizerDocumento5 pagineGraphic OrganizerAzimah100% (1)
- Phases of TeachingDocumento17 paginePhases of TeachingDr. Nisanth.P.MNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Planning: Unit - 2Documento40 pagineLesson Planning: Unit - 2Yahya RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay of BEHAVIOUR AND CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT. EDUP3043Documento6 pagineEssay of BEHAVIOUR AND CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT. EDUP3043Mohd TarmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- The Implication of Socio Cultural Diversity To SchoolDocumento2 pagineThe Implication of Socio Cultural Diversity To SchoolSyafiq AddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tyler ModelDocumento10 pagineTyler ModelJohn Bishop100% (1)
- Classroom ManagementDocumento5 pagineClassroom ManagementAva ElviraNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 2 Topic 6 Delicious Food Language Art RPHDocumento4 pagineYear 2 Topic 6 Delicious Food Language Art RPHnonsensewatson100% (3)
- Teori BrunerDocumento27 pagineTeori Bruner870622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assure Model LESSON PLANDocumento2 pagineAssure Model LESSON PLANHaszlina Che MudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Approaches To Classroom ManagementDocumento7 pagineApproaches To Classroom Managementapi-257657916Nessuna valutazione finora
- TSL 3105Documento11 pagineTSL 3105Fadziela MaidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of Classroom Management As Applied To The Secondary Classroom PDFDocumento5 pagineModels of Classroom Management As Applied To The Secondary Classroom PDFIzzat Ismail100% (1)
- Principles of Instructional TechnologyDocumento12 paginePrinciples of Instructional TechnologySumathy Lakshamanan100% (1)
- Skpmg2 Malaysian Education Quality Standard: Alya Farra AuniDocumento8 pagineSkpmg2 Malaysian Education Quality Standard: Alya Farra AuniOhorat129Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muslim Philosophers' Perspective On EducationDocumento24 pagineMuslim Philosophers' Perspective On EducationMuhammad Sarmad AnwaarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Teaching Reading and WritingDocumento5 pagineChapter 5 Teaching Reading and WritingKanageswary SaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher DevelopmentDocumento10 pagineTeacher Developmentmkunalan23Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Daily Lesson Plan Year 5 - KSSRDocumento3 pagineEnglish Daily Lesson Plan Year 5 - KSSRpinpit282Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Components and ApproachesDocumento6 pagineCurriculum Components and ApproachesRico BasilioNessuna valutazione finora
- Content From Subjects Is Used in Language-Learning Classes. The Teacher Incorporates TheDocumento21 pagineContent From Subjects Is Used in Language-Learning Classes. The Teacher Incorporates TheMelina MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Issues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianDocumento11 pagineIssues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysiansweetzazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior and Classroom ManagementDocumento22 pagineBehavior and Classroom Managementsmxlpxngx98Nessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 2 - Personal, Academic and Aesthetic ValuesDocumento19 pagineTOPIC 2 - Personal, Academic and Aesthetic ValuesLiving LegacyNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 3 MR GDocumento5 pagineTask 3 MR Gfernandez ngalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Science Tahun 2 - The Magic of Batteries Part 2Documento5 pagineLesson Plan Science Tahun 2 - The Magic of Batteries Part 2gengkapakNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom ManagementDocumento50 pagineClassroom ManagementGeorgia Benjamin100% (1)
- Topic 4 KBSR Science Curriculum IDocumento16 pagineTopic 4 KBSR Science Curriculum IIsmah WinahNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4Documento38 pagineTopic 4Allison RNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 - PMTA - BSA1 EDocumento26 pagineGroup 4 - PMTA - BSA1 EAvegail MagtuboNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL ASSIGNMENT 6. Importance of Classroom Management 26th May 2022Documento9 pagineFINAL ASSIGNMENT 6. Importance of Classroom Management 26th May 2022Jennifer BotheloNessuna valutazione finora
- G.O of Ele 3102 Study of PhonologyDocumento4 pagineG.O of Ele 3102 Study of PhonologyOrewa Appiku DesNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 7&8 BuildingDocumento11 pagineWeek 7&8 BuildingMaybe Calunsag - AbucayNessuna valutazione finora
- FS 2 Episode 6Documento20 pagineFS 2 Episode 6May Ann OmoyonNessuna valutazione finora
- Managementul Clasei de EleviDocumento13 pagineManagementul Clasei de EleviAndreea ManeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Simple Quiz - Grammar - EnglishClub PDFDocumento1 paginaPast Simple Quiz - Grammar - EnglishClub PDFKhairunnisa Sharom100% (1)
- Flipped ClassroomDocumento4 pagineFlipped ClassroomKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Carta Penilaian Prestasi MuridDocumento5 pagineCarta Penilaian Prestasi MuridKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages of Audio Media in Teaching and Learning, and How It Can Be UsedDocumento6 pagineAdvantages of Audio Media in Teaching and Learning, and How It Can Be UsedKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Bubble MapDocumento1 paginaDouble Bubble MapKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- LP Listening and Speaking Unit 4Documento3 pagineLP Listening and Speaking Unit 4Khairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Snakes and Ladders InstructionsDocumento8 pagine04 Snakes and Ladders InstructionssuryasanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Very Hungry Caterpillar Power Point (Autosaved)Documento30 pagineThe Very Hungry Caterpillar Power Point (Autosaved)Khairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Lga3033e Outlines Week6Documento1 paginaLga3033e Outlines Week6Khairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Owl Babies Simplified ScriptDocumento2 pagineOwl Babies Simplified ScriptKhairunnisa Sharom100% (3)
- Final Version 7314Documento15 pagineFinal Version 7314Khairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sandwich Swap Calif Young ReadersDocumento10 pagineThe Sandwich Swap Calif Young ReadersKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 Note 2 Before ClassDocumento13 pagineWeek 6 Note 2 Before ClassKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction: Listen To The Conversation. Write The Correct AnswersDocumento2 pagineInstruction: Listen To The Conversation. Write The Correct AnswersKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Arjen de Korte - To Teach or Not To Teach GrammarDocumento9 pagineArjen de Korte - To Teach or Not To Teach GrammarKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Constructivism in The Classroom: By: Khairunnisa Ainur Adhwa Syazwi Nur Arina Zafirah Nur Haniffa Nur Ain SyafinazDocumento15 pagineConstructivism in The Classroom: By: Khairunnisa Ainur Adhwa Syazwi Nur Arina Zafirah Nur Haniffa Nur Ain SyafinazKhairunnisa Sharom100% (2)
- Information Transfer WritingDocumento1 paginaInformation Transfer WritingKhairunnisa SharomNessuna valutazione finora
- Collective NounsDocumento3 pagineCollective NounsEmma EmilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of Writing StyleDocumento12 pagineElements of Writing StyleMuhammad SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- PreviewpdfDocumento39 paginePreviewpdfMaria Sofia Angela LiguanNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 5 - Q3 - W5 DLLDocumento5 pagineScience 5 - Q3 - W5 DLLninsantocildes100% (2)
- (CO Validation) Enclosure No. 2 - School Readiness ChecklistDocumento1 pagina(CO Validation) Enclosure No. 2 - School Readiness ChecklistBryan MoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 1 9 5 16Documento3 pagineLesson Plan 1 9 5 16api-319269853Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 and 6Documento8 pagineChapter 5 and 6Johna BelardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lucena032018-Sec-Social Studies PDFDocumento44 pagineLucena032018-Sec-Social Studies PDFPhilBoardResultsNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Psyche Program University of VictoriaDocumento80 pagineClinical Psyche Program University of VictorianonamebrandNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009science11 12Documento295 pagine2009science11 12ash ketchup100% (1)
- The Impact of Online Learning in The Mental Health of ABM StudentsDocumento3 pagineThe Impact of Online Learning in The Mental Health of ABM StudentsJenny Rose Libo-on100% (3)
- Myself As A Communicator Part 1Documento3 pagineMyself As A Communicator Part 1api-3067928820% (1)
- Cbse PCB Test No 14 Breathing & Exc of GasesDocumento3 pagineCbse PCB Test No 14 Breathing & Exc of GasesFᏞ么MES々ʀᴇʙᴇʟ GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Anuj Pathak Returns To IndiaDocumento2 pagineAnuj Pathak Returns To IndiaApurvAdarsh100% (1)
- Top 3 IIT JEE Coaching Centers in IndoreDocumento8 pagineTop 3 IIT JEE Coaching Centers in IndorelichensmarketingNessuna valutazione finora
- Accomplishment Report-HGP - AbgfilesDocumento2 pagineAccomplishment Report-HGP - AbgfilesNerissa EstebanNessuna valutazione finora
- Neda ProjectsDocumento23 pagineNeda Projectsminus25Nessuna valutazione finora
- CXC English A Examination Preparation GuideDocumento14 pagineCXC English A Examination Preparation GuideRoland Connor100% (11)
- Illusions ExperientialExercisesDocumento25 pagineIllusions ExperientialExerciseselidasdaughter2501Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sixth Grade Social Studies SyllabusDocumento2 pagineSixth Grade Social Studies Syllabusapi-234198752Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transactional AnalysisDocumento31 pagineTransactional AnalysisCostel PopNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm EvaluationDocumento3 pagineMidterm Evaluationapi-312642927Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trifuffrcated Colleges ListDocumento34 pagineTrifuffrcated Colleges ListMohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Greek Literature and The Lost Legacy of PDFDocumento54 pagineGreek Literature and The Lost Legacy of PDFhenareta100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Deductive GeometryDocumento34 pagineChapter 4 Deductive GeometryEric Mooi100% (1)
- NEP 2020 Suggested ChangesDocumento21 pagineNEP 2020 Suggested ChangesAnuragNessuna valutazione finora
- Context and RationaleDocumento11 pagineContext and RationaleRichelle Fe Torralba HabanNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP # 43 Summative TestDocumento5 pagineDLP # 43 Summative TestRitz Anton Lim100% (1)
- Schopenhauer S LebenDocumento345 pagineSchopenhauer S LebenVeRa100% (1)
- Intro To ManagementDocumento31 pagineIntro To ManagementBrandon LowNessuna valutazione finora