Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Form 4 Penggal 1 2011
Caricato da
jesunathan44@yahoo.comCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Form 4 Penggal 1 2011
Caricato da
jesunathan44@yahoo.comCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SECTION A (ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS)
Which one of the following is not a base quantity?
A
Length
Kilogram
Second
miligram
kilogram
microgram
Volume
Force
Acceleration
D 0.152 x 10 -4
1.52 x 10-5
The standard form for 15200 is
B 1.52 x 10 3
C 1.52 x 10 4
The prefixes according to their value in ascending order are
A Giga,mega,kilo,centi
Time
Ampere
A 15.2 x 10 2
6
Which of the followinq quantity is a scalar quantity.
A Weight
Current
The S.I. base unit for mass is
A gram
Which one of the following is not a base unit?
A Celcius
Weight
B Mikro,mili,centi,kilo
C Mega,giga,kilo,centi
D Centi,giga,mikro,mili
Radio 5 RTM station operates at 105 .6 M Hz.The expression of the frequency in units of Hz is
A 1.056 x 10 8 Hz
B 1.056 x 10 6 Hz
D 1.056 x 10 - 4 Hz
C 1.056 x 10 4 Hz
E 1.056 x 10 - 8 Hz
8
The volume of a metal sphere is 12 cm 3. This volume in units of m 3 is
B 1.2 x 10 -
A 1.2 x 10 - 2
9
C 1.2 x 10 - 5
D 1.2 x 10 7
E 1.2 x 10 - 9
The velocity of a car is 108 km j-1. What is the velocity in units of ms-1 ?
A 20
10
30
50
D 60
E 90
Which one of the following measurements is different?
A 2.3 x 10 2 m
2.3 x 10 4 cm
11
5 x 10 - 4 seconds is equivalent to
0.05 s
0.5 s
C 50 s
C 2.3 x 10 6 mm
D 500 s
E 5000 s
12
The ability of an instrument to detect a slight change that occurs in the measured quantity is called as
A precision
13
accuracy
sensitivity
error
The ability of an instrument gives consistent reading , when repeated readings are taken is called as
A accuracy
precision
sensitivity
14
Which of the following is most likely to show a precise shooting?
15
Which of the following statements about errors is correct?
A Zero error is random error
error
B Random errors can be reduced by taking repeat readings.
C Systematic errors can be due to instruments which are not sensitive.
16
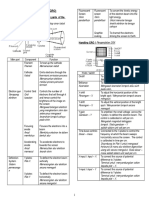
Table shows readings of the thickness of a book measured by four different students. Which of the students recorded the true
readings.
A
B
C
D
17
Student
W
X
Y
Z
Ruler / cm
2.17
2.174
2.17
2.2
Vernier calipers / cm
2.2
2.2
2.174
2.17
Diagram shows a micrometer screw gauge reading when it is closed at its gap.
The subsequent readings must be corrected by
A adding 0.02 mm
B subtracting 0.02 mm
18
Mikrometer screw gauge /mm
2.1
2
2.174
2.17
C adding 0.03 mm
D subtracting 0.03 mm
The diagram shows the existence of zero errors of a vernier calipers.
What is the value of the zero error?
A + 0.04 cm
B
- 0.04 cm
+ 0.06 cm
- 0.06 cm
2
19
Which of the following graphs show that y increases linearly with x?
20
P
10
Q
5
The equation of the graph above is
A P = 10Q + 5
P = 2Q + 10
P = -2Q + 10
P = 5Q 10
SECTION B (ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS)
Diagram 1.1
1.
Diagram above shows the reading of a micrometer screw gauge for the thickness of 5 sheets of paper.
(a) State is the sensitivity of a micrometer screw gauge.
...(1 mark)
(b)
Name the parts labelled M.
...(1 mark)
(c)
State the function of the parts labelled M.
..........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(d)
State the reading of the micrometer screw gauge shown Diagram 1.1
..........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(e)
Calculate the thickness of on sheet of paper.
..........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
metal bob
Diagram 2.2
2.
Diagram 2.2 shows the reading of a vernier callipers used to determine the diameter of a metal bob.
(a) State the the type and the value of the error shown in Diagarm 2.2 (a).
..(2 marks)
(b)
State the function of the part labelled P.
...(1 mark)
(c)
State the reading of the vernier callipers on Diagram 2.2 (b).
..........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(d)
State the actual diameter of the metal bob
..........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
3.
A student carries out an experiment to investigate the relationship between mass of a spring, m and the period of oscillation, T
of a steel spring. The students uses different weights of springs and record the corresponding period, T The student then plots
a graph of T2 against m as shown in Diagram 3.
(a) Based on the graph on Diagram 3,
(i) state the relationship between T2 and m.
.........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(ii) calculate the value of T when m = 0.4 kg. Show on the graph how you determine the value.
( 3 marks)
(iii) calculate the gradient, n of the graph T2 against m . Show on the graph how you determine the value.
( 3 marks)
(b) Elasticity of the spring, k given by the quation k = 4 2 , where n is the gradient of the graph T2 against m.
n
Calculate the value of k.
(2 marks)
(c) State a precaution that can be taken during the experiment.
.........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(d)
Diagram 3
4.
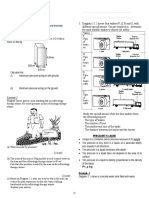
A student carries out an experiment to investigate the relationship between mass, m of a material and its volume, V. A slotted
weight of mass 50.0 g is gently immersed into a measuring cylinder containing water. The arrangement of the apparatus for
this experiment is shown in Diagram 4.1.
Diagram 4.2 shows the initial water level, V0, in the measuring cylinder before the slotted weight is immersed in it.
Diagram 4.3 shows the water level in the measuring cylinder when a 50.0 g slotted weight is immersed in it.
The procedure is repeated with masses, m = 100.0 g, 150.0 g, 200.0 g and 250.0 g. The corresponding water levels in the
measuring cylinder are shown in Diagram 4.4, 4.5, 4.6 and 4.7 on page 6 .
Diagram 4.2
Diagram 4.1
Diagram 4.4
Diagram 4.5
Diagram 4.6
Diagram 4.3
Diagram 4.7
(a) For the experiment described on page 6, identify:
(i) The manipulated variable
........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(ii) The responding variable
.......................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(iii) Constant variable
.......................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
(b) For this part of the question, write your answers in the spaces provided in the corresponding diagrams.
(i) Based on Diagarm 1.2 on page 6, record the reading of, Vo.
(ii) Based on Diagram 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6 and 1.7 on page 6 record the reading of Vi.
(1 mark)
(2 marks)
(iii) Calculate V for each value of Vi in 4(b)(ii), using the formula V = (Vi - Vo). Record value of V. (2 marks)
(c) Tabulate your results for all values of m, Vi and V in the space below.
(2 marks)
(d) On the graph paper on page 8, plot a graph V against m.
(5 marks)
(d) Based on the graph in 4 (d), state the relationship between V and m.
.........................................................................................................................................................(1 mark)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- U and V ExperimentDocumento2 pagineU and V Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay Force and MotionDocumento6 pagineEssay Force and Motionjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Gate 2Documento7 pagineLogic Gate 2jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Inertia Mass ExperimentDocumento1 paginaInertia Mass Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Ohms Law ExperimentDocumento1 paginaOhms Law Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- MRSM Past Years Form 4Documento39 pagineMRSM Past Years Form 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Force EsaiDocumento8 pagineForce Esaijesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento10 pagineChapter 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- (9.7.17) Gallery Walk (Environment), 4ODocumento4 pagine(9.7.17) Gallery Walk (Environment), 4Ojesunathan44@yahoo.com100% (1)
- (9.4.17) Cause and EffectDocumento3 pagine(9.4.17) Cause and Effectjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Paper 2 Esai 2010Documento30 pagineSeminar Paper 2 Esai 2010jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)Documento2 pagineCathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3Documento30 paginePaper 3jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference of Wave 1Documento4 pagineInterference of Wave 1jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota PadatDocumento13 pagineNota Padatjesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Padat ForceDocumento22 pagineNota Padat Forcejesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento23 pagineChapter 2jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento15 pagineChapter 5jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Esay Section B@C Ting 4Documento4 pagineEsay Section B@C Ting 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Radiotherapy & OncologyDocumento18 pagineRadiotherapy & OncologyAnjihartsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bifilar Experiment: Length Vs PeriodDocumento8 pagineBifilar Experiment: Length Vs PeriodsaNessuna valutazione finora
- EIM - Unit II PDFDocumento48 pagineEIM - Unit II PDFSubhashree DashNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory and Design For Mechanical Measurements 6th Edition 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocumento62 pagineTheory and Design For Mechanical Measurements 6th Edition 6th Edition Ebook PDFgeorge.lopez984100% (32)
- Stem12 Physics 1 q1 w1 LeapDocumento4 pagineStem12 Physics 1 q1 w1 LeapGreg Aeron Del MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical ErrorsDocumento39 pagineAnalytical ErrorsSrikrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Uncertainty CalculationsDocumento20 pagineUncertainty CalculationsSonal WanigasooriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Accounting: Key Differences Between Management Accounting (MA) and Financial Accounting (FA)Documento3 pagineFinancial Accounting: Key Differences Between Management Accounting (MA) and Financial Accounting (FA)Meghan Kaye LiwenNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Geotechnical Resistance Factors PDFDocumento49 pagineDevelopment of Geotechnical Resistance Factors PDFNader MehdawiNessuna valutazione finora
- ME8501 Metrology and Measurements PDFDocumento93 pagineME8501 Metrology and Measurements PDFpuneetNessuna valutazione finora
- Ib Biology BookletDocumento63 pagineIb Biology Bookletjoey!!100% (2)
- 05 Chp1 and Chp2 LectureDocumento19 pagine05 Chp1 and Chp2 LectureNathan WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Data AnalysisDocumento13 pagineAdvances in Data AnalysisNorbey Arcila QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Wolfpack Oberkommando Der Kriegsmarine: Navigation GuideDocumento60 pagineWolfpack Oberkommando Der Kriegsmarine: Navigation GuideJuan DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Error AnalysisDocumento6 pagineError AnalysisMaestro Pisika LptNessuna valutazione finora
- WEBSTER - Measurement, Instrumentation, and Sensors Handbook, John G. Webster, Halit Eren-Halaman-121-135Documento15 pagineWEBSTER - Measurement, Instrumentation, and Sensors Handbook, John G. Webster, Halit Eren-Halaman-121-135rizka rianiNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Standard Operating ProcedureDocumento122 pagineWHO Standard Operating Procedurerenjithgp100% (1)
- 6940 Dieck Measurement5 PDFDocumento36 pagine6940 Dieck Measurement5 PDFJGlobexNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of MeasurementDocumento10 pagineMethods of Measurementanon_633165161Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics For Analytical ChemistryDocumento49 pagineStatistics For Analytical ChemistryDragana Srdic100% (2)
- Chapter 1 For StudentDocumento19 pagineChapter 1 For StudentEyoel Yo'otaNessuna valutazione finora
- Christine PDFDocumento4 pagineChristine PDFSubesh ShanmugamNessuna valutazione finora
- For Calculation of CaCO3Documento2 pagineFor Calculation of CaCO3Omkaar KamathNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1-3Documento36 pagineChapter 1-3Babyin LowNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Practical Physics: For StudentsDocumento30 pagineAdvanced Practical Physics: For Studentsmatchbook54-sl1257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hansen 1985 PDFDocumento19 pagineHansen 1985 PDFadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacholski Practical MAM 6 2015Documento4 paginePacholski Practical MAM 6 2015dacaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics For UsersDocumento222 pagineMathematics For UsersbongoherbertNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 System Accuracy PDFDocumento8 pagine1.4 System Accuracy PDFRavi Chandra PenumartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisis Instrumental 2Documento5 pagineAnalisis Instrumental 2Patricio VillarrealNessuna valutazione finora