Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
McKinsey Matrix - GE Business Screen
Caricato da
pallav86Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
McKinsey Matrix - GE Business Screen
Caricato da
pallav86Copyright:
Formati disponibili
WHAT IS THE MCKINSEY MATRIX?
The McKinsey Matrix is a model to perform a business portfolio analysis on the Strategic
Business Units of a corporation. Synonyms for this method are; GE Matrix, Business
Assessment Array and GE Business Screen.
WHAT IS A PORTFOLIO?
A business portfolio is the collection of Strategic Business Units that together form a corporation.
The optimal business portfolio is one that fits perfectly to the company's strengths and helps to
exploit the most attractive industries or markets.
WHAT IS A STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT?
A Strategic Business Unit (SBU) can either be an entire medium size company or a division of a
large corporation. As long as it formulates its own business level strategy and has separate
objectives from the parent company.
THE AIM OF PORTFOLIO ANALYSIS
1. Analyze its current business portfolio and decide which SBU's should receive
more or less investment
2. Develop growth strategies for adding new products and businesses to the
portfolio
3. Decide which businesses or products should no longer be retained.
The BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group Matrix) is the best-known portfolio planning
framework. The McKinsey Matrix is a later and more advanced form of the BCG Matrix.
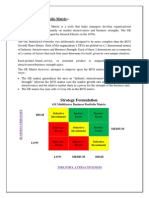
THE MCKINSEY MATRIX
The McKinsey Matrix is more sophisticated than the BCG Matrix in three aspects:
1. Market (Industry) attractiveness is used as the dimension of industry
attractiveness, instead of market growth. Market Attractiveness includes a broader range
of factors other than just the market growth rate that can determine the attractiveness of
an industry / market. Compare also: Five Forces
2. Competitive strength replaces market share as the dimension by which the
competitive position of each SBU is assessed. Competitive strength likewise includes a
broader range of factors other than just the market share that can determine the
competitive strength of a Strategic Business Unit.
3. Finally, the GE Matrix works with a 3*3 matrix, while the BCG Matrix has only
2*2. This also allows more sophistication.
Typical (internal) factors that affect
Competitive Strength of a Strategic
Typical (external) factors that affect Market
Business Unit:
Attractiveness:
- Strength of assets and competencies
- Market size
- Relative brand strength (marketing)
- Market growth rate
- Market share
- Market profitability
- Market share growth
- Pricing trends
- Customer loyalty
- Competitive intensity / rivalry
- Relative cost position (cost structure compared
- Overall risk of returns in the industry
with competitors)
- Entry barriers
- Relative profit margins (compared to
- Opportunity to differentiate products and
competitors)
services
- Distribution strength and production capacity
- Demand variability
- Record of technological or other innovation
- Segmentation
- Quality
- Distribution structure
- Access to financial and other investment
- Technology development
resources
- Management strength
Often, Strategic Business Units are portrayed as a circle plotted in the GE Matrix, whereby:
• The size of the circles represent the Market Size
• The size of the pies represent the Market Share of the SBU's
• Arrows represent the direction and the movement of the SBU's in the future
A SIX-STEP APPROACH FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MCKINSEY MATRIX
1. Specify drivers of each dimension. The corporation must carefully determine
those factors that are important to its overall strategy.
2. Determine the weight of each driver. The corporation must assign relative
importance weights to the drivers.
3. Score the SBU's on each driver.
4. Multiply weights and scores for each SBU.
5. View resulting graph and interpret it.
6. Perform a review/sensitivity analysis. Make use of adjusted other weights and
scores (there may be no consensus).
SOME LIMITATIONS OF THE MCKINSEY MATRIX
• The valuation of the realization of the various factors.
• Aggregation of the indicators is difficult.
• Core Competences are not represented.
• Interactions between Strategic Business Units are not considered.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionDa EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Questions and AnswersDocumento12 pagineQuestions and Answersaparajita rai100% (3)
- Ge MatrixDocumento4 pagineGe MatrixhaiderhusainNessuna valutazione finora
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementDa EverandThe BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Cambridge Software Corporation - Q1Documento2 pagineCambridge Software Corporation - Q1kkayathwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CT1 Assignment Chapter 14Documento5 pagineCT1 Assignment Chapter 14Gaurav satraNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey GEC MatrixDocumento5 pagineMcKinsey GEC MatrixFaiz Kazi100% (1)
- Ge Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Documento18 pagineGe Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Hassan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Approach To StrategyDocumento7 paginePortfolio Approach To StrategyRenitaFerreira100% (2)
- GE MatrixDocumento3 pagineGE Matrixr.jeyashankar9550Nessuna valutazione finora
- GE MatrixDocumento2 pagineGE MatrixMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge MatrixDocumento3 pagineGe MatrixSantosh JhawarNessuna valutazione finora
- GE MatrixDocumento6 pagineGE MatrixManish JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - HandoutDocumento21 pagineChapter 5 - HandoutNinh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- NotesDocumento10 pagineNotesvarun rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 HandoutDocumento21 pagineChapter 5 HandoutDuc Trieu MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- STRATEGYDocumento21 pagineSTRATEGYSikendra KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Nine Cell MatrixDocumento21 pagineGE Nine Cell MatrixMadhuri Bhojwani67% (3)
- GE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisDocumento13 pagineGE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisRabia MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisDocumento13 pagineGE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio Analysisadnanulhaq12963650% (2)
- Chapter 5 - HandoutDocumento21 pagineChapter 5 - HandoutNhật HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management: Birat Shrestha/ Resta JhaDocumento21 pagineStrategic Management: Birat Shrestha/ Resta Jhapuspa Raj upadhayayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge MatrixDocumento9 pagineGe MatrixAshiq NobitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento15 pagineModule 2Omkar MulekarNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Business Screen/ Mckinsey MatrixDocumento11 pagineGE Business Screen/ Mckinsey MatrixashishgadbailNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 2 - BCG - 27 - 08 - 2017Documento123 pagineChapter - 2 - BCG - 27 - 08 - 2017Pavneet Kaur BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- (SBU) of A Corporation. It Analyzes Market Attractiveness and Competitive Strength ToDocumento3 pagine(SBU) of A Corporation. It Analyzes Market Attractiveness and Competitive Strength ToJite PiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge / Mckinsey MatrixDocumento4 pagineGe / Mckinsey MatrixVishh ChennNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Ge MateDocumento10 pagineSPM Ge Mateashutosh kankaneNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG Matrix: Individual Sale This Year - Individual Sale Last Year Individual Sale Last YearDocumento12 pagineBCG Matrix: Individual Sale This Year - Individual Sale Last Year Individual Sale Last YearRitika DiwakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - 1 Strategic Management: Submitted ToDocumento14 pagineAssignment - 1 Strategic Management: Submitted ToNakulNessuna valutazione finora
- GE McKinsey MatrixDocumento14 pagineGE McKinsey MatrixSASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG GrowthDocumento4 pagineBCG GrowthMuralidhar CVNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Strategic Marketing AnalysisDocumento26 pagineOverview of Strategic Marketing AnalysisSaron GebreNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG GrowthDocumento5 pagineBCG GrowthAmol NirgudkarNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonDocumento6 pagineWEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonVanesa AgootNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Analysis and Valuation - Strategic AnalysisDocumento40 pagineBusiness Analysis and Valuation - Strategic AnalysiscapassoaNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsDocumento15 pagineGE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsPratyay DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive and Functional StrategiesDocumento20 pagineCompetitive and Functional StrategiesprabodhNessuna valutazione finora
- GE MatrixDocumento26 pagineGE MatrixFijo JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- GE 9 CellDocumento20 pagineGE 9 CellakhilNessuna valutazione finora
- General ElectricDocumento12 pagineGeneral ElectricAitm Mba BelagaviNessuna valutazione finora
- External AnalysisDocumento26 pagineExternal AnalysisPragya ChakshooNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - Lecture PDFDocumento15 pagineWeek 2 - Lecture PDFYuan LiNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG Growth-Share MatrixDocumento9 pagineBCG Growth-Share MatrixSaurabh ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Nine MatrixDocumento12 pagineGE Nine MatrixmysterioussurferNessuna valutazione finora
- September 3rd Session5Documento19 pagineSeptember 3rd Session5Andrés RedondoNessuna valutazione finora
- September 3rd Session5Documento19 pagineSeptember 3rd Session5Andrés RedondoNessuna valutazione finora
- KIG4067 Week 2 and 3 Developing Operational Strategy-1Documento37 pagineKIG4067 Week 2 and 3 Developing Operational Strategy-1Lucy siiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge MckinseyDocumento9 pagineGe MckinseyAnjaliMoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge Nine Cell Matrix: Submitted To Ms. Sakshi Mam Submitted by TammanaDocumento12 pagineGe Nine Cell Matrix: Submitted To Ms. Sakshi Mam Submitted by TammanaTamannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Strategy Analysis and Management Decision - SVDocumento76 pagineChapter 3 - Strategy Analysis and Management Decision - SV8.Nguyễn Việt HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Marketing II Unit 6Documento20 paginePrinciples of Marketing II Unit 6Addisu TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix:-: Strategy FormulationDocumento4 pagineGE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix:-: Strategy FormulationHemant TejwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The General Electric/Mckinsey Model: Portfolio PlanningDocumento3 pagineThe General Electric/Mckinsey Model: Portfolio Planningvivekch06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Analysis PDFDocumento5 paginePortfolio Analysis PDFsreenath appuNessuna valutazione finora
- GE 9 Cell MatrixDocumento22 pagineGE 9 Cell MatrixAnonymous f8tAzEb3oNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Portfolio AnalysisDocumento44 pagineProduct Portfolio AnalysisSanchi SurveNessuna valutazione finora
- Nine Cell Matrix PresDocumento16 pagineNine Cell Matrix PresjyothirajscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- GE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKDocumento3 pagineGE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKViz PrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Matters: A Market Analysis Methodology Leading to a Marketing Simulation CapabilityDa EverandMarketing Matters: A Market Analysis Methodology Leading to a Marketing Simulation CapabilityNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Consulting Frameworks: Consulting PreparationDa EverandStrategic Consulting Frameworks: Consulting PreparationNessuna valutazione finora
- Competition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)Da EverandCompetition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)Nessuna valutazione finora
- BCG MatrixDocumento2 pagineBCG Matrixpallav86Nessuna valutazione finora
- RESEARCH PAPER Cross Cultural Training PallavDocumento15 pagineRESEARCH PAPER Cross Cultural Training Pallavpallav86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Territory ManagementDocumento11 pagineSales Territory Managementpallav86Nessuna valutazione finora
- ISM Modified by PallavDocumento28 pagineISM Modified by Pallavpallav86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse Engineering Rsi PDF FreeDocumento7 pagineReverse Engineering Rsi PDF FreeJitkaSamakNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash To AccrualDocumento23 pagineCash To Accruallascona.christinerheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maynard Case 3 1 PDFDocumento2 pagineMaynard Case 3 1 PDFTating Bootan Kaayo YangNessuna valutazione finora
- BF2 AssignmentDocumento5 pagineBF2 AssignmentIbaad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento20 pagineChapter 1Anonymous wNKY5dNessuna valutazione finora
- Gratittude Manufacturing Company Post-Closing Trial Balance DECEMBER 31, 2017Documento3 pagineGratittude Manufacturing Company Post-Closing Trial Balance DECEMBER 31, 2017Charles TuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Two Instructions S2 2021Documento2 pagineAssignment Two Instructions S2 2021Dat HuynhNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Management: Nominal and Effective Interest RateDocumento14 pagineMoney Management: Nominal and Effective Interest RateJane Erestain BuenaobraNessuna valutazione finora
- EPC and ERGP - The NexusDocumento37 pagineEPC and ERGP - The NexusOyinleye AdebowaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunnix Memo To BoardDocumento4 pagineSunnix Memo To BoardDennie IdeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Albuquerque Journal Homestyle 01/06/2017Documento15 pagineAlbuquerque Journal Homestyle 01/06/2017Albuquerque JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fac1601 Exam Pack 2018 - Financial Accounting ReportingDocumento97 pagineFac1601 Exam Pack 2018 - Financial Accounting ReportingandreqwNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Bazaartrading.in: in Which Bazaar Trading Had Mentioned Itself AsDocumento27 pagineWWW - Bazaartrading.in: in Which Bazaar Trading Had Mentioned Itself AsPratim MajumderNessuna valutazione finora
- PhonePe Statement Nov2023 Jan2024Documento33 paginePhonePe Statement Nov2023 Jan2024Arvind KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ITrade Individual Application FormDocumento10 pagineITrade Individual Application FormPrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- G.R. No. L-108638 March 11, 1994 Spouses RAMON R. NACU and LOURDES I. NACU, Petitioners, The Court of Appeals and Pilipinas Bank, RespondentsDocumento9 pagineG.R. No. L-108638 March 11, 1994 Spouses RAMON R. NACU and LOURDES I. NACU, Petitioners, The Court of Appeals and Pilipinas Bank, RespondentsJimcris Posadas HermosadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Revati Krishna CV (1) - 1Documento2 pagineRevati Krishna CV (1) - 1shivram.antallkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Yogesh 19Documento3 pagineYogesh 19DeltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Becamex Presentation - Full Version 4Documento34 pagineBecamex Presentation - Full Version 4Trường Hoàng XuânNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4 QAsDocumento6 pagineTutorial 4 QAsJin HueyNessuna valutazione finora
- Indicators XDDocumento17 pagineIndicators XDAniket jaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporation QuizDocumento1 paginaCorporation QuizAngelo Andro Suan100% (5)
- Chapter 7Documento45 pagineChapter 7Chitose HarukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparism Between Pricing in Industrial Product and Consumer ProductDocumento8 pagineComparism Between Pricing in Industrial Product and Consumer ProductLawal Musibaudeem Obafemi100% (2)
- Day Trading - 15 Secrets To SuccessDocumento8 pagineDay Trading - 15 Secrets To SuccessSunny100% (1)
- Full Download Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Asia Global 2nd Edition Ross Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineFull Download Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Asia Global 2nd Edition Ross Solutions Manualempiercefibberucql19100% (36)
- FS PT Acset 31 Maret 2023Documento79 pagineFS PT Acset 31 Maret 2023Nanda WulanNessuna valutazione finora