Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
How Are Global Patterns of Development Identified?
Caricato da
demigod290 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
29 visualizzazioni1 paginadevelopment
Titolo originale
Development A3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentodevelopment
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
29 visualizzazioni1 paginaHow Are Global Patterns of Development Identified?
Caricato da
demigod29development
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
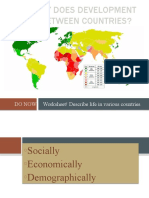
How are global patterns of development identified?
How is economic and social development measured and what
are the global patterns?
Today development is measured using the HDI (Human
Development Index). The HDI is worked out by putting
together 3 important pieces of information:
Life expectancy
Literacy
Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product is how much money is
earned) real GDP looks at that compared to how much it
would buy against a typical basket of food.
In the past development was usually measured using just one
simple measure such as GDP per capita (how much money is
earned per person in US$ per year) life expectancy or infant
mortality (number of children dying per year per 100 live
births).
The global pattern of development has not changed much since
1986 when the Brandt report first published a world map
which divided the world into a rich NORTH and a poor SOUTH.
The line which was drawn on the map is called the Brandt
line.
The countries in the poor south have changed relative to
each other most countries in South America and South
Asia have improved relative to most countries in Africa.
Countries in South America and South Asia have benefitted
from increased trade because of globalisation.
Many countries in Africa have stayed the same (not
developed) and some have even gone backwards.
Often countries in Africa have not developed because of
drought, debt, war, bad government or diseases such as
HIV/AIDS.
What are the regional patterns of economic and/or social
development in one LEDC?
In Uganda there are big differences in development between
the Central Region around the capital city Kampala and the
rest of the country.
Central region is more developed.
Central region has a HDI of 0.650 (middle income country
between 0.5-0.8).
The Central region would be described as the core region.
Mbale is in the East of Uganda.
The East of Uganda has an average HDI below 0.5 (low
income country).
Moroto district in the North-East has a HDI of 0.216
(lower than the HDI of Niger the least developed country
which has a HDI of 0.34).
The East of Uganda is an example of a peripheral region.
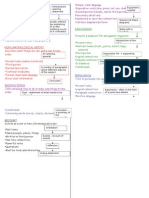
Economic Characteristics
Core Region
Peripheral Region
More paid jobs
Subsistence farming
More taxes collected
Less taxes collected
More spent on schools etc.
Less spent on schools etc.
Investment from banks
Lack of investment
Social Characteristics
Core Region
Peripheral Region
Better schools
Worse schools
Better Healthcare
Worse healthcare
Better housing
Worse housing
Security
War/fighting
Many opportunities
Few opportunities
What progress is being made towards achieving the
Millennium Development goals?
What are the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and how
are governments and non-governmental organisations
addressing them?
The MDGs were 8 targets set in the year 2000 to halve global
poverty by 2015; they are:
MDG 1:
Eradicate Extreme Poverty and Hunger.
MDG 2:
Universal Primary Education.
MDG 3:
Improve Gender Equality and Womens
Empowerment.
MDG 4:
Reducing Child Mortality
MDG 5:
Improve Maternal Mortality
MDG 6:
Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
MDG 7:
Ensure Environmental Sustainability
MDG 8:
Global Partnership for Development
You need to know at least two MDGs in detail:
MDG 4 Reducing Child Mortality:
Feeding programmes e.g. in schools
Vaccination/healthcare programmes
Education of children and parents
Providing ARV gel during birth
Clean water
Sanitation/latrines
Many aspects of MDG 4 overlap with MDG 6 - Combat
HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases:
Vaccination programmes
Free HIV testing
Education campaigns
Provide condoms
Provide ARV gel during birth
Provide free ARV drugs
Malaria nets
Free malaria drugs and testing
Drain swamps to get rid of mosquitoes
Free testing and drugs for T.B.
Develop cheaper treatments for drug resistant T.B.
What progress is being made by sub-Saharan African
countries towards the MDGs?
Some countries where there has been stability good
government such as Uganda have made good progress.
This is mainly because aid from international donors has
been tied to progress in MFGs no progress = no aid.
In countries suffering from war and bad government such
as the D.R. of Congo there has been little or no progress.
Uganda is on track to achieve MDGs 1, 3, 6, 7 & 8 and
probably 2. Uganda is making progress on 4 & 5 but will
probably not make the target.
What progress is being made by South Asian countries
towards the MDGs?
South Asian countries with stable government such as India
have made much worse progress than comparable SubSaharan countries such as Uganda.
These countries have benefited more from globalisation
and have much more money.
The development has not been spread fairly to help the
poorest who are not benefitting.
India has not provided enough evidence to judge MDGs 6, 7
& 8 and is currently off track to achieve 1 5!
42% of households without latrines globally are in India
Indian children make up one-third of the worlds
malnourished children - every second young child in India is
malnourished.
Only 4 out of 10 girls who enrol complete eight years of
schooling.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MGmag 1Documento35 pagineMGmag 1Flores Romeo JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature of EconomyDocumento29 pagineNature of EconomyDeepika BhadauriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Developed Countries: Sustainable Human DevelopmentDocumento7 pagineDeveloped Countries: Sustainable Human Developmentkrystalj94Nessuna valutazione finora
- North South DivideDocumento17 pagineNorth South DividejunNessuna valutazione finora
- CH9 DevelopmentDocumento52 pagineCH9 DevelopmentshineNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 11 Devt Geo NotesDocumento3 pagineGR 11 Devt Geo NotesFidelis ChihambakweNessuna valutazione finora
- Actionaid: Messagis Guest Piece Was Originally Published On Abc The Drum On The 22Nd September atDocumento13 pagineActionaid: Messagis Guest Piece Was Originally Published On Abc The Drum On The 22Nd September atChua Jia YunNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is MDGDocumento16 pagineWhat Is MDGvivien kate perix50% (2)
- Global DivideDocumento41 pagineGlobal DivideDave Mariano BataraNessuna valutazione finora
- My Report On The MDGS'Documento7 pagineMy Report On The MDGS'Onyemenam ChinodebemNessuna valutazione finora
- What The Hdi IndicatesDocumento1 paginaWhat The Hdi IndicatesfegabuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Development DefinitionsDocumento3 pagineDevelopment DefinitionsAkshun VirkNessuna valutazione finora
- Fastest Growing Free Market Democracy in A Global Economy IndiaDocumento37 pagineFastest Growing Free Market Democracy in A Global Economy IndiaVaibhav MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Research.: Abhay Kaundinya - Chairperson Madhureema Roy Moulik - RapporteurDocumento10 pagineResearch.: Abhay Kaundinya - Chairperson Madhureema Roy Moulik - RapporteurMadhureema RoyMoulikNessuna valutazione finora
- Development - The Basics: Making Sense of The WorldDocumento16 pagineDevelopment - The Basics: Making Sense of The WorldmicjenNessuna valutazione finora
- Core 2: Disparities in Wealth and DevelopmentDocumento17 pagineCore 2: Disparities in Wealth and DevelopmentOmar GobranNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooperation & CollaborationDocumento31 pagineCooperation & CollaborationJed FarrellNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship and Human-Development-ReportDocumento16 pagineEntrepreneurship and Human-Development-ReportrjanepadayNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO Assignment 2Documento5 pagineECO Assignment 2FăÍż SăįYąðNessuna valutazione finora
- Globalization: Julio Sebastián Quijano Angie Lorena Ramírez Paula Natalia MorenoDocumento2 pagineGlobalization: Julio Sebastián Quijano Angie Lorena Ramírez Paula Natalia MorenoPaula Natalia MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Poverty Develop 2019 IntroDocumento34 pagine02 Poverty Develop 2019 IntroHemanth AshokanNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Economics Unit 1 and 2Documento64 pagineDevelopment Economics Unit 1 and 2ibsa100% (1)
- Development Indicators and Indices: GDP Per Capita - Growing Development PopulationDocumento12 pagineDevelopment Indicators and Indices: GDP Per Capita - Growing Development PopulationhjbkhbjtNessuna valutazione finora
- 7point Agenda2Documento7 pagine7point Agenda2olayinka_belloNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 13 Global Divides and GlobalizationDocumento4 pagineLesson 13 Global Divides and GlobalizationMari Carreon TulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Development in IndiaDocumento7 pagineEconomic Development in IndiaSahil ThappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Underdevelopment PresentationDocumento27 pagineUnderdevelopment Presentationapi-270480976Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of AcronymsDocumento9 pagineList of AcronymssylvesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Democracy and Development: The Global PolityDocumento11 pagineDemocracy and Development: The Global Politymgenimkubwa85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Development Studies New VersionDocumento175 pagineDevelopment Studies New Versionj33966141Nessuna valutazione finora
- 305 S23 2a DevelopmentIntroductionDocumento33 pagine305 S23 2a DevelopmentIntroductionYousef BerbarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Zealand The Most Prosperous Country in The World International Press Release - 3 November 2016Documento3 pagineNew Zealand The Most Prosperous Country in The World International Press Release - 3 November 2016Janko OgorevcNessuna valutazione finora
- PovertyDocumento12 paginePovertyandrew.collananNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 9 Slides Global DividesDocumento32 pagineLesson 9 Slides Global DividesRhica Audrey GloriosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap. 2. Comparative Economic DevelopmentDocumento42 pagineChap. 2. Comparative Economic DevelopmentJericho LegaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- Type and Indicators of DevelopmentDocumento9 pagineType and Indicators of DevelopmentQuazi Moshrur-Ul-AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer ContempDocumento5 pagineReviewer ContempGreely Mae GumunotNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicsDocumento4 pagineEconomicsch4 knuNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis On Millennium Development GoalsDocumento4 pagineThesis On Millennium Development GoalsChristina Bauer100% (2)
- Developing Countries PowerpointDocumento15 pagineDeveloping Countries PowerpointGenevieve PokuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Economic DevelopmentDocumento35 pagine1 Economic Development温埃德Nessuna valutazione finora
- Making Globalization Work For All: Development Programme One United Nations Plaza New York, NY 10017Documento48 pagineMaking Globalization Work For All: Development Programme One United Nations Plaza New York, NY 10017Bagoes Muhammad100% (1)
- Activity 1 ECODocumento3 pagineActivity 1 ECOEugene AlipioNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Divide: North and SouthDocumento24 pagineGlobal Divide: North and SouthAngelica AlejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 The Meaning and Measurement of Economic DevelopmentDocumento29 pagineModule 1 The Meaning and Measurement of Economic DevelopmentGhellsuuu MainarNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Aid and Remittance: Crash Course Economics Video AnalysisDocumento7 pagineForeign Aid and Remittance: Crash Course Economics Video AnalysisElise Smoll (Elise)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Topic 1Documento38 pagineUnit 3 Topic 1JODETH NAVAJANessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Economic DevelopmentDocumento25 pagineMeasuring Economic DevelopmentZannath HabibNessuna valutazione finora
- BMS3058 IPHN Global Nutrition Transition: DR Laura Tripkovic Laura - Tripkovic@surrey - Ac.ukDocumento32 pagineBMS3058 IPHN Global Nutrition Transition: DR Laura Tripkovic Laura - Tripkovic@surrey - Ac.ukgobNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco Short Ans Chapter 1 and 2Documento5 pagineEco Short Ans Chapter 1 and 2Sabbir Hossain MustakimNessuna valutazione finora
- World Studies Hybrid 2 13 15Documento6 pagineWorld Studies Hybrid 2 13 15api-278067566Nessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Economics: ProjectDocumento17 pagineMacro Economics: ProjectNishchal AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Aid Blessing or CurseDocumento25 pagineForeign Aid Blessing or CursePrashanth PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Millennium Development GoalsDocumento16 pagineMillennium Development GoalsCSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Topic 1Documento38 pagineUnit 3 Topic 1Jodeth NavajaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Development GapDocumento148 pagineThe Development Gapb_osborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Mortality in More-Developed Countries Population - CALIMLIMDocumento19 pagineMortality in More-Developed Countries Population - CALIMLIMCalimlim, Keith Joshua A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensions of PovertyDocumento4 pagineDimensions of PovertybrendaNessuna valutazione finora
- United Nations Millennium Development GoalsDocumento5 pagineUnited Nations Millennium Development GoalsAnbul TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Failed Nations and Communities (The Second Mental Independence)Da EverandFailed Nations and Communities (The Second Mental Independence)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lunch Menu December 2018 PDFDocumento2 pagineLunch Menu December 2018 PDFdemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Causes and Evidence For Climate Change?Documento1 paginaWhat Are The Causes and Evidence For Climate Change?demigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Candidate Name: Interviewer Name:: A. Assessment of CandidateDocumento1 paginaCandidate Name: Interviewer Name:: A. Assessment of Candidatedemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Characteristics of One European and One Tropical Climate TypeDocumento11 pagineThe Characteristics of One European and One Tropical Climate Typedemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- A View From The Bridge QuotesDocumento3 pagineA View From The Bridge Quotesdemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non Fiction Genre HandoutDocumento2 pagineNon Fiction Genre Handoutdemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Longitudinal Studies - SociologyDocumento1 paginaLongitudinal Studies - Sociologydemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unusually Advanced or Mature in Development, Especially Development: A Precocious ChildDocumento2 pagineUnusually Advanced or Mature in Development, Especially Development: A Precocious Childdemigod29Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0223523417309327 MainDocumento12 pagine1 s2.0 S0223523417309327 MainDan NechitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of National Certification System For Tissue Culture Raised PlantsDocumento56 pagineOverview of National Certification System For Tissue Culture Raised Plantsmashfuq100% (1)
- General Properties of VirusesDocumento24 pagineGeneral Properties of VirusesPeachy PieNessuna valutazione finora
- Art Integrated Project of Biology Class XII-BDocumento10 pagineArt Integrated Project of Biology Class XII-BRonit AdhikaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Tle Ii Beauty Care First Quarter ExaminationsDocumento3 pagineTle Ii Beauty Care First Quarter ExaminationsMercyTribunalo100% (3)
- This House Would Promote Safe Sex Through Education in SchoolDocumento5 pagineThis House Would Promote Safe Sex Through Education in SchoolHazel Lyn Paga Parajes100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 pagineDaftar Pustakacute_chooeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Immuno SeroDocumento80 pagineImmuno SeroDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Documento2 pagineRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Liver Biopsy - H. Takahashi (Intech, 2011) WWDocumento414 pagineLiver Biopsy - H. Takahashi (Intech, 2011) WWmientweg100% (1)
- Nutrition Exam - CanadaDocumento93 pagineNutrition Exam - Canadamarco100% (2)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaDocumento10 pagineRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaMIR SARTAJNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 N318 30162Documento21 pagine05 N318 30162Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- HPV PCRDocumento34 pagineHPV PCRGuneyden GuneydenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Life Cycle of WormsDocumento5 pagineThe Life Cycle of WormsNikko Adhitama100% (2)
- Campbells Operative More InfoDocumento2 pagineCampbells Operative More InfoZ Tariq100% (1)
- DSFDSFDSFDSFDocumento108 pagineDSFDSFDSFDSFbarzulkakNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological ClassificationDocumento30 pagineBiological ClassificationSureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and LarynxDocumento3 pagineNose, Sinuses, Mouth, and LarynxjottowagNessuna valutazione finora
- HIV ManagmentDocumento44 pagineHIV ManagmentSarvesh PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Typhoid 21Documento9 pagineTyphoid 21Nanda Hikma LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial Infections of Human ProjectDocumento29 pagineBacterial Infections of Human ProjectCute AkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences Section V. Environmental and Applied MicrobiologyDocumento32 pagineBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences Section V. Environmental and Applied MicrobiologyMitzi Audrey100% (1)
- Kode Diagnosa P-Care - SimpusDocumento2 pagineKode Diagnosa P-Care - SimpusiqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Microbial ControlDocumento36 pagine6 Microbial ControlGladish RindraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rife Morris FishbeinDocumento9 pagineRife Morris FishbeinuncoveringconsciousNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Activity-5Documento6 pagineLab Activity-5Kristine MerhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fevers: Usually A Positive Sign That The Body Is Fighting Infection."Documento3 pagineFevers: Usually A Positive Sign That The Body Is Fighting Infection."Theresa OsmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Review On Dermatomycosis Jurnal 2Documento23 pagineReview On Dermatomycosis Jurnal 2Laela NurrochmahNessuna valutazione finora