Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Guide To Contraindications To Vaccination
Caricato da
Gabriel GarrisonDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Guide To Contraindications To Vaccination
Caricato da
Gabriel GarrisonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
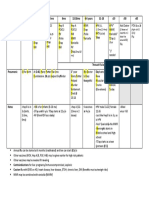
Guide to Contraindications1 and Precautions1 to Commonly Used Vaccines*,
(Page 1 of 2)
Vaccine
Contraindications1
Precautions1
Hepatitis B (HepB)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Infant weighing less than 2000 grams (4 lbs, 6.4 oz)2
Rotavirus
(RV5 [RotaTeq],
RV1 [Rotarix])
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
History of intussusception or of uncorrected congenital
malformation of the gastrointestinal tract that would
predispose the infant to intussusception
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Altered immunocompetence other than SCID
Chronic gastrointestinal disease3
Spina bifida or bladder exstrophy3
Diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis (DTaP)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Encephalopathy (e.g., coma, decreased level of
consciousness, prolonged seizures) not attributable to another identifiable cause within 7 days of administration of
previous dose of DTP or DTaP (for DTaP); or of previous
dose of DTP, DTaP, or Tdap (for Tdap)
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Guillain-Barr syndrome (GBS) within 6 weeks after a previous
dose of tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine
History of arthus-type hypersensitivity reactions after a previous
dose of tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine; defer vaccination until at least 10 years have elapsed since the last tetanustoxoid containing vaccine
Progressive or unstable neurologic disorder (including infantile
spasms for DTaP), uncontrolled seizures, or progressive encephalopathy until a treatment regimen has been established and the
condition has stabilized
For DTaP only:
Temperature of 105 F or higher (40.5 C or higher) within
48 hours after vaccination with a previous dose of DTP/DTaP
Collapse or shock-like state (i.e., hypotonic hyporesponsive episode) within 48 hours after receiving a previous dose of DTP/DTaP
Seizure within 3 days after receiving a previous dose of DTP/DTaP
Persistent, inconsolable crying lasting 3 or more hours within
48 hours after receiving a previous dose of DTP/DTaP
Tetanus, diphtheria
(DT, Td)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
GBS within 6 weeks after a previous dose of tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine
History of arthus-type hypersensitivity reactions after a previous
dose of tetanus or diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine; defer vaccination until at least 10 years have elapsed since the last tetanustoxoid containing vaccine
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Age younger than 6 weeks
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Inactivated poliovirus
vaccine (IPV)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Pregnancy
Pneumococcal
(PCV13 or PPSV23)
For PCV13, severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis)
after a previous dose of PCV7 or PCV13 or to a vaccine
component, including to any vaccine containing diphtheria
toxoid
For PPSV23, severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis)
after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Measles, mumps,
rubella (MMR)4
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic
and solid tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, congenital immunodeficiency, or long-term immunosuppressive therapy5
or patients with human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]
infection who are severely immunocompromised)6
Pregnancy
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood
product (specific interval depends on product)7
History of thrombocytopenia or thrombocytopenic purpura
Need for tuberculin skin testing8
Tetanus, diphtheria,
pertussis (Tdap)
(continued on page 2)
Technical content reviewed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3072a.pdf Item #P3072a (3/13)
Immunization Action Coalition 1573 Selby Ave. St. Paul, MN 55104 (651) 647-9009 www.immunize.org www.vaccineinformation.org
Guide to Contraindications1 and Precautions1 to Commonly Used Vaccines*, (continued)
(Page 2 of 2)
Vaccine
Contraindications1
Precautions1
Varicella (Var)4
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic
and solid tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, primary or
acquired immunodeficiency, or long-term immunosuppressive therapy5 or patients with HIV infection who are
severely immunocompromised)6
Pregnancy
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood
product (specific interval depends on product)7
Receipt of specific antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24 hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs
for 14 days after vaccination.
Hepatitis A (HepA)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Influenza, inactivated
injectable (IIV)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a
previous dose of any influenza vaccine or to a vaccine
component, including egg protein
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
History of GBS within 6 weeks of previous influenza vaccination
Persons who experience only hives with exposure to eggs should
receive IIV with additional safety precautions found in the 201213
ACIP influenza recommendations, pages 613618 at www.cdc.gov/
mmwr/pdf/wk/mm6132.pdf.
Influenza, live attenuated (LAIV)4
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a
previous dose of any influenza vaccine or to a vaccine
component, including egg protein
Conditions for which the ACIP recommends against use,
but which are not contraindications in vaccine package
insert: immune suppression, certain chronic medical conditions such as asthma, diabetes, heart or kidney disease,
and pregnancy9
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
History of GBS within 6 weeks of previous influenza vaccination
Receipt of specific antivirals (i.e., amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, or oseltamivir) 48 hours before vaccination. Avoid use of these
antiviral drugs for 14 days after vaccination.
Human papillomavirus
(HPV)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Pregnancy
Meningococcal:
conjugate (MCV4),
polysaccharide (MPSV4)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to a vaccine component
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Zoster (HZV)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a vaccine
component
Known severe immunodeficiency (e.g., from hematologic
and solid tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, or long-term
immunosuppressive therapy5 or patients with HIV infection
who are severely immunocompromised).
Pregnancy
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever
Receipt of specific antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24 hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs
for 14 days after vaccination.
Footnotes
1. Vaccine package inserts and the full ACIP recommendations for these vaccines should be consulted for additional information on vaccine-related contraindications and precautions and for
more information on vaccine excipients. Events or conditions listed as precautions should be
reviewed carefully. Benefits of and risks for administering a specific vaccine to a person under
these circumstances should be considered. If the risk from the vaccine is believed to outweigh
the benefit, the vaccine should not be administered. If the benefit of vaccination is believed to
outweigh the risk, the vaccine should be administered. Whether and when to administer DTaP
to children with proven or suspected underlying neurologic disorders should be decided on a
case-by-case basis.
2. Hepatitis B vaccination should be deferred for preterm infants and infants weighing less than
2000 g if the mother is documented to be hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-negative at
the time of the infants birth. Vaccination can commence at chronological age 1 month or at
hospital discharge. For infants born to women who are HBsAg-positive, hepatitis B immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccine should be administered within 12 hours of birth, regardless
of weight.
3. For details, see CDC. Prevention of Rotavirus Gastroenteritis among Infants and Children:
Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. (ACIP) MMWR
2009;58(No. RR2), available at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/acip-list.htm.
4. LAIV, MMR, and varicella vaccines can be administered on the same day. If not administered
on the same day, these vaccines should be separated by at least 28 days.
5. Immunosuppressive steroid dose is considered to be 2 or more weeks of daily receipt of
20 mg prednisone or equivalent. Vaccination should be deferred for at least 1 month after
discontinuation of such therapy. Providers should consult ACIP recommendations for complete information on the use of specific live vaccines among persons on immune-suppressing
medications or with immune suppression because of other reasons.
6. HIV-infected children may receive varicella and measles vaccine if CD4+ T-lymphocyte count
is >15%. (Source: Adapted from American Academy of Pediatrics. Immunization in Special
Clinical Circumstances. In: Pickering LK, ed. Red Book: 2012 Report of the Committee on
Infectious Diseases. 29th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics: 2012.)
7. Vaccine should be deferred for the appropriate interval if replacement immune globulin products are being administered (see Table 5 in CDC. General Recommendations on Immunization: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) at
www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/acip-list.htm.)
8. Measles vaccination might suppress tuberculin reactivity temporarily. Measles-containing
vaccine can be administered on the same day as tuberculin skin testing. If testing cannot be
performed until after the day of MMR vaccination, the test should be postponed for at least 4
weeks after the vaccination. If an urgent need exists to skin test, do so with the understanding that reactivity might be reduced by the vaccine.
9. For a complete list of conditions that CDC considers to be reasons to avoid getting LAIV, see
CDC Prevention and Control of Influenza with Vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory
Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2010. MMWR 2010;59(No. RR-8), available
at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/acip-list.htm.
* Adapted from Table 6. Contraindications and Precautions to Commonly Used Vaccines found in: CDC. General Recommendations on Immunization: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
(ACIP). MMWR 2011; 60(No. RR-2), p. 4041, and from Atkinson W, Wolfe S, Hamborsky J, eds. Appendix A. Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/index.html).
Regarding latex allergy: some types of prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex or dry natural latex rubber. Consult the package insert for any vaccine given.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Guide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesDocumento2 pagineGuide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesMariana E. GutiérrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesDocumento2 pagineGuide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesalbortoNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesDocumento2 pagineGuide To Contraindications and Precautions To Commonly Used VaccinesEliNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Documento5 pagineSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Hannah Caburian RemoNessuna valutazione finora
- Surfactant Replacement TherapyDocumento96 pagineSurfactant Replacement TherapyabhivnairNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurul Hassanah Binti MuslimDocumento11 pagineNurul Hassanah Binti MuslimLi FaungNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetravac Suspension For Injection ENG SMPCDocumento15 pagineTetravac Suspension For Injection ENG SMPCFelix Daniel ParvuNessuna valutazione finora
- Contraindications VaccinesDocumento19 pagineContraindications VaccinesAbbyFerNessuna valutazione finora
- Aip Assessment Prior AdministrationDocumento6 pagineAip Assessment Prior AdministrationElaine Frances IlloNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH ProgramsDocumento24 pagineExpanded Program On Immunization and Reproductive Health DOH ProgramsPrince Jhessie L. AbellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)Documento4 pagineSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)gyna_2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Influenza Vaccine Medical Exemption FormDocumento1 paginaInfluenza Vaccine Medical Exemption FormSatine EvansNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocumento12 pagineExpanded Program On ImmunizationRosechelle Baggao Siupan-Elarco100% (1)
- Vaccination in Special Situations SeminarDocumento21 pagineVaccination in Special Situations SeminarDeep ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Handbook On Adult Immunization 2012 PDFDocumento140 paginePhilippine Handbook On Adult Immunization 2012 PDFLinius CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 ImmunizationDocumento60 pagine14 Immunizationrahamathunnisha100% (2)
- Immunisation and Under 5 CardDocumento31 pagineImmunisation and Under 5 CardStephen AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Contraindications and Precautionary Conditions For VaccinatiDocumento25 pagineContraindications and Precautionary Conditions For VaccinatikrishnasreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rota VirusDocumento30 pagineRota VirusboomboompakNessuna valutazione finora
- Pentaxim-Pi-Sg Pen 0118 Spc0914Documento10 paginePentaxim-Pi-Sg Pen 0118 Spc0914walkrogNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 CombineDocumento726 pagine1 CombineSong Hành Vạn KiếpNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction: Hepatitis A Maurice HillemanDocumento19 pagineIntroduction: Hepatitis A Maurice Hillemanahmed solimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination Requirements and Form I-693: Mary Naughton, MD, MPHDocumento55 pagineVaccination Requirements and Form I-693: Mary Naughton, MD, MPHErinaNessuna valutazione finora
- VaccinesDocumento4 pagineVaccinesSam smithNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocumento4 pagineExpanded Program On ImmunizationMac Lester DumagNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization Part 3Documento12 pagineImmunization Part 3Marleen ShehadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination 2023-1Documento59 pagineVaccination 2023-1Mohammad Moufaq El-BashabshehNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocumento12 pagineExpanded Program On ImmunizationRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Documento5 pagineSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Annie AnnaNessuna valutazione finora
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocumento14 pagineEPI Vaccines HandoutsMeryville JacildoNessuna valutazione finora
- National Immunization Program: Ray Anthony A. Camaliga, M.D Level 1 Resident DFCMDocumento39 pagineNational Immunization Program: Ray Anthony A. Camaliga, M.D Level 1 Resident DFCMAnthony AbulNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization and Prophylaxis: Childhood Immunization Has Reduced The Impact - Active Immunization Is TheDocumento18 pagineImmunization and Prophylaxis: Childhood Immunization Has Reduced The Impact - Active Immunization Is TheCabdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization: Mei Neni S Pediatric Dept. Faculty of Medicine, Gadjah Mada UniversityDocumento35 pagineImmunization: Mei Neni S Pediatric Dept. Faculty of Medicine, Gadjah Mada UniversityadystiNessuna valutazione finora
- CPM17th Adult Immunization ScheduleDocumento7 pagineCPM17th Adult Immunization ScheduleAlexious Marie CalluengNessuna valutazione finora
- III. ContraindicationsDocumento2 pagineIII. ContraindicationsChristine AlmoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Immunization Report 1Documento54 pagineExpanded Immunization Report 1RIK HAROLD GATPANDAN100% (1)
- Chn-Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocumento2 pagineChn-Expanded Program On ImmunizationBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccine Indication and ContraindicationDocumento34 pagineVaccine Indication and ContraindicationMusa yohanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotateq Epar Product Information enDocumento29 pagineRotateq Epar Product Information enjjpepNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Solis - Midterms - Preventive Pediatrics 1&2 & HandoutsDocumento12 pagineDR Solis - Midterms - Preventive Pediatrics 1&2 & HandoutschristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccine Information Statement Hepatitis A Vaccine What You Need To KnowDocumento5 pagineVaccine Information Statement Hepatitis A Vaccine What You Need To KnowsovianNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)Documento4 pagineSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)enquzerNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization: Presenter: Ahmad Tahir Siti Nurul Farahah Supervised By: DR MuhaireenDocumento40 pagineImmunization: Presenter: Ahmad Tahir Siti Nurul Farahah Supervised By: DR MuhaireenNadia SalwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program On Immunization CHNDocumento4 pagineExpanded Program On Immunization CHNgeralynroseNessuna valutazione finora
- Epi NotesDocumento5 pagineEpi NoteshoneykrizelNessuna valutazione finora
- Unknown PDFDocumento56 pagineUnknown PDFMuhammad AdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine - 7303Documento14 pagineGuidelines Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine - 7303Wpress PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Qdenga Epar Product Information enDocumento47 pagineQdenga Epar Product Information enNovrina Wahidah RestiNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunisation of Cardiac Patients and Specific Immunodeficient ConditionsDocumento20 pagineImmunisation of Cardiac Patients and Specific Immunodeficient ConditionsanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Elham Bukhari: Aediatri Nfectious IseaseDocumento56 pagineDr. Elham Bukhari: Aediatri Nfectious IseaseJim Jose AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanded Program For Immunization CHD ReportDocumento12 pagineExpanded Program For Immunization CHD ReportCristalPagcaliwangan0% (1)
- VaccineDocumento3 pagineVaccinePapitas FritasNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaksin DPTDocumento5 pagineVaksin DPTali subchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Vaccination Screening FormDocumento10 paginePre Vaccination Screening Formbersabeh abayNessuna valutazione finora
- Childhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Documento53 pagineChildhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Haters ExterminatorNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult ScheduleDocumento3 pagineAdult ScheduleerilarchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ImmunizationsDocumento21 pagineTypes of Immunizationsmacmactongos100% (6)
- Expanded Program On ImmunuzationDocumento37 pagineExpanded Program On ImmunuzationRose AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersDa EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersDa EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNessuna valutazione finora
- Influenza Vaccine Production Consideration (Ethan Settembre)Documento6 pagineInfluenza Vaccine Production Consideration (Ethan Settembre)National Academies of Science, Engineering, and MedicineNessuna valutazione finora
- ND Lokal Genotype 7Documento61 pagineND Lokal Genotype 7Yud KhamidahNessuna valutazione finora
- National Calendar For Vaccination: Doses Vaccine Child's AgeDocumento1 paginaNational Calendar For Vaccination: Doses Vaccine Child's AgeĐH ĐỊNH HƯỚNGNessuna valutazione finora
- Encyclopedia of Virology Fourth Edition V1 5 Dennis Bamford Full ChapterDocumento67 pagineEncyclopedia of Virology Fourth Edition V1 5 Dennis Bamford Full Chapterrobert.hanson139100% (5)
- Vaccination ScheduleDocumento1 paginaVaccination ScheduleAmanda KamienNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 3 Sem 1 2015 - 16 QuestionDocumento8 pagineTutorial 3 Sem 1 2015 - 16 QuestionPutri SyalieyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of VirologyDocumento20 pagineHistory of VirologyshiyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Timetable - VirologyDocumento3 pagineTimetable - VirologytheredcornerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Big Picture Book of Viruses. EP Rybicki & R KightleyDocumento106 pagineThe Big Picture Book of Viruses. EP Rybicki & R KightleyDNessuna valutazione finora
- KMTC Microbiology Notes March 2022 ClsaaDocumento31 pagineKMTC Microbiology Notes March 2022 ClsaaFrancis ChegeNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Viral Hepatitis: Jonathan WalaDocumento49 pagineAcute Viral Hepatitis: Jonathan WalaAntony WaithakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel Ilmiah - Nov Dion FuadillahDocumento13 pagineArtikel Ilmiah - Nov Dion FuadillahNov Dion FuadillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiplication of VirusesDocumento5 pagineMultiplication of Viruseshely shahNessuna valutazione finora
- ColloidalSilver Nanoparticles Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses (Ebola)Documento22 pagineColloidalSilver Nanoparticles Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses (Ebola)KatieNessuna valutazione finora
- RTPCRDocumento2 pagineRTPCRAaqib KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alltest CatalogDocumento22 pagineAlltest CatalogAngelo PlataNessuna valutazione finora
- HERPESVIRUSES, PARVO 2021 Students - KopieDocumento38 pagineHERPESVIRUSES, PARVO 2021 Students - KopieMr.FantasthiccNessuna valutazione finora
- Gg. Sistem IntegumenDocumento5 pagineGg. Sistem IntegumenSuci Denita SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Measles Basic Info EnglishDocumento2 pagineMeasles Basic Info EnglishSinclair Broadcast Group - EugeneNessuna valutazione finora
- Each Province Immune ScheduleDocumento2 pagineEach Province Immune ScheduleScribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronavirus pptx3Documento15 pagineCoronavirus pptx3Ace Ashley Baron75% (4)
- CH-1 IGCSE Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocumento21 pagineCH-1 IGCSE Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsSarika AhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mr. Janeesh Pal Singh: Test Description Observed Value Biological Reference RangeDocumento1 paginaMr. Janeesh Pal Singh: Test Description Observed Value Biological Reference RangeJaneesh Pal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Oncogenic VirusesDocumento25 pagineOncogenic VirusesMedicina 19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Virus Zoster VaricelaDocumento204 pagineVirus Zoster VaricelaJosǝ Luiis BrjsNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 KuzmanDocumento7 pagine13 KuzmanSinhad Dadi GolubovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing Lab: Quality Healthcare Is A Human RightDocumento1 paginaTesting Lab: Quality Healthcare Is A Human RightRaghuraj BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Scientists Now Say On Covid Origin in Wuhan Lab and What They Dismissed PrematurelyDocumento32 pagineWhat Scientists Now Say On Covid Origin in Wuhan Lab and What They Dismissed Prematurelykpkdhar 36Nessuna valutazione finora
- A New Nodavirus Is Associated With Covert Mortality Disease of ShrimpDocumento10 pagineA New Nodavirus Is Associated With Covert Mortality Disease of ShrimpmiftahuddinmadjidNessuna valutazione finora
- Kode ICD 10 THTDocumento11 pagineKode ICD 10 THTFirman ZakyNessuna valutazione finora