Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DNA Gel Electrophoresis
Caricato da
Tok WanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DNA Gel Electrophoresis
Caricato da
Tok WanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2ND YEAR MLT
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LAB
2010
DNA Gel Electrophoresis
Principle:
Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments including PCR products
according to their size and charge.
The product is loaded on the gel that helps DNA filter through itself.
DNA is negatively charged because of the phosphate back bone.
Different sizes of these fragments will cause variation in migration through the gel,
allowing smaller fragments to move faster than the larger ones.
Two types of gels can be used for gel electrophoresis; Agarose gel and acrylamide.
Application of Gel Electrophoresis in Molecular Biology:
1. Estimate DNA molecule size after restriction enzyme digestion (RFLP).
2. Check PCR amplified product.
3. Preparation of DNA to be used in other techniques such as Southern blotting.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
It's extracted from seaweed and consists of tiny pores allowing the smaller fragments of DNA to
migrate faster and farther to anode (+ve). Larger fragments face more friction while migrating
through the gel, therefore remaining closer to the cathode (-ve).
Visualization of the gel:
The most common dye used to make DNA bands visible for both type of gel electrophoresis is
Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) dye. It's a highly carcinogenic dye that penetrates Hydrogen bonds of
DNA and fluoresce under UV light.
Prepared by: Ms. Thoraia Shinawi
2ND YEAR MLT
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LAB
2010
Preparation:
A. Gel Preparation:
1. Select the appropriate gel concentration and prepare it in a flask according to the following table:
Concentrations
0.5%
1%
1.5%
2%
2.5%
3%
Agarose (powder) in
gms
0.5
1.5
2.5
1X TBE Buffer in mls
(liquid)
100
100
100
100
100
100
2. Microwave heated for ~ 1 minute to dissolve the agarose until you get a translucent mixture.
3. Add 5 L of EtBr and swirl to mix.
4. Leave it to cool down at room temperature on the bench for 2 minutes.
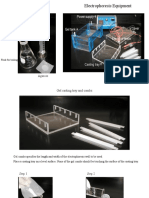
5. Pour the gel slowly into the tray. Ensure gel is free from bubbles otherwise push them aside
using a disposable tip.
6. Insert the comb and double check that it is correctly positioned.
7. Allow the gel to set for at least 45 min to 1 hour.
8. Disengage the comb gently.
9. Place the gel in the electrophoresis tank.
10. Pour 1.0x TBE buffer into the gel tank ensuring the gel is completely submerged.
B. Sample Preparation:
1. Pipette 2 l of loading dye into a new tube.
(Loading dye is composed of Bromophenol blue and glycerol. Bromophenol is colored and
helps keep track of the migrating bands and glycerol allows DNA to settle into the wells
avoiding the product to float).
2. Transfer 5l of sample into the tube containing the dye and mix well.
3. Load the sample slowly and carefully into the well.
Prepared by: Ms. Thoraia Shinawi
2ND YEAR MLT
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LAB
2010
4. Meanwhile load 5l of DNA ladder marker in one of the wells independently.
(DNA marker contains a mixture of DNA molecules of known fragment sizes. After
migration, the unknown sample band is compared to these DNA marker fragments for
size determination).
5. Electrophoresis tank is connected to power supply, making sure the anode and cathode are
correctly connected to ensure proper direction of current flow.
6. The current is adjusted at 100 amperes.
7. Migration of the bands is monitored by visualizing bromophenol blue.
8. The apparatus is switched off and the wires disconnected. The gel is carefully exposed to UV
trans-illuminator. The bands are analyzed and picture taken, while the file is saved in PC.
Prepared by: Ms. Thoraia Shinawi
2ND YEAR MLT
Patient
1
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LAB
Patient
2
Patient
3
Positive 100 bp
Negative
control
control
Marker
2010
500 bp
400 bp
300 bp
200 bp
100 bp
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Acrylamide (polyacrylamide) Gel:
This is made from the synthetic polymerization of acrylamide. Acrylamide is neurotoxic in
monomeric form however; it is used for high resolution electrophoresis of small molecules.
Prepared by: Ms. Thoraia Shinawi
2ND YEAR MLT
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LAB
2010
Materials needed for gel preparation:
1. TBE Buffer: To maintain the optimum pH.
2. Acrylamide: Its a monomeric substance that can be activated to form long chain of
polymers (polyacrylamide).
3. Ammonium persulfate (APS): initiates gel formation by activating polymerization of
acrylamide monomers.
4. TEMED: Accelerate the process of polymerization in conjunction with APS.
Buffer
Gel Chamber
A table summarizing differences between Agarose & Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis:
Agarose Gel
Polyacrylamide Gel
Poured Horizontally
Poured Vertically
Separate large molecules
Separate small molecules
Non-toxic
neurotoxic
Mostly used for DNA separation
Used for DNA or Protein separation
Staining step: before or after pouring the gel
Staining step: after pouring the gel
Prepared by: Ms. Thoraia Shinawi
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento10 pagineAgarose Gel Electrophoresisvenkat satyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology Lab Manual FinalDocumento19 pagineMolecular Biology Lab Manual FinalAnupriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2. Gel Extraction and PurificationDocumento5 pagineActivity 2. Gel Extraction and Purificationgarcia.zaniabNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformation ConfirmationDocumento5 pagineTransformation ConfirmationMuhammad MoeezNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 7 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: Cell and Molecular Biology LaboratoryDocumento8 pagineExercise 7 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: Cell and Molecular Biology LaboratoryDham DoñosNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principle: To Study The Isolation of Plant Genomic DNA by Using Modified CTAB MethodDocumento35 pagineBasic Principle: To Study The Isolation of Plant Genomic DNA by Using Modified CTAB MethodPAWANKUMAR S. K.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4Documento5 pagineExperiment 4imenmezhoud1122Nessuna valutazione finora
- PMT 324 Molecular Biology of The GeneDocumento6 paginePMT 324 Molecular Biology of The GeneBlameless ArikoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceb Practical: 1. TitleDocumento8 pagineCeb Practical: 1. TitleKischa DoesesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento6 pagineLab 4 Agarose Gel Electrophoresisjimmy_ncop4702Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agaroe Gel Electrophoresis-2023Documento34 pagineAgaroe Gel Electrophoresis-2023abrahamkwandor5678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento6 pagineAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisJêyà BharathìNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasmid DNA Extraction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento5 paginePlasmid DNA Extraction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisPrithvi ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Gel Electrophoresis 9Documento2 pagineGel Electrophoresis 9Sasa AbassNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3. Electrphoresis and Its TypesDocumento59 pagineLecture 3. Electrphoresis and Its TypesMoiz AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Bchem10 2 PDFDocumento6 pagineBchem10 2 PDFEsther MathengeNessuna valutazione finora
- Departments: SDMVM'S College of Agricultural BiotechnologyDocumento45 pagineDepartments: SDMVM'S College of Agricultural BiotechnologyPAWANKUMAR S. K.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter ColiDocumento11 pagineCampylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter ColinadbucukNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis PDFDocumento3 pagineAgarose Gel Electrophoresis PDF9001 Trisha BakshiBBT2Nessuna valutazione finora
- ProtgelsDocumento2 pagineProtgelsbettcorporationNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento56 pagineLab 4 Gel Electrophoresisreeda essamNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment:5: Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento16 pagineExperiment:5: Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisANKIT KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- 5. Agarose gel مختبرDocumento2 pagine5. Agarose gel مختبرAbrar 111Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Report On: Separation of RNA by Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento3 pagineA Report On: Separation of RNA by Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisAtanu SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20BTC502J-lab-manual-Cell BiologyDocumento42 pagine20BTC502J-lab-manual-Cell BiologyMohana MarimuthuNessuna valutazione finora
- PCR TechniqueDocumento5 paginePCR Techniquemuthuraja6728Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrophoresis Lab-SlidesDocumento14 pagineElectrophoresis Lab-SlidesghustoNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Documento7 pagineHandout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Michael KahnwaldNessuna valutazione finora
- POB Lab ManualDocumento11 paginePOB Lab ManualWEY LOON LIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (Full Report)Documento10 pagineAgarose Gel Electrophoresis (Full Report)El LisNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins2022 InstructionsDocumento12 pagineProteins2022 InstructionsmrashrafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento4 pagineGel ElectrophoresisSharmilaJeromeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4.isolation of PlasmidDocumento7 pagineLab 4.isolation of PlasmidJane MargarethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Quality and Quantification: Genetic LabDocumento3 pagineDna Quality and Quantification: Genetic LabNgọc Phương Anh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento1 paginaC. Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisAbdulla Rahmah AlTeneijiNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE)Documento16 pagineAgarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE)Nenita AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento12 pagineLab Reporthuwatu petrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt-6 (Isolation of Plasmid DNA)Documento4 pagineExpt-6 (Isolation of Plasmid DNA)Anne Nirmani RodrigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento7 paginePrinciple of Gel ElectrophoresisArhum KhNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 06 MSC Botany MorningDocumento4 paginePractical 06 MSC Botany Morninghely shahNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology Laboratory Report: Background: Bacteria Morphology Can Be Divided Into Different Types Based OnDocumento7 pagineGeneral Biology Laboratory Report: Background: Bacteria Morphology Can Be Divided Into Different Types Based OnNẻro OwONessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2:dna TechnologyDocumento6 pagineExperiment 2:dna TechnologycheckerskNessuna valutazione finora
- 1kb Dna Ladder HPR 301 50tDocumento2 pagine1kb Dna Ladder HPR 301 50tDr. Ali ZohaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Genomic Dna ManualDocumento7 pagineGenomic Dna ManualZafran KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dhawan Chemistry Project WordDocumento14 pagineDhawan Chemistry Project Wordkundanshingh5785Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Report Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: National University of Ho Chi Minh City International UniversityDocumento19 pagineLaboratory Report Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: National University of Ho Chi Minh City International UniversityAn Ngoc HoaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 626 PCR Amplification Gel VisualizationDocumento5 pagine626 PCR Amplification Gel VisualizationUgnė KasperavičiūtėNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology - Amity University RajasthanDocumento13 pagineMolecular Biology - Amity University Rajasthanabash_u1Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Extraction and Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento12 pagineDNA Extraction and Gel ElectrophoresisSowbhagya Laxmi100% (1)
- Practical 3. Analyzing DNA FragmentsDocumento9 paginePractical 3. Analyzing DNA FragmentsLloaana 12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrophoresis: Daheeya Alenazi Cls 332Documento35 pagineElectrophoresis: Daheeya Alenazi Cls 332Terez ŠevčíkováNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento5 pagineAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisSanmugam SubbaramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- Making An Agarose Gel Electrophoresis EquipmentDocumento18 pagineMaking An Agarose Gel Electrophoresis EquipmentBảo NhiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual GMBDocumento3 pagineLab Manual GMBDeepika ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Analysis of Plasmid Dna by Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento3 pagineQualitative Analysis of Plasmid Dna by Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisSindhu LakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento6 paginePrinciples of Gel ElectrophoresisCarmen Lopez100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocumento7 pagineLab ReportShafiqahFazyaziqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ElectrophoresisDocumento3 pagineTypes of ElectrophoresisSridharan VNessuna valutazione finora
- MCB 307 - 1Documento15 pagineMCB 307 - 1marvelloussamuel771Nessuna valutazione finora
- zj2092 PDFDocumento6 paginezj2092 PDFTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- FTIR TablesDocumento1 paginaFTIR TablesvandykavidurgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph BacteriaDocumento5 pagineGraph BacteriaTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Disc DiffDocumento3 pagineData Disc DiffTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- RARBGDocumento1 paginaRARBGTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Compounds: Dibenzylammonium Hydrogen Maleate and A Redetermination at 120 K of Bis (Dibenzylamino) MethaneDocumento15 pagineOrganic Compounds: Dibenzylammonium Hydrogen Maleate and A Redetermination at 120 K of Bis (Dibenzylamino) MethaneTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 145 SRCC 3 (1) 2012 PDocumento15 pagine1 145 SRCC 3 (1) 2012 PTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Forest Landscape Research 51 2012 Nor Aziz Green SpaceDocumento71 pagineForest Landscape Research 51 2012 Nor Aziz Green SpaceTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- M Nova Quick GuideDocumento6 pagineM Nova Quick GuideALI MUHAMMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Dota 2 UiTM Championship RulesDocumento3 pagineDota 2 UiTM Championship RulesTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- FAME Method Short Oct-2007-2Documento11 pagineFAME Method Short Oct-2007-2Ravi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Luminescence Prelab RiboflavinDocumento4 pagineLuminescence Prelab RiboflavinTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 20 Reduction of Vanillin HANDOUTDocumento9 pagineExperiment 20 Reduction of Vanillin HANDOUTTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Art 3A10.1007 2Fs10947 006 0418 1Documento4 pagineArt 3A10.1007 2Fs10947 006 0418 1Tok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Proposal Formatting PDFDocumento3 pagineThesis Proposal Formatting PDFRehab ShabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Word Like HowtotexDocumento1 paginaWord Like HowtotexTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Carroll Lab Chap 2Documento10 pagineCarroll Lab Chap 2Tok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimenjournal 2 1 4pdfDocumento9 pagineExperimenjournal 2 1 4pdfTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Weekly Time Table1Documento1 paginaWeekly Time Table1Tok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Ketone Reduce F 09Documento3 pagine1 Ketone Reduce F 09Tok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumental HPLCDocumento7 pagineInstrumental HPLCTok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocumento11 pagineExp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium Borohydrideakuserai100% (3)
- Chemistry 119: Experiment 8Documento6 pagineChemistry 119: Experiment 8Tok WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bases Moleculares Enfermedades NeurodegenerativasDocumento53 pagineBases Moleculares Enfermedades NeurodegenerativasLaura Paola Corredor NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription FactorsDocumento25 pagineTranscription FactorsPriya.RNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)Documento8 pagineStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)shyngysNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Molecules 2 2013Documento32 pagineBiological Molecules 2 2013Eugenia Migranova100% (1)
- PCR Puzzle Patrick StoreyDocumento4 paginePCR Puzzle Patrick StoreyWall ShopNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Sciences Research3Documento21 pagineBiological Sciences Research3Neeta M UdariNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem QuestionsDocumento13 pagineBiochem Questionsshalialoo22Nessuna valutazione finora
- PAPER 0703 Basics Concepts and Techniques in Molecular BiologyDocumento70 paginePAPER 0703 Basics Concepts and Techniques in Molecular BiologyDiksha Gahlot100% (1)
- DNA MethylationDocumento11 pagineDNA MethylationswjaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Molecular Biology ConceptsDocumento30 pagineSummary Molecular Biology ConceptsDuduetsang MosalakataneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleotide Metabolism: Introduction and de Novo Purine MetabolismDocumento4 pagineNucleotide Metabolism: Introduction and de Novo Purine Metabolismkang seulgi can set me on fire with her gaze aloneNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1038@s41570 020 00223 8Documento22 pagine10.1038@s41570 020 00223 8Khaira Rusdi NumlilNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology Midterm Study GuideDocumento3 pagineMolecular Biology Midterm Study GuideSamer MetriNessuna valutazione finora
- General PCR ProtocolDocumento2 pagineGeneral PCR ProtocolSanju KaramNessuna valutazione finora
- MCAT BiologyDocumento167 pagineMCAT BiologyChris WongNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Lac OPERONDocumento14 pagine08 Lac OPERONAlok SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Adhesion Molecules 300107Documento32 pagineCell Adhesion Molecules 300107V Lee 'Nozhat'100% (1)
- Mcqs Test: Biology Hssc-IDocumento4 pagineMcqs Test: Biology Hssc-IZulfiqar ali Zulfiqar ali farhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYDocumento4 pagineClinical Chemistry 2 ENZYMES. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGYBib imbapNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic ReportDocumento4 pagineForensic ReportMouli MusiqsNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular BiotechnologyDocumento109 pagineMolecular BiotechnologyVipin100% (5)
- DNA Damage & RepairDocumento48 pagineDNA Damage & Repairbukan siapa siapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fastdigest Restriction Enzymes LabaidDocumento2 pagineFastdigest Restriction Enzymes Labaidfnf102030Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arabidopsis Lab ReportDocumento14 pagineArabidopsis Lab Reportapi-342081300Nessuna valutazione finora
- HemostasisDocumento36 pagineHemostasisPutri Rara BalernaPratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocumento5 pagineHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- St. Thomas Academy: Part A. Classify Each As A Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipid or Nucleic Acid (Only Used Once)Documento2 pagineSt. Thomas Academy: Part A. Classify Each As A Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipid or Nucleic Acid (Only Used Once)Kate Ashly Mae AteradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asymmetrical Cell: Submitted byDocumento5 pagineAsymmetrical Cell: Submitted byJeffrey VictoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Plan Working Draft Trascription and Traslation Nick and Adrian 1Documento30 pagineUnit Plan Working Draft Trascription and Traslation Nick and Adrian 1api-504578754Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ On CarbohydratesDocumento6 pagineMCQ On CarbohydrateskumarNessuna valutazione finora